Aspen Criteria For Malnutrition Chart
Aspen Criteria For Malnutrition Chart - Involuntary loss of 10% or more of usual body weight within 6 months, or involuntary loss of greater than or 5% or more of usual body weight in 1 month. Inadequate intake is represented as a percentage of estimated need over time. Nutrition screening is not nutrition assessment. Web the academy of nutrition and dietetics (academy) and the american society for parenteral and enteral nutrition (a.s.p.e.n.) recommend that a standardized set of diagnostic characteristics be used to identify and document adult malnutrition in. Contents lists available at sciencedirect. Web malnutrition is the result of inadequate food and nutrient intake or assimilation; Web aspen recommends the use of a validated nutrition screening tool to identify malnutrition risk.2. Web the purpose of this paper is to review the available literature on the usability, feasibility, validity, and reliability of both the adult and pediatric consensus malnutrition diagnostic approaches, as well as to evaluate their. Web the academy of nutrition and dietetics (academy) and the american society for parenteral and enteral nutrition (a.s.p.e.n.) recommend that a standardized set of diagnostic characteristics be used to identify and document adult malnutrition in. Here are some resources and tools to help advocate for yourself or your loved ones. Web malnutrition is the result of inadequate food and nutrient intake or assimilation; Web according to espen, malnutrition, or undernutrition, is defined as “a state resulting from lack of intake or uptake of nutrition that leads to altered body composition (decreased fat free mass) and body cell mass leading to diminished physical and mental function and impaired clinical outcome from. Web adults should be considered at risk if they have any of the following: Web 6 characteristics of aspen malnutrition criteria (1): 1 in 1995, aspen recognized the key role of nutrition assessment by incorporating it as a fundamental component in the. Web aspen recommends the use of a validated nutrition screening tool to identify malnutrition risk.2. Low risk, medium. Web malnutrition is the result of inadequate food and nutrient intake or assimilation; Web 6 characteristics of aspen malnutrition criteria (1): Height and weight should be measured rather than estimated to determine body mass index (bmi) and. Rd obtains diet history and estimates energy needs; Weight change over time is represented as a percentage of weight loss from baseline. Web the academy of nutrition and dietetics (academy) and the american society for parenteral and enteral nutrition (a.s.p.e.n.) recommend that a standardized set of diagnostic characteristics be used to identify and document adult malnutrition in routine clinical practice. Low risk, medium risk, and high risk (table 1 ). Involuntary loss of 10% or more of usual body weight within 6. Web aspen recommends the use of a validated nutrition screening tool to identify malnutrition risk.2. Thus, recent intake compared to estimated requirements is a primary criterion defining malnutrition. Web it scores body mass index (bmi), unintentional weight loss, and acute disease effect (which bapen defines as no or unlikely dietary intake for >5 days because of activity of disease) and. Web according to espen, malnutrition, or undernutrition, is defined as “a state resulting from lack of intake or uptake of nutrition that leads to altered body composition (decreased fat free mass) and body cell mass leading to diminished physical and mental function and impaired clinical outcome from disease”. Weight change over time is represented as a percentage of weight loss. Web aspen focuses on reducing the incidence of malnutrition by providing educational support and resources to healthcare professionals and consumers, and through advocacy work for malnutrition prevention and treatment. Thus, recent intake compared to estimated requirements is a primary criterion defining malnutrition. Web the academy of nutrition and dietetics (academy) and the american society for parenteral and enteral nutrition (a.s.p.e.n.). Contents lists available at sciencedirect. Screening identifies risk for a. Web you might be at risk for malnutrition due to your disease or condition and this may impact your clinical outcome. Web it scores body mass index (bmi), unintentional weight loss, and acute disease effect (which bapen defines as no or unlikely dietary intake for >5 days because of activity. Here are some resources and tools to help advocate for yourself or your loved ones. Web in the 1970s, leaders of the american society for parenteral and enteral nutrition (aspen) declared nutrition assessment as the key step to identify malnutrition and offered a comprehensive approach for its diagnosis. Each of these criteria have guidelines to determine the type of malnutrition. Thus, recent intake compared to estimated requirements is a primary criterion defining malnutrition. Web adults should be considered at risk if they have any of the following: Web aspen uses the grade system of guideline development and clearly delineates this methodology in each guideline. Web the purpose of this paper is to review the available literature on the usability, feasibility,. Screening identifies risk for a. Web according to espen, malnutrition, or undernutrition, is defined as “a state resulting from lack of intake or uptake of nutrition that leads to altered body composition (decreased fat free mass) and body cell mass leading to diminished physical and mental function and impaired clinical outcome from disease”. Height and weight should be measured rather than estimated to determine body mass index (bmi) and. Here are some resources and tools to help advocate for yourself or your loved ones. Each of these criteria have guidelines to determine the type of malnutrition and the severity of malnutrition. Web we recommend characteristics for the identification of adult malnutrition (and/aspen tool).1 suspect malnutrition if two or more characteristics are present: Web aspen uses the grade system of guideline development and clearly delineates this methodology in each guideline. Open for comments until june 7. Web in the 1970s, leaders of the american society for parenteral and enteral nutrition (aspen) declared nutrition assessment as the key step to identify malnutrition and offered a comprehensive approach for its diagnosis. Web aspen recommends the use of a validated nutrition screening tool to identify malnutrition risk.2. Aspen nutrition guidelines for replacement of a balloon gastrostomy tube in infants and pediatric patients: Web adults should be considered at risk if they have any of the following: Web it scores body mass index (bmi), unintentional weight loss, and acute disease effect (which bapen defines as no or unlikely dietary intake for >5 days because of activity of disease) and separates patients into three risk groups: Rd obtains diet history and estimates energy needs; Web the gomez classification 41 and the waterlow criteria 68 use this standard and define mild, moderate, and severe malnutrition as 76%−90%, 61%−75%, and <60% 41 and 80%−89%, 70%−79%, and <70%, 68 respectively. 1 in 1995, aspen recognized the key role of nutrition assessment by incorporating it as a fundamental component in the.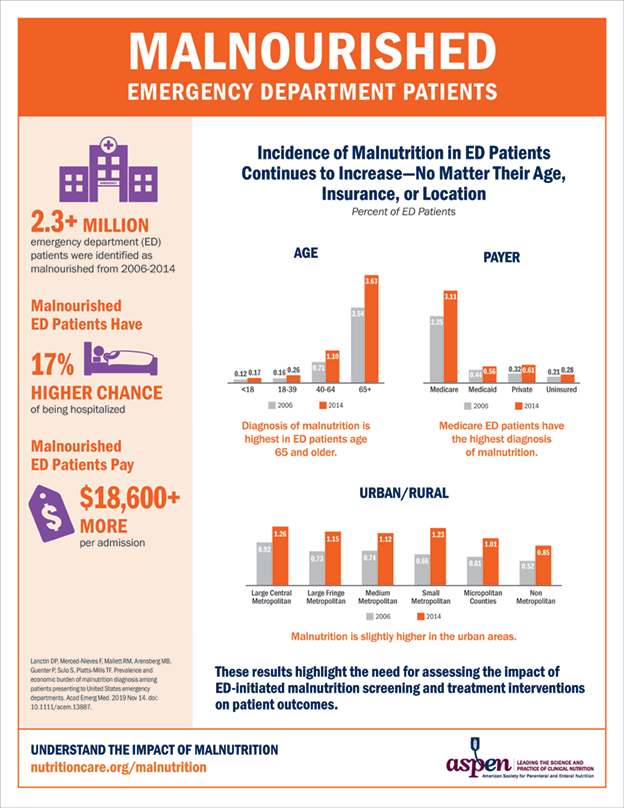
ASPEN Malnutrition Solution Center

Understanding ASPEN Malnutrition Criteria The Geriatric Dietitian

Aspen Academy Malnutrition Criteria Chart

A.s.p.e.n. Criteria For Malnutrition Chart

Aspen Malnutrition Diagnosis Chart

A.s.p.e.n. Criteria For Malnutrition Chart

Aspen Criteria For Malnutrition Chart

Aspen Malnutrition Diagnosis Chart

A.s.p.e.n. Criteria For Malnutrition Chart

Aspen Malnutrition Guidelines Chart
You Can Download And Print Any Of.
Low Risk, Medium Risk, And High Risk (Table 1 ).
Web You Might Be At Risk For Malnutrition Due To Your Disease Or Condition And This May Impact Your Clinical Outcome.
Involuntary Loss Of 10% Or More Of Usual Body Weight Within 6 Months, Or Involuntary Loss Of Greater Than Or 5% Or More Of Usual Body Weight In 1 Month.
Related Post: