Benzene Reactivity Chart
Benzene Reactivity Chart - Web common benzene reactions are nitration of benzene. This section with focus on three side chain reactions: Of these, the most common type is electrophilic substitution. It’s one thing to learn about electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions of benzene itself. The most characteristic reaction of aromatic compounds is substitution at a ring carbon: But once you move toward substituted benzenes, that’s when things start getting really interesting. Furthermore, s n 1, s n 2 and e1 reactions of benzylic halides, show enhanced reactivity, due to the adjacent aromatic ring. Web the chemical reactivity of benzene contrasts with that of the alkenes in that substitution reactions occur in preference to addition reactions, as illustrated in the following diagram (some comparable reactions of cyclohexene are shown in the green box). Web check out this reaction map of over 25 different organic chemistry reactions of benzene and related compounds, allowing for easy synthetic planning. Benzene has a high electron density and so attracts electrophiles. Web check out this reaction map of over 25 different organic chemistry reactions of benzene and related compounds, allowing for easy synthetic planning. Web reactions of benzene. Web the chemical reactivity of benzene contrasts with that of the alkenes in that substitution reactions occur in preference to addition reactions, as illustrated in the following diagram (some comparable reactions of cyclohexene. Web the chemical reactivity of benzene contrasts with that of the alkenes in that substitution reactions occur in preference to addition reactions, as illustrated in the following diagram (some comparable reactions of cyclohexene are shown in the green box). This section with focus on three side chain reactions: Of these, the most common type is electrophilic substitution. Most of benzene’s. This reaction is known as nitration of benzene. Most of benzene’s reactions involve substituting one h for another atom or group of atoms. Web the reactivity of substituted benzenes. Of these, the most common type is electrophilic substitution. Web compare the reactivity of a typical alkene with that of benzene. A demonstration of bromine substitution and addition reactions is helpful at this point. Web two important reaction patterns: Web the benzylic hydrogens of alkyl substituents on a benzene ring are activated toward free radical attack, as noted earlier. Side chain reactions can be used to create a wider range of aromatic compounds. This reaction is known as nitration of benzene. Web reactions of benzene. Measuring reaction rates can provide insight into the mechanism. To investigate the reactivity of substituted benzenes and to examine the relationship between electron withdrawing/donating groups and reactivity. Of these, the most common type is electrophilic substitution. Web in the following diagram we see that electron donating substituents (blue dipoles) activate the benzene ring toward electrophilic attack,. Web two important reaction patterns: Web in the following diagram we see that electron donating substituents (blue dipoles) activate the benzene ring toward electrophilic attack, and electron withdrawing substituents (red dipoles) deactivate the ring (make it less reactive to electrophilic attack). “sigma” (σ) donors and acceptors (otherwise known as “inductive effects”) Web the chemical reactivity of benzene contrasts with that. Web the chemical reactivity of benzene contrasts with that of the alkenes in that substitution reactions occur in preference to addition reactions, as illustrated in the following diagram (some comparable reactions of cyclohexene are shown in the green box). Measuring reaction rates can provide insight into the mechanism. To investigate the reactivity of substituted benzenes and to examine the relationship. Web the chemical reactivity of benzene contrasts with that of the alkenes in that substitution reactions occur in preference to addition reactions, as illustrated in the following diagram (some comparable reactions of cyclohexene are shown in the green box). This reaction is known as nitration of benzene. A demonstration of bromine substitution and addition reactions is helpful at this point.. Measuring reaction rates can provide insight into the mechanism. Benzene has a high electron density and so attracts electrophiles. Web the chemical reactivity of benzene contrasts with that of the alkenes in that substitution reactions occur in preference to addition reactions, as illustrated in the following diagram (some comparable reactions of cyclohexene are shown in the green box). Web compare. Side chain reactions can be used to create a wider range of aromatic compounds. Most of benzene’s reactions involve substituting one h for another atom or group of atoms. Web there’s a lot to this post, so here’s a quick index: It’s one thing to learn about electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions of benzene itself. The most characteristic reaction of aromatic. Of these, the most common type is electrophilic substitution. A demonstration of bromine substitution and addition reactions is helpful at this point. Molecular formula of c6h 6 molecular mass of 78 hybridization= sp2 bond angles= 120o. To complement the the organic reaction map posted a week or so ago, here’s a reaction map looking at reactions that allow you to vary the substituents on a benzene ring. Measuring reaction rates can provide insight into the mechanism. Web common benzene reactions are nitration of benzene. Web in the following diagram we see that electron donating substituents (blue dipoles) activate the benzene ring toward electrophilic attack, and electron withdrawing substituents (red dipoles) deactivate the ring (make it less reactive to electrophilic attack). Web in the following diagram we see that electron donating substituents (blue dipoles) activate the benzene ring toward electrophilic attack, and electron withdrawing substituents (red dipoles) deactivate the ring (make it less reactive to electrophilic attack). Web check out this reaction map of over 25 different organic chemistry reactions of benzene and related compounds, allowing for easy synthetic planning. Web there’s a lot to this post, so here’s a quick index: “sigma” (σ) donors and acceptors (otherwise known as “inductive effects”) Web the chemical reactivity of benzene contrasts with that of the alkenes in that substitution reactions occur in preference to addition reactions, as illustrated in the following diagram (some comparable reactions of cyclohexene are shown in the green box). Furthermore, s n 1, s n 2 and e1 reactions of benzylic halides, show enhanced reactivity, due to the adjacent aromatic ring. Web benzene reacts with strong electrophiles. Web compare the reactivity of a typical alkene with that of benzene. Web reactions of benzene.
Summarize of benzene reactions ChemicalEngineering

CHEMISTRY OF BENZENE ELECTROPHILIC AROMATIC SUBSTITUTION CHEM 2425

A Reaction Map (PDF) for Benzene and Aromatic Compounds in 2021

Benzene Flow Chart Organic chemistry, Organic chemistry reactions

A Reaction Map (PDF) for Benzene and Aromatic Compounds Organic

A Reaction Map (PDF) for Benzene and Aromatic Compounds Organic

Summarize of benzene reactions r/ChemicalEngineering

Organic Chemistry Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions
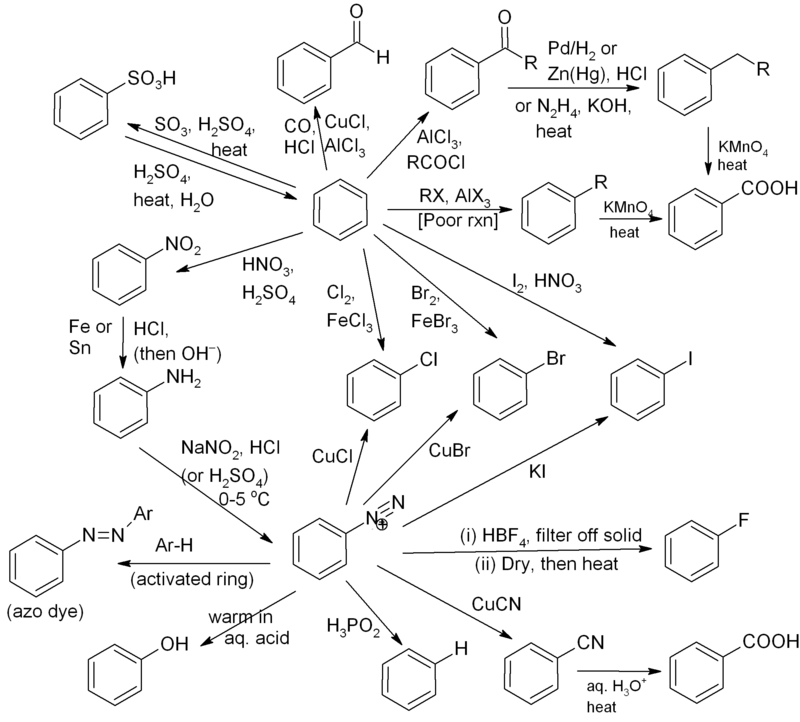
Nail down the reactions associated with Benzene on your fingertips!
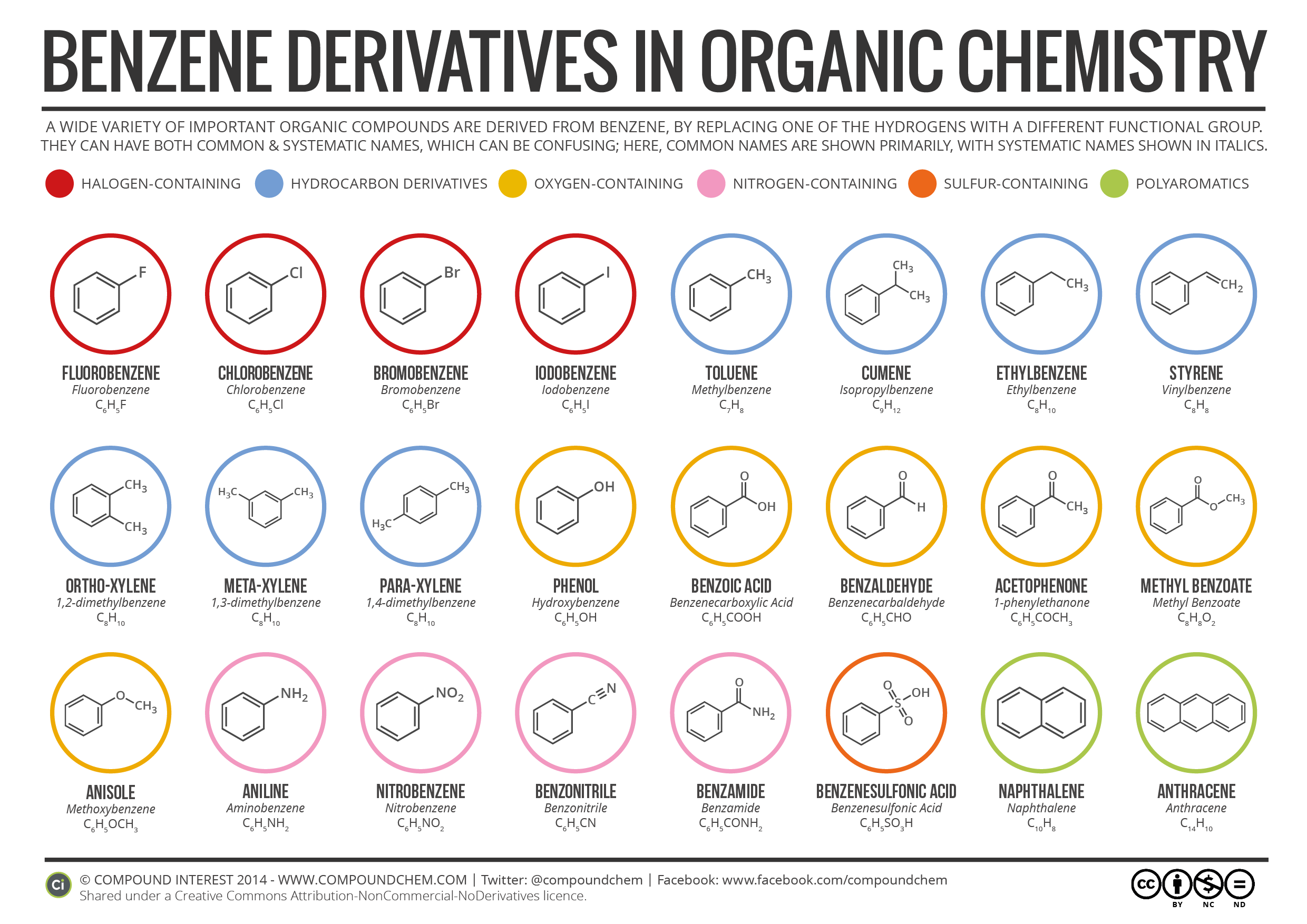
Benzene Derivatives and Their Nomenclature in Organic Chemistry
The Most Characteristic Reaction Of Aromatic Compounds Is Substitution At A Ring Carbon:
Benzene Has A High Electron Density And So Attracts Electrophiles.
Primary Analysis Revealed Benzene Had.
Oxidation Of Alkyl Groups, Bromination Of Alkyl Groups,.
Related Post: