Anatomical Foot Chart
Anatomical Foot Chart - Upper ankle joint (tibiotarsal), talocalcaneonavicular, and subtalar joints. While other shoe brands may use similar size scales, it’s best to check out a shoe brand’s size charts before purchasing a new pair of shoes from them, as each brand’s exact approach to size and fit may vary. The muscles acting on the foot can be divided into two distinct groups; Bones of the foot and ankle. A clinician's ability to understand the anatomical structures of the foot is crucial for assessment and treatment, especially for clinicians working with clients with musculoskeletal conditions. It functions as a rigid structure for weight bearing and it can also function as a flexible structure to conform to uneven terrain. Web the anatomic structures below the ankle joint comprise the foot, which includes 26 bones; These bones give structure to the foot and allow for all foot movements like flexing the toes and ankle, walking, and running. The ankle joint, also known as the talocrural joint, allows dorsiflexion and plantar flexion of the foot. The last two together are called the lower ankle joint. Web with a detailed anatomical chart of the foot, students will find new ways to study and learn about anatomy. Web now that you’ve measured your foot size, compare the measurements against a nike size chart to find the best shoe size for you. The last two together are called the lower ankle joint. They are complex structures with 26. Upper ankle joint (tibiotarsal), talocalcaneonavicular, and subtalar joints. How to ease foot pain at home. Web now that you’ve measured your foot size, compare the measurements against a nike size chart to find the best shoe size for you. Web foot and ankle anatomy consists of 33 bones, 26 joints and over a hundred muscles, ligaments and tendons. It is. Web foot and ankle anatomy consists of 33 bones, 26 joints and over a hundred muscles, ligaments and tendons. The foot subdivides into hindfoot, midfoot, and forefoot. How to ease foot pain at home. Web the anatomic structures below the ankle joint comprise the foot, which includes 26 bones; The last two together are called the lower ankle joint. Web the foot is divided into three parts: This may sound like overkill for a flat structure that supports your weight, but you may not realize how much work your foot does! Web with a detailed anatomical chart of the foot, students will find new ways to study and learn about anatomy. Bones of the foot and ankle. The foot. Web the foot pain identifier diagrams you find here will help you to identify the possible causes of your foot problem and then help you find out everything you need to know about the causes, symptoms, diagnosis and best treatment options for each. Bones of the foot and ankle. These bones are divided into three main regions: These will be. Web foot and ankle anatomy consists of 33 bones, 26 joints and over a hundred muscles, ligaments and tendons. Web the foot is divided into three parts: Web this article will outline some of the main anatomical features of the foot. The ankle joint, also known as the talocrural joint, allows dorsiflexion and plantar flexion of the foot. Web the. While other shoe brands may use similar size scales, it’s best to check out a shoe brand’s size charts before purchasing a new pair of shoes from them, as each brand’s exact approach to size and fit may vary. And the forefoot, which includes the metatarsals and phalanges. Web the feet support the human body when standing, walking, running, and. Web the anatomy of the foot. It functions as a rigid structure for weight bearing and it can also function as a flexible structure to conform to uneven terrain. [3] [4] this article discusses the key anatomical structures of the foot. They are complex structures with 26 bones. The foot is subdivided into the rearfoot, midfoot, and forefoot. Web foot and ankle anatomy consists of 33 bones, 26 joints and over a hundred muscles, ligaments and tendons. Web the many bones, ligaments, and tendons of the foot help you move, but they can also be injured and limit your mobility. They are complex structures with 26 bones. Bones of the foot and ankle. Web the anatomy of the. These will be reviewed in the sections of this chapter. Web this article will outline some of the main anatomical features of the foot. The foot is subdivided into the rearfoot, midfoot, and forefoot. Web the 26 bones of the foot consist of eight distinct types, including the tarsals, metatarsals, phalanges, cuneiforms, talus, navicular, and cuboid bones. Web foot and. This may sound like overkill for a flat structure that supports your weight, but you may not realize how much work your foot does! It will also look at some of the common conditions that affect the foot and their possible treatment options. Web now that you’ve measured your foot size, compare the measurements against a nike size chart to find the best shoe size for you. This complex network of structures fit and work together to bear weight, allow movement and provide a stable base for us to stand and move on. Upper ankle joint (tibiotarsal), talocalcaneonavicular, and subtalar joints. Web the feet support the human body when standing, walking, running, and more. Web the foot and ankle form a complex system which consists of 28 bones, 33 joints, 112 ligaments, controlled by 13 extrinsic and 21 intrinsic muscles. The midfoot, containing the navicular, cuboid, and cuneiforms; Web the foot pain identifier diagrams you find here will help you to identify the possible causes of your foot problem and then help you find out everything you need to know about the causes, symptoms, diagnosis and best treatment options for each. Web there are a variety of anatomical structures that make up the anatomy of the foot and ankle (figure 1) including bones, joints, ligaments, muscles, tendons, and nerves. Web last updated march 1, 2024 • 47 revisions •. Covering joint anatomy of the bones, ligaments, muscles, tendons and nerves, plus information on pathologies and common conditions affecting the feet and ankle, our foot anatomical posters are ideal for teaching and learning. A clinician's ability to understand the anatomical structures of the foot is crucial for assessment and treatment, especially for clinicians working with clients with musculoskeletal conditions. Extrinsic muscles arise from the anterior, posterior and lateral compartments of the leg. How to ease foot pain at home. The muscles acting on the foot can be divided into two distinct groups;![[DIAGRAM] Anatomical Diagram Of Foot](https://images-na.ssl-images-amazon.com/images/I/91oYQrXEdpL._SL1500_.jpg)
[DIAGRAM] Anatomical Diagram Of Foot

Understanding the Foot and Ankle 1004 Anatomical Parts & Charts

Ankle+Anatomy+Muscles.jpg 1,166×1,500 pixels Anatomía del tobillo

Foot Anatomy 101 A Quick Lesson From a New Hampshire Podiatrist Nagy
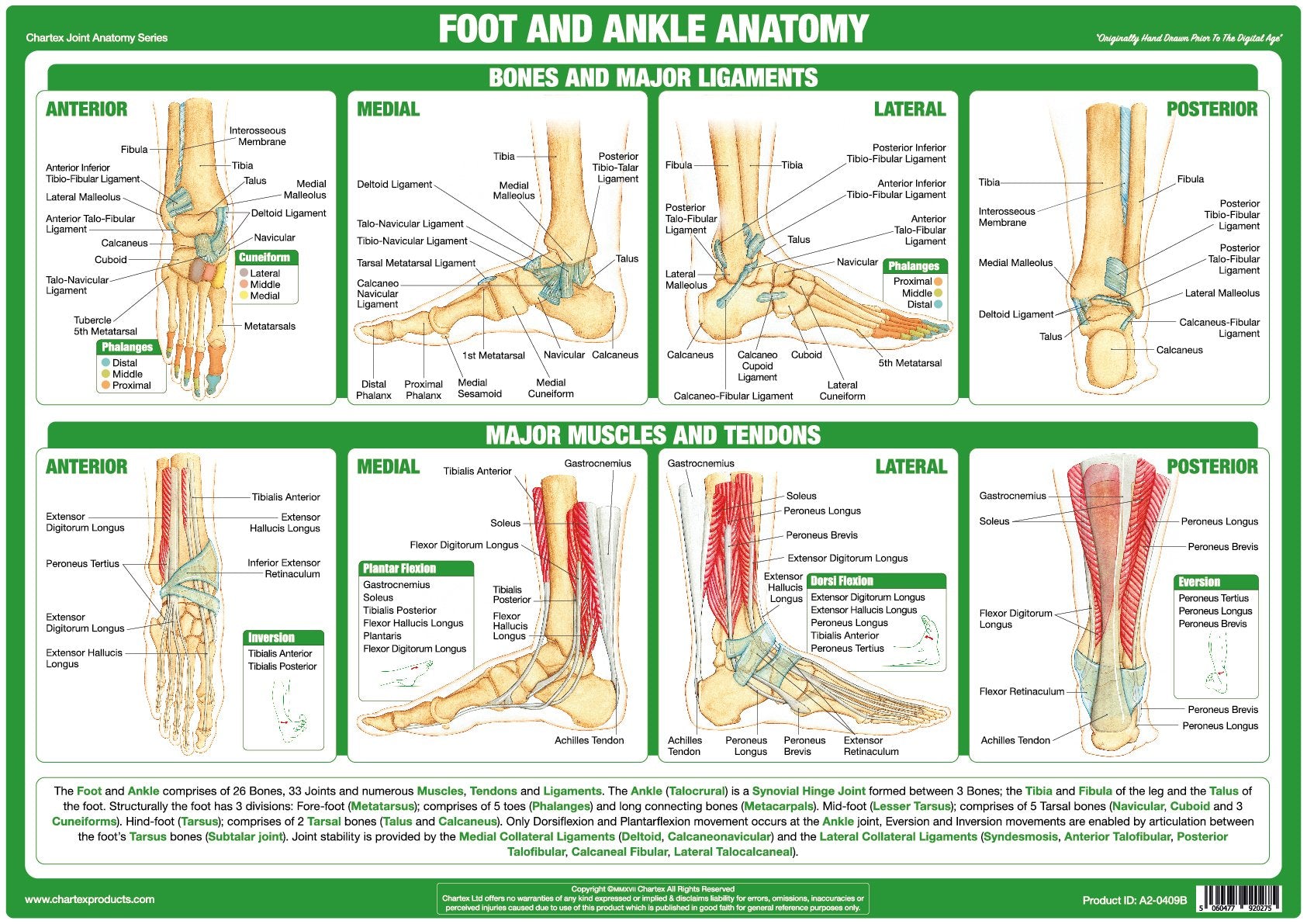
Chartex Foot and Ankle Joint Anatomy Chart
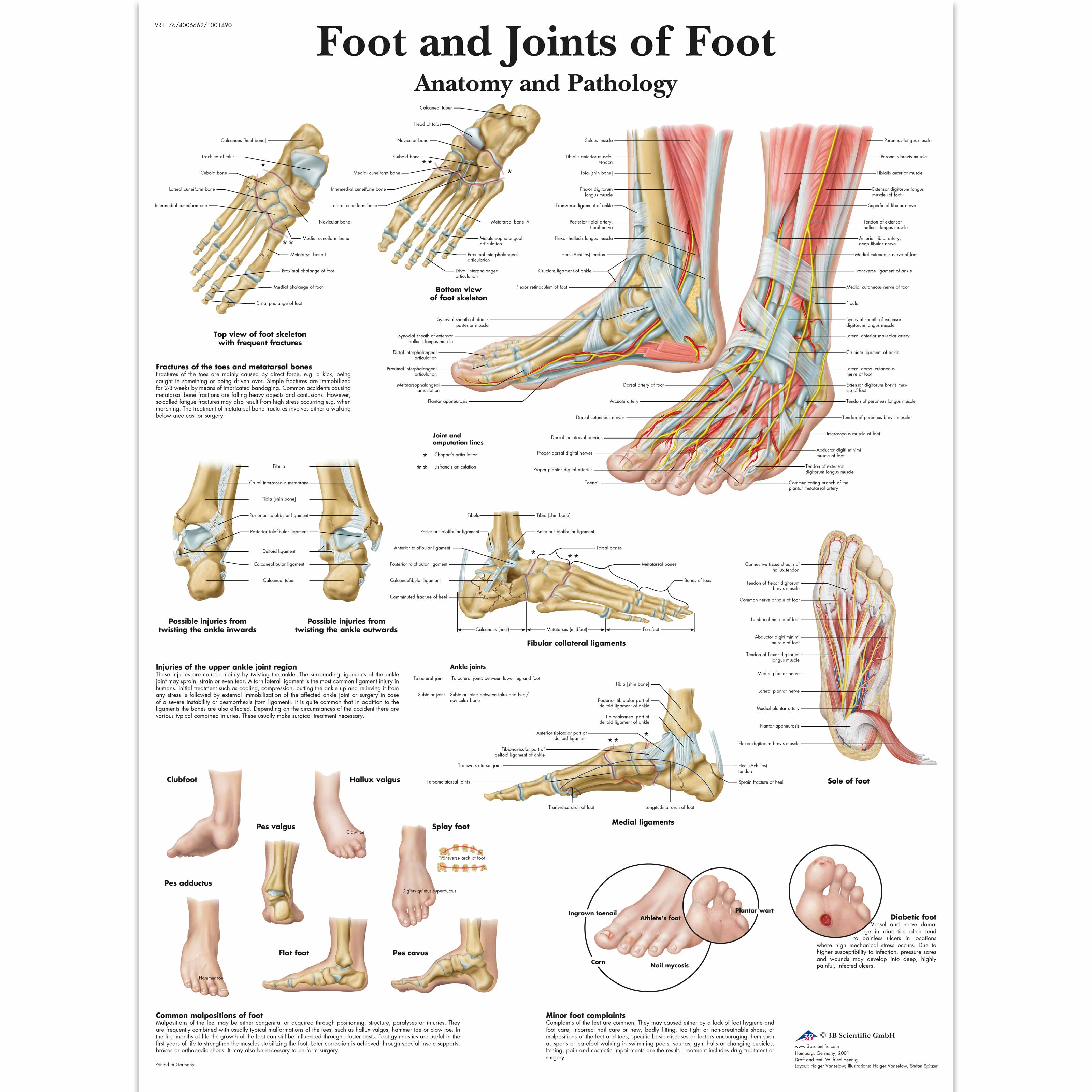
Anatomical Charts and Posters Anatomy Charts Foot and Ankle

Foot Ankle Anatomy Chart Poster Laminated ubicaciondepersonas.cdmx.gob.mx
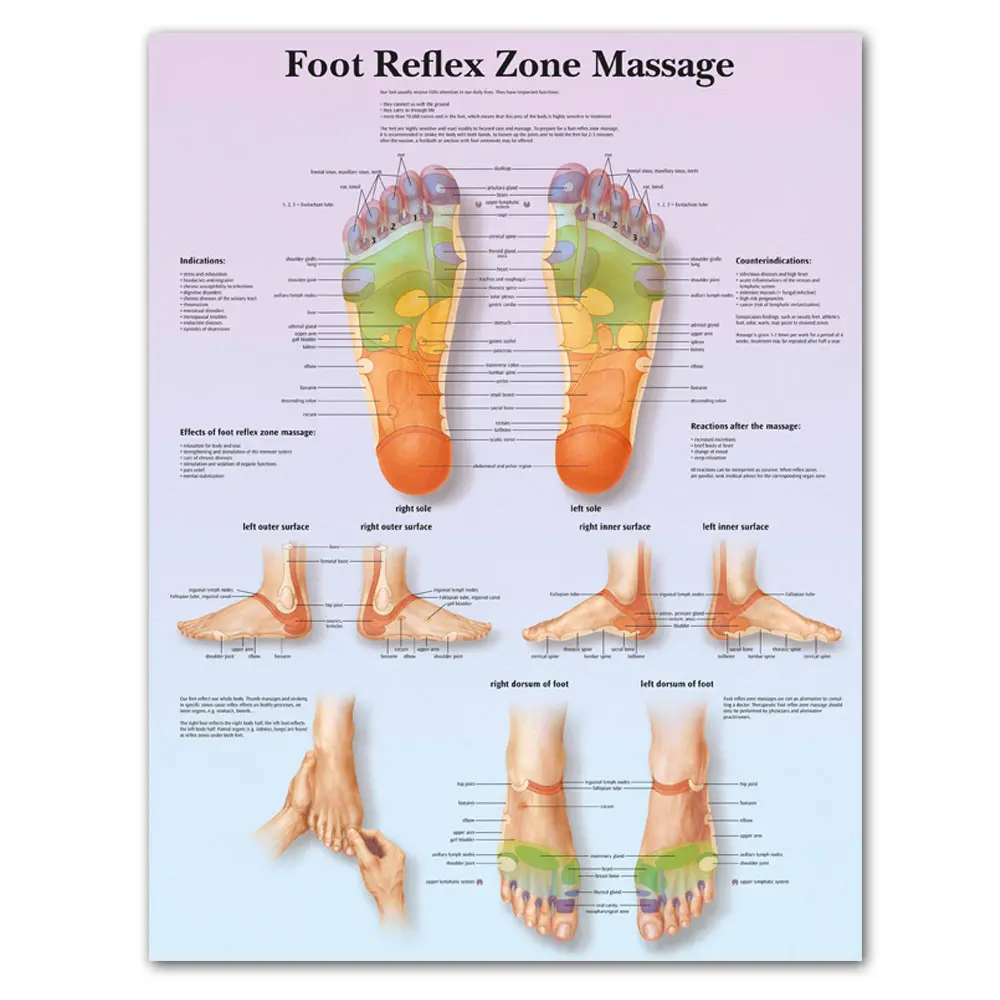
Foot Symptom Chart Anatomy Of Foot Anatomical Charts Posters Anatomy
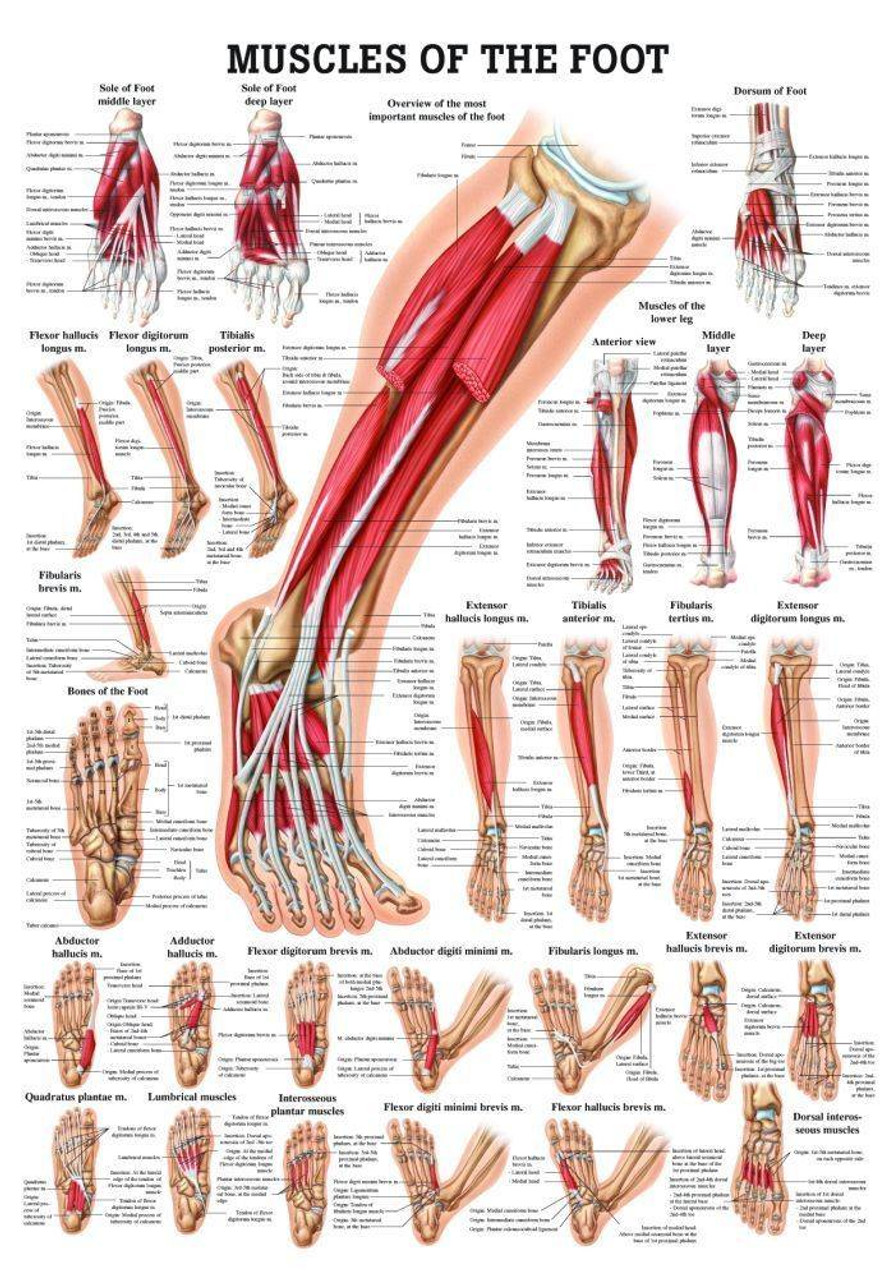
Foot Ankle Anatomy Chart Poster Laminated ubicaciondepersonas.cdmx.gob.mx
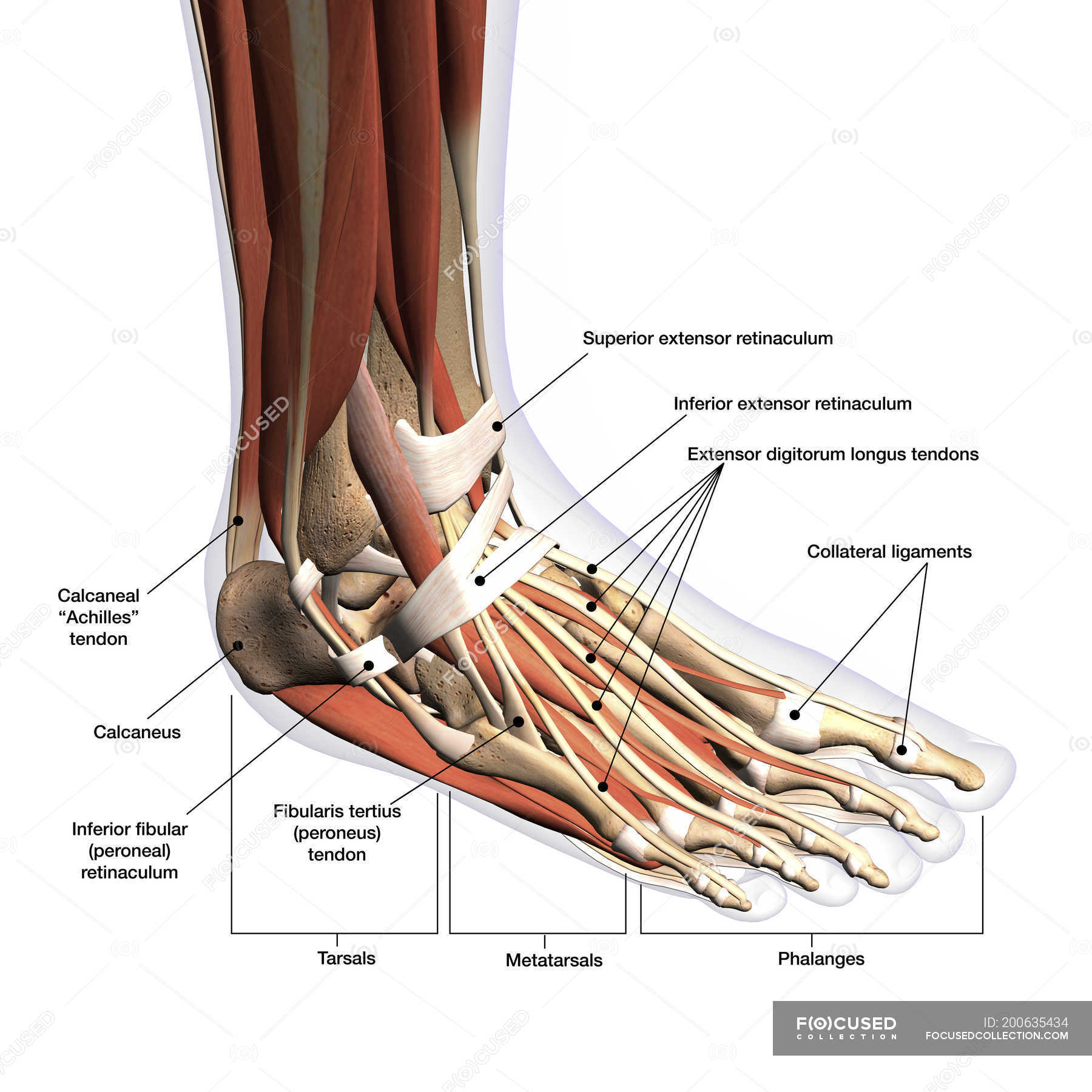
Anatomy of human foot with labels on white background — ankle, leg
Web With A Detailed Anatomical Chart Of The Foot, Students Will Find New Ways To Study And Learn About Anatomy.
Web The Anatomic Structures Below The Ankle Joint Comprise The Foot, Which Includes 26 Bones;
Web View Our Range Of Foot And Ankle Anatomy Charts And Posters, Designed By Our Team Of Professional Medical Illustrators.
Web The Foot Can Also Be Divided Up Into Three Regions:
Related Post: