Cranial Drawer Test Dog
Cranial Drawer Test Dog - The examiner stands behind the dog and places a thumb on the caudal aspect of the femoral. Web cranial cruciate ligament disease is considered to be the most common cause of pelvic limb lameness in the canine, affecting approximately 2.55% of the population [ 3, 4 ]. In a mature dog, a healthy, intact cranial cruciate ligament will not permit cranial tibial translation with the stifle held in extension or in flexion.3 in an immature dog, puppy laxity may permit a few millimeters of cranial and caudal tibial translation, but. Web the diagnosis of cclr is typically based on the presence of the “cranial drawer sign”. Web dog acl tear (cranial cruciate… what is it? Web definitive diagnosis of rupture of the ccl demands an assessment of stifle joint stability by means of the cranial “drawer” test, the tibial compression test, or both tests. The cranial drawer test and tibial compression tests are important for assessing palpable instability. Web if it is suspected that your dog has a cranial cruciate ligament tear or rupture, your veterinarian will perform a physical exam to determine whether or not this type of injury can be ruled out. Web specific palpation techniques that veterinarians use to assess the crcl include the ‘cranial drawer test’ and the ‘tibial compression test.’ these tests can confirm abnormal motion within the knee consistent with rupture of the crcl. What is the prognosis for my dog? Web however, a dog presented with an intermittent hindlimb lameness with normal or minimal cranial drawer, having a positive sit test, knee pain on hyperextension and mild joint effusion and minimal cranial tibial translation on radiographic exam is. What is the prognosis for my dog? In general, radiographic images are used to visualize the instability of the stifle joint by. One of the difficult orthopedic test to learn when you are just starting out as a rehabilitation practitioner or veterinarian is the cranial drawer test.in t. Normal joint laxity in the young dog may be confused with a pathologically unstable joint. If you suspect your dog has a torn cruciate ligament or your veterinarian has diagnosed it, you’re not alone.. Drawer test and cranial tibial thrust test on a 85 lb dog with a torn acl. This stifle is normal, and thus the tests are negative. Web if it is suspected that your dog has a cranial cruciate ligament tear or rupture, your veterinarian will perform a physical exam to determine whether or not this type of injury can be. Web ccl injury is diagnosed through a physical exam and a cranial drawer test, which functions to elicit instability of the joint. The cranial drawer assessment is best done on the laterally recumbent animal. This stifle is normal, and thus the tests are negative. 161k views 11 years ago. The cranial drawer test and tibial compression tests are important for. This test involves manual manipulation of the knee joint and is referred to as the drawer test. (see figure 1 & cranial drawer & cranial tibial thrust tests.) Web high desert veterinary. Extension & range of motion. This is due to the fact that a high percentage of hindlimb lameness in dogs is caused by crclr, especially in patients with. Web ccl injury is diagnosed through a physical exam and a cranial drawer test, which functions to elicit instability of the joint. Web © 2024 google llc. Web dog acl tear (cranial cruciate… what is it? If you suspect your dog has a torn cruciate ligament or your veterinarian has diagnosed it, you’re not alone. In a mature dog, a. Web the cranial drawer test should be done with the leg in flexion and extension, to test both parts of the crcl. One of the difficult orthopedic test to learn when you are just starting out as a rehabilitation practitioner or veterinarian is the cranial drawer test.in t. Web © 2024 google llc. Osteoarthritis (oa) of the joint occurs secondary. Osteoarthritis (oa) of the joint occurs secondary to ligament rupture and advances rapidly if. Drawer test and cranial tibial thrust test on a 85 lb dog with a torn acl. Web dog acl tear (cranial cruciate… what is it? What is the prognosis for my dog? Web to test for cranial tibial translation, perform the cranial drawer test (figure 6). Web during the lameness examination, your veterinarian will try to demonstrate a particular movement, called a cranial or anterior drawer sign. Web specific palpation techniques that veterinarians use to assess the crcl include the ‘cranial drawer test’ and the ‘tibial compression test.’ these tests can confirm abnormal motion within the knee consistent with rupture of the crcl. Web definition cranial. Web pain upon forced full extension of the stifle is a simple test that is suggestive of early crcld. Web cranial cruciate ligament disease is considered to be the most common cause of pelvic limb lameness in the canine, affecting approximately 2.55% of the population [ 3, 4 ]. Web a diagnosis of crclr should be considered in any dog. Osteoarthritis (oa) of the joint occurs secondary to ligament rupture and advances rapidly if. Web dog acl tear (cranial cruciate… what is it? Web during the lameness examination, your veterinarian will try to demonstrate a particular movement, called a cranial or anterior drawer sign. This stifle is normal, and thus the tests are negative. The cranial drawer test and tibial compression tests are important for assessing palpable instability. This procedure is not painful; Web if it is suspected that your dog has a cranial cruciate ligament tear or rupture, your veterinarian will perform a physical exam to determine whether or not this type of injury can be ruled out. Web specific palpation techniques that veterinarians use to confirm a problem with the ccl are the “cranial drawer test” and the “tibial thrust test.” these tests confirm abnormal motion in the knee and hence a rupture of the ccl. Web diagnosis of cranial cruciate ligament rupture is usually made by a positive cranial drawer sign. Web the cranial drawer test should be done with the leg in flexion and extension, to test both parts of the crcl. In this test, the dog’s knee is slightly bent and anterior pressure is applied to the distal femur while posterior pressure is applied to the proximal tibia. Web this video demonstrates how to perform the cranial drawer and tibial compression (tibial thrust) tests. Drawer test and cranial tibial thrust test on a 85 lb dog with a torn acl. Cranial cruciate ligament insufficiency stifle: This test involves manual manipulation of the knee joint and is referred to as the drawer test. Web the diagnosis of cclr is typically based on the presence of the “cranial drawer sign”.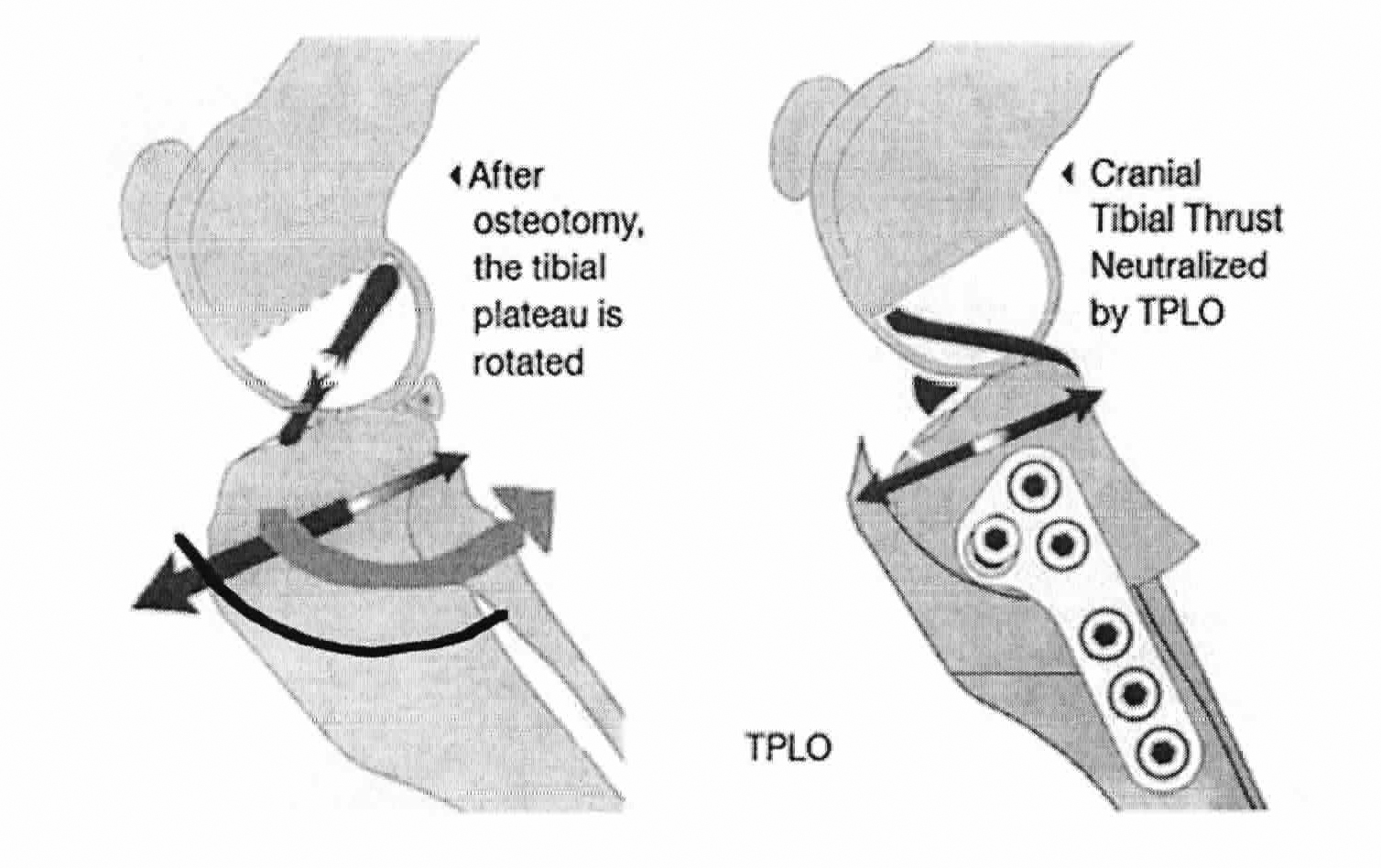
Tibial Plateau Leveling Osteotomy
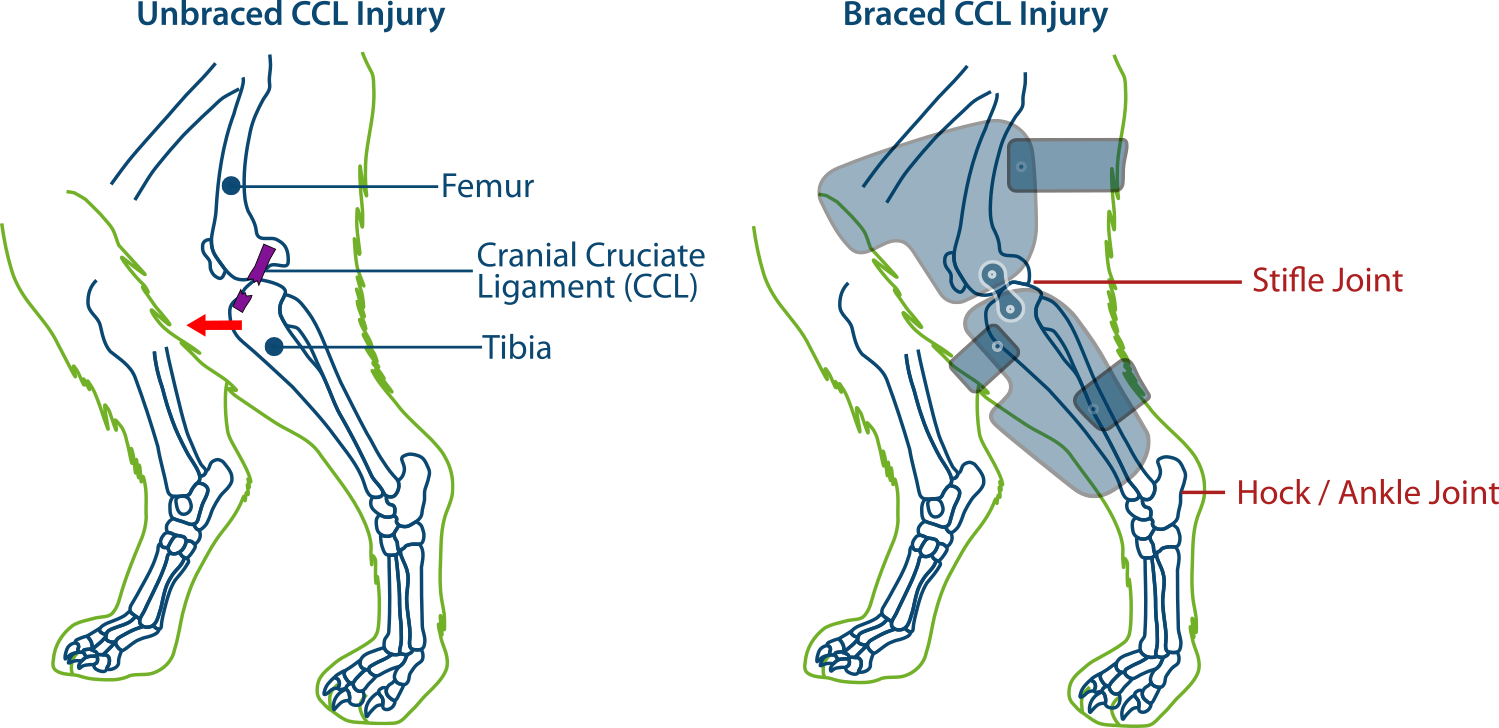
Dog Stifle CCL/ACL Injury Support Brace — PawOpedic

4 Tips To The Perfect Dog Brace Cast Hero Blog
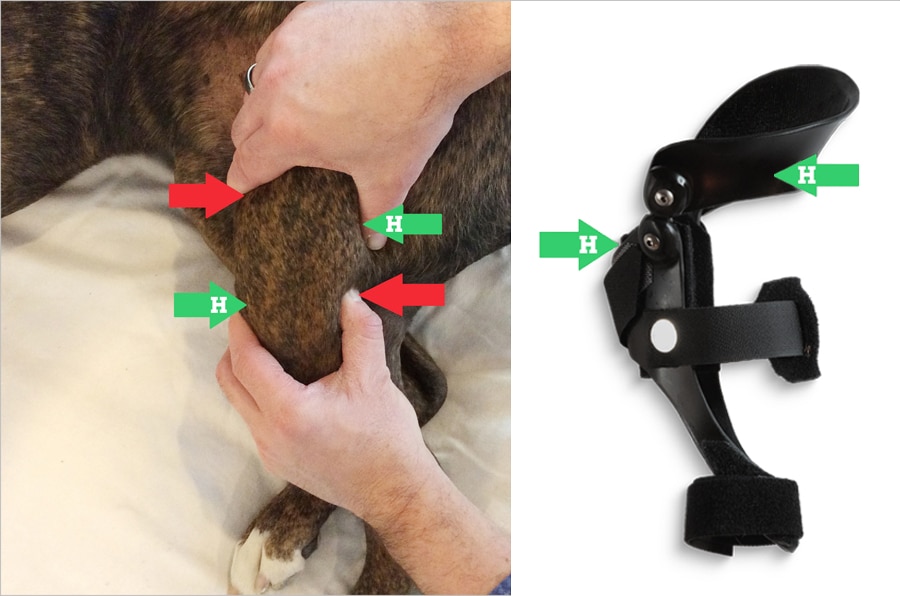
Surgery NOT An Option? Torn ACL Dog Knee Braces

Pathology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Goals of Cranial Cruciate Ligament
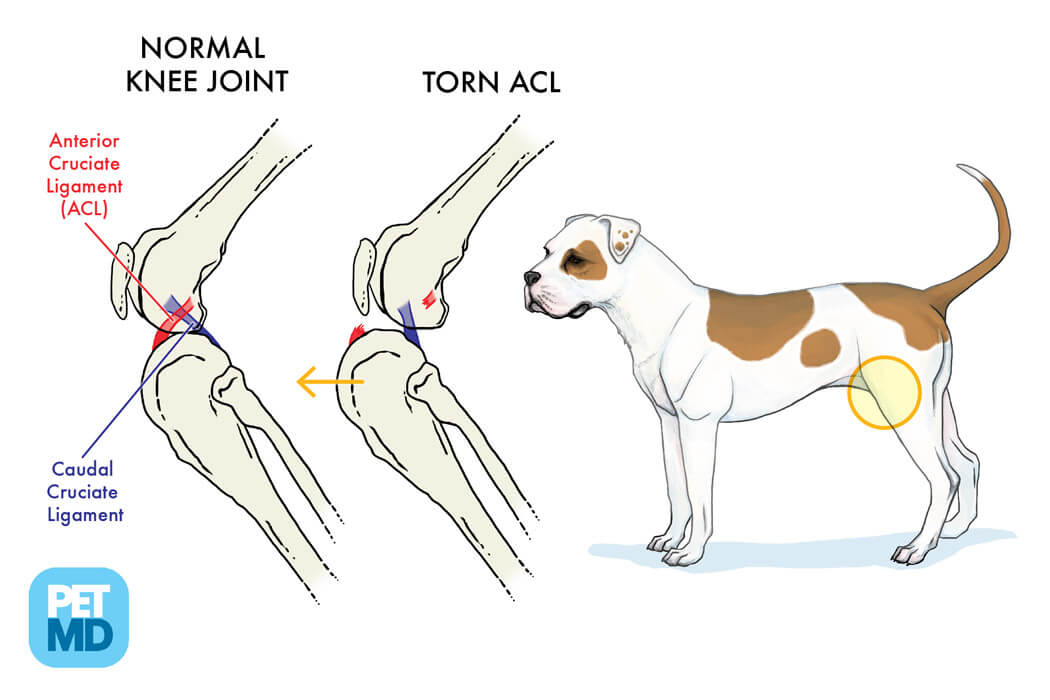
ACL and CCL diagram provided by PetMD

Positive cranial drawer sign in a dog with a cranial (anterior

Cruciate Disease The Cranial Drawer Test YouTube

Cranial Nerve Assessment Cranial nerves, Pharmacology nursing, Vet school

Pathology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Goals of Cranial Cruciate Ligament
To Assess Stifle Joint Instability By Attempting To Subluxate The Tibia Cranially With Respect To The Femur.
In A Mature Dog, A Healthy, Intact Cranial Cruciate Ligament Will Not Permit Cranial Tibial Translation With The Stifle Held In Extension Or In Flexion.3 In An Immature Dog, Puppy Laxity May Permit A Few Millimeters Of Cranial And Caudal Tibial Translation, But.
This Abnormal Forward Movement Of The Lower Leg Bone (Tibia) In Front Of The Thigh Bone (Femur) Indicates Laxity Or Instability In.
Web To Test For Cranial Tibial Translation, Perform The Cranial Drawer Test (Figure 6).
Related Post: