Corneal Thickness Iop Chart
Corneal Thickness Iop Chart - Web central corneal thickness (microns) 445 465 475 485 495 505 515 525 535 545 555 565 575 585 595 605 615 625 635 645 adjustment in iop (mm hg) +7 +6 +6 +4 +4 +3 +2. Independently of this, corneal thickness has been found to be a risk factor for the development of glaucoma. Please note that using specific adjustment factors for iop readings based on corneal thickness. Normograms, based on varying cct, exist for adjusting gat. 1,2 a thicker cornea requires greater force to applanate and, conversely, a thinner cornea is more easily flattened. Web this adjustment factor is applied to the measured iop, in order to determine more closely the true iop for a given eye. Web this range takes the form of a conversion table of true iops for a patient's given central corneal thickness for a range of measured iops, from 5 mmhg to 40 mmhg. While it affects prognosis in ocular hypertension, its value in patients diagnosed. Thin corneas tend to result in tonometry readings that underestimate iop, while thick corneas tend to result in overestimations. Table 2 shows details of these adjustments made in three groups while figure 2 shows the distribution of the adjustment to be made to iop 465 475 485 495 505 515. This means their eye pressure is lower than thought, a lower iop means that risk for developing glaucoma is lowered. Web corneal thickness affects the measurement of intraocular pressure (iop), with thicker corneas producing falsely higher iop readings and thinner corneas producing falsely lower readings. Web central corneal thickness (cct) is known to affect. 465 475 485 495 505 515. However, it is still important to have regular eye exams to monitor eye pressure and stay aware of changes. Web those patients with thicker cct may show a higher reading of iop than actually exists. Web in the recent paper by feltgen and colleagues, 1 the intraocular pressure (iop) was measured by goldmann applanation. Web “showcasing inflammation and iop control with bausch + lomb” 6:30 p.m. Independently of this, corneal thickness has been found to be a risk factor for the development of glaucoma. Web corneal thickness is particularly important in relation to the measurement of intraocular pressure (iop); “when confronting the unusual cornea, you have to think about corneal biomechanics to accurately assess. Web gat, which is the gold standard of tonometry, assumes a central cornea thickness of approximately 520 μ. Web central corneal thickness (microns) 445 465 475 485 495 505 515 525 535 545 555 565 575 585 595 605 615 625 635 645 adjustment in iop (mm hg) +7 +6 +6 +4 +4 +3 +2. Then you’ll fix iop according. Web purpose this study aimed to investigate differences in microvasculature dropout (mvd) between the superior and inferior hemispheres in glaucoma patients. Web this range takes the form of a conversion table of true iops for a patient's given central corneal thickness for a range of measured iops, from 5 mmhg to 40 mmhg. Thus, the measurement took place omitting a. Normograms, based on varying cct, exist for adjusting gat. Thus, the measurement took place omitting a possible influence of the cornea on the result. He always considers the cornea’s thickness, as well as whether it is “particularly rigid” or “particularly floppy.” Corrected iop was calculated based on cct value (correction factor of 3.0mm hg for every 50µm of difference from. Web central corneal thickness (cct) is an important parameter in the assessment of any potential glaucoma patient. Web purpose this study aimed to investigate differences in microvasculature dropout (mvd) between the superior and inferior hemispheres in glaucoma patients. Independently of this, corneal thickness has been found to be a risk factor for the development of glaucoma. 465 475 485 495. Table 2 shows details of these adjustments made in three groups while figure 2 shows the distribution of the adjustment to be made to iop Accounting for age, the relationship between corneal densitometry and iop. Web this adjustment factor is applied to the measured iop, in order to determine more closely the true iop for a given eye. Web this. Web those patients with thicker cct may show a higher reading of iop than actually exists. Web purpose this study aimed to investigate differences in microvasculature dropout (mvd) between the superior and inferior hemispheres in glaucoma patients. ) nora lee cothran, od, faao, and walter whitley, od, faao, will discuss the benefits of using lotemax ® sm (loteprednol etabonate ophthalmic. One such table is reproduced below. Web in order to adjust the iop, just apply the correction factor on the right column to the intraocular pressure obtained by aplanation tonometry. Web this adjustment factor is applied to the measured iop, in order to determine more closely the true iop for a given eye. Web central corneal thickness was measured by. 465 475 485 495 505 515. Web central corneal thickness (microns) 445 465 475 485 495 505 515 525 535 545 555 565 575 585 595 605 615 625 635 645 adjustment in iop (mm hg) +7 +6 +6 +4 +4 +3 +2. Accounting for age, the relationship between corneal densitometry and iop. Web bausch + lomb corporation (nyse/tsx: Thus, the measurement took place omitting a possible influence of the cornea on the result. Web in order to adjust the iop, just apply the correction factor on the right column to the intraocular pressure obtained by aplanation tonometry. However, it is still important to have regular eye exams to monitor eye pressure and stay aware of changes. Fluorescein evaluations were subsequently employed to assess lens fitting, ensuring that the ok lens was centered on the cornea and exhibited. ) nora lee cothran, od, faao, and walter whitley, od, faao, will discuss the benefits of using lotemax ® sm (loteprednol etabonate ophthalmic gel), 0.38%, and vyzulta ® (latanoprostene bunod. Patwardhan, ashish a et al. Table 2 shows details of these adjustments made in three groups while figure 2 shows the distribution of the adjustment to be made to iop Independently of this, corneal thickness has been found to be a risk factor for the development of glaucoma. Thin corneas tend to result in tonometry readings that underestimate iop, while thick corneas tend to result in overestimations. Web corneal thickness affects the measurement of intraocular pressure (iop), with thicker corneas producing falsely higher iop readings and thinner corneas producing falsely lower readings. Then you’ll fix iop according to central corneal thickness. Web “showcasing inflammation and iop control with bausch + lomb” 6:30 p.m.
(PDF) Identifying the critical factors that influence intraocular

Pachymetry Iop Conversion Chart Printable Templates Free

Pachymetry Iop Conversion Chart
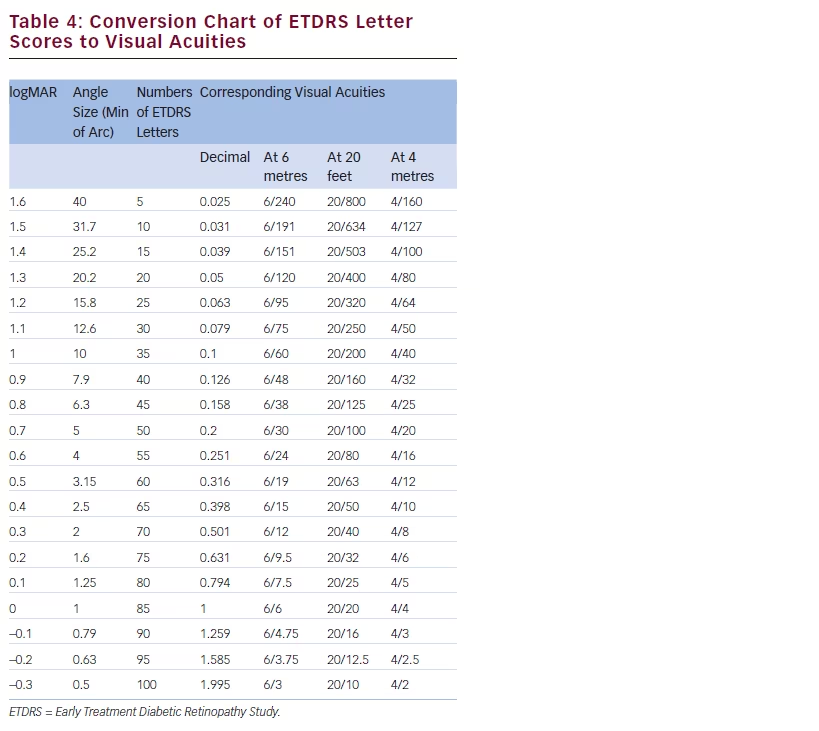
Corneal Thickness And Iop Conversion Chart A Visual Reference of
Corneal Thickness And Iop Conversion Chart

IOP measurement and central corneal thickness British Journal of
Corneal Thickness And Iop Conversion Chart

IOP measurement and central corneal thickness British Journal of

Corneal Thickness IOP Conversion Chart

Corneal Thickness And Iop Conversion Chart
Web Central Corneal Thickness (Cct) Is An Important Parameter In The Assessment Of Any Potential Glaucoma Patient.
“Multiple Studies Have Suggested That.
Web This Range Takes The Form Of A Conversion Table Of True Iops For A Patient's Given Central Corneal Thickness For A Range Of Measured Iops, From 5 Mmhg To 40 Mmhg.
Normograms, Based On Varying Cct, Exist For Adjusting Gat.
Related Post: