Cranial Drawer Sign
Cranial Drawer Sign - Web on an orthopedic examination, muscle mass asymmetry, joint effusion, tissue warmth, painful flexion and extension of the stifle joint and decreased joint range of motion point towards knee involvement can be observed. The patient should be supine with the hips flexed to 45 degrees, the knees flexed to. Palpation of the joint compartment may show increased joint fluid or joint capsular thickening. The other thumb is placed on the head of the fibula with the index finger on the tibial crest. Web positive for cranial drawer sign (may not appreciate if a partial tear present or if animal is fighting palpation) positive tibial thrust. Pain upon forced full extension of the stifle is a simple test that is suggestive of early crcld. Web however, if a partial tear is present, the cranial drawer sign may reveal only 2 mm to 3 mm of instability when the test is done with the stifle flexed and no instability with the stifle in extension [ 13 ]. This procedure is not painful; Web it is important to note that, after tplo or tta procedures, dogs continue to exhibit a positive cranial drawer sign but should not have a positive tibial compression (tibial thrust) test. The examiner stands behind the dog and places a thumb on the caudal aspect of the femoral condylar region with the index finger on the patella. The patient should be supine with the hips flexed to 45 degrees, the knees flexed to. The ability to move the tibia forward (cranially) with respect to a fixed femur is a. Web in obvious cases, the keys to diagnosing cranial cruciate rupture are a positive cranial drawer sign and tibial thrust. Web is a reliable clinical sign of cruciate. The drawer test can be best performed with the stifle in a 135 degree angle which also is the regular standing angle. The ability to move the tibia forward (cranially) with respect to a fixed femur is a. Comparing the affected stifle with the normal stifle provides a ready frame of reference. Web this article describes characteristics of normal and. Web an audible “clicking” may be heard when the patient walks or the stifle is palpated through range of motion, indicating possible medial meniscus tear. Web a positive cranial drawer sign can be elicited, and radiographs show joint effusion and cranial dislocation of the tibia (fig. Web it is important to note that, after tplo or tta procedures, dogs continue. The other thumb is placed on the head of the fibula with the index finger on the tibial crest. Web the key to diagnosis of a ruptured ccl is the demonstration of an abnormal knee motion called the 'cranial drawer sign'. Pain upon forced full extension of the stifle is a simple test that is suggestive of early crcld. But. This procedure is not painful; Web the clinical diagnosis is based on a positive drawer test in which the tibial plateau is manually displaced cranially with a fixed distal femur. A small bony fragment may be seen at the tibial insertion site of the cranial cruciate ligament in cases of ligament avulsion (22). Provides ample indication for surgical joint exploration. Drawer test and cranial tibial thrust test on a 85 lb dog with a torn acl. The cranial drawer test and tibial compression tests are. Web the cranial drawer sign is definitive for diagnosing ccl rupture. This procedure is not painful; A small bony fragment may be seen at the tibial insertion site of the cranial cruciate ligament in cases. The drawer test can be best performed with the stifle in a 135 degree angle which also is the regular standing angle. In order to feel this, you dog will be placed on his/ her side, and the veterinarian will feel the knee for cranial drawer motion. This procedure is not painful; Veterinary surgery & radiology education. A positive tibial. Web this article describes characteristics of normal and pathologic cranial cruciate ligaments and details clinical techniques to help you diagnose cranial cruciate ligament pathology earlier. This procedure is not painful; The cranial drawer sign or cranial tibial thrust may be positive. Web an audible “clicking” may be heard when the patient walks or the stifle is palpated through range of. In some cases, however, a crisp endpoint to the cranial drawer motion. Occurs rapidly after ligament rupture in most dogs. The drawer test can be best performed with the stifle in a 135 degree angle which also is the regular standing angle. The other thumb is placed on the head of the fibula with the index finger on the tibial. Web it is important to note that, after tplo or tta procedures, dogs continue to exhibit a positive cranial drawer sign but should not have a positive tibial compression (tibial thrust) test. A positive tibial compression test and cranial drawer test confirm cclr. Web this article describes characteristics of normal and pathologic cranial cruciate ligaments and details clinical techniques to. Occurs rapidly after ligament rupture in most dogs. Web the cranial drawer sign is definitive for diagnosing ccl rupture. This procedure is not painful; 161k views 11 years ago. Orthopedic examination reveals various degrees of stifle pain with flexion and extension, variable crepitus, and possibly clicking associated with a meniscal tear. Pain upon forced full extension of the stifle is a simple test that is suggestive of early crcld. The drawer test can be best performed with the stifle in a 135 degree angle which also is the regular standing angle. Provides ample indication for surgical joint exploration even in the absence of a. The patient should be supine with the hips flexed to 45 degrees, the knees flexed to. The examiner stands behind the dog and places a thumb on the caudal aspect of the femoral condylar region with the index finger on the patella. Web is a reliable clinical sign of cruciate rupturepalpation of a medial buttress over the proximal tibia of the affected leg: Web positive for cranial drawer sign (may not appreciate if a partial tear present or if animal is fighting palpation) positive tibial thrust. A positive tibial compression test and cranial drawer test confirm cclr. A small bony fragment may be seen at the tibial insertion site of the cranial cruciate ligament in cases of ligament avulsion (22). But what about less obvious cases? Drawer test and cranial tibial thrust test on a 85 lb dog with a torn acl.
Cruciate Disease The Cranial Drawer Test YouTube
+drawer+test.jpg)
Anterior Drawer Sign Positive Drawer Gallery
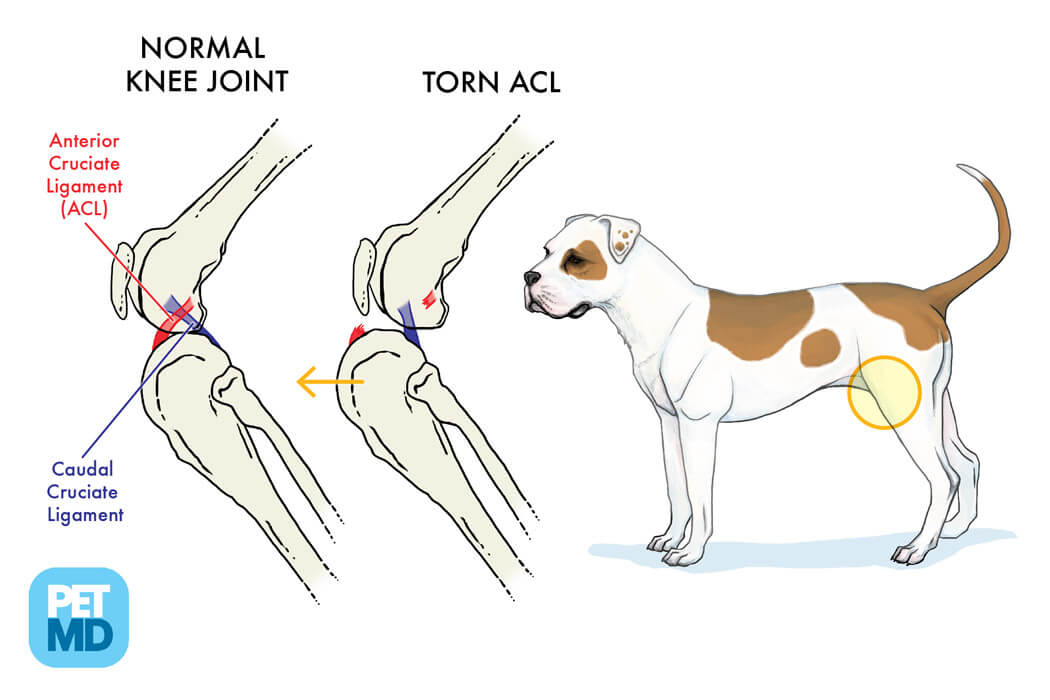
ACL and CCL diagram provided by PetMD

Medicine Notes, Emergency Medicine, Physical Therapy Education, Nurse

Cranial Or Anterior Drawer Sign Drawer Gallery

Cranial Or Anterior Drawer Sign Drawer Gallery

Positive cranial drawer sign in a dog with a cranial (anterior
Ortolani Test OrthoFixar 2023
Drawer Test Bruin Blog

Pathology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Goals of Cranial Cruciate Ligament
This Is An Accumulation Of Fibrous Scar Tissue That The Body Deposits In An Effort To Stabilize The Knee.
Web This Article Describes Characteristics Of Normal And Pathologic Cranial Cruciate Ligaments And Details Clinical Techniques To Help You Diagnose Cranial Cruciate Ligament Pathology Earlier.
Veterinary Surgery & Radiology Education.
Web In Obvious Cases, The Keys To Diagnosing Cranial Cruciate Rupture Are A Positive Cranial Drawer Sign And Tibial Thrust.
Related Post: