Boiling Point Chart
Boiling Point Chart - Web the boiling point is defined as the temperature at which the saturated vapor pressure of a liquid is equal to the surrounding atmospheric pressure. With our boiling point calculator, you can quickly determine the atmospheric boiling point of various substances. The standard boiling point, as defined by the iupac in 1982, is the temperature at which boiling occurs when the pressure is 1 bar. Web information on the properties of common solvents used in organic chemistry including boiling points, solubility, density, dielectric constants, and flash points. The boiling point is a higher temperature below sea level and a lower temperature above sea level. Molweight, melting and boiling point, density, flash point and autoignition temperature, as well as number of carbon and hydrogen atoms in each molecule for 200 different hydrocarbons. Factors that affect the boiling point of water. American elements toolbox of conversion tables, properties, identifiers and size charts. Web this is a list of the various reported boiling points for the elements, with recommended values to be used elsewhere on wikipedia. Web the boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the pressure surrounding the liquid and the liquid changes into a vapor. Web the boiling point is the temperature at which boiling occurs for a specific liquid. The simplest of the aromatics have 6 carbon atoms and contains 3 double bounds. The distance between molecules in a crystal lattice is small and regular, with intermolecular forces serving to constrain the motion of the molecules more severely than in the liquid state. Web. Whether you want to analyze water, ethanol, or ammonia, simply provide some reference values, and this calculator will do the work for you. Web table of contents: The simplest of the aromatics have 6 carbon atoms and contains 3 double bounds. Web explore how boiling point changes with atomic number in the periodic table of elements via interactive plots. Values. Please find below a table of common materials (liquid, gas, or solid at ambient temperature and pressure) and their boiling points, aggregated from different sources, measured under 1 atm. See water and heavy water for thermodynamic properties at standard condtions. Values were not verified individually. The distance between molecules in a crystal lattice is small and regular, with intermolecular forces. Whether you want to analyze water, ethanol, or ammonia, simply provide some reference values, and this calculator will do the work for you. Most know that water boils at 100 degrees celsius. Boiling point data for the elements presented in two ways: However, in this section we learn that the boiling point of a liquid depends on pressure. Data table. Please find below a table of common materials (liquid, gas, or solid at ambient temperature and pressure) and their boiling points, aggregated from different sources, measured under 1 atm. The chemical element with the lowest boiling point is helium and the element with the highest boiling point is tungsten. When the atmospheric pressure is equal to the vapor pressure of. The distance between molecules in a crystal lattice is small and regular, with intermolecular forces serving to constrain the motion of the molecules more severely than in the liquid state. Estimate boiling point and vapor pressure. In more technical terms, it is when a liquid's vapor pressure equals its applied pressure (typically the atmospheric pressure). The boiling point at atmospheric. The unity used for the melting point is celsius (c). The chemical element with the lowest boiling point is helium and the element with the highest boiling point is tungsten. Web for chemistry students and teachers: Data table of boiling points of common liquids and solids. Web the normal boiling point or the atmospheric boiling point is the boiling point. The standard boiling point, as defined by the iupac in 1982, is the temperature at which boiling occurs when the pressure is 1 bar. The distance between molecules in a crystal lattice is small and regular, with intermolecular forces serving to constrain the motion of the molecules more severely than in the liquid state. However, in this section we learn. Molweight, melting and boiling point, density, flash point and autoignition temperature, as well as number of carbon and hydrogen atoms in each molecule for 200 different hydrocarbons. How to use the boiling point calculator. Factors that affect the boiling point of water. In more technical terms, it is when a liquid's vapor pressure equals its applied pressure (typically the atmospheric. Estimate boiling point and vapor pressure. Web table of contents: Whether you want to analyze water, ethanol, or ammonia, simply provide some reference values, and this calculator will do the work for you. The standard boiling point of water is 99.61 °c at 1 bar of pressure. Web 1 atm = 760 mmhg. The unity used for the melting point is celsius (c). Use the interactive controls above to simplify calculations and improve the efficiency of your distillation or evaporation requirements. The boiling point is a higher temperature below sea level and a lower temperature above sea level. The boiling point of a liquid varies depending upon the surrounding environmental pressure. Web the normal boiling point of water is 100 °c, 212 °f, or 373.1 k. Web 1 ia 1a 18 viiia 8a 2 iia 2a 13 iiia 3a 14 iva 4a 15 va 5a 16 via 6a 17 viia 7a 3 iiib 3b 4 ivb 4b 5 vb 5b 6 vib 6b 7 viib 7b 8 9 viii 8 10 11 ib 1b 12 iib 2b. Data table of boiling points of common liquids and solids. The standard boiling point of water is 99.61 °c at 1 bar of pressure. The “normal” refers to sea level or an elevation of 0 meters or feet. The distance between molecules in a crystal lattice is small and regular, with intermolecular forces serving to constrain the motion of the molecules more severely than in the liquid state. The standard boiling point, as defined by the iupac in 1982, is the temperature at which boiling occurs when the pressure is 1 bar. However, in this section we learn that the boiling point of a liquid depends on pressure. Web the boiling point is the temperature at which boiling occurs for a specific liquid. Web boiling point of gases, liquids & solids: With our boiling point calculator, you can quickly determine the atmospheric boiling point of various substances. Factors that affect the boiling point of water.
Melting And Boiling Point Chart
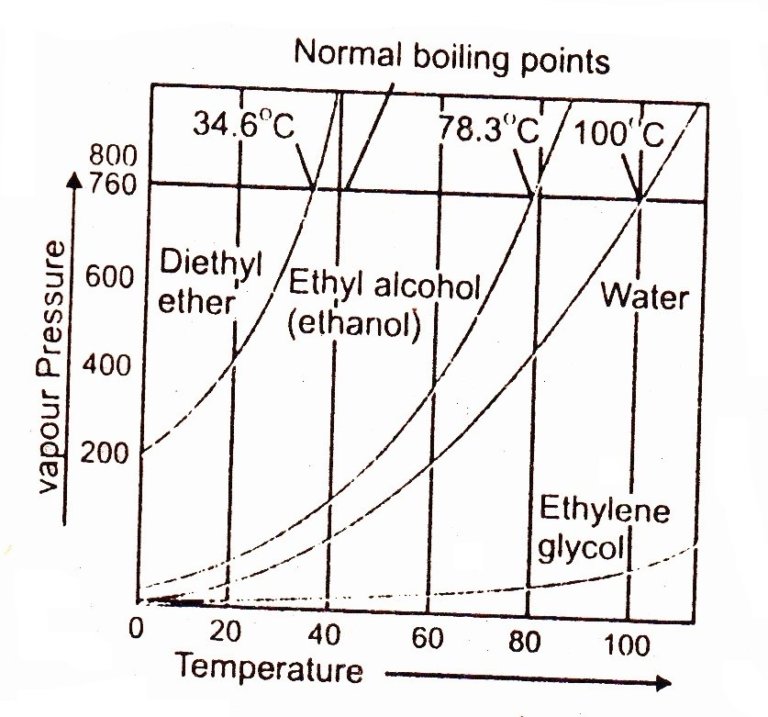
Definition and Explanation of Boiling Point Chemistry Skills

Organic Chemistry Boiling Point Chart
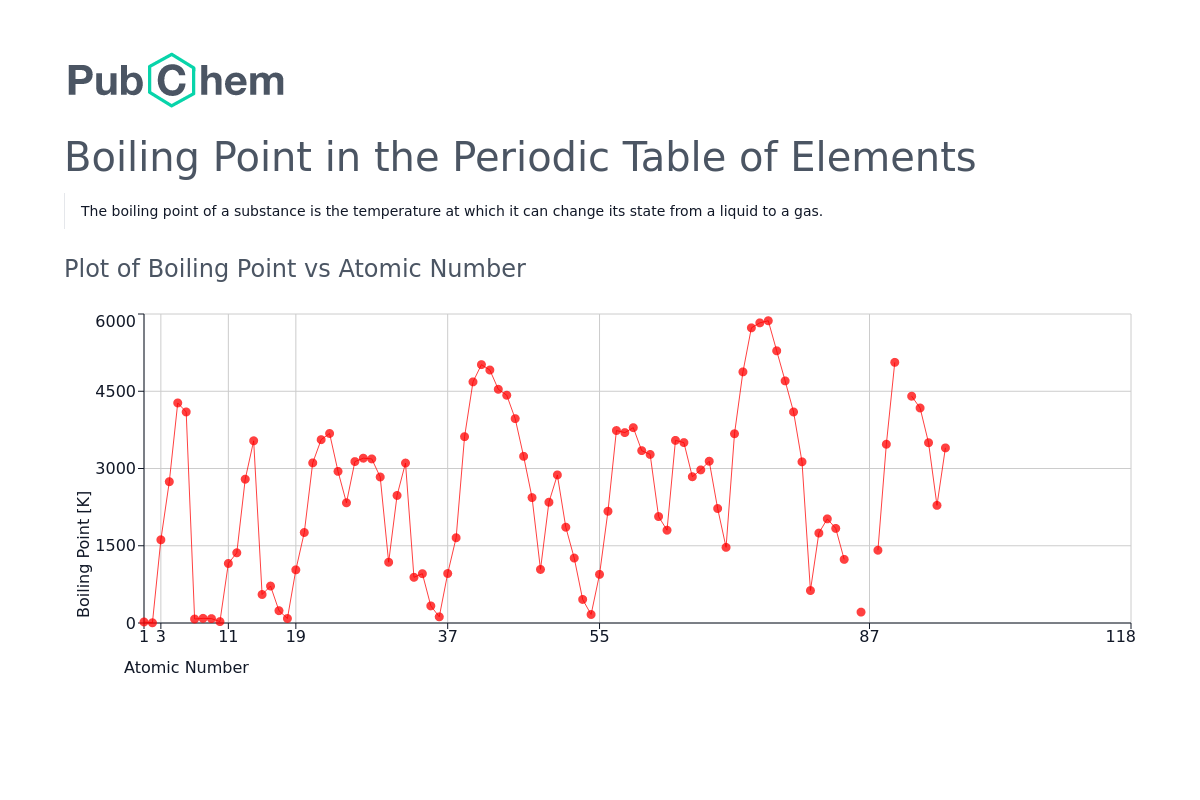
Boiling Point Periodic Table of Elements PubChem
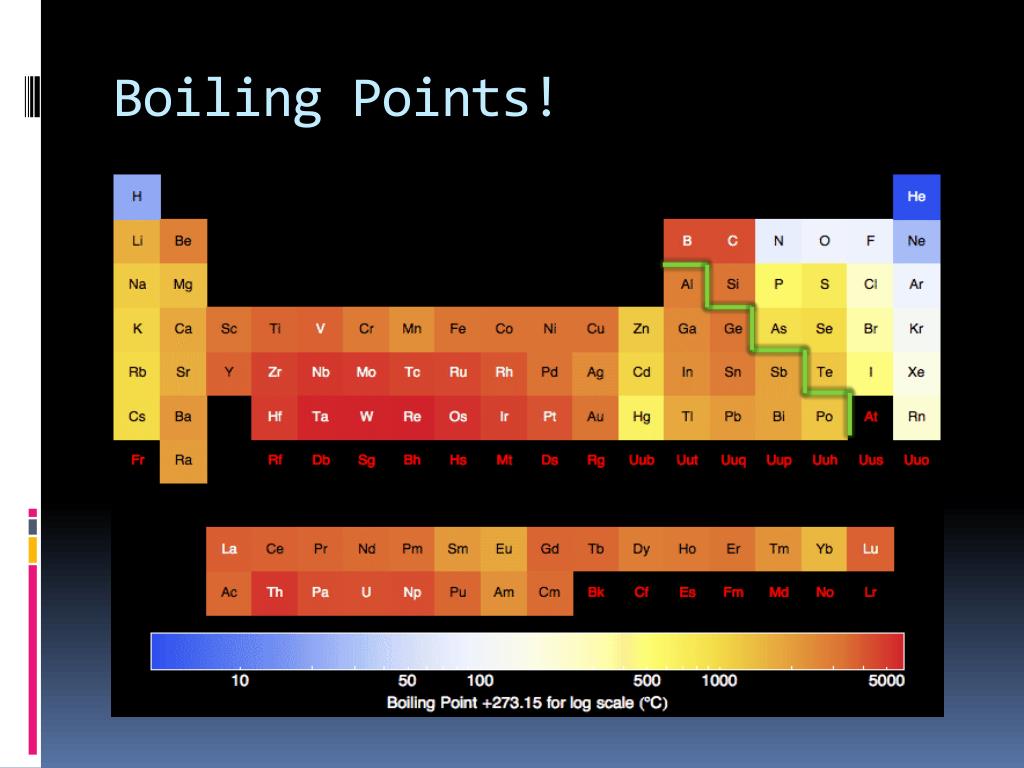
PPT Melting Point and Boiling Point PowerPoint Presentation, free
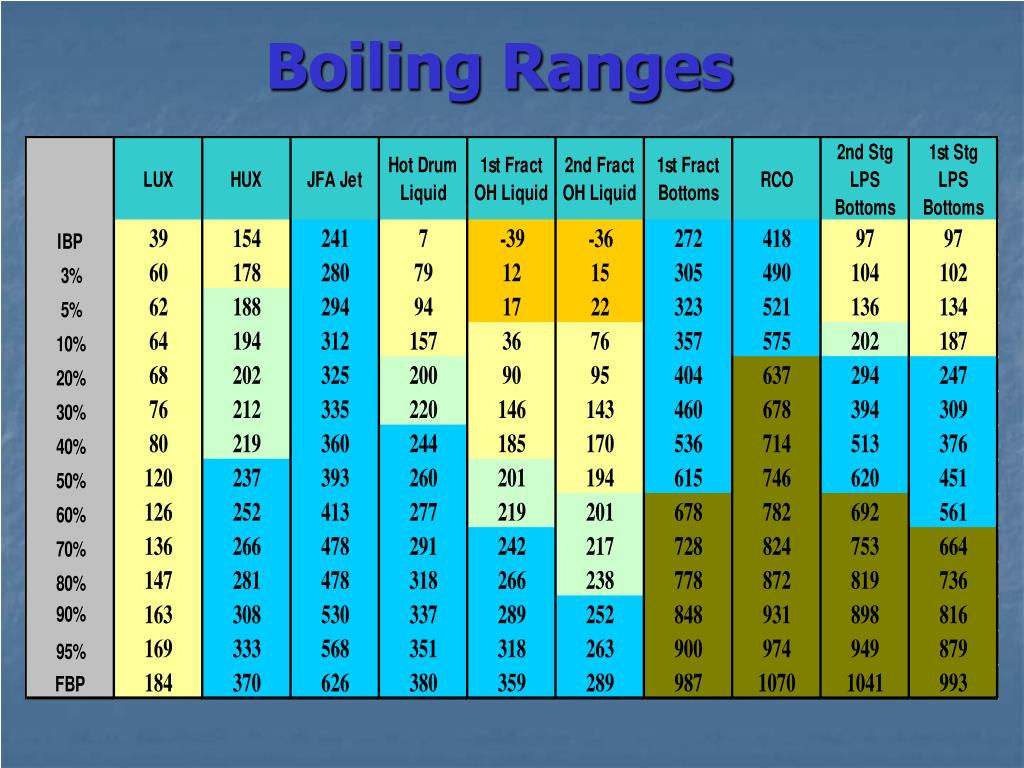
Organic Chemistry Boiling Point Chart

Boiling Point of Water What Temperature Does Water Boil?
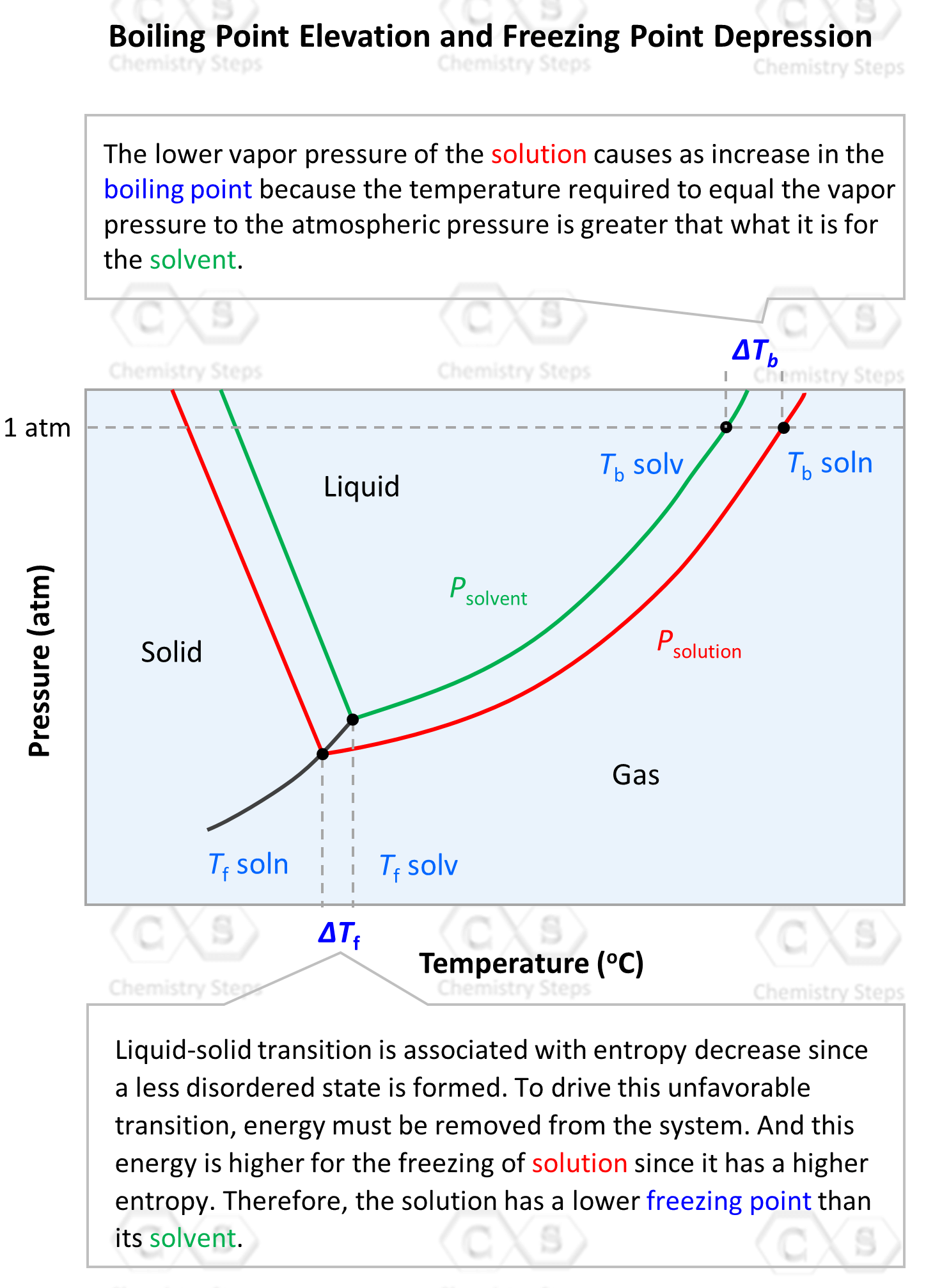
Boiling Point Elevation Chemistry Steps

A Level Chemistry Revision Organic Chemistry Alcohols
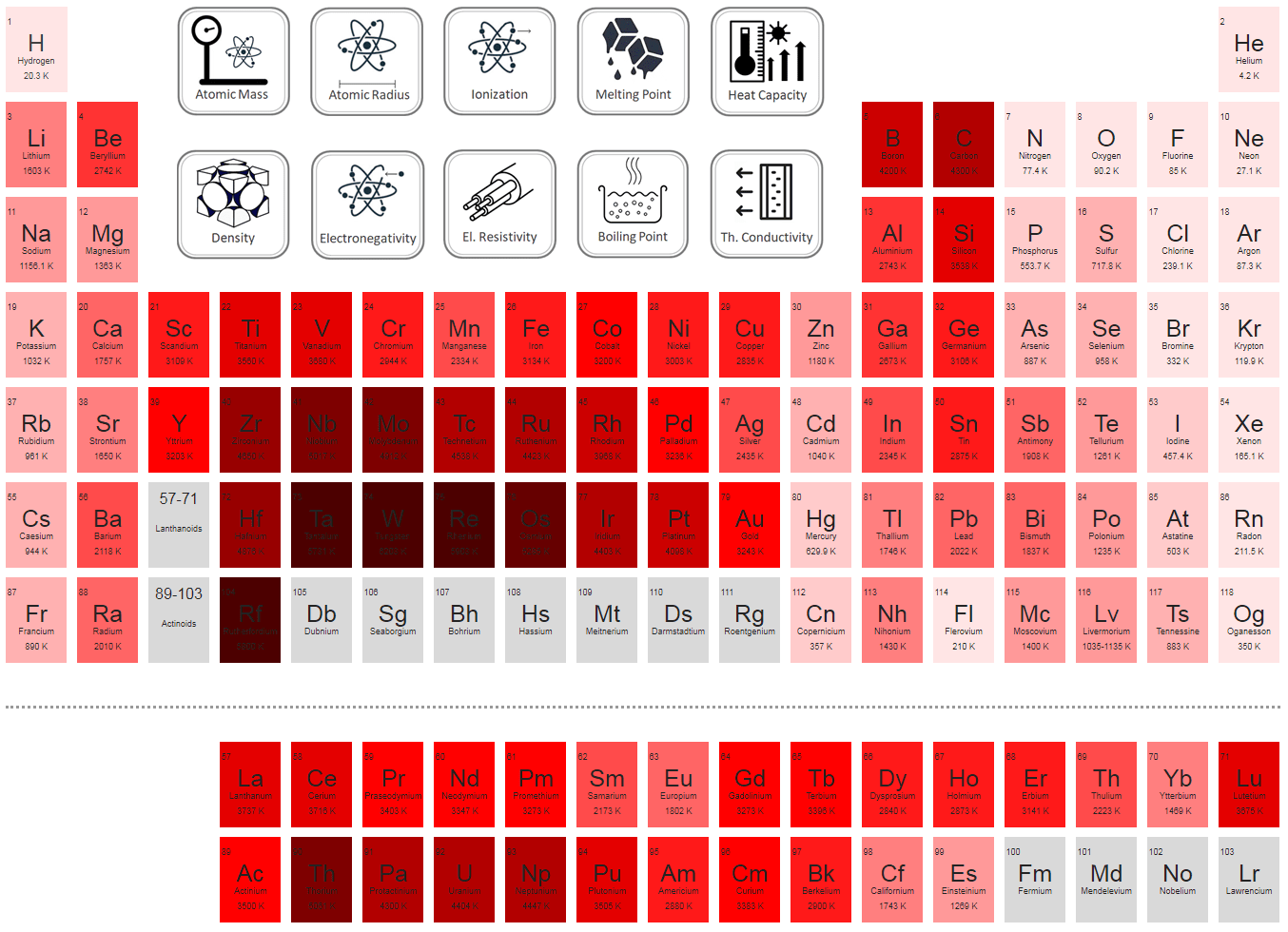
Boiling Point of Chemical Elements Material Properties
Estimate Boiling Point And Vapor Pressure.
In More Technical Terms, It Is When A Liquid's Vapor Pressure Equals Its Applied Pressure (Typically The Atmospheric Pressure).
Boiling Points Are Very Sensitive To Changes In Applied Pressure, So All Boiling Points Should Be Reported Along With The.
Web Table Of Contents:
Related Post: