Compression Ratio To Octane Chart
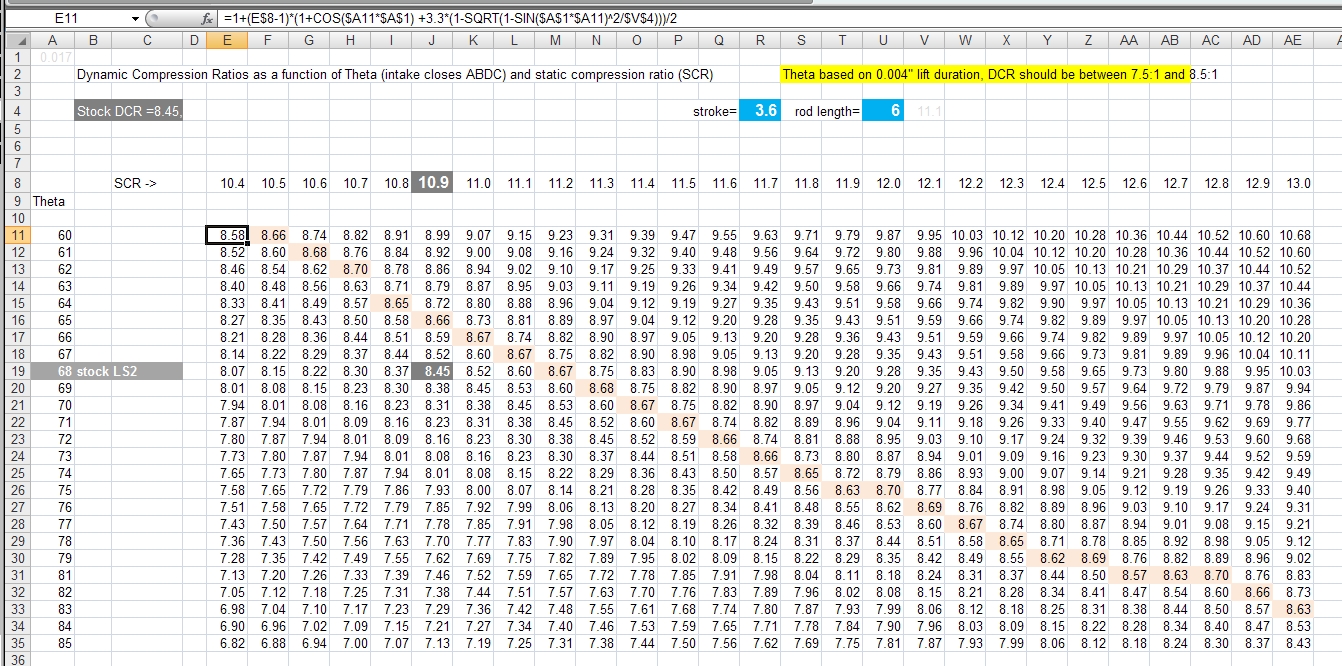
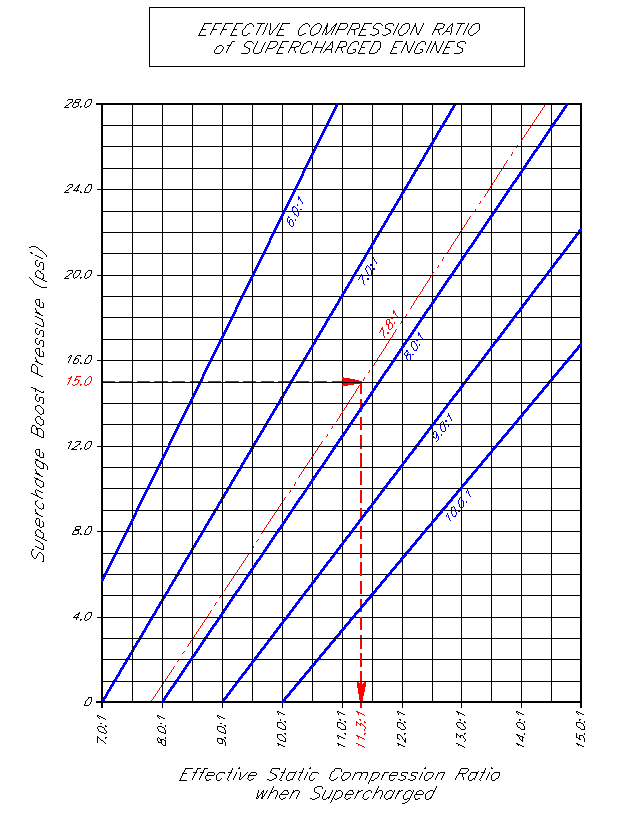
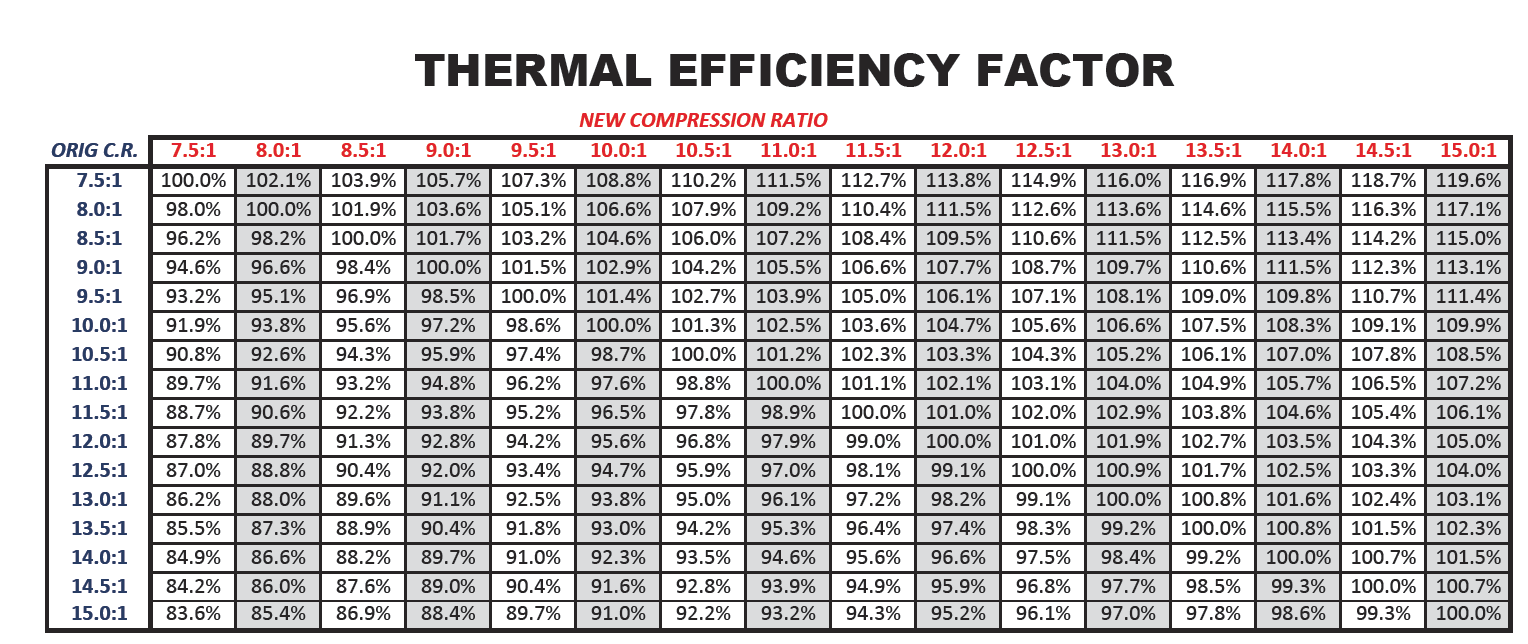
Compression Ratio To Octane Chart - What is the compression ratio? Web it's easy to find what octane rating a gas has: If an engine is optimised for high octane fuel the designers can increase compression and add ignition advance, because the fuel is more resistant to autoignition. To help determine compression if you have forced induction (supercharger, turbocharger, or procharger) follow the chart below. Other factors also influence your car’s knocking characteristics: Modern engines can handle much higher compression at lower octanes. The higher the octane rating, the more pressure the fuel can withstand within the compression stroke of an engine prior to igniting. Click ahead to discover what compression ratio is and how an engine can alert you to knocking and pinging. Web higher octane fuels are often required or recommended for engines that use a higher compression ratio and/or use supercharging or turbocharging to force more air into the engine. Web the engine compression ratio of new cars and light trucks (black markers below) improved along a similar course as octane rating from the 1920s to the 1970s. Our compression ratio calculator is the. There are many other factors such as head material, timing, and direct injection that come into play. Is mixing race fuel with pump gas recommended, and if so, how much do you use? Premium or midgrade fuel may be advisable to prevent knock. Stations are required to post them on bright yellow stickers on. If an engine is optimised for high octane fuel the designers can increase compression and add ignition advance, because the fuel is more resistant to autoignition. Premium or midgrade fuel may be advisable to prevent knock. Web it's easy to find what octane rating a gas has: And those questions are just. Web higher octane levels can enable higher compression. Is mixing race fuel with pump gas recommended, and if so, how much do you use? This can reduce efficiency or damage the engine if knock sensors are not present to modify the ignition timing. These calculators are rough approximations and none of the numbers here are absolute. Web calculate compression + boost for octane. Web as a general rule,. After that time, the average compression ratio continued to improve due to advanced engine design and controls, diverging from the octane trend. Web the engine compression ratio of new cars and light trucks (black markers below) improved along a similar course as octane rating from the 1920s to the 1970s. Web higher octane levels can enable higher compression ratios, which. Stations are required to post them on bright yellow stickers on each pump. Web the engine compression ratio of new cars and light trucks (black markers below) improved along a similar course as octane rating from the 1920s to the 1970s. Web higher octane levels can enable higher compression ratios, which would further improve engine efficiency. Swept volume = chamber. The higher the octane rating, the more pressure the fuel can withstand within the compression stroke of an engine prior to igniting. What is the compression ratio? It's all the volume of a cylinder above the compression ring. While 9:1 is a safe number, maximizing compression is a great way to increase power while also improving fuel. This can reduce. This is why some engines require 100+ octane with an 11:1 compression ratio while others are perfectly fine on 91 octane with a 13:1 compression. Average octane rating based on refiner sales volumes and is based on a calendar year. Web higher octane fuels are often required or recommended for engines that use a higher compression ratio and/or use supercharging. Should you buy oxygenated race fuel or not? An octane rating is defined as the standard measure of the performance of a motor fuel. These calculators are rough approximations and none of the numbers here are absolute. Web as a general rule, the best available pump gas will work with an 8.0:1 dynamic compression ratio. Web higher octane levels can. And those questions are just. Web we might be covering ground that's well trampled for many, but the static compression ratio of an engine is simple to understand: And it’s these two things that lead to a peak power increase for engines optimised for high octane fuel. Web to determine octane to your compression, follow our easy to use chart. If an engine is optimised for high octane fuel the designers can increase compression and add ignition advance, because the fuel is more resistant to autoignition. And those questions are just. Average octane rating based on refiner sales volumes and is based on a calendar year. Swept volume = chamber volume + piston volume + gasket volume + clearance volume. Web it's easy to find what octane rating a gas has: And it’s these two things that lead to a peak power increase for engines optimised for high octane fuel. This is why some engines require 100+ octane with an 11:1 compression ratio while others are perfectly fine on 91 octane with a 13:1 compression. While 9:1 is a safe number, maximizing compression is a great way to increase power while also improving fuel. Web the engine compression ratio of new cars and light trucks (black markers below) improved along a similar course as octane rating from the 1920s to the 1970s. The higher the octane rating, the more pressure the fuel can withstand within the compression stroke of an engine prior to igniting. Web what is an ‘octane rating’? What's the best compression ratio? Web higher octane levels can enable higher compression ratios, which would further improve engine efficiency. This can reduce efficiency or damage the engine if knock sensors are not present to modify the ignition timing. Web as a general rule, the best available pump gas will work with an 8.0:1 dynamic compression ratio. Web the octane number is a measure of how resistant the fuel is to detonation, which is very bad for an engine that is designed to run on gasoline and so must be avoided. To get 8.0:1 with the preceding rod, stroke, and cam intake closing event, you would need. Other factors also influence your car’s knocking characteristics: To help determine compression if you have forced induction (supercharger, turbocharger, or procharger) follow the chart below. Click ahead to discover what compression ratio is and how an engine can alert you to knocking and pinging.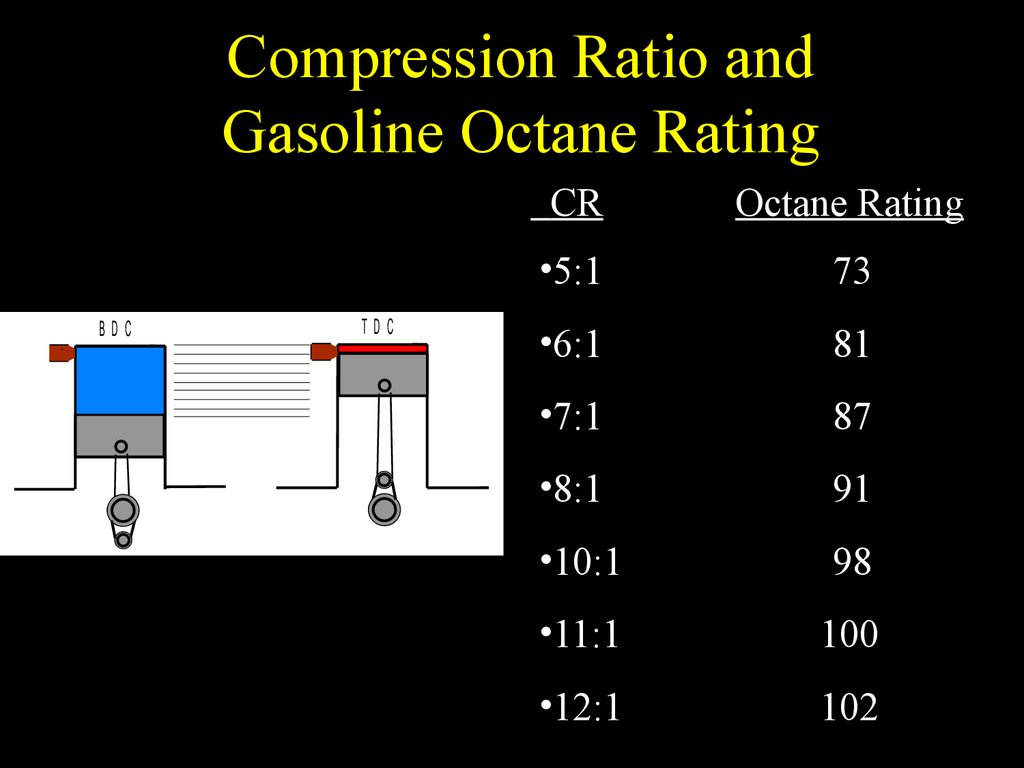
Engine Components and Operation презентация онлайн
Compression Ratio To Octane Chart

Compression Ratio VS Octane Requirement Chart

Mechanical Engineering Octane Number

Compression Ratio Fuel Octane Chart
Calculate Required Octane For Compression Ratio Maniac Mechanic
What octane gas do big bore high compression guys run?
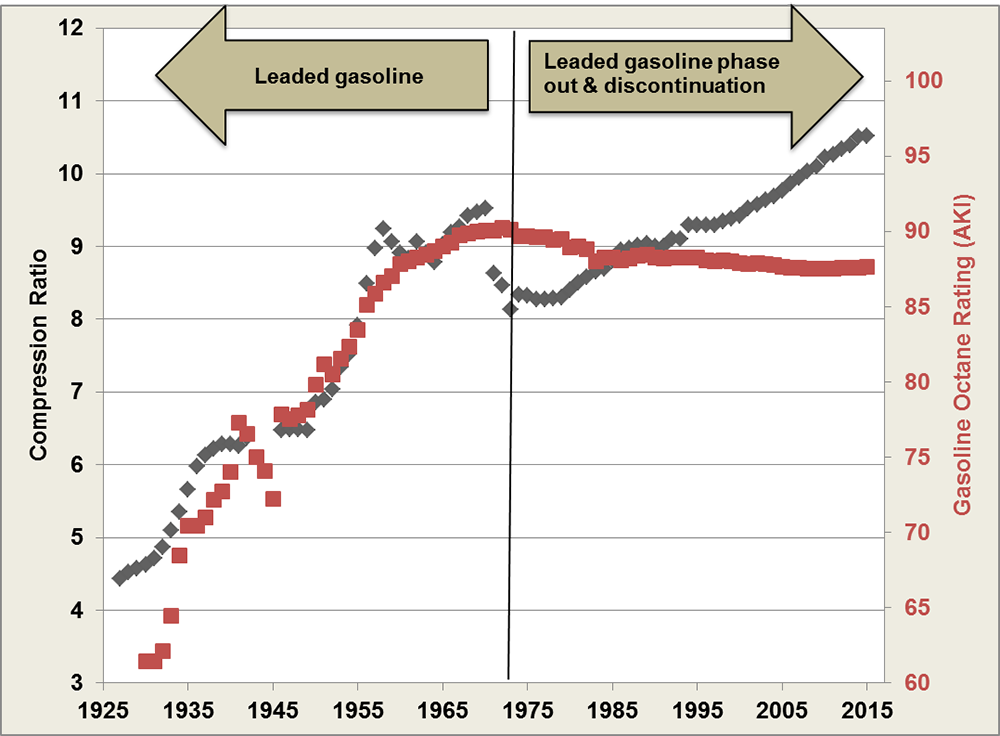
Fact 940 August 29, 2016 Diverging Trends of Engine Compression Ratio
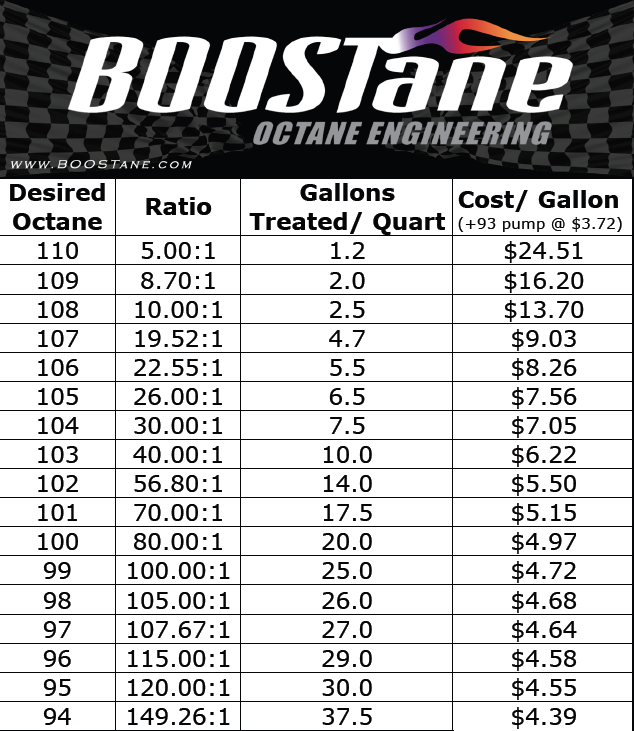
Compression Ratio Octane Chart

What octane? Polaris ATV Forum
A Higher Compression Ratio Requires High Octane Fuel To Prevent Knocking, While A Lower Compression Ratio Allows For The Use Of Lower Octane Fuel.
It's All The Volume Of A Cylinder Above The Compression Ring.
Modern Engines Can Handle Much Higher Compression At Lower Octanes.
Our Compression Ratio Calculator Is The.
Related Post: