Chart Of Cellular Respiration
Chart Of Cellular Respiration - Every machine needs specific parts and fuel to function. This handout will primarily focus on aerobic respiration, which is when oxygen is present. The citric acid (tca) or the krebs cycle; Cellular respiration is a process that happens inside an organism’s cells. Graphic shows glycolysis, the krebs cycle and electron transport chain. Web cellular respiration is a biochemical process of breaking down food, usually glucose, into simpler substances. Identify the reactants and products of cellular respiration and where these reactions occur in a cell; _image modified from etc4 by fvasconcellos ( public domain )._ is that really what a mitochondrion looks like? Many food molecules are broken down into glucose, a simple sugar. Glycolysis is an anaerobic process, while the other two pathways are aerobic. This type of cellular respiration occurs in the absence of free oxygen, producing acid or alcohol as the end product. Glycolysis, transformation of pyruvate, the krebs cycle (also called the citric acid cycle), and oxidative phosphorylation. When organic fuels like glucose are broken down using an electron transport chain, the breakdown process is known as cellular respiration. It includes glycolysis,. C6h12o6 + 6 o2 → 6 co2 + 6 h2o + 38*atp. Web the four main steps of aerobic respiration are glycolysis, pyruvate decarboxylation (link reaction), the krebs cycle (citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid cycle), and the electron transport chain with oxidative phosphorylation. To create atp and other forms of energy to power cellular reactions, cells require fuel and. This is accomplished through the digestive process where. Graphic shows glycolysis, the krebs cycle and electron transport chain. C 6 h 12 o 6 (glucose) + 6o 2 (oxygen) → 6co 2 (carbon dioxide) + 6h 2 o (water) + 36 atp. Many food molecules are broken down into glucose, a simple sugar. Heterotrophs (like humans) ingest other living things. Many food molecules are broken down into glucose, a simple sugar. _image modified from etc4 by fvasconcellos ( public domain )._ is that really what a mitochondrion looks like? Every machine needs specific parts and fuel to function. Web cellular respiration is a collection of three unique metabolic pathways: Figure \(\pageindex{3}\) gives an overview of these three stages, which are. Though it releases only 2 atps, it occurs more quickly than aerobic respiration. Web in sequential order, the four stages of aerobic cellular respiration are (1) glycolysis, (2) the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex intermediary step, (3) the citric acid cycle, and (4) the electron. And the electron transport chain, where oxidative phosphorylation occurs. Figure \(\pageindex{3}\) gives an overview of these three. The citric acid (tca) or the krebs cycle; Heterotrophs (like humans) ingest other living things to obtain glucose. Web what you’ll learn to do: Cellular respiration involves four steps: While the process can seem complex, this page takes you through the key elements of each part of cellular respiration. Glycolysis, transformation of pyruvate, the krebs cycle (also called the citric acid cycle), and oxidative phosphorylation. And the electron transport chain, where oxidative phosphorylation occurs. Overview of cellular respiration equation, types, stages & products. To access the energy stored in the foods we eat, biological molecules composing foods (carbohydrates, proteins, etc,) must be broken down into forms that the body. And the electron transport chain, where oxidative phosphorylation occurs. Web the reactions of cellular respiration can be grouped into three main stages and an intermediate stage: When organic fuels like glucose are broken down using an electron transport chain, the breakdown process is known as cellular respiration. Web cellular respiration is a collection of three unique metabolic pathways: Overview of. Many food molecules are broken down into glucose, a simple sugar. Identify the reactants and products of cellular respiration and where these reactions occur in a cell; Web cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces atp. C 6 h 12 o 6 (glucose) + 6o 2 (oxygen) → 6co 2 (carbon dioxide) + 6h 2. Is the process by which living cells break down. Web cellular respiration is a process that all living things use to convert glucose into energy. This is accomplished through the digestive process where. Many food molecules are broken down into glucose, a simple sugar. Cellular respiration is a process that happens inside an organism’s cells. _image modified from etc4 by fvasconcellos ( public domain )._ is that really what a mitochondrion looks like? This is because cellular respiration releases the energy in glucose slowly and in many small steps. Many food molecules are broken down into glucose, a simple sugar. The process is similar to burning, although it doesn’t produce light or intense heat as a campfire does. To access the energy stored in the foods we eat, biological molecules composing foods (carbohydrates, proteins, etc,) must be broken down into forms that the body can utilize. The citric acid (tca) or the krebs cycle; And the electron transport chain, where oxidative phosphorylation occurs. Graphic shows glycolysis, the krebs cycle and electron transport chain. When organic fuels like glucose are broken down using an electron transport chain, the breakdown process is known as cellular respiration. To create atp and other forms of energy to power cellular reactions, cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of. Describe the process of the citric acid cycle (krebs. Web cellular respiration is the process by which biological fuels are oxidized in the presence of an inorganic electron acceptor, such as oxygen, to drive the bulk production of adenosine triphosphate (atp), which contains energy. It includes glycolysis, the tca cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Web cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces atp. Glucose, 2 nad +, 2 adp + 2 pi. Is the process by which living cells break down.
Cellular Respiration Steps Chart
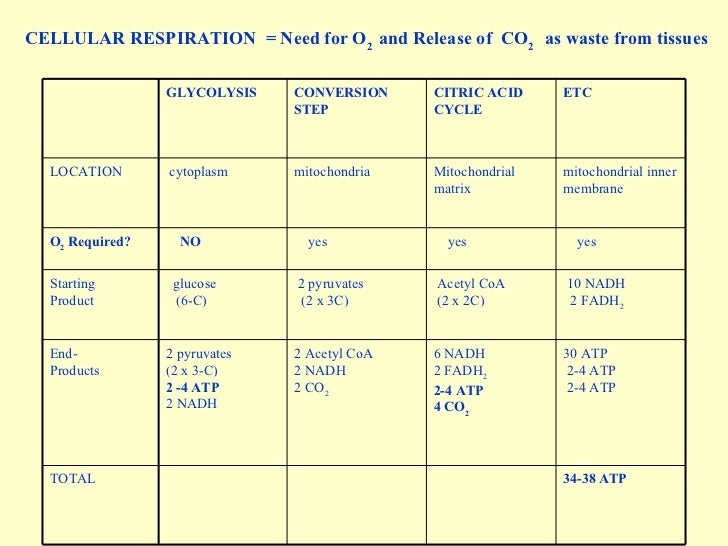
Cellular Respiration Summary Chart
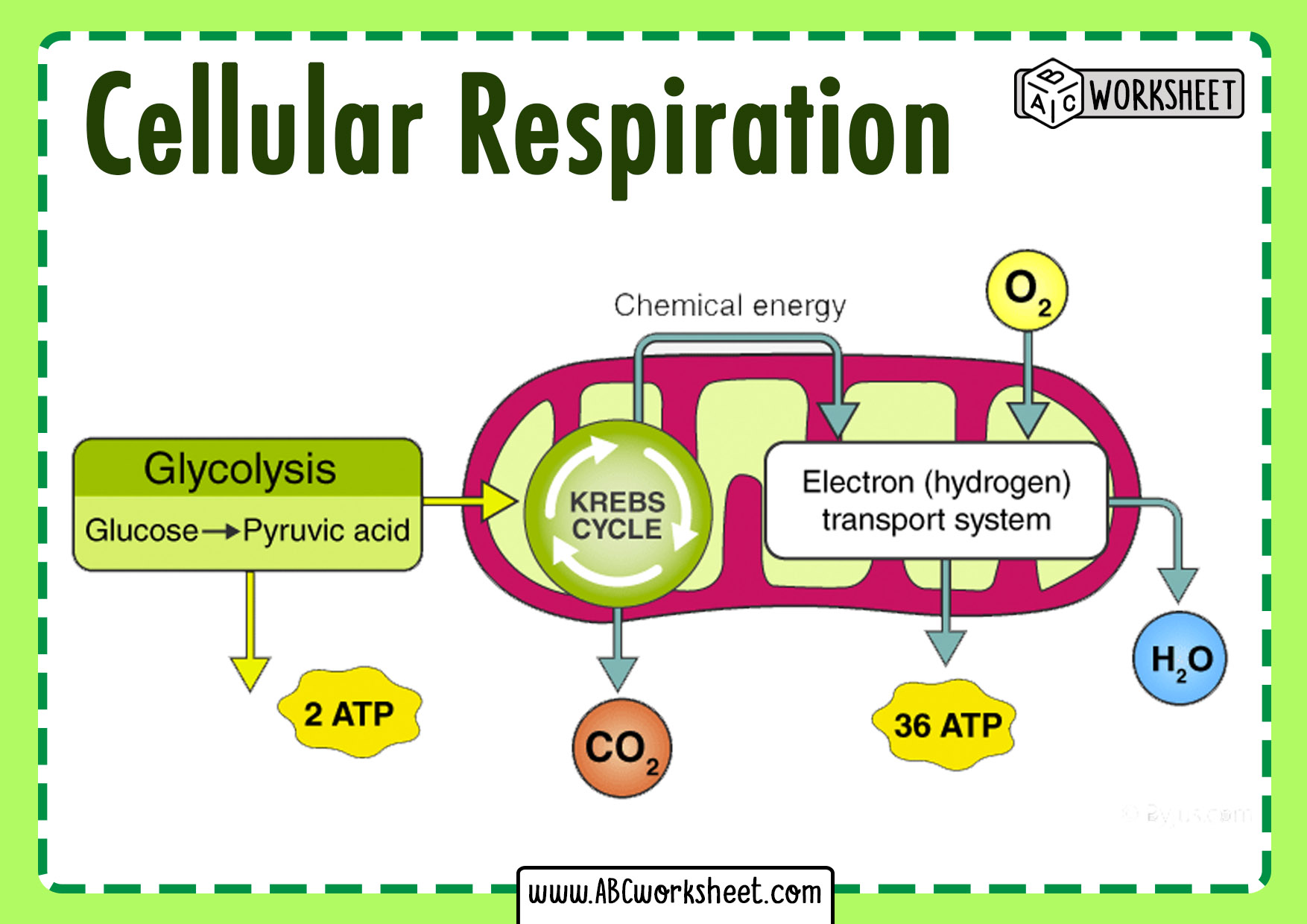
What Are The Reactants In The Equation For Cellular Respiration? The
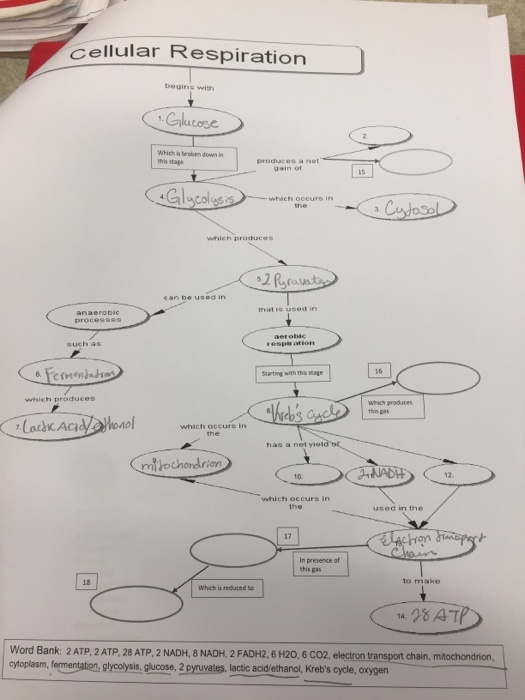
Cellular Respiration Summary Chart

Unit 7 Cellular Respiration and Energy Metabolism Douglas College
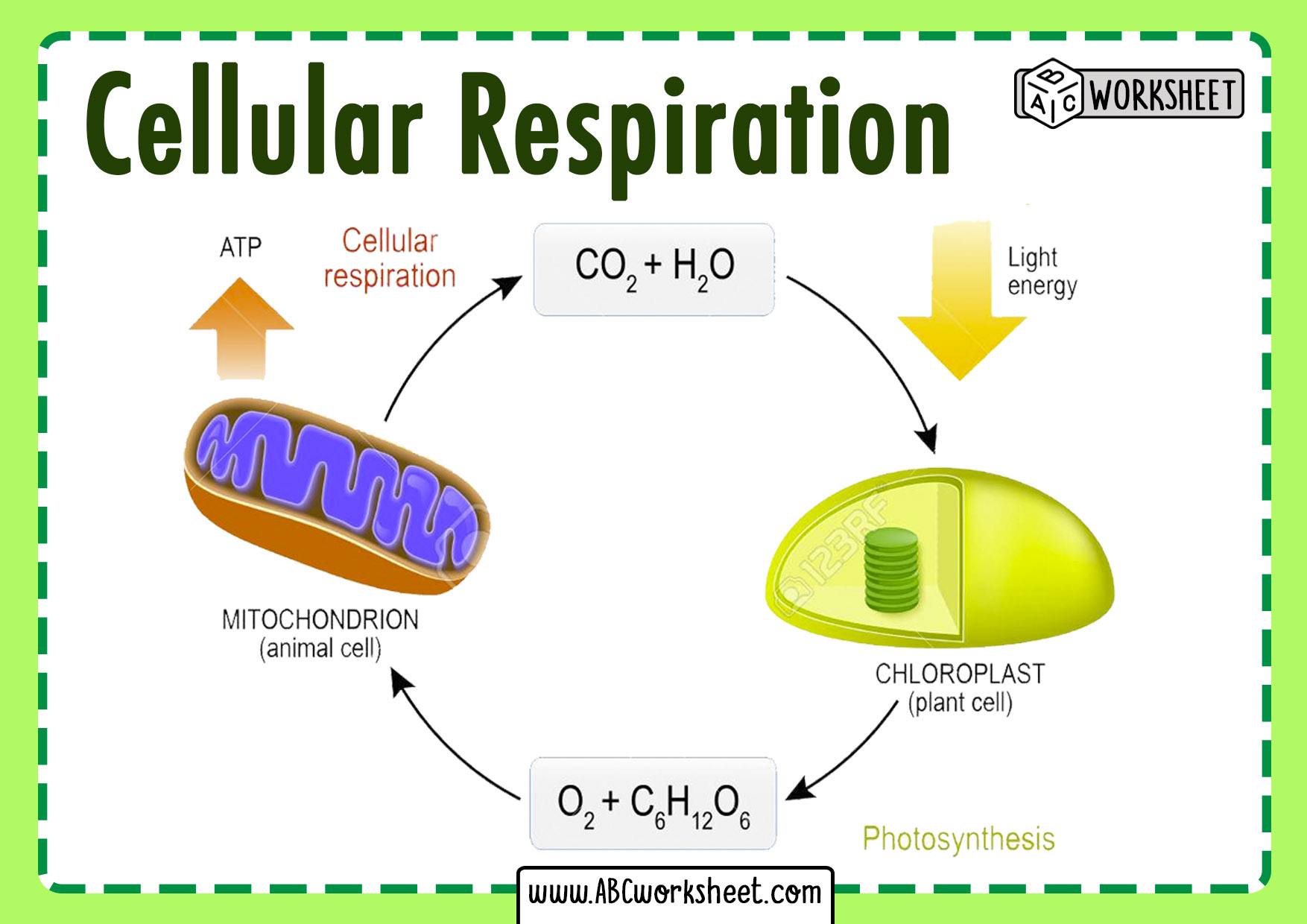
Cellular Respiration Chart Worksheet
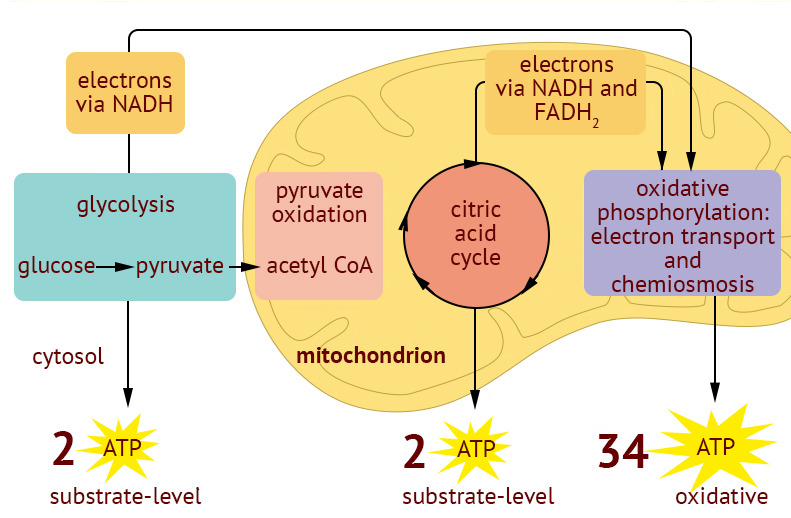
Cellular Respiration Diagram Quizlet

Cellular Respiration Labeled Diagram Seeds Wiring
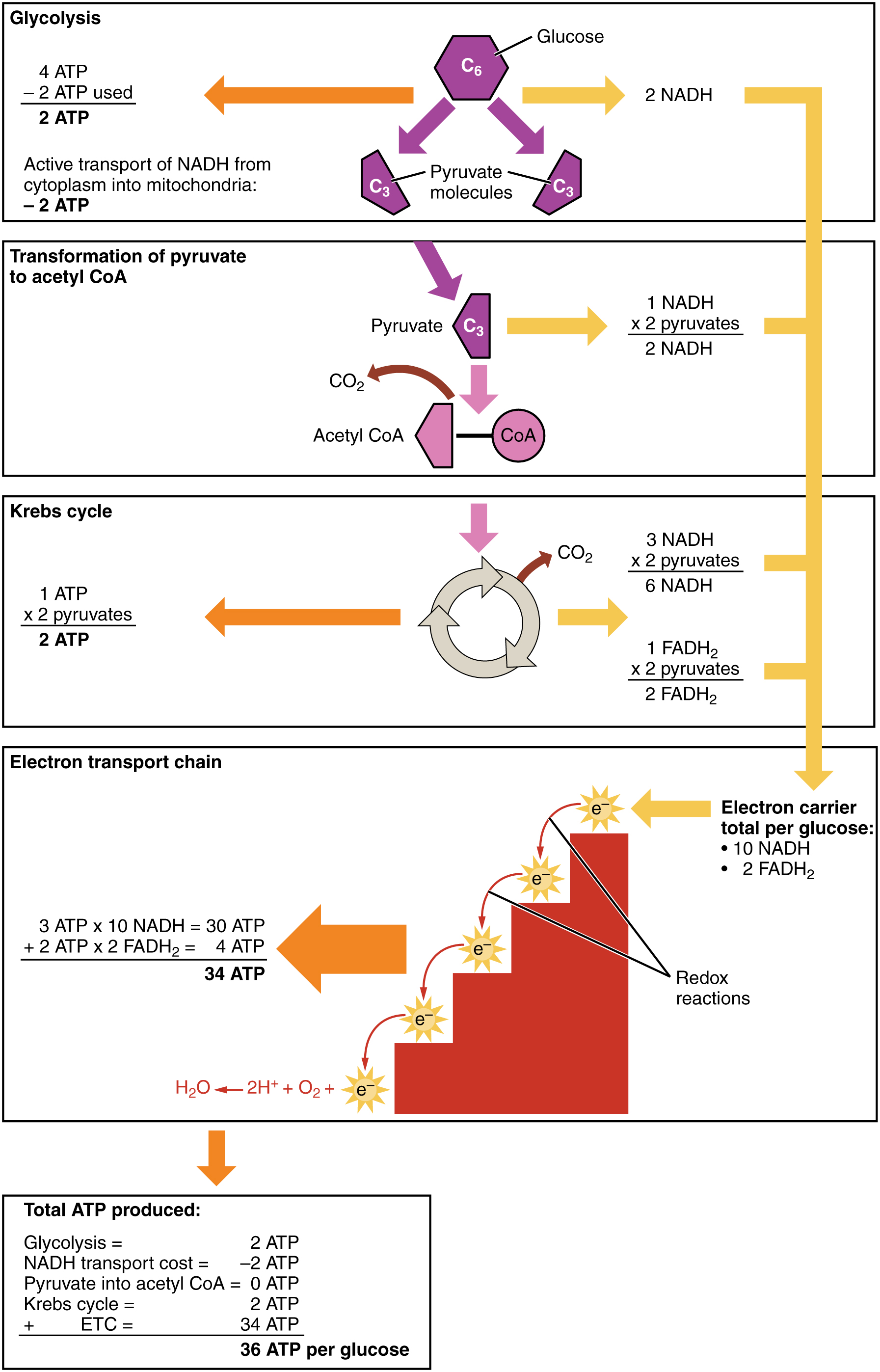
4.10 Cellular Respiration Human Biology
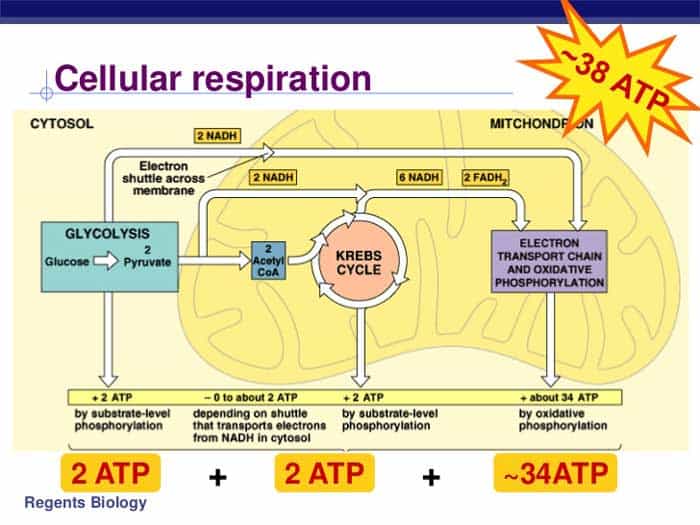
Cellular Respiration Equation, Types, Stages, Products & Diagrams
Though It Releases Only 2 Atps, It Occurs More Quickly Than Aerobic Respiration.
Web There Are Two Types Of Respiration:
C 6 H 12 O 6 (Glucose) + 6O 2 (Oxygen) → 6Co 2 (Carbon Dioxide) + 6H 2 O (Water) + 36 Atp.
Identify The Reactants And Products Of Cellular Respiration And Where These Reactions Occur In A Cell;
Related Post: