Bowens Reaction Series Chart
Bowens Reaction Series Chart - Web this sequence can be used to identify the original composition of the magma and the conditions under which it cooled and solidified. Web bowen’s reaction series describes the temperature at which minerals crystallize when cooled, or melt when heated. The lower the minerals fall on the chart, the more they resist. Web bowen's reaction series is usually diagramed as a y with horizontal lines drawn across the y. the first horizontal line—usually placed just above the top of the y—represents a temperature of 3272°f (1800°c). Web simply put, bowen’s reaction series describes the order at which minerals crystallise from a magma. Web the bowen reaction series is a description of how magma 's minerals change as they cool. It’s a means of ranking common igneous silicate minerals by the temperature at which they crystallise. Bowen, who summarized, based on experiments and observations of natural rocks, the sequence of crystallization of common silicate minerals from typical basaltic magma undergoing fractional crystallization (i.e. Web bowen’s reaction series describes the temperature at which minerals crystallize when cooled, or melt when heated. Higher temperature minerals shown at top (olivine) and lower temperature minerals shown at bottom (quartz). Web sunday, may 24, 1998. Web drag each word to the correct location on the bowen’s reaction series diagram. The discontinuous branch and the continuous branch. Web bowen’s reaction series describes the temperature at which minerals crystallize when cooled, or melt when heated. Bowen carried out experiments to characterize the process of crystallization of igneous rocks from magma. Web the bowen reaction series is a description of how magma 's minerals change as they cool. At the higher temperatures associated with mafic and intermediate magmas, the general progression can be separated into two branches. Bowen in the early part of this century proposed a mechanism now called the bowen's reaction series to account for the production of different. Web bowen’s reaction series. Web sunday, may 24, 1998. Web bowen’s reaction series is a critical concept in geology that describes the sequence in which minerals crystallize from a cooling magma. Instructor rebecca gillaspy view bio. Web the bowen reaction series is a description of how magma's minerals change as they cool. Web bowen's reaction series is a way of organizing minerals by the temperature at which they crystallize from magma. Web within the field of geology, bowen's reaction series is the work of the canadian petrologist norman l. Web in this post, i’ll introduce the important rock forming minerals of bowen’s reaction series, and place this in the context of stability. The discontinuous branch and the continuous branch. Bowen in the early 1900s. Author andria emerson view bio. Web bowen’s reaction series shows the (hypothetical) order in which minerals crystallize from cooling magma. Web bowen’s reaction series. Learn about the continuous and discontinuous bowen's reaction series. At the higher temperatures associated with mafic and intermediate magmas, the general progression can be separated into two branches. Web drag each word to the correct location on the bowen’s reaction series diagram. Web bowen’s reaction series describes the temperature at which minerals crystallize when cooled, or melt when heated. Web. Instructor rebecca gillaspy view bio. Learn about the continuous and discontinuous bowen's reaction series. (source colivine, modified from bowen, 1922) by colivine (own work) [ cc0 ], via wikimedia commons. Web within the field of geology, bowen's reaction series is the work of the canadian petrologist norman l. Bowen’s reaction series can help predict which minerals are most susceptible to. In the early part of the 20th century, n. Web this sequence can be used to identify the original composition of the magma and the conditions under which it cooled and solidified. Web bowen’s reaction series describes the temperature at which minerals crystallize when cooled, or melt when heated. Web bowen’s reaction series. Web bowen's reaction series is usually diagramed. Bowen carried out experiments to characterize the process of crystallization of igneous rocks from magma. Bowen’s reaction series can help predict which minerals are most susceptible to weathering based on their chemical composition and stability. Instructor rebecca gillaspy view bio. Web sunday, may 24, 1998. The illustration below is patterned after lutgens. Return to table of contents. Web bowen’s reaction series. Web in this post, i’ll introduce the important rock forming minerals of bowen’s reaction series, and place this in the context of stability and composition that will help students of geology understand the history of a particular rock. The low end of the temperature scale where all minerals crystallize into solid. In the early part of the 20th century, n. Bowen carried out experiments to characterize the process of crystallization of igneous rocks from magma. The discontinuous branch and the continuous branch. Higher temperature minerals shown at top (olivine) and lower temperature minerals shown at bottom (quartz). Web bowen’s reaction series describes the temperature at which minerals crystallize when cooled, or melt when heated. The low end of the temperature scale where all minerals crystallize into solid rock is approximately 700°c (158°f). It’s a means of ranking common igneous silicate minerals by the temperature at which they crystallise. As the magma cools, crystals rich in calcium, iron and magnesium form first and those with silicon and oxygen last. Web this sequence can be used to identify the original composition of the magma and the conditions under which it cooled and solidified. Bowen determined that specific minerals form at specific temperatures as. Web bowen's reaction series is a way of organizing minerals by the temperature at which they crystallize from magma. Learn about the continuous and discontinuous bowen's reaction series. The low end of the temperature scale where all minerals crystallize into solid rock is approximately 700°c (158°f). Instructor rebecca gillaspy view bio. Bowen’s reaction series can help predict which minerals are most susceptible to weathering based on their chemical composition and stability. He found that as a basaltic melt slowly cooled, minerals formed crystals in a definite order.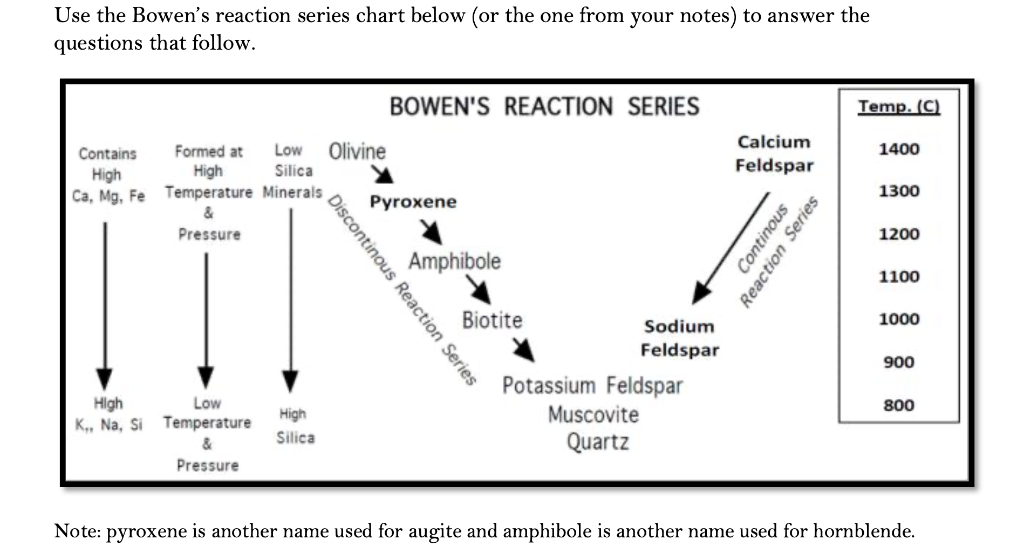
Solved Use the Bowen's reaction series chart below (or the

Bowen's Reaction Series (Geology) Diagram Quizlet
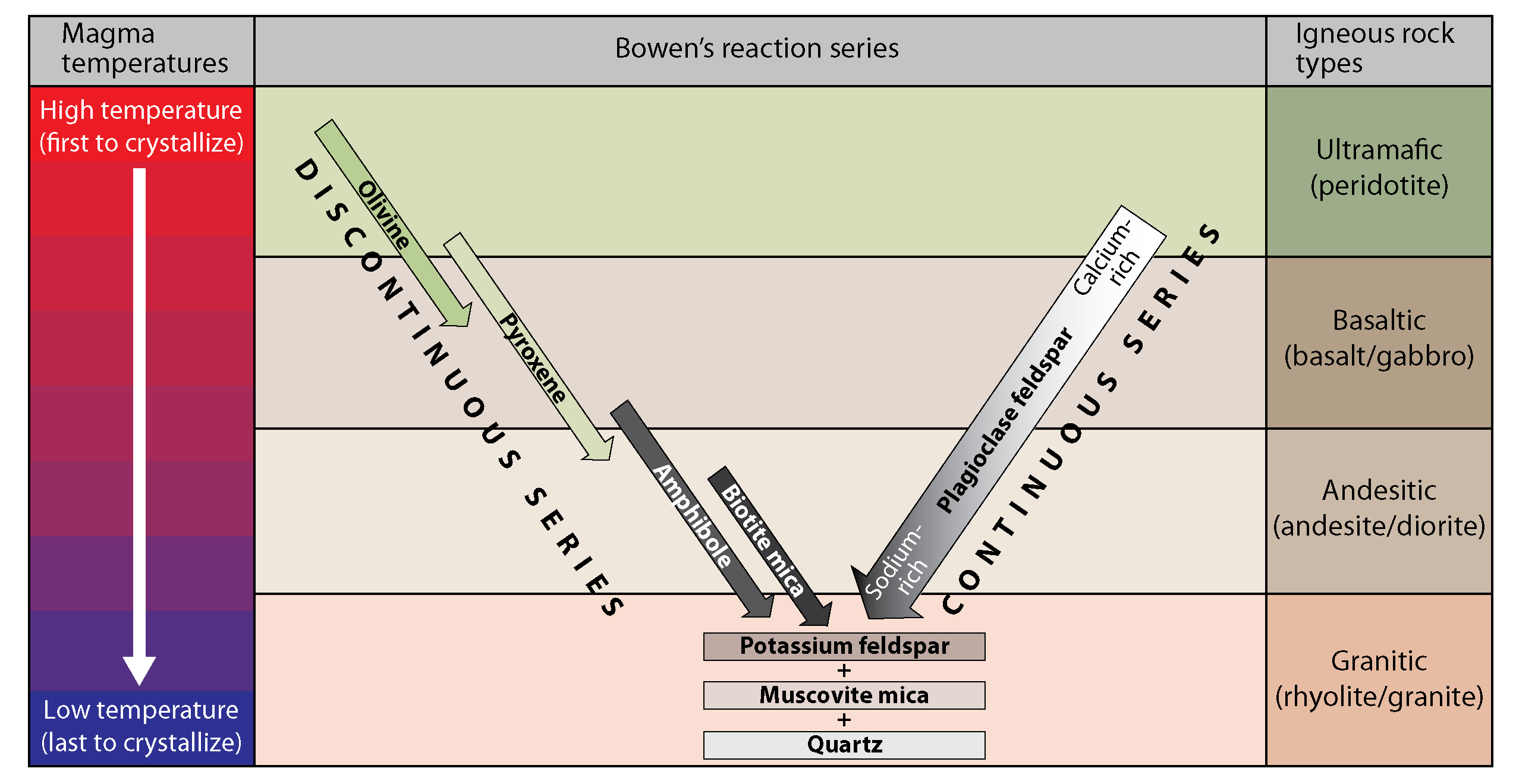
GEOG 400/500 Dr. Rodrigue
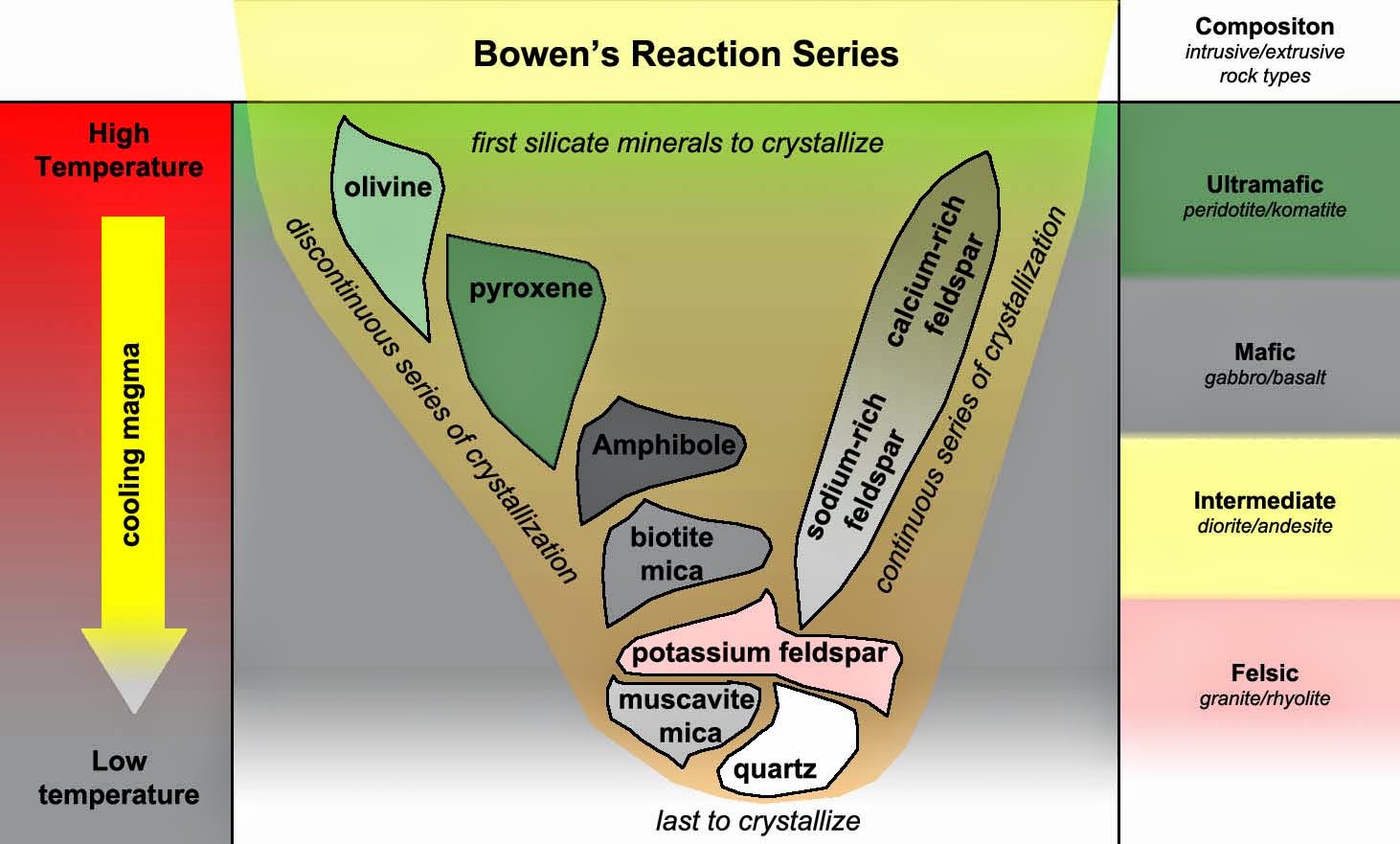
How Does Bowen's Reaction Series Relate to the Classification of
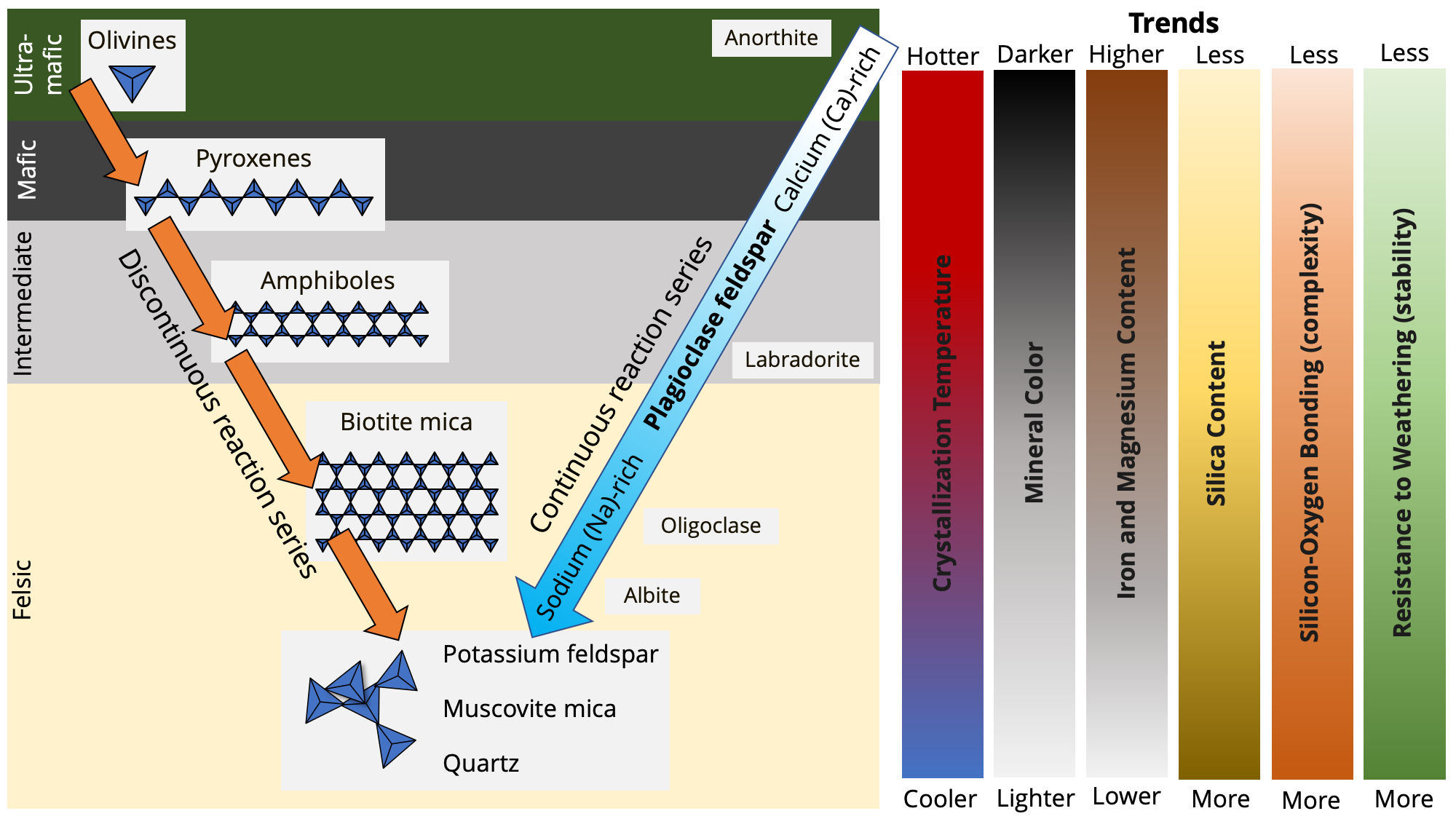
40 Bowen's Reaction Series Diagram Diagram Resource

Bowen's Reaction Series Worksheet
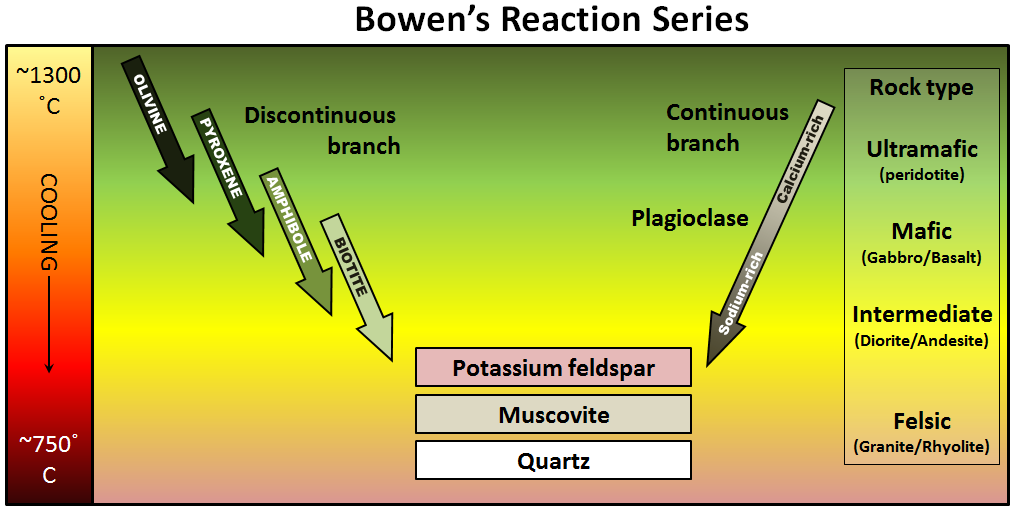
3.3 Crystallization of Magma Physical Geology

Bowen's Reaction Series Continuous and Discontinuous chart
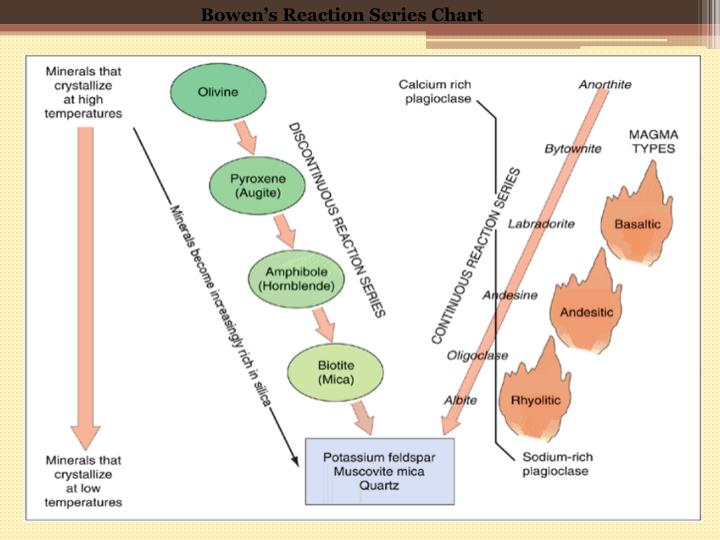
PPT Bowen’s Reaction Series PowerPoint Presentation ID2348378
[Solved] I am having issue with these questions. Please help me. Part A
Bowen In The Early Part Of This Century Proposed A Mechanism Now Called The Bowen's Reaction Series To Account For The Production Of Different Rocks From One Basaltic Magma.
It Was First Proposed By A Canadian Geologist Named Norman L.
The Lower The Minerals Fall On The Chart, The More They Resist.
Web The Bowen Reaction Series Is A Description Of How Magma 'S Minerals Change As They Cool.
Related Post: