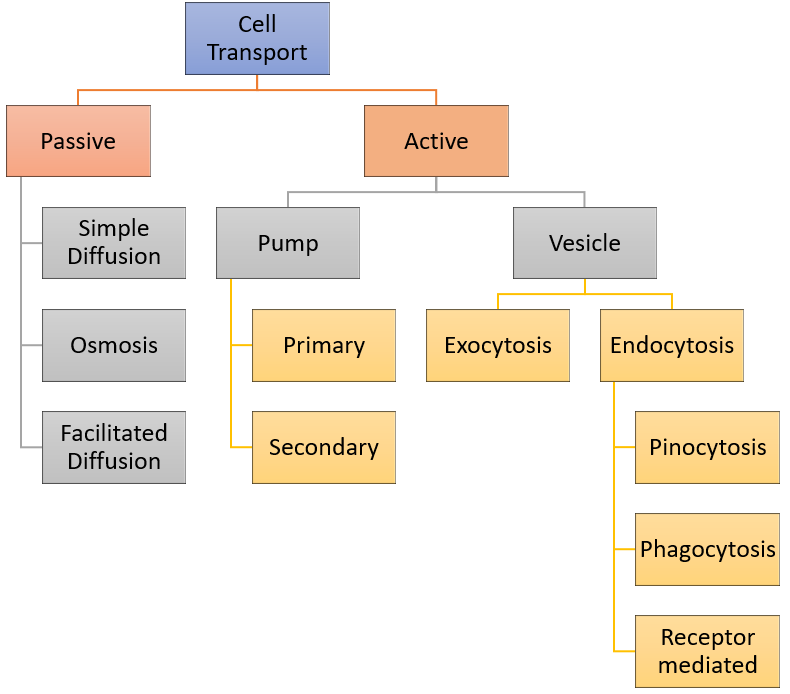
Cell Transport Chart
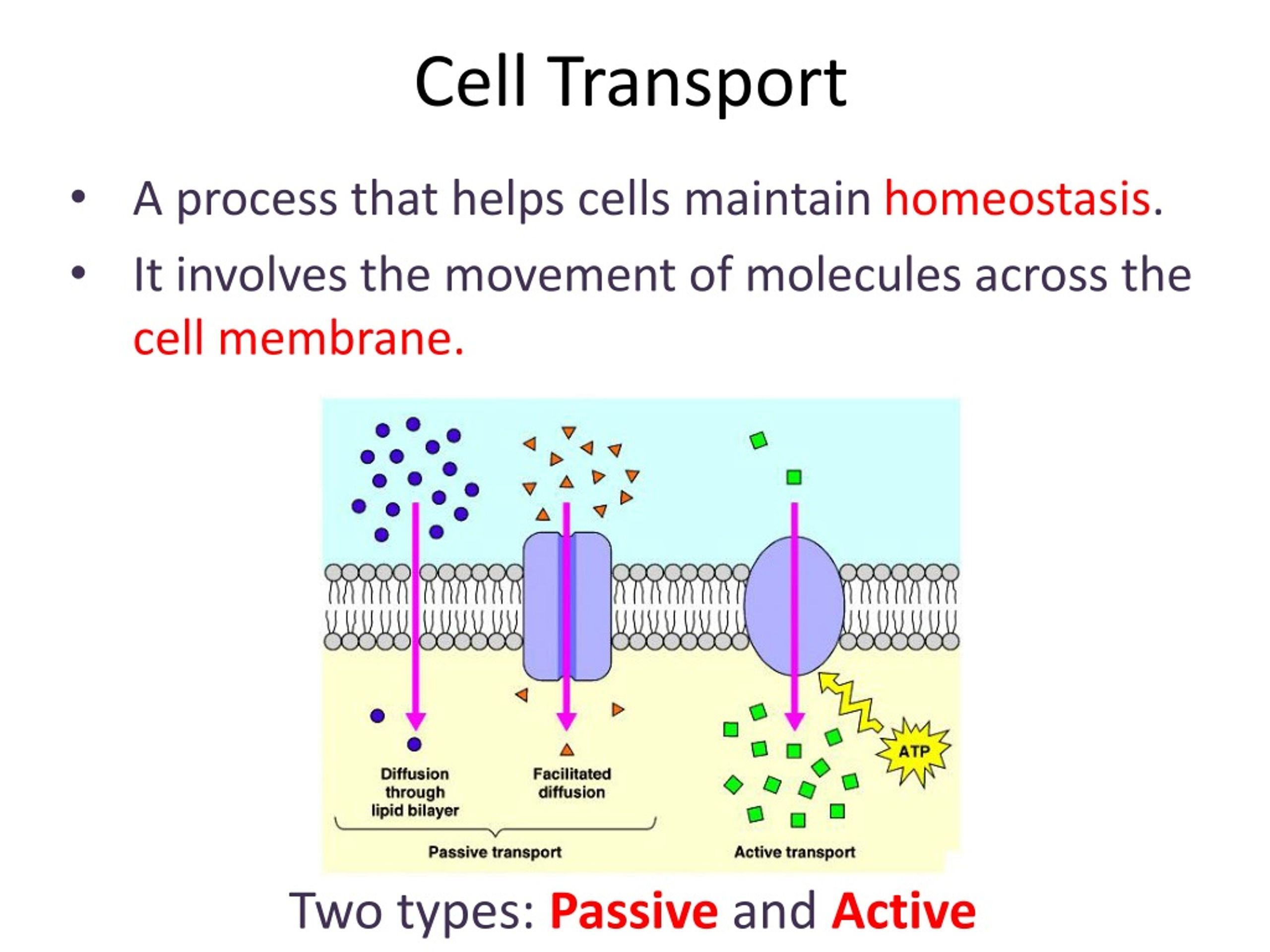
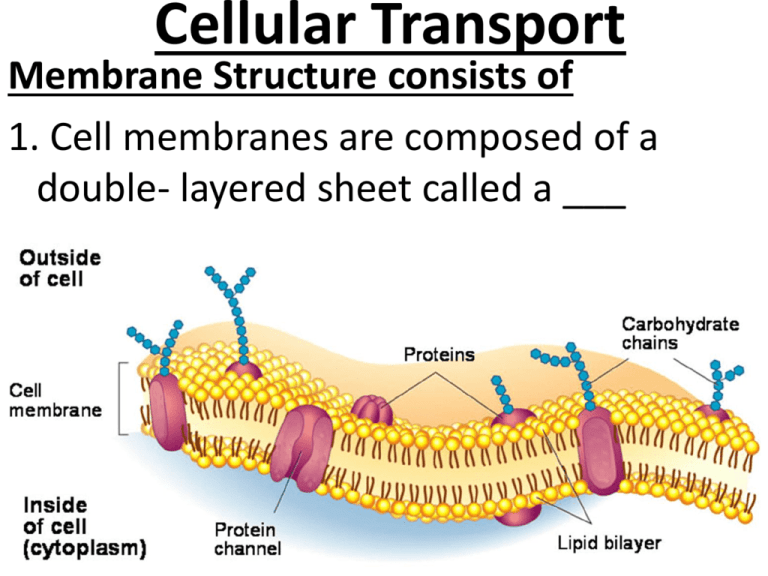
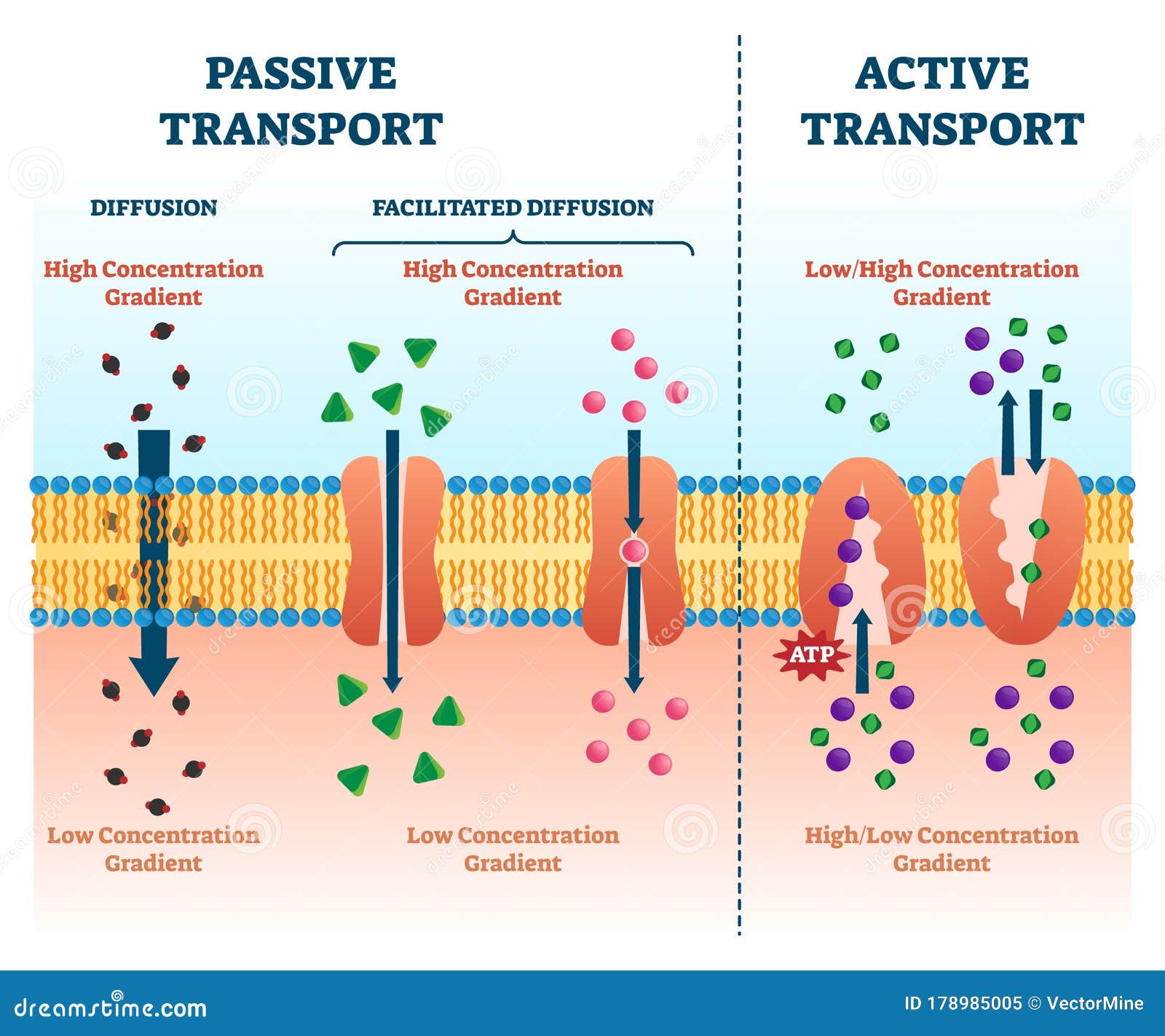
Cell Transport Chart - Web cell transport vocabulary cut out the definition and image cards and glue or tape them next to the correct term. Web active transport mechanisms require the use of the cell’s energy, usually in the form of adenosine triphosphate (atp). Web active, passive, and bulk cell transport. The chemical structure of the cell membrane makes it remarkably flexible, the ideal boundary for rapidly growing and dividing cells. Transport vesicles are used to move proteins around the cell and to release neurotransmitters into the synaptic space. Active transport can involve either a pump or a vesicle pump transport can be primary; The potassium ions bind to the carrier proteins. Active transport can involve either a pump or a vesicle pump transport can be primary; Yet the membrane is also a formidable barrier, allowing some dissolved substances, or solutes, to pass while blocking others. They are formed from budding of the plasma membrane of other organelles and release their contents through exocytosis. Web active transport is a kind of cellular transport in which substances like amino acids, glucose and ions are transported across cell membranes to a region that already has a high concentration of such substances. Active transport can involve either a pump or a vesicle pump transport can be primary; Passive transport does not require the cell to expend any. Web nerve cells in giant squids can reach up to 12m [39 ft] in length, while human eggs (the largest human cells) are about 0.1mm across. In some cases, the movement of substances can be accomplished by passive transport, which uses no energy. Passive transport does not require the cell to expend any energy and involves a substance diffusing down. As a result, active transport employs chemical energy like atp to move substances against their concentration gradient. Active transport can involve either a pump or a vesicle pump transport can be primary; Transport vesicles are used to move proteins around the cell and to release neurotransmitters into the synaptic space. A measurement of how much the concentration of a substance. Active transport can involve either a pump or a vesicle pump transport can be primary; Web transport vesicles are membrane bound sacs used to transport materials through the cytoplasm. As a result, active transport employs chemical energy like atp to move substances against their concentration gradient. Process of maintaining a stable environment inside a cell or an entire organism. Web. Web transport vesicles are membrane bound sacs used to transport materials through the cytoplasm. Web active transport is the process of transferring substances into, out of, and between cells, using energy. Click to get pearson+ app download. They are formed from budding of the plasma membrane of other organelles and release their contents through exocytosis. This may happen passively, as. Cell structures and their functions a cell is like a whole city. As a result, active transport employs chemical energy like atp to move substances against their concentration gradient. Web the different categories of cell transport are outlined in figure \(\pageindex{2}\). Cell transport can be classified as follows: The potassium ions bind to the carrier proteins. They are formed from budding of the plasma membrane of other organelles and release their contents through exocytosis. Yet the membrane is also a formidable barrier, allowing some dissolved substances, or solutes, to pass while blocking others. Passive transport which includes simple diffusion; They must have a way of obtaining these materials from the extracellular fluids. Click to get pearson+. They must have a way of obtaining these materials from the extracellular fluids. Active transport can involve either a pump or a vesicle pump transport can be primary; Process of maintaining a stable environment inside a cell or an entire organism. 4.4 the endomembrane system and proteins. As a result, active transport employs chemical energy like atp to move substances. Web some cells require larger amounts of specific substances than other cells; In some cases, the movement of substances can be accomplished by passive transport, which uses no energy. Web nerve cells in giant squids can reach up to 12m [39 ft] in length, while human eggs (the largest human cells) are about 0.1mm across. 4.7 plasma membrane components and. In contrast, active transport is the movement of substances across the membrane using energy from adenosine triphosphate (atp). Web cell transport vocabulary cut out the definition and image cards and glue or tape them next to the correct term. Explore the concepts and examples of passive and active transport, osmosis, diffusion, and membrane potential. Web passive and active passage through. Yet the membrane is also a formidable barrier, allowing some dissolved substances, or solutes, to pass while blocking others. Vocabulary term definition image protein equilibrium diffusion cell membrane homeostasis active. Cell transport can be classified as follows: Web active transport mechanisms require the use of the cell’s energy, usually in the form of adenosine triphosphate (atp). The chemical structure of the cell membrane makes it remarkably flexible, the ideal boundary for rapidly growing and dividing cells. Web cell transport vocabulary cut out the definition and image cards and glue or tape them next to the correct term. Transport vesicles are used to move proteins around the cell and to release neurotransmitters into the synaptic space. Web learn about the structure and function of biological membranes and how they regulate the movement of substances across the cell boundary. Active transport can involve either a pump or a vesicle pump transport can be primary; Plant cells have protective walls made of cellulose (which also makes up the strings in celery that make it so hard to eat) while fungal cell walls are made from the same stuff as lobster shells. Web active transport is the process of transferring substances into, out of, and between cells, using energy. Khan academy's biology library offers videos, articles, and exercises to help you master this unit. 4.6 connections between cells and cellular activities. Web passive and active passage through the cell membrane. Web transport vesicles are membrane bound sacs used to transport materials through the cytoplasm. Passive transport is the movement of substances across the membrane without the expenditure of cellular energy.
This is a Cell Transport Flow Chart. Materials that move through the
3.7 Cell Transport Biology LibreTexts

Membrane Transport ION CHANNEL LIBRARY

Cell Biology Study Guides Study biology, Cell biology, Biology study

Summary of Membrane Transport Processes PhysiologyWeb
PPT Cell Transport Review PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Cellular Transport
Active Passive Transport Vector Illustration. Labeled Educational Cell

Chapter 7 Cell Structure & Function PreAice Biology
1.4 Membrane Transport Biology 2016
Web The Different Categories Of Cell Transport Are Outlined In Figure \(\Pageindex{2}\).
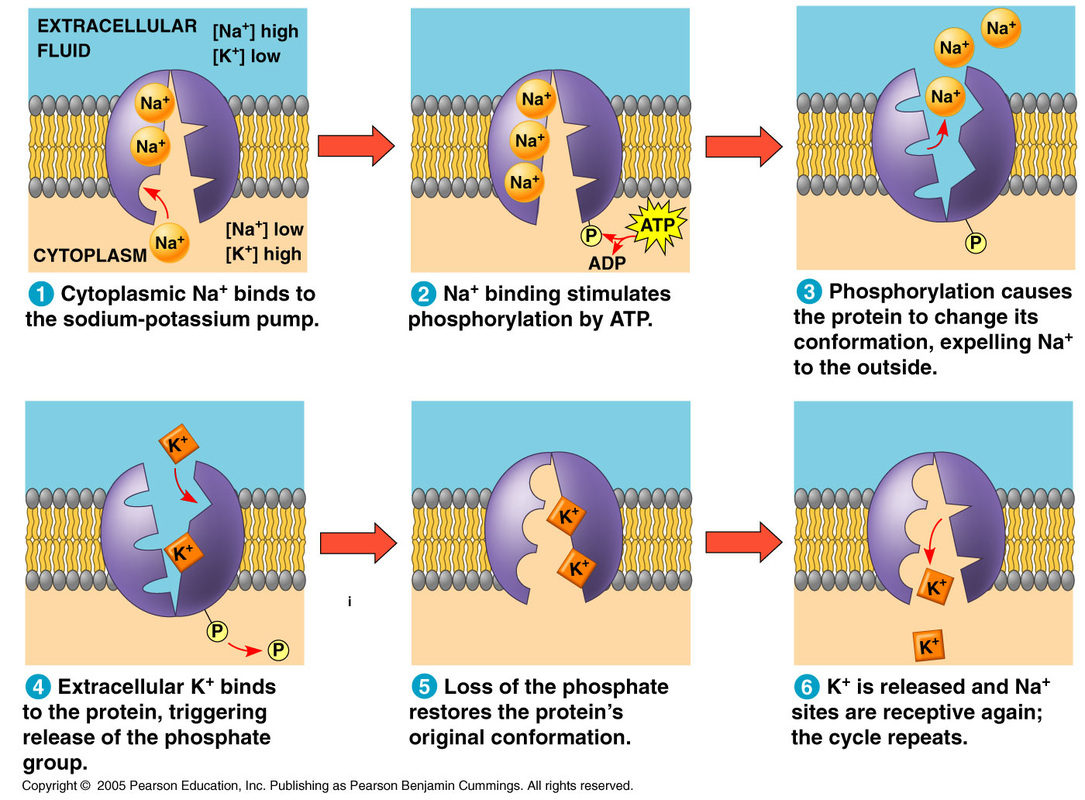
Web Sodium Potassium Pump Continued.
Passive Transport Which Includes Simple Diffusion;
Web Active, Passive, And Bulk Cell Transport.
Related Post: