Comparing Macromolecules Chart
Comparing Macromolecules Chart - The polymer is more than the sum of. Cut and paste comparison table for macromolecules. Web for example, a carbohydrate is a macromolecule that is classified as a polymer because it is made up of repeating monosaccharides, but a fat (lipid) is a macromolecule that cannot be further classified because if you look under the 'monomers' column, it is built up by more than one monomer. Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Results of the indian general elections were out on tuesday with the national democratic alliance (nda), led by the bharatiya janata. This document has been uploaded by a student, just like you, who decided to remain. Web distinguish between the four classes of macromolecules carbohydrates are a group of macromolecules that are a vital energy source for the cell, provide structural support to many organisms, and can be found on the surface of the cell as receptors or. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like lipids (fats) function, lipids (fats) monomer (subunit), lipids (fats) examples and more. Web use the chart to identify the chemicals that appear in every type of monomer. Where can we find them? Web proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids are the four major classes of biological macromolecules—large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules. As we’ve learned, there are four major classes of biological macromolecules: You can create a table using ms word. Anatomy and physiology i (bsc 1093) 26documents. Proteins (polymers of amino acids) carbohydrates (polymers of. Macromolecules are made up of single units known as monomers that are joined by covalent bonds to form larger polymers. The national assembly will choose the president for the next five. Last updated june 4, 2024 08:00 pm pdt. Web as we’ve learned, there are four major classes of biological macromolecules: Create a table comparing the four major biological macromolecules: They will compare the polarity, solubility, composition, monomer, polymers, common names, food sources, word. As we’ve learned, there are four major classes of biological macromolecules: Macromolecules are made up of single units known as monomers that are joined by covalent bonds to form larger polymers. Organic compound composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen ratio of 1:2:1 monomer is monosaccharide (ch2o)n, where. Your table must include the following elements: Students shared 26 documents in this course. They will compare the polarity, solubility, composition, monomer, polymers, common names, food sources, word. Web the document describes the main types of macromolecules and their functions. Web on may 29, south africans will vote in national and provincial elections to elect a new national assembly and. Web the document describes the main types of macromolecules and their functions. Web proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids are the four major classes of biological macromolecules—large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules. Web distinguish between the four classes of macromolecules carbohydrates are a group of macromolecules that are a vital energy source for the. The national assembly will choose the president for the next five. Proteins (polymers of amino acids) carbohydrates (polymers of sugars) lipids (polymers of lipid monomers) nucleic acids (dna and rna; Polymers of nucleotides) let’s take a closer look at the differences between the difference classes. Web as we’ve learned, there are four major classes of biological macromolecules: Within all cells,. Proteins (polymers of amino acids) carbohydrates (polymers of sugars) lipids (polymers of lipid monomers) nucleic acids (dna and rna; Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Macromolecules, biomolecules, organic compunds elements *from the periodic table of elements subunits monomers, building blocks functions: As we’ve learned, there are four major classes of biological macromolecules: Polymers of nucleotides) let’s take a closer look. Proteins (polymers of amino acids) carbohydrates (polymers of sugars) lipids (polymers of lipid monomers) nucleic acids (dna and rna; Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Nucleic acids are complex macromolecules that store and transmit. Proteins (polymers of amino acids) carbohydrates (polymers of sugars) lipids (polymers of lipid monomers) nucleic acids (dna and rna; Web this is a biomolecule chart for. Looking at the chemicals available can help you to determine which monomers can be formed. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like elements in carbohydrates, monomers of carbs, dimers of carbohydrates and more. Where can we find them? Web discuss biological macromolecules and the differences between the four classes. As we’ve learned, there are four major classes of. Macromolecules are made up of single units known as monomers that are joined by covalent bonds to form larger polymers. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what is the macromolecule, carbohydrates subclasses?, what is the macromolecule, nucleic acids subclasses?, what is the macromolecule, proteins subclasses? Looking at the chemicals available can help you to determine which. Web distinguish between the four classes of macromolecules carbohydrates are a group of macromolecules that are a vital energy source for the cell, provide structural support to many organisms, and can be found on the surface of the cell as receptors or. Create a table comparing the four major biological macromolecules: Proteins (polymers of amino acids) carbohydrates (polymers of sugars) lipids (polymers of lipid monomers) nucleic acids (dna and rna; Within all cells, small organic molecules are joined together to form larger molecules. Organic compound composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen ratio of 1:2:1 monomer is monosaccharide (ch2o)n, where n is any whole number from 3 to 8, commonly 3, 5, or 6 animals store glucose in form of polysaccharide glycogen and plants do the same in form of starch. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like lipids (fats) function, lipids (fats) monomer (subunit), lipids (fats) examples and more. Web for example, a carbohydrate is a macromolecule that is classified as a polymer because it is made up of repeating monosaccharides, but a fat (lipid) is a macromolecule that cannot be further classified because if you look under the 'monomers' column, it is built up by more than one monomer. Web this is a biomolecule chart for the students to fill in. Web discuss biological macromolecules and the differences between the four classes. Web proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids are the four major classes of biological macromolecules—large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules. Carbohydrates are compounds composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a ratio of one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms for each carbon atom. Your table must include the following elements: Polymers of nucleotides) let’s take a closer look at the differences between the difference classes. They will compare the polarity, solubility, composition, monomer, polymers, common names, food sources, word. Web macromolecule comparison chart organic molecules are based on carbon. Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.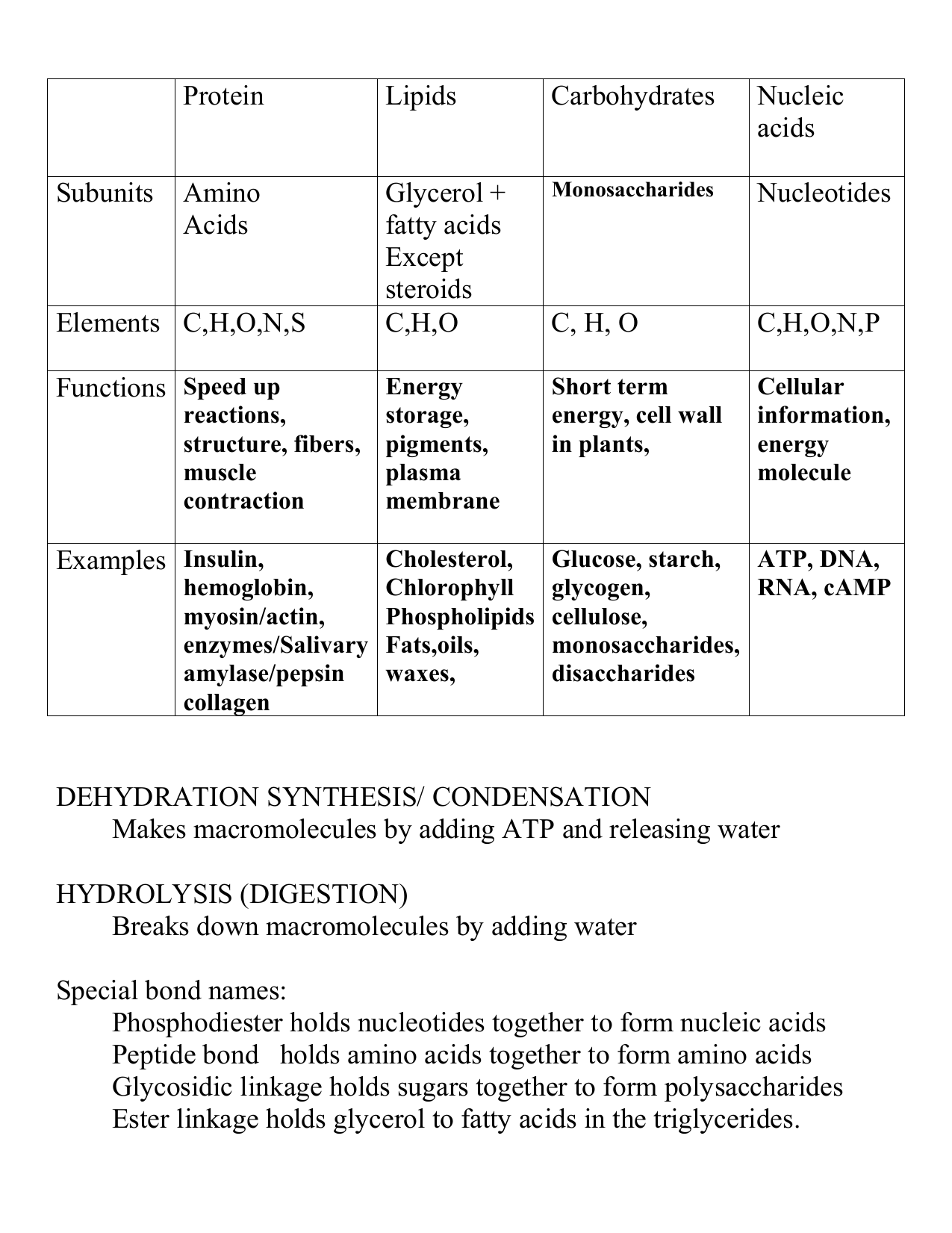
Biochemistry Macromolecules Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart
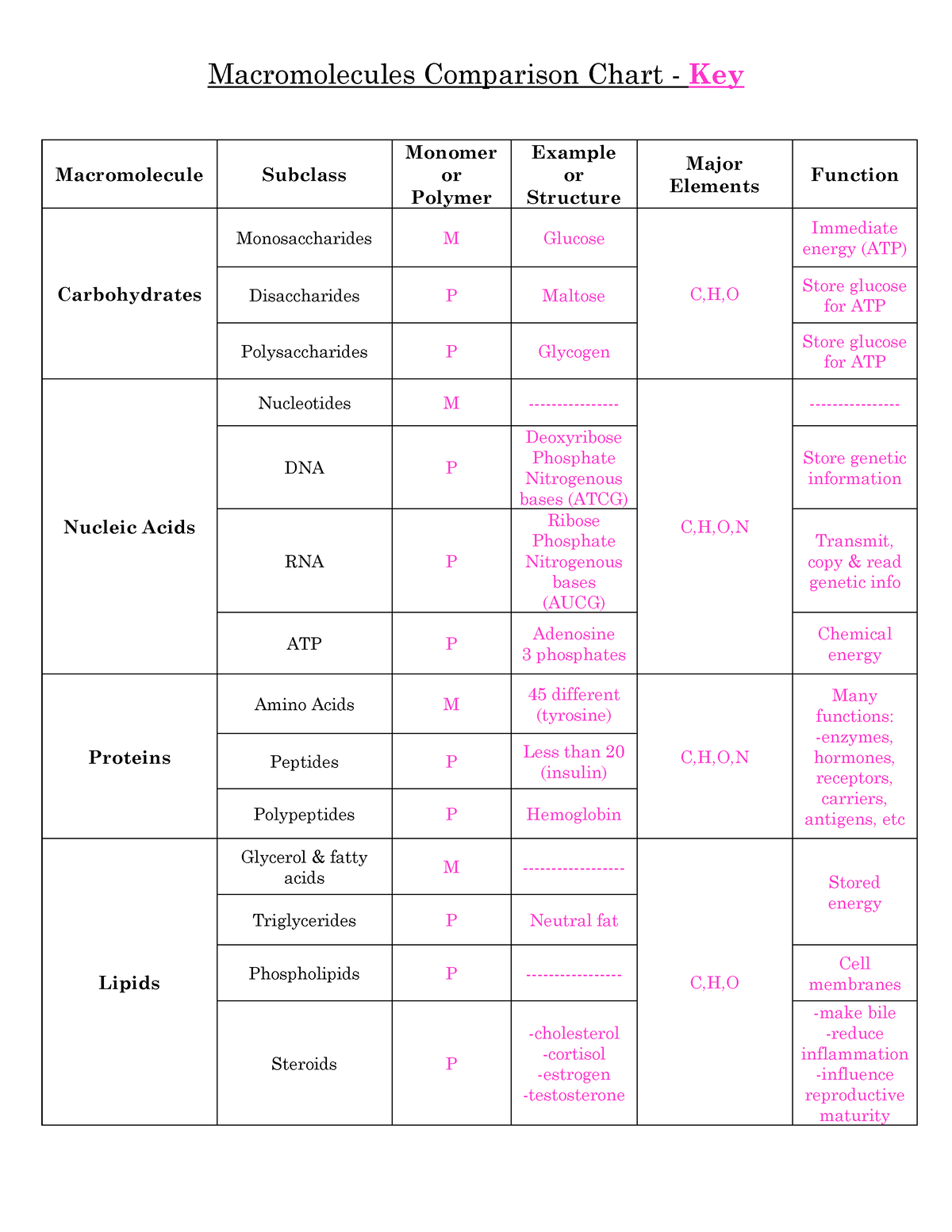
Macromolecules Comparison Chart KEY Macromolecules Comparison Chart

Pre IB/GT Biology 1 Macromolecules Chart Diagram Quizlet

Organic Molecules Chart Organic Molecules Contrast Chart

24 best images about Macromolecules (B.9A) on Pinterest
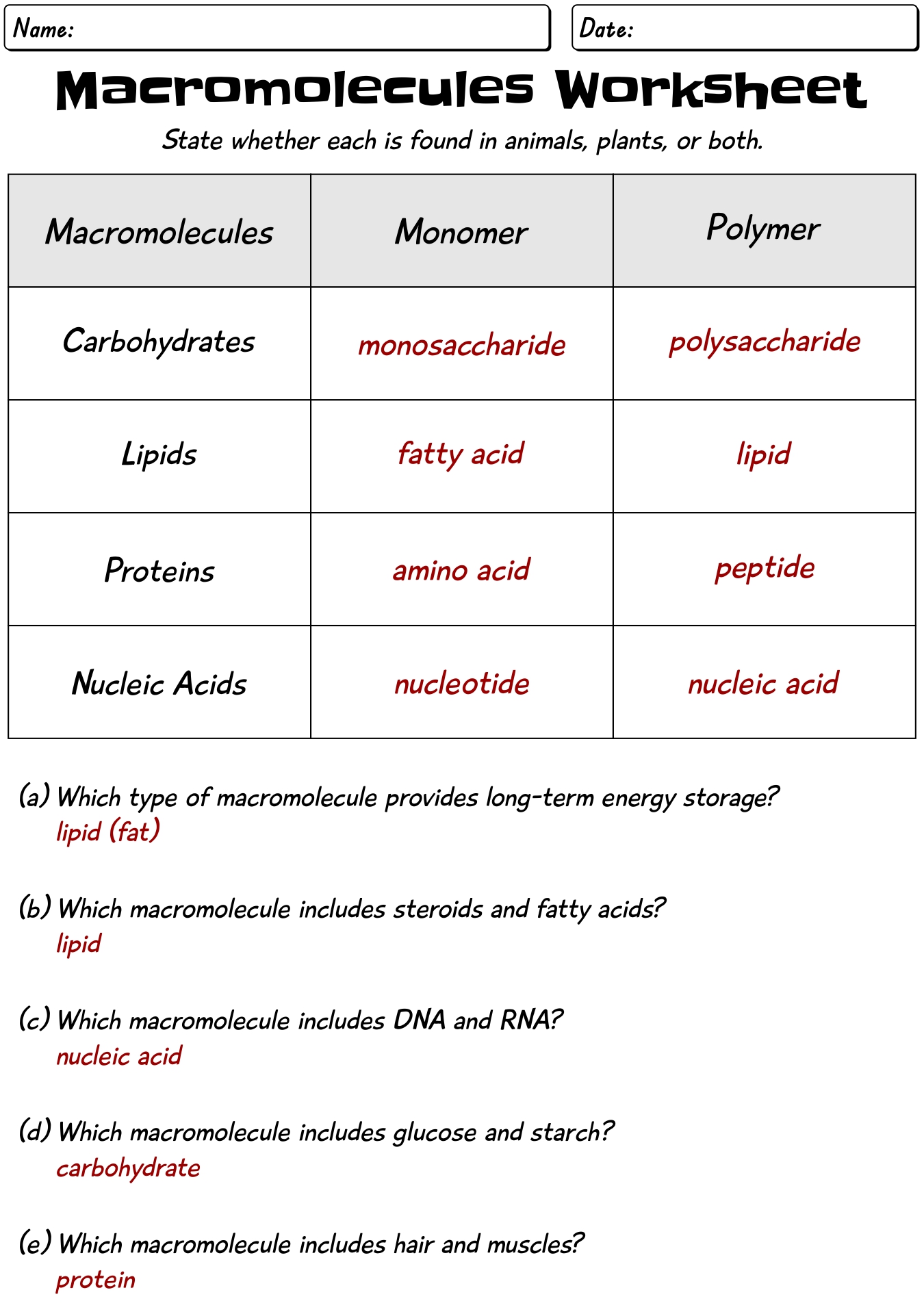
14 Biology Macromolecules Worksheets And Answers /
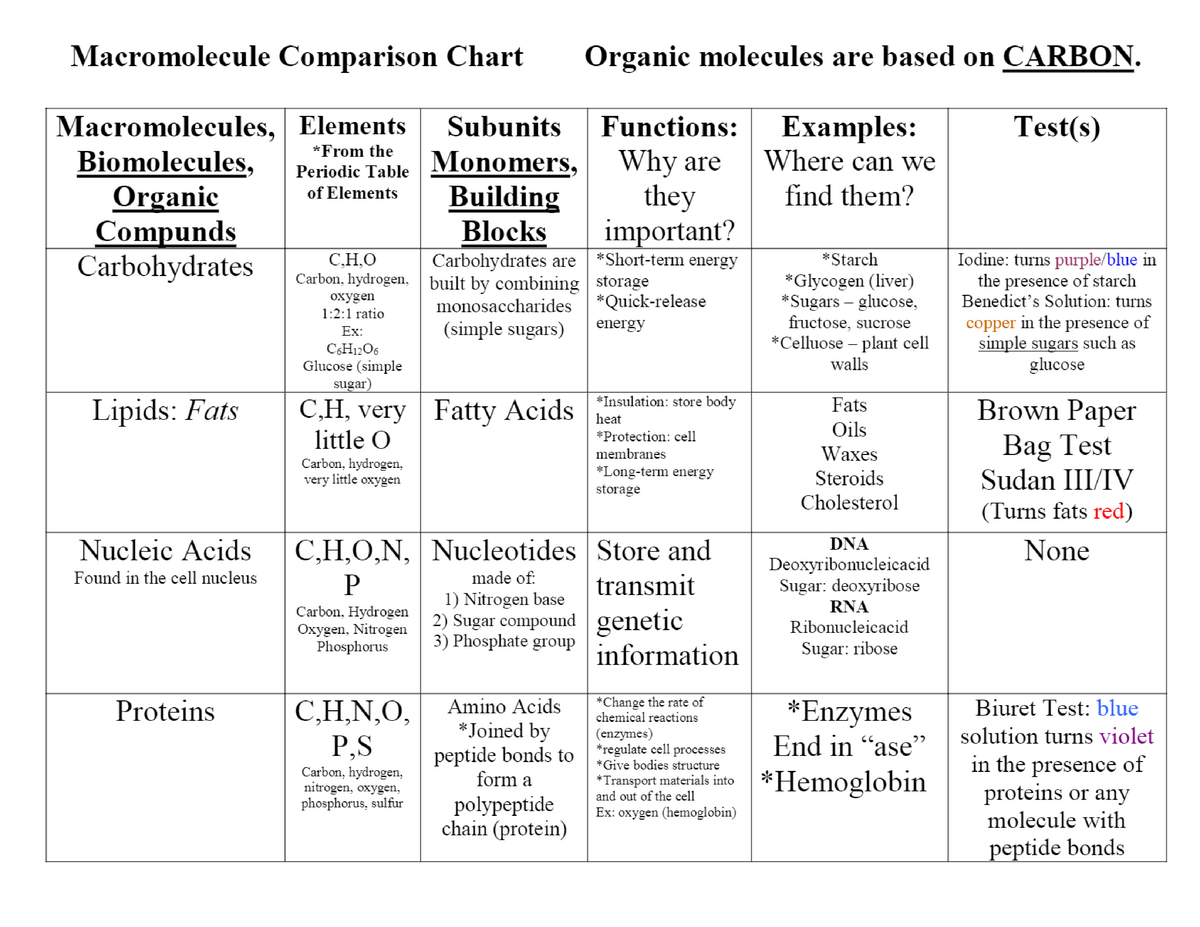
Macromolecule Comparison Chart Organic Bio201 Studocu
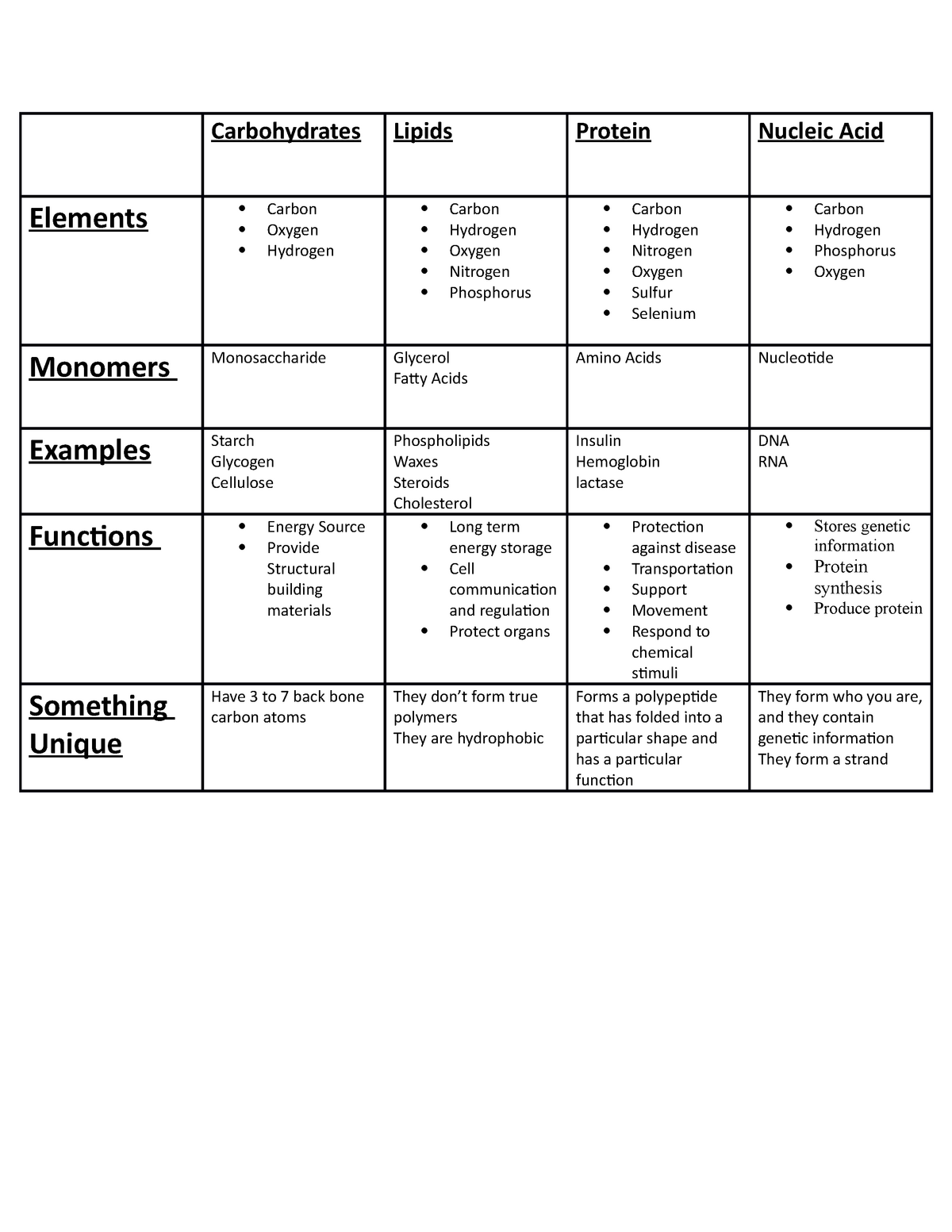
Macromolecules chart Lecture notes A Carbohydrates Elements Carbon

Macromolecules Worksheet Chart
Macromolecules Chart Rae Rocks Teaching
Web Proteins, Carbohydrates, Nucleic Acids, And Lipids Are The Four Major Classes Of Biological Macromolecules—Large Molecules Necessary For Life That Are Built From Smaller Organic Molecules.
It Lists Macromolecules Such As Proteins, Lipids, Carbohydrates, And Nucleic Acids And Notes Their Monomer Subunits And Examples.
The Polymer Is More Than The Sum Of.
Web Discuss Biological Macromolecules And The Differences Between The Four Classes.
Related Post: