Chart Of Soil
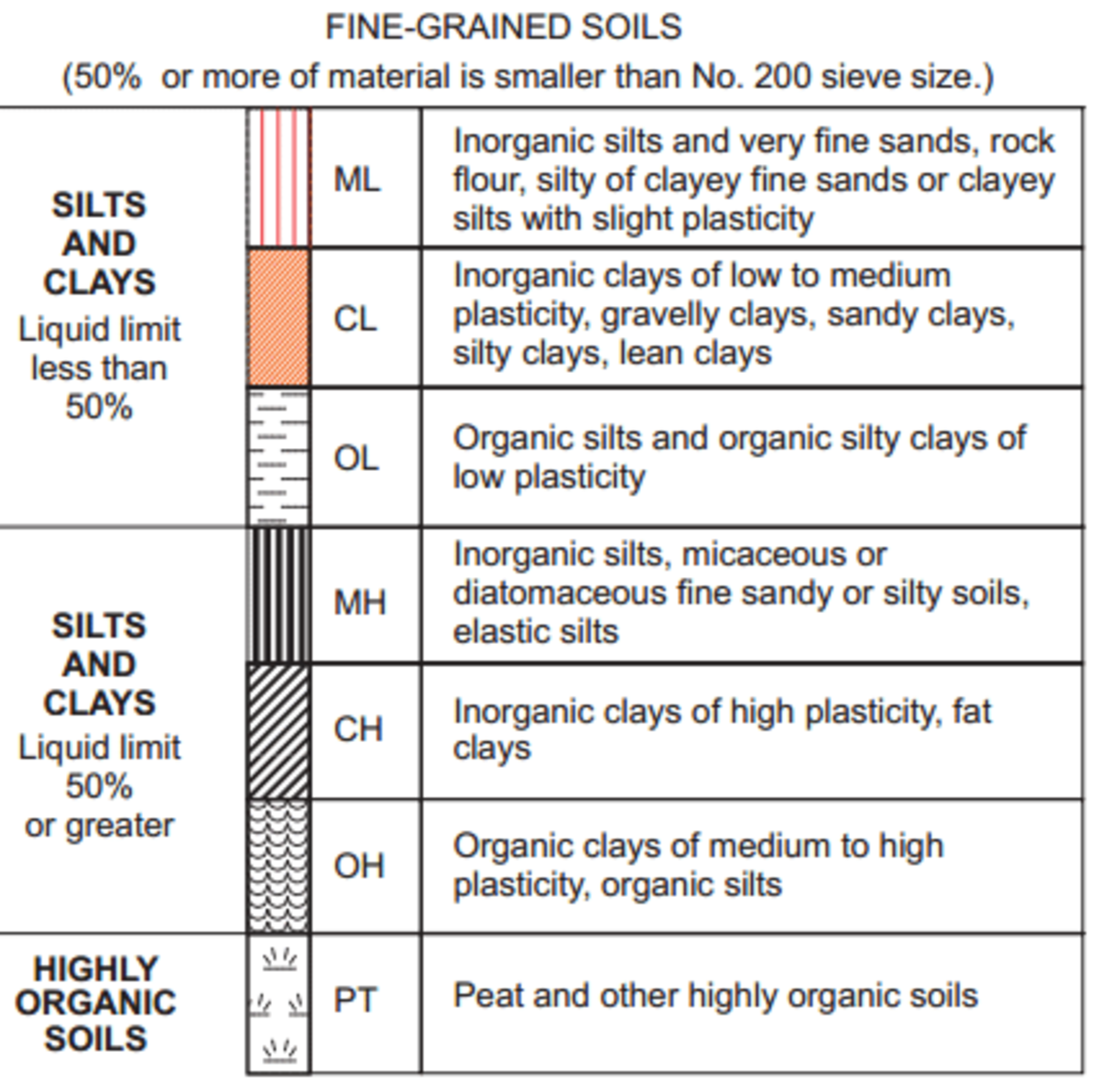
Chart Of Soil - Soil horizons and profiles a residual soil forms over many years, as mechanical and chemical weathering slowly change solid rock into soil. Soil as an engineering material. Web typical soil types include black earth and brown earth, with subsequent differentiation levels comprising the soil types per se. What are the five factors of soil formation? The two principal systems of soil classification in use today are the soil order system of the u.s. In coarse grained soils, where the grains are larger than 0.075 mm (or 75 µm), the engineering behaviour is influenced mainly by the relative proportions of the different sizes present, the shapes of the soil grains, and the density of packing. A common language for sharing scientific knowledge and interpreting soil survey information. The natural resources conservation service (nrcs)—part of the u.s. Web a list of soil properties affecting the use. Web what is soil? Web in short, soil is a mixture of minerals, dead and living organisms (organic materials), air, and water. Web the uscs has three major classification groups: Limits for each soil property that would be favorable or unfavorable for the land use. The two principal systems of soil classification in use today are the soil order system of the u.s. It. The higher the amount of hydrogen in the soil, the lower the soil ph. Entire region of the northern plain is made up of alluvial soil. These four ingredients react with one another in amazing ways, making soil one of our planet’s most dynamic and important natural resources. Web soil composition is a mix of soil ingredients that varies from. Soil texture and structure are considered “master variables”, meaning that texture and structure directly influence a large number of other soil properties. Soil horizons and profiles a residual soil forms over many years, as mechanical and chemical weathering slowly change solid rock into soil. Web basic characteristics of soils. Web the most popular methods of soil classification are the unified. And (3) highly organic soils (referred to as peat ). Web the uscs has three major classification groups: Sandy soil, clayey soil, loamy soil, laterite soil, black soil, red soil, alluvial soil and desert soil. The two principal systems of soil classification in use today are the soil order system of the u.s. Web the main types of soil are: Soil types are classified according to characteristic soil strata, which occur in a specific order depending on type. Soil texture and structure are considered “master variables”, meaning that texture and structure directly influence a large number of other soil properties. Soil, the biologically active, porous medium that has developed in the uppermost layer of earth’s crust. Web soil composition is. Information found on this page. The higher the amount of hydrogen in the soil, the lower the soil ph. Soil texture and structure are considered “master variables”, meaning that texture and structure directly influence a large number of other soil properties. And (3) highly organic soils (referred to as peat ). Soil, the biologically active, porous medium that has developed. Web the main types of soil are: Sandy soil, clayey soil, loamy soil, laterite soil, black soil, red soil, alluvial soil and desert soil. Deposited by the indus, the ganga and the brahmaputra. Web in short, soil is a mixture of minerals, dead and living organisms (organic materials), air, and water. Department of agriculture—has compiled soil maps and data for. A comprehensive classification system is important for any science: Web soils can behave quite differently depending on their geotechnical characteristics. Web modern soil classification started with the publication of the 7th approximation of the usda soil taxonomy, where precisely defined and quantified soil properties as such, or in combination, were used to define “diagnostic soil horizons”. They contain technical information. Web soils can behave quite differently depending on their geotechnical characteristics. What are the five factors of soil formation? Web if you would like to determine soil type by feel, here’s a chart from the usda to help you. Soils consist of grains (mineral grains, rock fragments, etc.) with water and air in the voids between grains. Web the uscs. The abbreviation ph stands for potential hydrogen” and indicates the concentration of hydrogen in the soil. Web in short, soil is a mixture of minerals, dead and living organisms (organic materials), air, and water. Soils consist of grains (mineral grains, rock fragments, etc.) with water and air in the voids between grains. The two principal systems of soil classification in. These four ingredients react with one another in amazing ways, making soil one of our planet’s most dynamic and important natural resources. Web this chart reflects a tremendous amount of information available for your understanding of the composition of a healthy productive soil environment. Mineral particles (sand, silt, and clay), organic matter, water, and air. The unified soil classification system ( uscs) is a soil classification system used in engineering and geology to describe the texture and grain size of a soil. Web a list of soil properties affecting the use. The uscs further subdivides the three major soil classes for clarification. In coarse grained soils, where the grains are larger than 0.075 mm (or 75 µm), the engineering behaviour is influenced mainly by the relative proportions of the different sizes present, the shapes of the soil grains, and the density of packing. What are the five factors of soil formation? The scale ranges from 0 (most acidic) to 14 (most alkaline). Web soil ph is a measurement of how acidic (sour) or alkaline (sweet) your soil is. Deposited by the indus, the ganga and the brahmaputra. Web technical guides are the primary scientific references for nrcs. Soil, the biologically active, porous medium that has developed in the uppermost layer of earth’s crust. Sandy soil, clayey soil, loamy soil, laterite soil, black soil, red soil, alluvial soil and desert soil. The natural resources conservation service (nrcs)—part of the u.s. Soil types are classified according to characteristic soil strata, which occur in a specific order depending on type.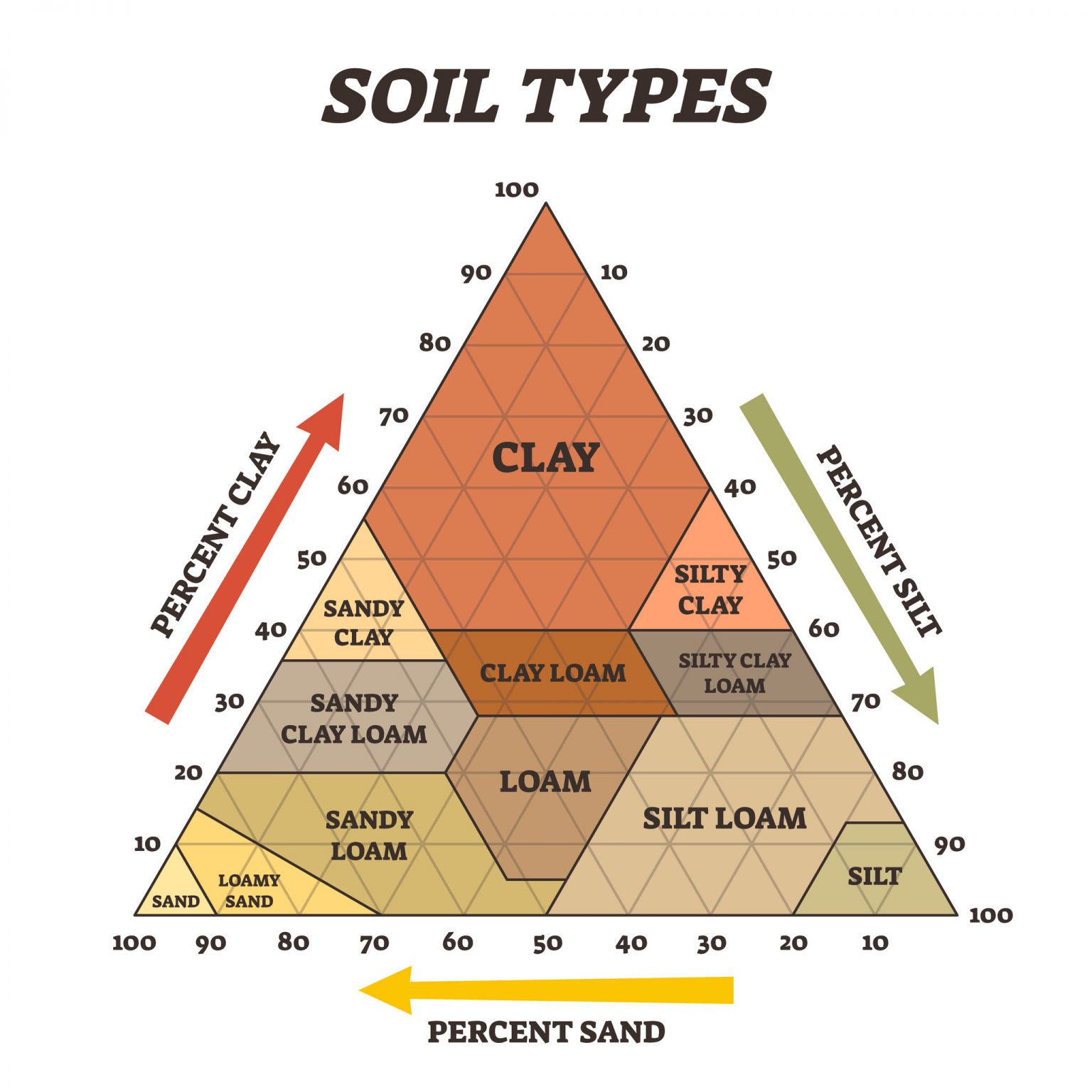
Soil is the thin layer of material covering the earth’s surface
Types Of Soil Chart

Top 4 common soil types

Soil is the thin layer of material covering the earth’s surface
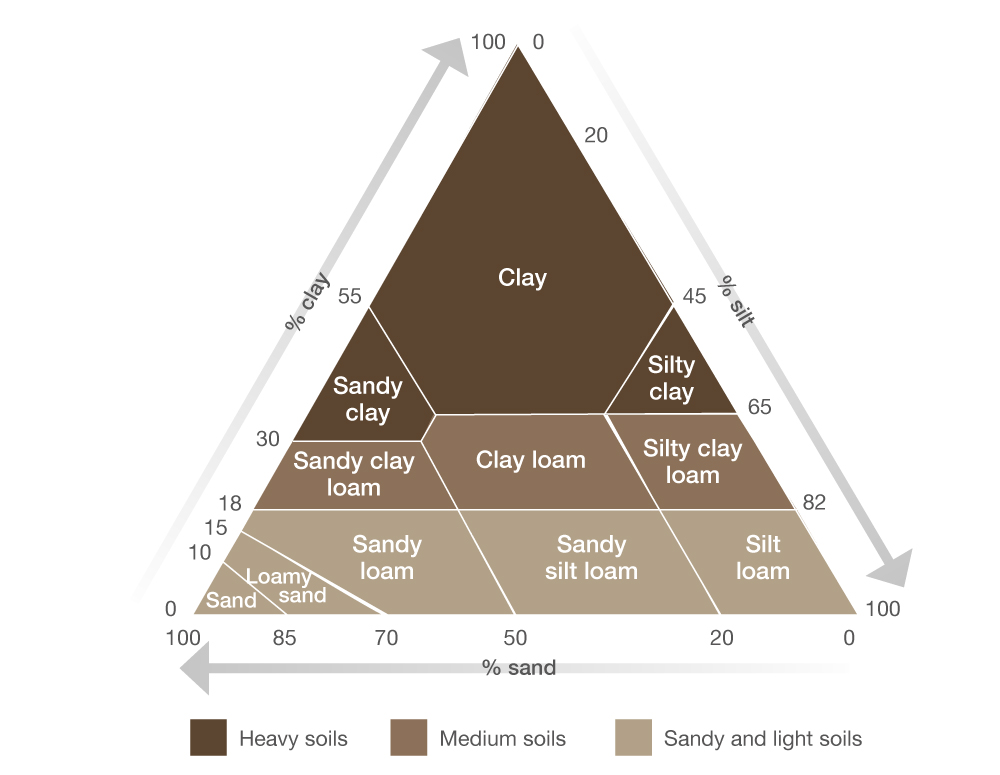
Soil texture and cation exchange capacity AHDB
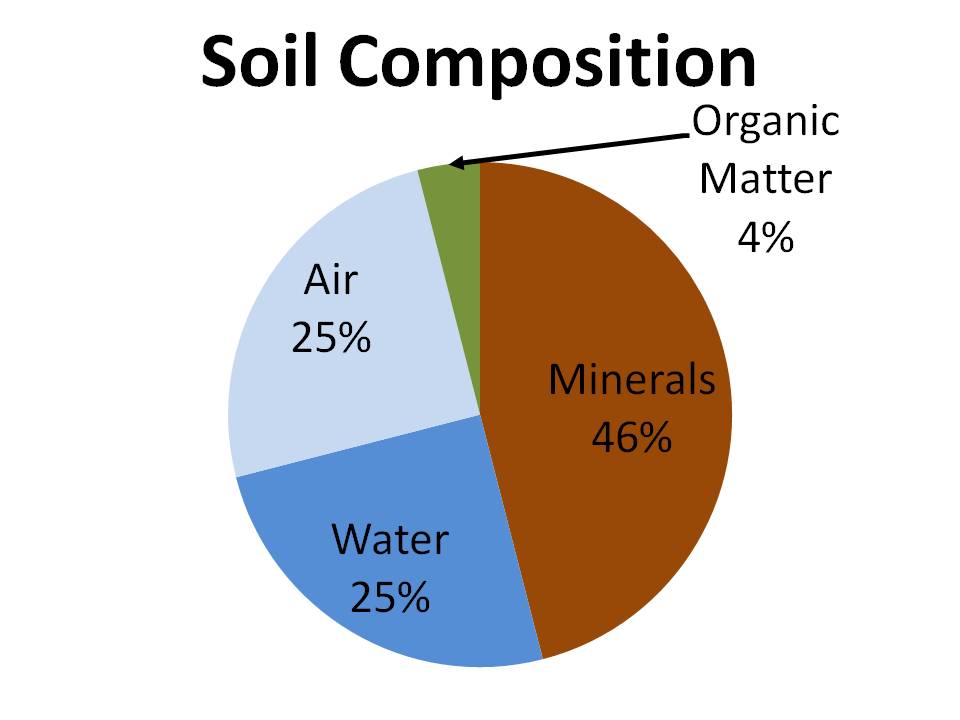
Soil Composition

The Twelve Orders of Soil Taxonomy NRCS Soil, Agriculture education
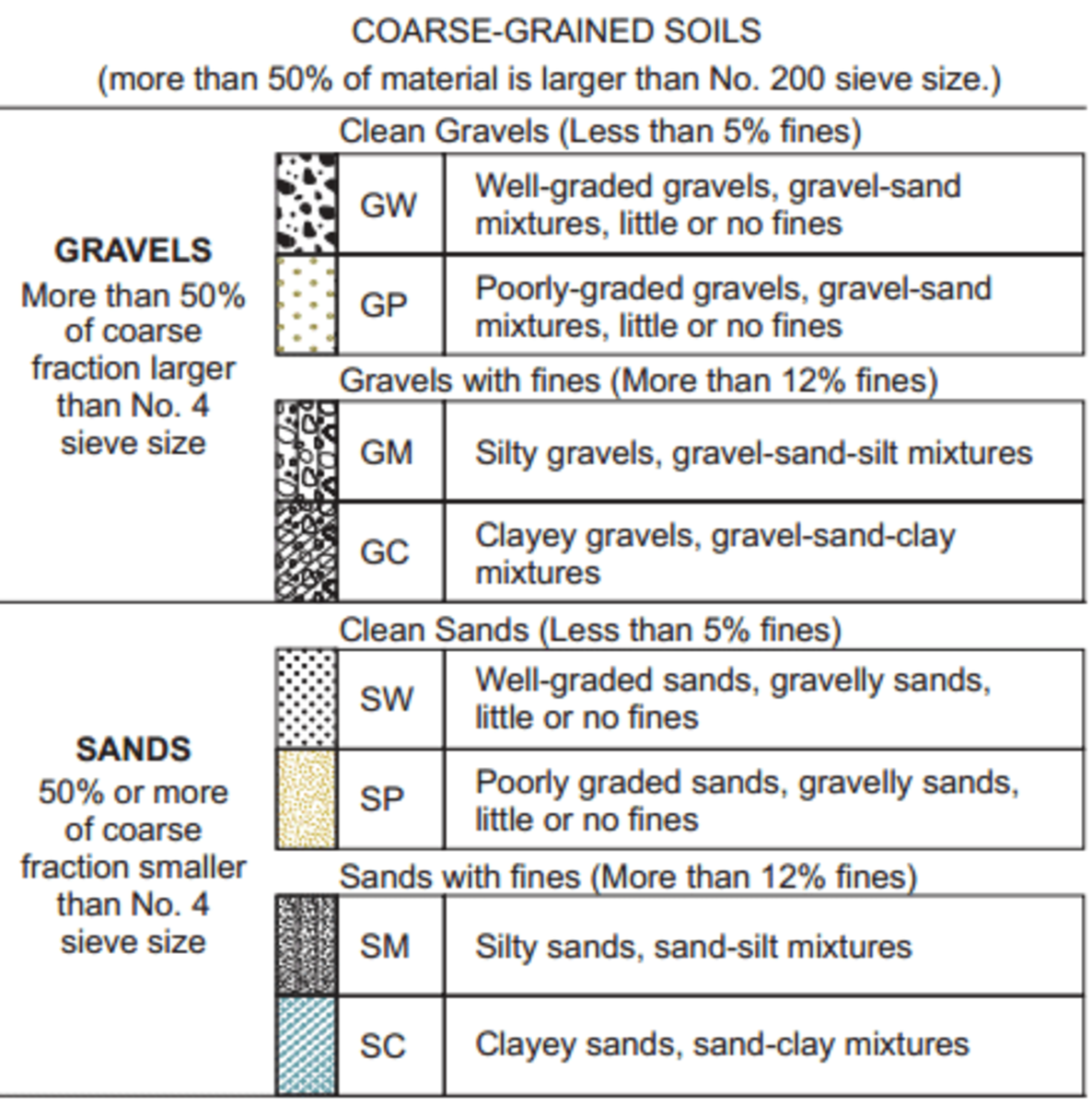
VisualManual Soil Classification and Description Owlcation
Soil Structure Decline Tas Fact Sheets
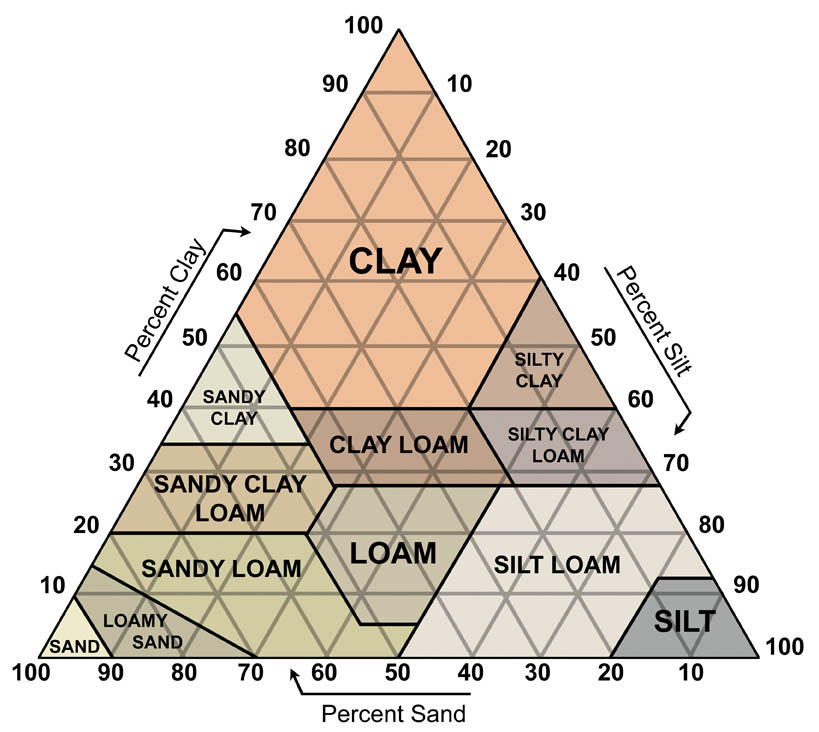
dickinson_ryan_enb150 Types of Soil
The Physical Properties Of Soil, In Order Of Decreasing Importance For Ecosystem Services Such As Crop Production, Are Texture, Structure, Bulk Density, Porosity, Consistency, Temperature, Colour And Resistivity.
The Two Principal Systems Of Soil Classification In Use Today Are The Soil Order System Of The U.s.
There Are Many Different Types Of Soil In Maryland.
Healthy Soils Grow Healthy Plants That Keep People Healthy.
Related Post:
_Fig2.PNG?1390545528)