Apple Frost Damage Chart
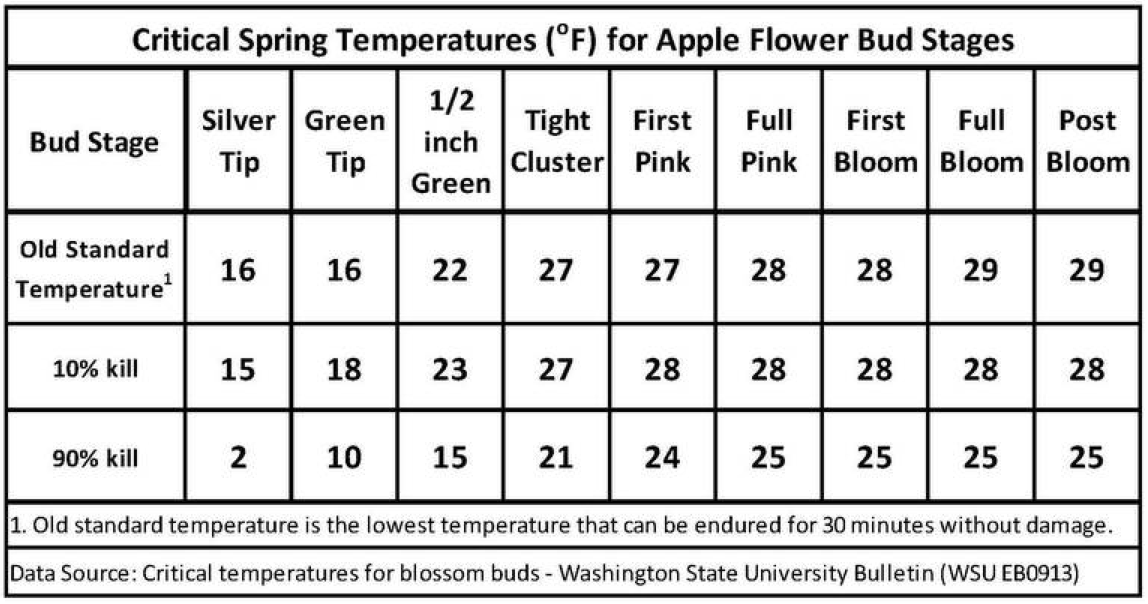
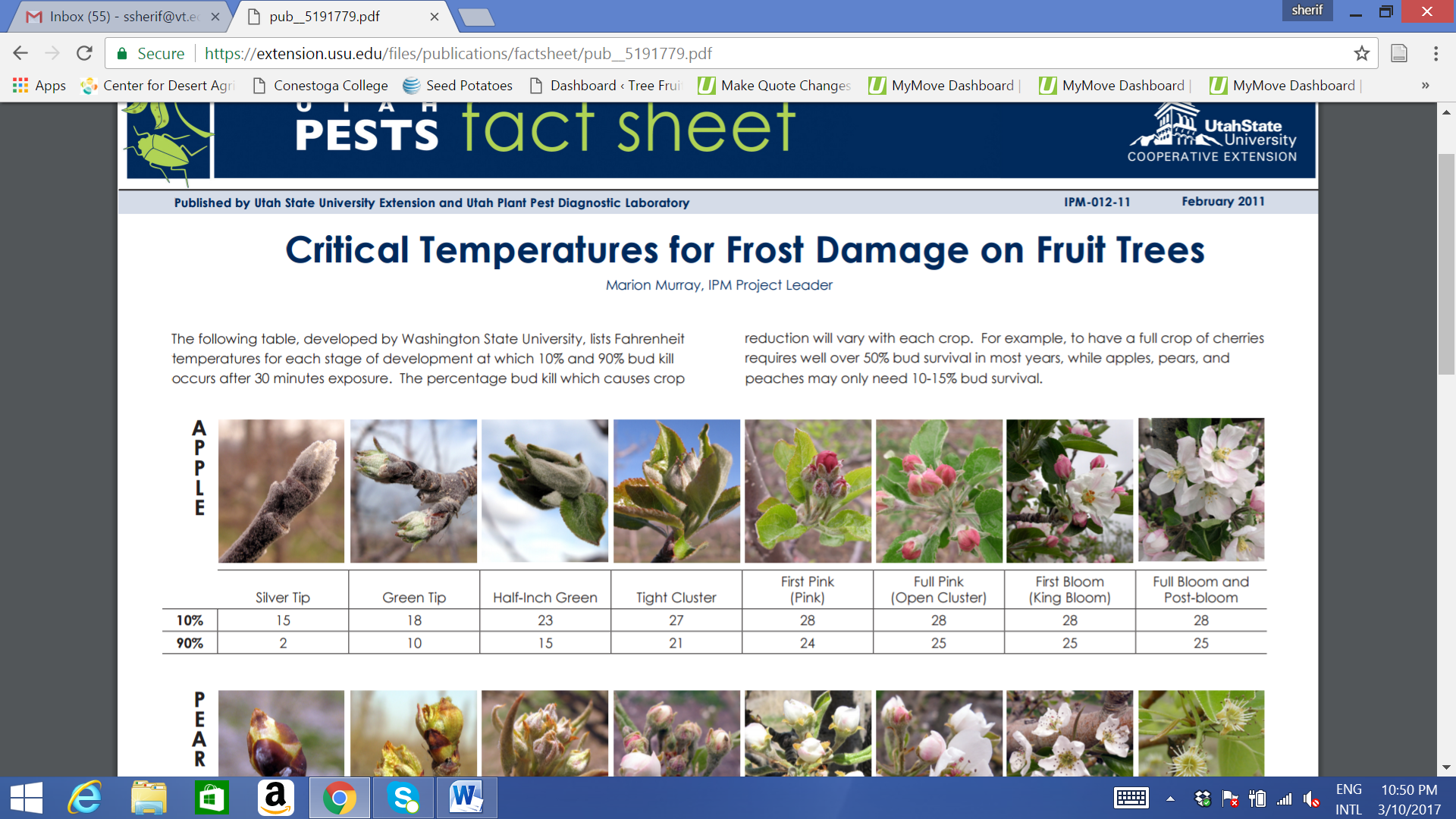
Apple Frost Damage Chart - Web critical temperatures for frost damage on fruit trees the following table, developed by washington state university, lists fahrenheit temperatures for each stage of development at which 10% and 90% bud kill occurs after 30 minutes exposure. Web although the absolute number of frost days is declining, warmer winters also lead to earlier blossom of fruit trees, which in turn can lead to regionally dependent increased risks of the occurrence of frost days after apple blossom. Web apple yield is negatively affected by a lack of sufficient amount of cold days to trigger the seasonal response of the trees. Tianna dupont, tree fruit extension specialist. Such affected fruit, although edible, are not salable and often are removed by hand thinning if possible. 1972, larcher 1981, 1985 ). Web 47 rows the table below shows the average temperatures required to kill. Web the limited frost resistance of xylem parenchyma cells (xpcs) is critical to winter frost survival of apple trees. Web old standard temperature is the lowest temperature that can be endured for 30 minutes without damage. The flesh of fruits with frost rings contained higher content of fructose and in the flesh directly under the rings there was higher sorbitol and malic acid content. Web critical temperatures for frost damage on fruit trees the following table, developed by washington state university, lists fahrenheit temperatures for each stage of development at which 10% and 90% bud kill occurs after 30 minutes exposure. The percentage bud kill which. This chart also shows the temperature that will kill 10 % and 90 % of normal fruit buds.. Web the limited frost resistance of xylem parenchyma cells (xpcs) is critical to winter frost survival of apple trees. A frost ring on an. These numbers were taken from washington (wsu) and michigan (msu) bulletins. Our results show how cropping system responses to seasonal climate can lead to unexpected effects of increased risk of frost damage as a result of. Web the results show that the frost damage from spring frost affects compounds in the peel, as well as in the flesh of ripe apples. Web how do you know if your fruit trees have been frost damaged? Web 47 rows the table below shows the average temperatures required to kill. This chart also shows the temperature that will kill. Web old standard temperature is the lowest temperature that can be endured for 30 minutes without damage. Web learn about different types of frost, how frost injury occurs, the risks in 2021, and mitigation strategies against frost damage. Web the limited frost resistance of xylem parenchyma cells (xpcs) is critical to winter frost survival of apple trees. Dates of average. These numbers were taken from washington (wsu) and michigan (msu) bulletins. Web learn about different types of frost, how frost injury occurs, the risks in 2021, and mitigation strategies against frost damage. Frost damage to xpcs can produce the symptoms of ‘blackheart injury’ in apple which can cause dieback of whole trees ( kemmer and schulz 1955, quamme et al.. The flesh of fruits with frost rings contained higher content of fructose and in the flesh directly under the rings there was higher sorbitol and malic acid content. Web the limited frost resistance of xylem parenchyma cells (xpcs) is critical to winter frost survival of apple trees. In the spring flower damage is based upon the critical temperature for flowers.. Such affected fruit, although edible, are not salable and often are removed by hand thinning if possible. Web young injured apple and pear fruit often have the surface cells and tissues killed and develop a pronounced scabby pattern on the fruit surface that is termed “frost ring” (figure11: Web although the absolute number of frost days is declining, warmer winters. Web frost injury to apple and pear fruit kills the surface cells and tissues, causing a pronounced scabby pattern on the fruit surface that is termed “frost ring”. Growers and home gardeners can use a razor blade and magnifying glass to check the amount of frost damage. Frost damage to xpcs can produce the symptoms of ‘blackheart injury’ in apple. In the spring flower damage is based upon the critical temperature for flowers. Web frost injury to apple and pear fruit kills the surface cells and tissues, causing a pronounced scabby pattern on the fruit surface that is termed “frost ring”. Web figures 2 through 5 show frost damage symptoms on apple, peach, cherry, and plum, respectively. Web apple yield. Web critical temperatures for frost damage on fruit trees the following table, developed by washington state university, lists fahrenheit temperatures for each stage of development at which 10% and 90% bud kill occurs after 30 minutes exposure. Our results show how cropping system responses to seasonal climate can lead to unexpected effects of increased risk of frost damage as a. Web figures 2 through 5 show frost damage symptoms on apple, peach, cherry, and plum, respectively. Dates of average last chance for freezing and first date of frost in the fall for select cities. Growers and home gardeners can use a razor blade and magnifying glass to check the amount of frost damage. Web 47 rows the table below shows the average temperatures required to kill. Web learn about different types of frost, how frost injury occurs, the risks in 2021, and mitigation strategies against frost damage. 1972, larcher 1981, 1985 ). Web young injured apple and pear fruit often have the surface cells and tissues killed and develop a pronounced scabby pattern on the fruit surface that is termed “frost ring” (figure11: Web critical temperatures and bud stage charts. Web the following table, developed by washington state university, lists fahrenheit temperatures for each stage of development at which 10% and 90% bud kill occurs after 30 minutes exposure. Web critical temperatures for frost damage on fruit trees the following table, developed by washington state university, lists fahrenheit temperatures for each stage of development at which 10% and 90% bud kill occurs after 30 minutes exposure. Web the results show that the frost damage from spring frost affects compounds in the peel, as well as in the flesh of ripe apples. Such affected fruit, although edible, are not salable and often are removed by hand thinning if possible. Web how do you know if your fruit trees have been frost damaged? Web apple yield is negatively affected by a lack of sufficient amount of cold days to trigger the seasonal response of the trees. Our results show how cropping system responses to seasonal climate can lead to unexpected effects of increased risk of frost damage as a result of warmer winters. Web although the absolute number of frost days is declining, warmer winters also lead to earlier blossom of fruit trees, which in turn can lead to regionally dependent increased risks of the occurrence of frost days after apple blossom.Critical Temperatures Frost Damage Fruit Trees Utah Plants
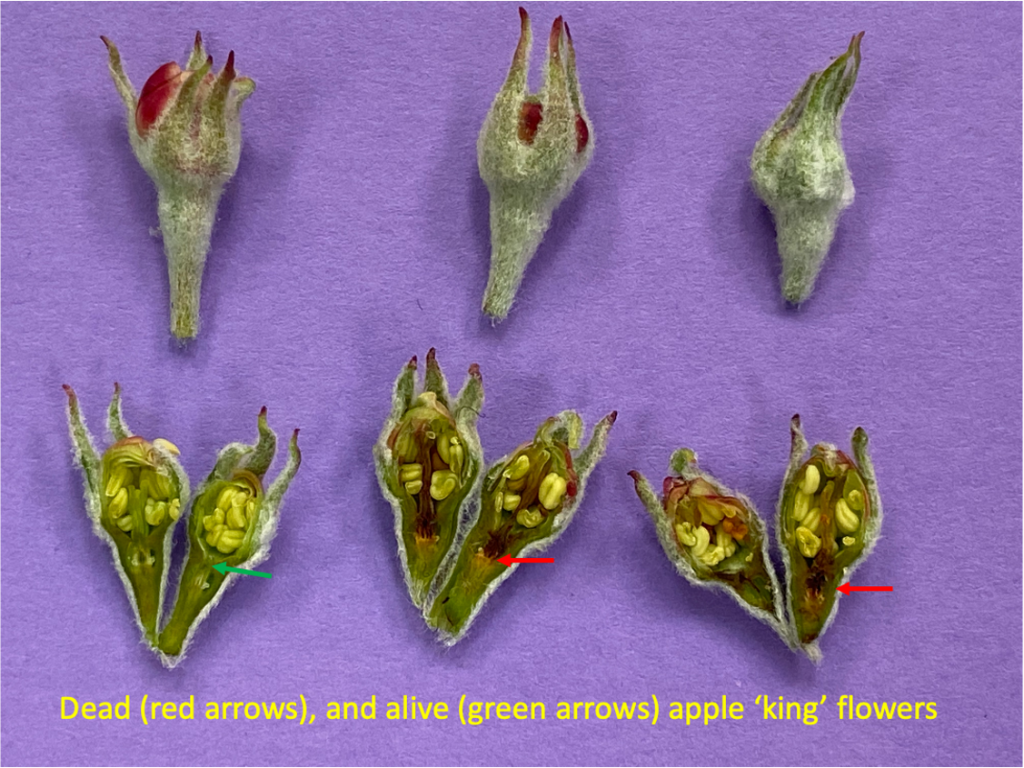
Flower Bud Damage Assessments of Hudson Valley Apple; April 8th, 2016

Critical Temperatures and Bud Stage Charts Chelan & Douglas Counties

Frost damage in apple and sweet cherry Tree Fruit Horticulture Updates
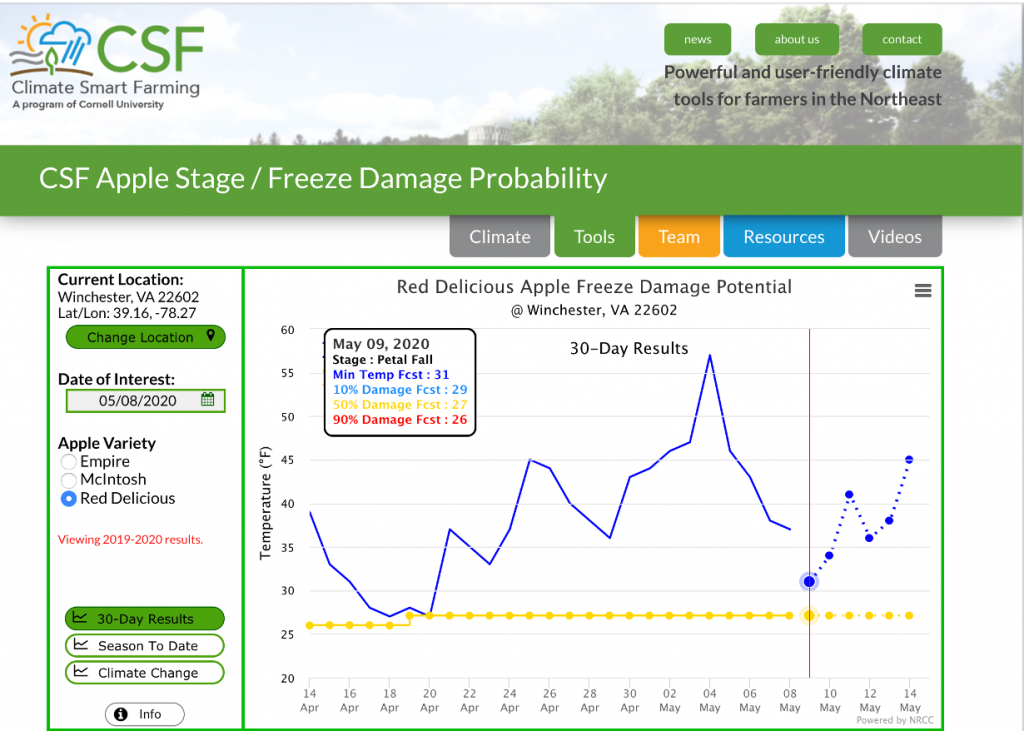
The freeze warning tonight (5/8/2020) Tree Fruit Horticulture Updates
What’s important to look at if concerned about potential frost? Tree
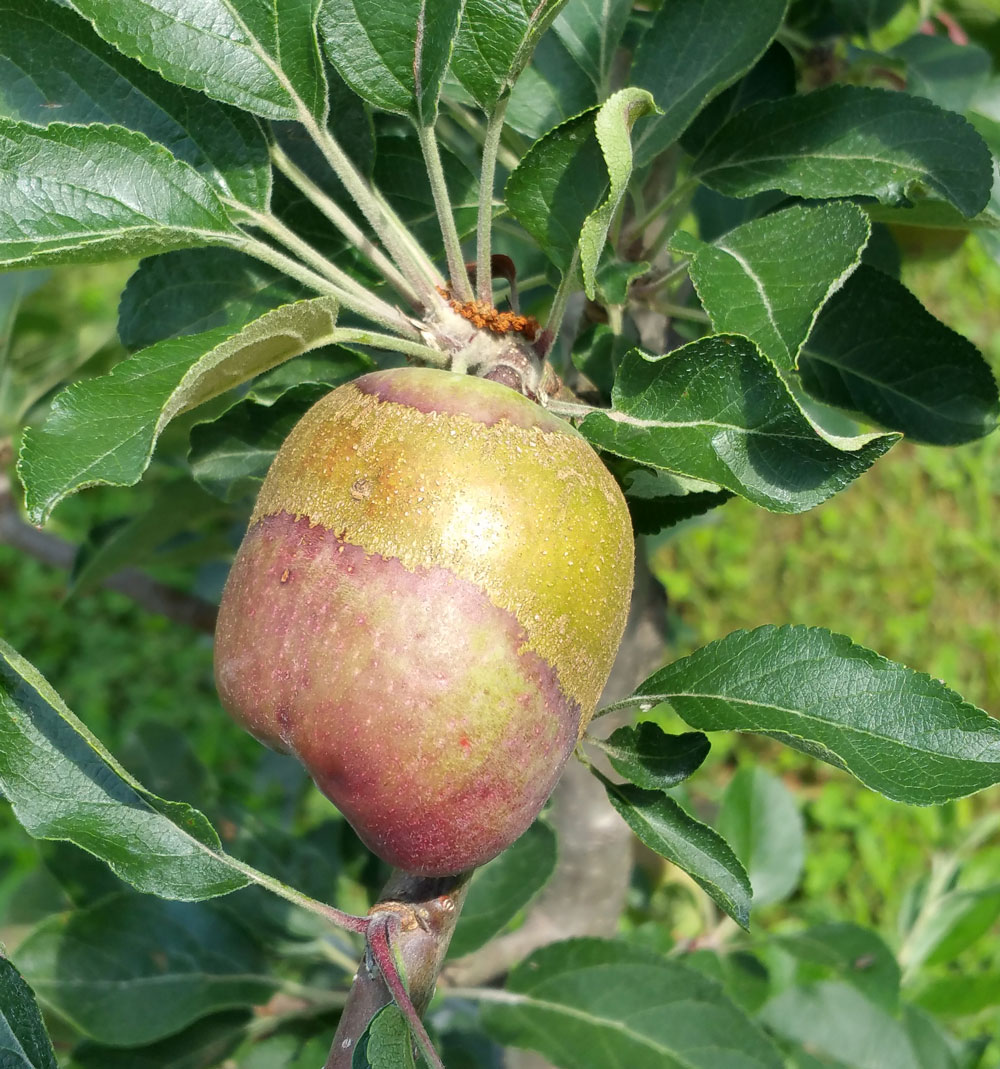

Frost Ring on Apples NC State Extension
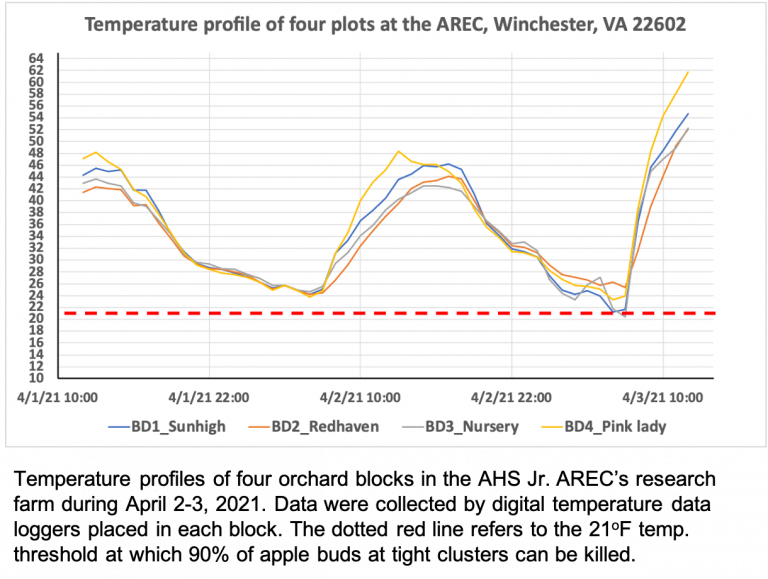
More frost damage recorded in Apples and Sweet Cherries in Winchester

PPT Biological Control Competitive Exclusion PowerPoint Presentation

Frost Damage on Apples Gloucestershire Organic Gardening Group
The Flesh Of Fruits With Frost Rings Contained Higher Content Of Fructose And In The Flesh Directly Under The Rings There Was Higher Sorbitol And Malic Acid Content.
Web Frost Injury To Apple And Pear Fruit Kills The Surface Cells And Tissues, Causing A Pronounced Scabby Pattern On The Fruit Surface That Is Termed “Frost Ring”.
Tianna Dupont, Tree Fruit Extension Specialist.
These Numbers Were Taken From Washington (Wsu) And Michigan (Msu) Bulletins.
Related Post:
