Cellular Respiration Chart Answers
Cellular Respiration Chart Answers - When there is less atp the rate increases. Describe the structure of a mitochondrion. Why is nadh called an electron shuttle bus? Cellular respiration is a chemical process in which the bonds of food molecules and oxygen molecules are broken and new compounds are formed that can transport energy to muscles. Outline the steps of the krebs cycle. Heterotrophs (like humans) ingest other living things to obtain glucose. The rate of the cycle is controlled by atp concentration. What are the products in anaerobic cellular respiration (fermentation) in yeast? The goal of cellular respiration is to. State what happens during glycolysis. A word bank is provided to help them trace the flow of atp and nadh in the process as well as identifying where each step occurs. Glucose is used in cellular respiration. What is the purpose of cellular respiration? 2 ethyl alcohol (2c) + 2 co2 + 2 atp + heat. Glucose, 2 nad +, 2 adp + 2 pi. When there is more atp available, the rate slows down; Carries electrons from glycolysis & krebs cycle to the etc, then returns to original processes as nad+ to get. C6h12o6 (glucose) + 2 nad+ + 2 adp + 2 pi → 2 ch3cocoo− + 2 nadh + 2 atp + 2 h2o + 2h+. When there is less atp the. C6h12o6 (glucose) + 2 nad+ + 2 adp + 2 pi → 2 ch3cocoo− + 2 nadh + 2 atp + 2 h2o + 2h+. A word bank is provided to help them trace the flow of atp and nadh in the process as well as identifying where each step occurs. Write the balanced word and chemical equation for aerobic. Heterotrophs (like humans) ingest other living things to obtain glucose. Outline the steps of the krebs cycle. What are the products in anaerobic cellular respiration (fermentation) in yeast? Glycolysis is the only step which is shared by all types of respiration. The equation for glycolysis is: Web cellular respiration is a biochemical process of breaking down food, usually glucose, into simpler substances. Many food molecules are broken down into glucose, a simple sugar. When there is less atp the rate increases. Glucose and oxygen are inputs of cellular respiration. Heterotrophs (like humans) ingest other living things to obtain glucose. State what happens during glycolysis. C6h12o6 (glucose) + 2 nad+ + 2 adp + 2 pi → 2 ch3cocoo− + 2 nadh + 2 atp + 2 h2o + 2h+. Web cellular respiration is the process of oxidizing food molecules, like glucose, to carbon dioxide and water. Many food molecules are broken down into glucose, a simple sugar. This process. Web in cellular respiration, electrons from glucose move gradually through the electron transport chain towards oxygen, passing to lower and lower energy states and releasing energy at each step. Autotrophs (like plants) produce glucose during photosynthesis. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like first is, if we have no oxygen present we go to:, glycolysis occurs in the?. Web the four main steps of aerobic respiration are glycolysis, pyruvate decarboxylation (link reaction), the krebs cycle (citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid cycle), and the electron transport chain with oxidative phosphorylation. Web cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces atp. Web what is the purpose of cellular respiration? \[c_6h_{12}o_{6} + 6o_2 + 6h_2o →. Now let’s take a more detailed look at how all eukaryotes—which includes humans!—make use of this stored energy. Provide a concise summary of the process. 2 ethyl alcohol (2c) + 2 co2 + 2 atp + heat. Figure below gives an overview of these three stages, which are further discussed in the concepts that follow. The stages of cellular respiration. The rate of the cycle is controlled by atp concentration. Glucose is used in cellular respiration. A word bank is provided to help them trace the flow of atp and nadh in the process as well as identifying where each step occurs. Provide a concise summary of the process. Figure below gives an overview of these three stages, which are. Web what is the purpose of cellular respiration? Glucose, 2 nad +, 2 adp + 2 pi. When there is more atp available, the rate slows down; Carries electrons from glycolysis & krebs cycle to the etc, then returns to original processes as nad+ to get. Web cellular respiration is a process that all living things use to convert glucose into energy. Web cellular respiration is the process of oxidizing food molecules, like glucose, to carbon dioxide and water. Web cellular respiration is the process by which the body gets energy from food. Web in cellular respiration, electrons from glucose move gradually through the electron transport chain towards oxygen, passing to lower and lower energy states and releasing energy at each step. Web students complete a graphic organizer that shows the process of cellular respiration. C6h12o6 (glucose) + 2 nad+ + 2 adp + 2 pi → 2 ch3cocoo− + 2 nadh + 2 atp + 2 h2o + 2h+. Cellular respiration is a process that happens inside an organism’s cells. What happens during the electron transport stage of cellular respiration? Want to join the conversation? Autotrophs (like plants) produce glucose during photosynthesis. Web answer key to the flow chart showing the main events and products in cellular respiration. Now let’s take a more detailed look at how all eukaryotes—which includes humans!—make use of this stored energy.
Biochemical Pathway Of Cell Respiration Flow Chart Awesome Answer Key

What is the function of cellular respiration
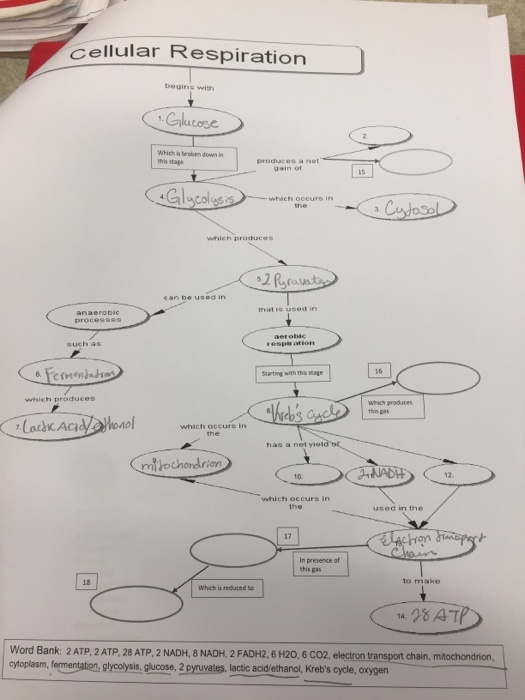
Cellular Respiration Summary Chart

What Are The 3 Stages Of Cellular Respiration
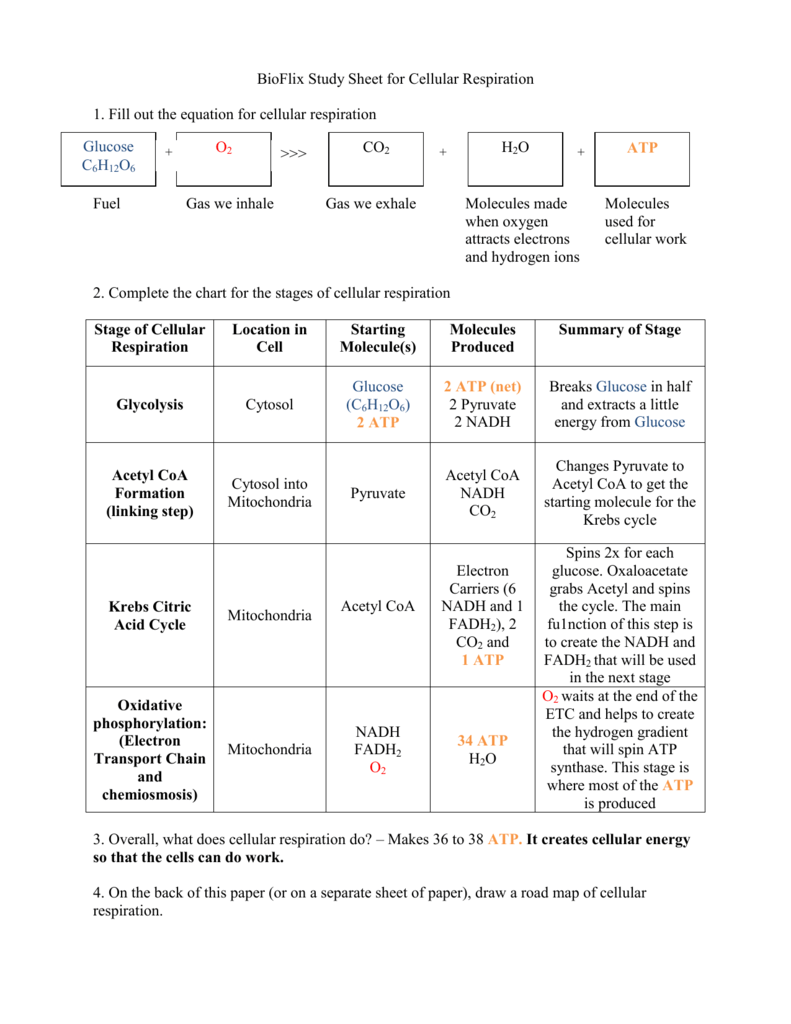
Bioflix Study Sheet For Cellular Respiration Answer Key Study Poster

Cellular Respiration Graphic Organizer Answer Key Biology Corner

Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration Equation • Suggested and Clear

Cellular Respiration Graphic Organizer Answer Key Biology Corner

Cellular Respiration Chart Worksheets

Cellular Respiration Concept Map Answers Map Vector
This Process Releases Energy That Can Be Used By The Organism To Live And Grow.
Outline The Steps Of The Krebs Cycle.
State What Happens During Glycolysis.
Web Cellular Respiration Is A Metabolic Pathway That Uses Glucose To Produce Adenosine Triphosphate (Atp), An Organic Compound The Body Can Use For Energy.
Related Post: