Calcium Pth Chart
Calcium Pth Chart - Random renal calcium:creatinine • ultrasound of renal tract. 2.6 mmol/litre or above on at least 2 separate occasions or. Hypercalcemia is considered mild if the total serum calcium level is between 10.5 and 12 mg per dl (2.63. Rapidly mobilizing calcium and phosphate from bone (bone resorption) increasing intestinal absorption of calcium by stimulating conversion of vitamin d to its most active form, calcitriol. Web parathyroid hormone (pth) is one of three key hormones modulating calcium and phosphate homeostasis; Web the parathyroid glands ( figure 1) make a hormone called parathyroid hormone (pth), which helps control the amount of calcium in the blood. Enhancing distal tubular calcium reabsorption. Its main job is to make parathyroid hormone (pth), which controls calcium levels in your bloodstream. Web the diagnosis of primary hyperparathyroidism (phpt) is usually made by finding a pth concentration that is frankly elevated or within the normal range but inappropriately normal given the patient's hypercalcemia ( figure 1 ). If hyperparathyroidism is not treated, it can lead to high blood calcium levels (hypercalcaemia), which may cause: Dunja voos , aktualisiert am 11.02.2013. Web the parathyroid glands ( figure 1) make a hormone called parathyroid hormone (pth), which helps control the amount of calcium in the blood. Promotes bone resorption and thus release of calcium into the blood. Der kalziumgehalt des blutes wird von vielen faktoren beeinflusst. Random renal calcium:creatinine • ultrasound of renal tract. It also controls phosphorus and vitamin d levels. Web pth then raises serum calcium levels by acting on various organs throughout the body: Das parathormon ist neben vitamin d, phosphat und calcitonin ein wichtiger faktor, der den kalziumspiegel auf dem normalwert hält. Random renal calcium:creatinine • ultrasound of renal tract. Der kalziumgehalt des blutes wird von vielen faktoren beeinflusst. Web parathyroid hormone (pth) values should be interpreted in conjunction with serum calcium, magnesium, phosphate levels and creatinine levels, and the overall clinical presentation and history of the patient. Stimulates calcium reabsorption in the distal convoluted tubule. Rapidly mobilizing calcium and phosphate from bone (bone resorption) increasing intestinal absorption of calcium by stimulating conversion of vitamin d to its most. Parathyroid hormone (pth) increases serum calcium by. Random renal calcium:creatinine • ultrasound of renal tract. Web this section is about that 25% of people with high calcium levels and normal pth levels, and much less frequently, those with normal calcium levels and high pth levels. Web parathyroid hormone is a polypeptide that is synthesized and cleaved into an active form. Der kalziumgehalt des blutes wird von vielen faktoren beeinflusst. Web if calcium is persistently raised parathyroid hormone (pth) should be checked. Primary hyperparathyroidism is when your parathyroid glands make excessive amounts of parathyroid hormone (pth). If your body has too much or too little parathyroid hormone, it can cause symptoms related to abnormal blood calcium levels. Web normal ionized calcium. Web parathyroid hormone is a polypeptide that is synthesized and cleaved into an active form within the parathyroid gland. Web parathyroid hormone (pth) values should be interpreted in conjunction with serum calcium, magnesium, phosphate levels and creatinine levels, and the overall clinical presentation and history of the patient. Web if calcium is persistently raised parathyroid hormone (pth) should be checked.. Web this section is about that 25% of people with high calcium levels and normal pth levels, and much less frequently, those with normal calcium levels and high pth levels. Web pth regulates the level of calcium in the blood, release of calcium from bone, absorption of calcium in the small intestine, and excretion of calcium in the urine. Fatigue,. Web parathyroid hormone (pth) is one of three key hormones modulating calcium and phosphate homeostasis; Web this section is about that 25% of people with high calcium levels and normal pth levels, and much less frequently, those with normal calcium levels and high pth levels. In people with primary hyperparathyroidism (phpt), one or more of the parathyroid glands become overactive. Rapidly mobilizing calcium and phosphate from bone (bone resorption) increasing intestinal absorption of calcium by stimulating conversion of vitamin d to its most active form, calcitriol. Raised pth and raised calcium. However, if calcium >3.4 mmol/l or the patient is symptomatic outpatient investigation is not appropriate and the patient should be admitted. Web primary hyperparathyroidism is the most common cause. However, if calcium >3.4 mmol/l or the patient is symptomatic outpatient investigation is not appropriate and the patient should be admitted. It also controls phosphorus and vitamin d levels. Promotes bone resorption and thus release of calcium into the blood. Its main job is to make parathyroid hormone (pth), which controls calcium levels in your bloodstream. Das parathormon ist neben. Promotes bone resorption and thus release of calcium into the blood. If your body has too much or too little parathyroid hormone, it can cause symptoms related to abnormal blood calcium levels. See the colorful calcium graph below. Web serum pth and calcium values are low in hypoparathyroidism (open blue boxes) and high in primary hyperparathyroidism (blue squares). Dunja voos , aktualisiert am 11.02.2013. Web primary hyperparathyroidism is the most common cause of high blood calcium level in the general population. Fatigue, muscle weakness, bony pain, depression/low mood (common) polyuria and polydipsia, kidney stones (hypercalcaemia causes a partial nephrogenic diabetes insipidus) If hyperparathyroidism is not treated, it can lead to high blood calcium levels (hypercalcaemia), which may cause: It also inhibits phosphate reabsorption, decreasing serum phosphate. Parathyroid hormone (pth) increases serum calcium by. 2.6 mmol/litre or above on at least 2 separate occasions or. Web the parathyroid glands ( figure 1) make a hormone called parathyroid hormone (pth), which helps control the amount of calcium in the blood. Web parathyroid hormone (pth) values should be interpreted in conjunction with serum calcium, magnesium, phosphate levels and creatinine levels, and the overall clinical presentation and history of the patient. Das parathormon ist neben vitamin d, phosphat und calcitonin ein wichtiger faktor, der den kalziumspiegel auf dem normalwert hält. Rapidly mobilizing calcium and phosphate from bone (bone resorption) increasing intestinal absorption of calcium by stimulating conversion of vitamin d to its most active form, calcitriol. Stimulates calcium reabsorption in the distal convoluted tubule.
Parathyroid Hormone and Calcium Levels Hyperparathyroidism Surgery

PTH INTACT ANALYZER REGIONAL MEDICAL LABORATORY

Parathyroid hormone (PTH)

How to Diagnose Hyperparathyroidism Easy Step by Step Diagnosis.
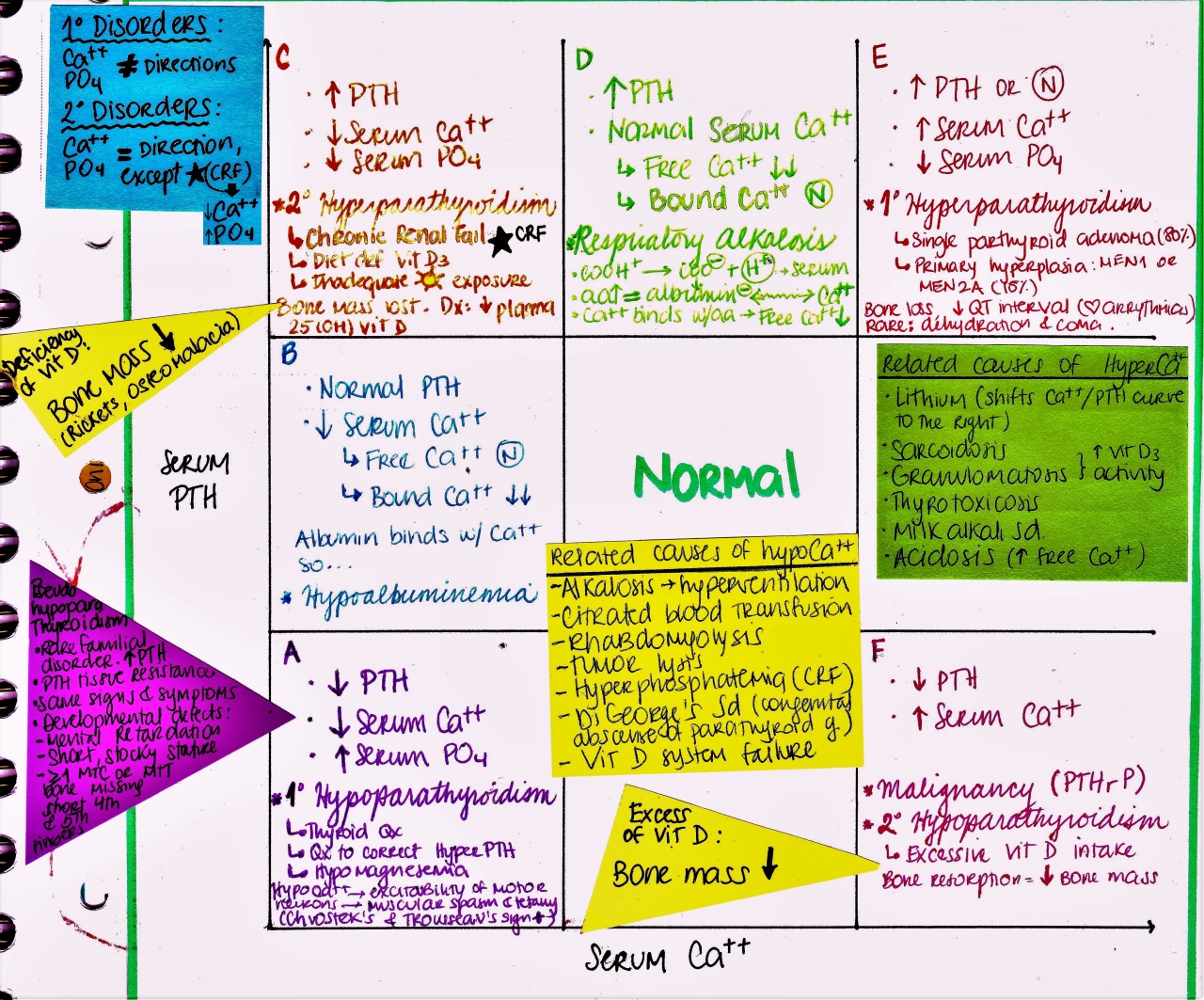
My Notes for USMLE — PTH & Calcium Chart drawn by 100lyric (Please,...
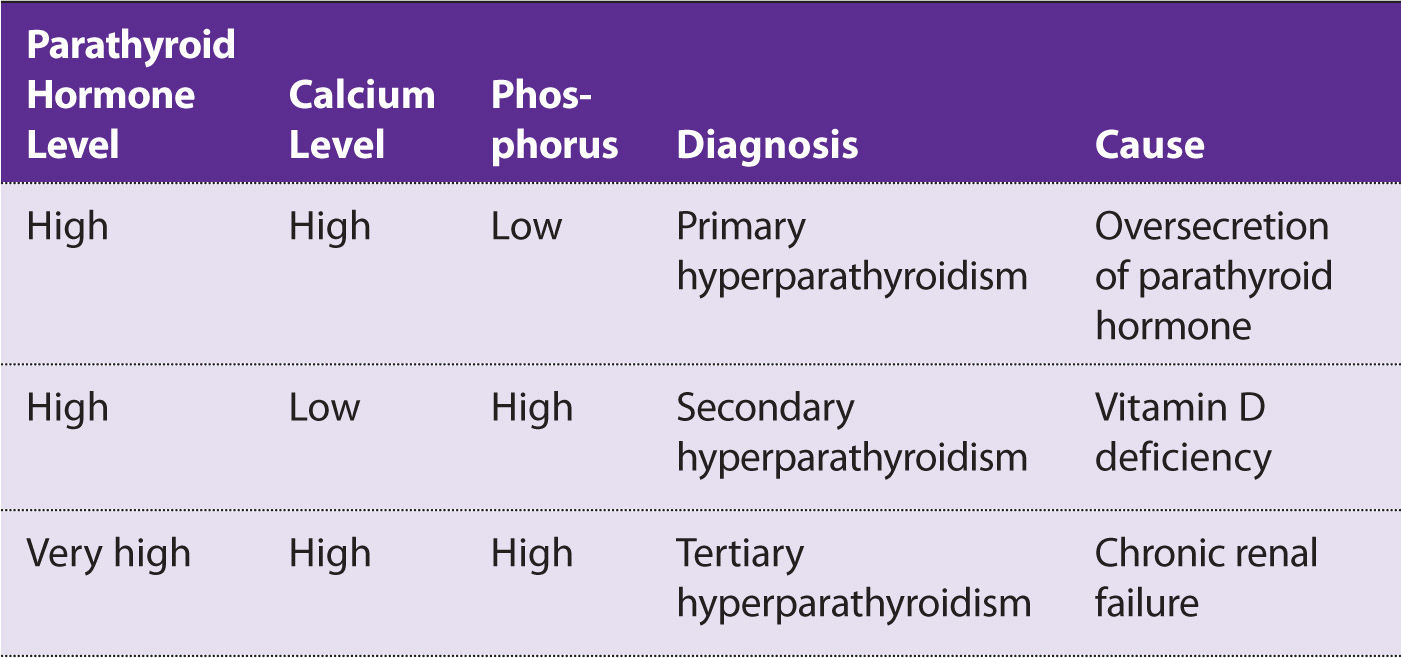
Endocrine Obgyn Key

Parathyroid Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master

9. Calcium Metabolism SimpleMed Learning Medicine, Simplified
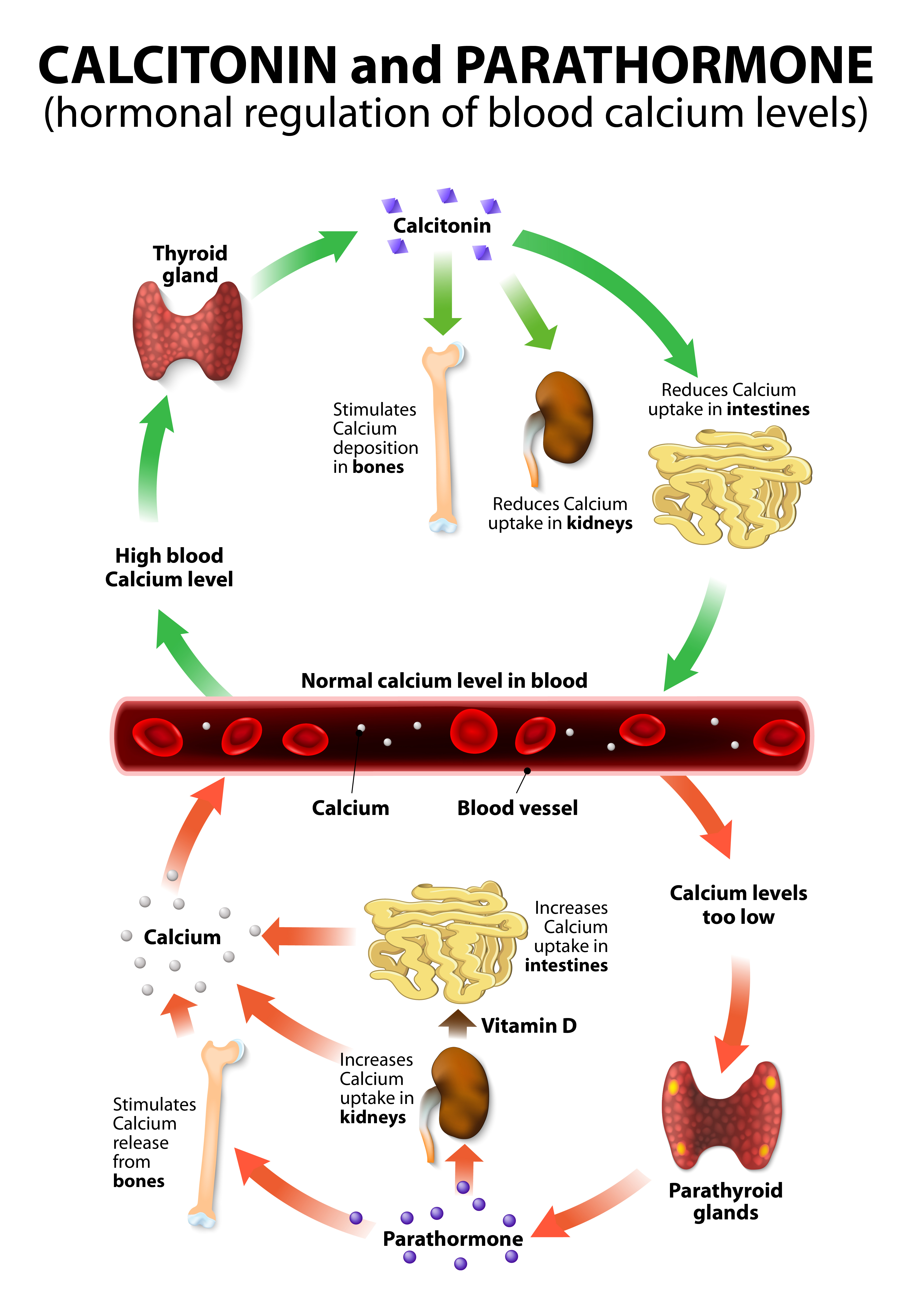
Calcium, phosphorus, parathyroid hormone and vitamin D basic information

PTH Calcium Flowchart
Random Renal Calcium:creatinine • Ultrasound Of Renal Tract.
However, If Calcium >3.4 Mmol/L Or The Patient Is Symptomatic Outpatient Investigation Is Not Appropriate And The Patient Should Be Admitted.
Web Pth Regulates The Level Of Calcium In The Blood, Release Of Calcium From Bone, Absorption Of Calcium In The Small Intestine, And Excretion Of Calcium In The Urine.
Enhancing Distal Tubular Calcium Reabsorption.
Related Post: