Cytoskeleton Drawing
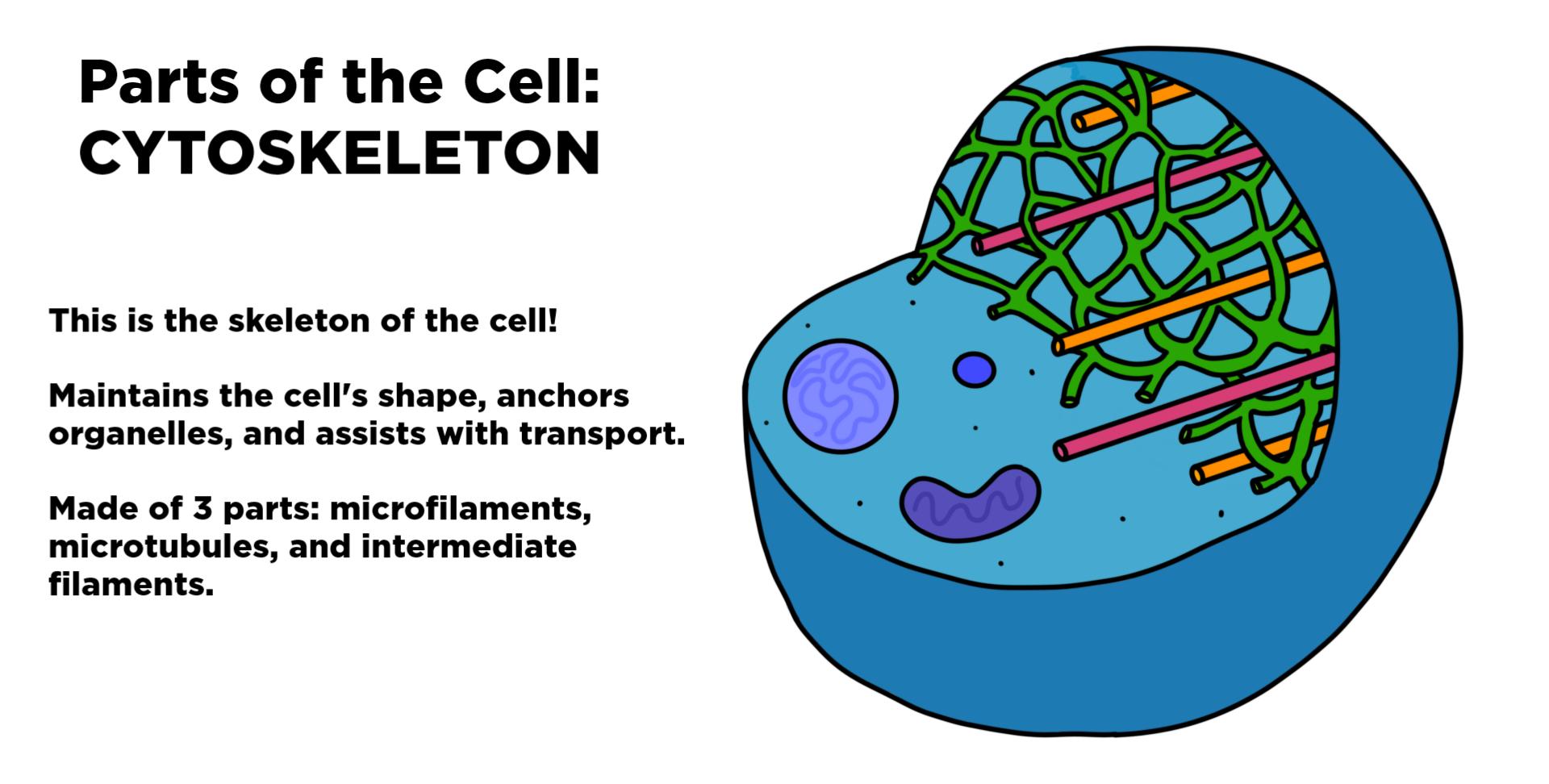
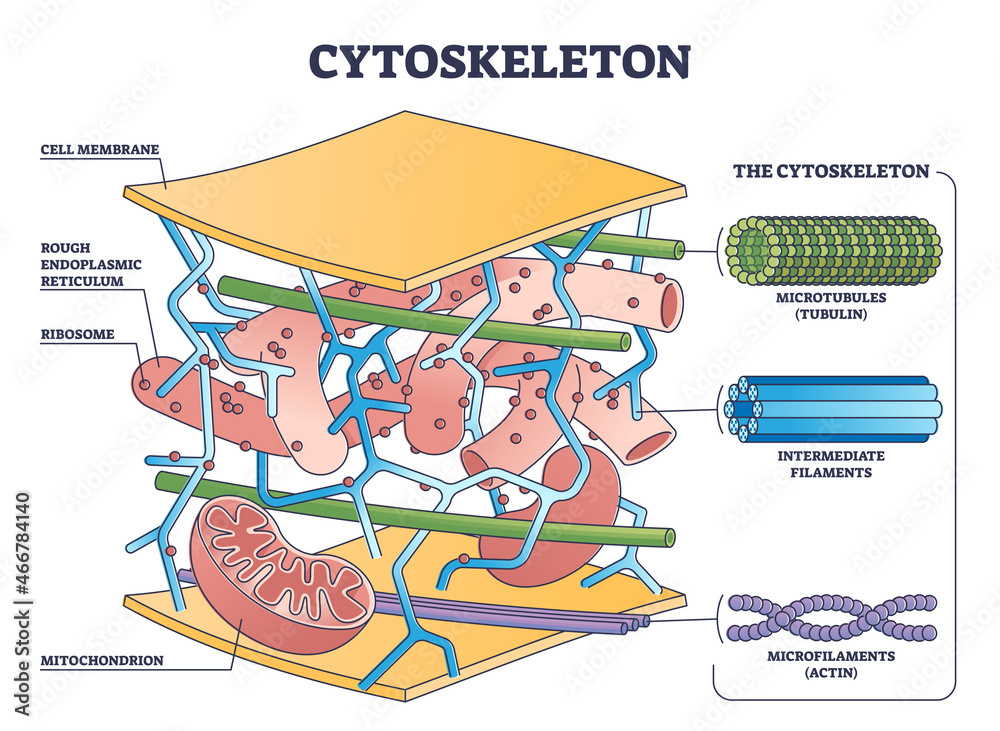
Cytoskeleton Drawing - Typically, they are utilised to draw organelles towards the cell membrane. 321 introduction to the cytoskeleton. [1] the cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. Explore the intricacies of the cytoskeleton, the cellular framework composed of microtubules, intermediate filaments, and microfilaments. It helps the cell maintain its shape and also helps to hold cell structures such as organelles in. The cytoskeleton influences the shape of the cell and aids in the relay of signals from one part of the cell to another. The cytoskeleton helps cells grow, move, retract, and even die. The cytoskeleton is a network of filaments and tubules that extends throughout a cell, through the cytoplasm, which is all of the material within a cell except for the nucleus. The cytoskeleton also helps the cell move its components around and organize cell contents. Web the view that the cytoskeleton was a feature unique to eukaryotes was dramatically overturned about 20 years ago by the discovery that bacteria possess homologues of both tubulin (de boer et al., 1992; 321 introduction to the cytoskeleton. These were suspected to be actin microfilaments. The main three components of the cytoskeleton are (in order of. It enables movement of cytoplasm and vesicles within the cell; Web about the author. It also has a variety of purposes beyond. These were suspected to be actin microfilaments. These structures give the cell its shape and help organize the cell's parts. The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers forming the infrastructure of eukaryotic cells, prokaryotic cells, and archaeans. The thickest are the microtubules (20 nm in diameter) which consist primarily of the tubulin. Web the cytoskeleton is a network of different protein fibers that provides many functions: [1] the cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. Web cytoskeleton, a system of filaments or fibres that is present in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells (cells containing a nucleus. Typically, they are utilised to draw organelles towards the cell membrane. The cytoskeleton is the cell's structural framework. Web cytoskeleton, a system of filaments or fibres that is present in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells (cells containing a nucleus ). Cells that travel use the cytoskeleton to do so. The three major components of the cytoskeleton are microtubules, microfilaments, and. These were suspected to be actin microfilaments. As the name implies, the cytoskeleton acts much like our own skeletons in supporting the general shape of a cell. Web the cytoskeleton is a collective term that refers to an extensive network of filamentous or tubular intracellular proteins of varying morphology and composition scattered within the cytoplasm of a cell.it consists of. It helps the cell maintain its shape and also helps to hold cell structures such as organelles in. The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers forming the infrastructure of eukaryotic cells, prokaryotic cells, and archaeans. Web cytoskeleton, a system of filaments or fibres that is present in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells (cells containing a nucleus ). Web the view. The main three components of the cytoskeleton are (in order of. For this reason, microfilaments are also known as actin filaments. The cytoskeleton is a network of filaments and tubules that extends throughout a cell, through the cytoplasm, which is all of the material within a cell except for the nucleus. How to draw structure of cytoskeleton in easy way. Cytoskeletal element distribution in a prototypical eukaryotic cell. As its name suggests, the cytoskeleton is like a cellular “skeleton.”. The purple ball is the nucleus. (~10 nm) filaments permeated the cytoskeleton of eukaryotic cells. Explore the intricacies of the cytoskeleton, the cellular framework composed of microtubules, intermediate filaments, and microfilaments. In this video, we will. Unlike our skeletons though, the cytoskeleton is highly dynamic and internally motile, shifting and rearranging in response to the needs of the cell. It also has a variety of purposes beyond. It enables movement of cytoplasm and vesicles within the cell; For this reason, microfilaments are also known as actin filaments. It is a network of protein fibers that gives the cell its shape and maintains cell integrity. Web the cytoskeletal “highways” help provide structure and connection within the cell and between cells. As its name suggests, the cytoskeleton is like a cellular “skeleton.”. It maintains or changes the shape of the cell; The cytoskeleton helps cells grow, move, retract, and. Web about the author. As the name implies, the cytoskeleton acts much like our own skeletons in supporting the general shape of a cell. Cells that travel use the cytoskeleton to do so. Explore the intricacies of the cytoskeleton, the cellular framework composed of microtubules, intermediate filaments, and microfilaments. The cytoskeleton supports the cell, gives it shape. Web cytoskeleton, a system of filaments or fibres that is present in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells (cells containing a nucleus ). It helps the cell maintain its shape and also helps to hold cell structures such as organelles in. Web the cytoskeleton of a biological cell is the framework of tiny tubes and filaments that forms the internal structure of the cell, helping to maintain the shape of the cell and hold the contents i.e. It secures some organelles in specific positions; The purple ball is the nucleus. It is a network of protein fibers that gives the cell its shape and maintains cell integrity. Web the cytoskeleton is a collective term that refers to an extensive network of filamentous or tubular intracellular proteins of varying morphology and composition scattered within the cytoplasm of a cell.it consists of three structurally and functionally distinct components: It maintains or changes the shape of the cell; Web the cytoplasm includes the fluid between those membranes (cytosol) as well as all structures (like the cytoskeleton) and organelles. And it enables the cell to move in response to stimuli. Web the cytoskeleton is a network of different protein fibers that provides many functions: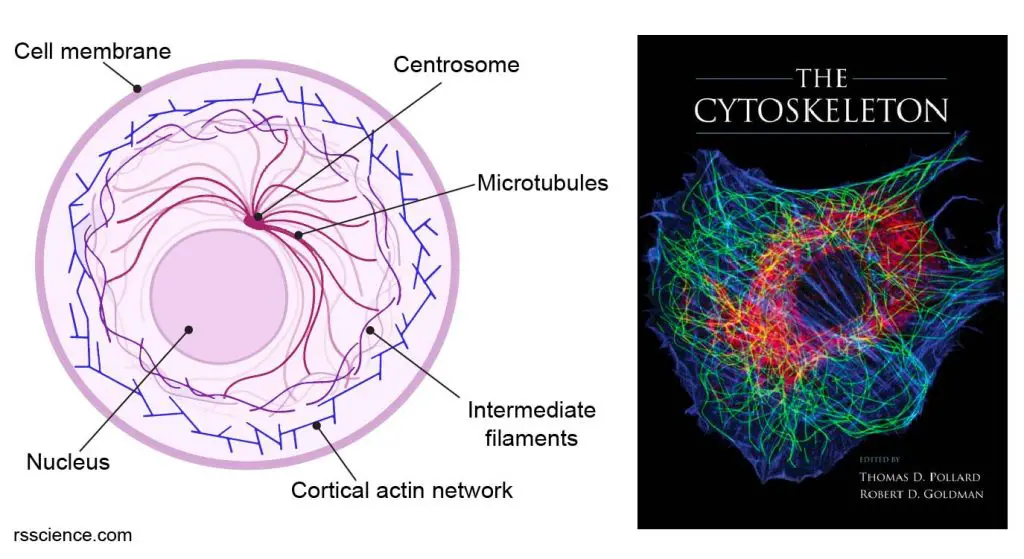
Cytoskeleton the muscle and the bone of a cell definition

Cytoskeleton Drawing

Cytoskeleton, illustration Stock Image C023/8760 Science Photo

Cytoskeleton Structure & Function, Cells, Body With Explanation

Cytoskeleton Definition, Structure & Function (with Diagram) Sciencing
Cytoskeleton Expii
cytoskeleton structure as complex dynamic network of interlinking
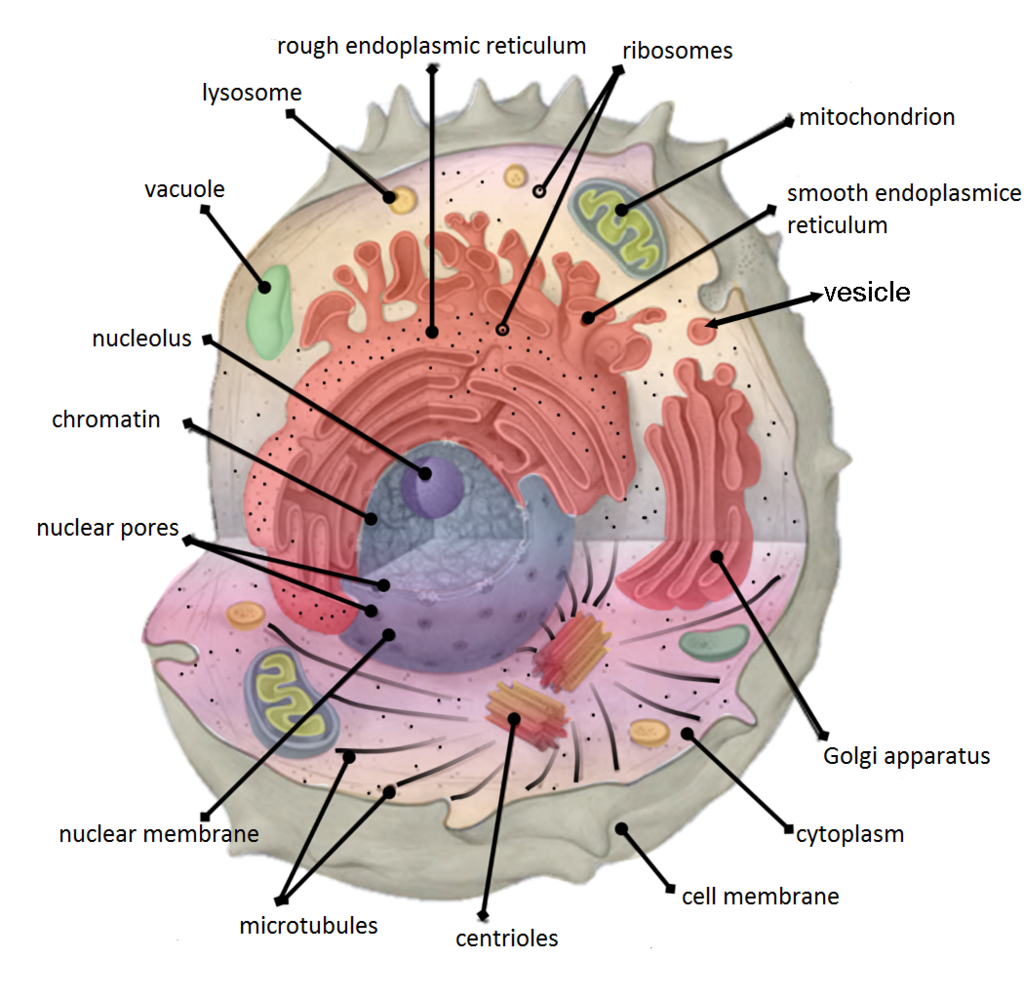
4.5 Cytoplasm and Cytoskeleton Human Biology

how to draw structure of cytoskeleton step by step in easy way

Cytoskeleton Drawing
The Cytoskeleton Is The Cell's Structural Framework.
The Cytoskeleton Also Helps The Cell Move Its Components Around And Organize Cell Contents.
It Is Found In All Cells, Though The Proteins That It Is Made Of Vary Between Organisms.
Web The Cytoskeleton Of A Cell Is Made Up Of Microtubules, Actin Filaments, And Intermediate Filaments.
Related Post: