Dielectric Corrosion Chart
Dielectric Corrosion Chart - The table, however, must be interpreted not only First there must be two electrochemically dissimilar metals present. The galvanic series indicates which dissimilar metal will tend to corrode (anode) and which dissimilar metal will tend to support the reduction reaction (cathode), when the requirements for galvanic corrosion are met. Web what is the galvanic series? Passive) under conditions which provide sufficient oxygen to the surface. Below, we have provided a galvanic series corrosion chart showcasing the metal combinations that carry the highest risk. To mitigate the risk of galvanic corrosion, there are certain metals that should not be used in conjunction. Such tables are of significant value in drawing the attention of designers to the dangers of unintended galvanic corrosion. Web the galvanic series chart below shows metals and their electrochemical voltage range (relative activity in flowing sea water). In a structure, this corrosion galvanic corrosion when different metals come into contact with each other, one is likely to corrode faster if they get wet, but there are ways to minimise or even prevent corrosion. The below galvanic corrion chart or anodic index table shows anodic index for different materials. When dissimilar metals are used together in the presence of an electrolyte, separate them with a dielectric material such as insulation, paint or similar surface coating. Such tables are of significant value in drawing the attention of designers to the dangers of unintended galvanic corrosion.. Web corrosion will cause a failure, nor does it mean that dielectric fittings must be used at transitions between materials. Tabular representation of the galvanic series. Types of galvanic corrosion in different metals and their alloys. A typical rule of thumb is that voltage differences of 0.2 volts or more suggest a galvanic corrosion risk. Web corrosion, with the use. What are the causes of galvanic corrosion? As a rule of thumb, if the wetted area of the corroding metal is 10 times the wetted area of the noble metal, then galvanic Basics of aqueous corrosion four conditions must be present for corrosion to occur in aqueous solutions: Web galvanic corrosion (some times called dissimilar metal corrosion) is the process. In a structure, this corrosion galvanic corrosion when different metals come into contact with each other, one is likely to corrode faster if they get wet, but there are ways to minimise or even prevent corrosion. Web this slide includes a chart of galvanic corrosion potential between common construction metals. Passive) under conditions which provide sufficient oxygen to the surface.. Web this slide includes a chart of galvanic corrosion potential between common construction metals. Types of galvanic corrosion in different metals and their alloys. This chart is designed to assist in broadly assessing the risk of galvanic corrosion associated with a given metal coming into contact with another metal. Web dielectric unions are designed to prevent galvanic corrosion, which can. See the chart with anodic, cathodic, and neutral metals, and learn more about the factors affecting galvanic corrosion. Such tables are of significant value in drawing the attention of designers to the dangers of unintended galvanic corrosion. Web nec sections 342.10 for intermediate metal conduit (imc), 344.10 for rigid metal conduit (rmc), and 358.10 for electrical metallic tubing (emt) allow. To mitigate the risk of galvanic corrosion, there are certain metals that should not be used in conjunction. When dissimilar metals are used together in the presence of an electrolyte, separate them with a dielectric material such as insulation, paint or similar surface coating. First there must be two electrochemically dissimilar metals present. The table, however, must be interpreted not. First there must be two electrochemically dissimilar metals present. Web galvanic corrosion (also called bimetallic corrosion or dissimilar metal corrosion) is an electrochemical process in which one metal corrodes preferentially when it is in electrical contact with another, in the presence of an electrolyte. Web corrosion will cause a failure, nor does it mean that dielectric fittings must be used. Types of galvanic corrosion in different metals and their alloys. Web nec sections 342.10 for intermediate metal conduit (imc), 344.10 for rigid metal conduit (rmc), and 358.10 for electrical metallic tubing (emt) allow galvanized steel in concrete, in direct contact with the earth and severely corrosive environments. Below is a galvanic reaction chart for dissimilar metals. What are the causes. Web nec sections 342.10 for intermediate metal conduit (imc), 344.10 for rigid metal conduit (rmc), and 358.10 for electrical metallic tubing (emt) allow galvanized steel in concrete, in direct contact with the earth and severely corrosive environments. This chart is designed to assist in broadly assessing the risk of galvanic corrosion associated with a given metal coming into contact with. In a structure, this corrosion galvanic corrosion when different metals come into contact with each other, one is likely to corrode faster if they get wet, but there are ways to minimise or even prevent corrosion. First there must be two electrochemically dissimilar metals present. Web galvanic corrosion (some times called dissimilar metal corrosion) is the process by which the materials in contact with each other oxidizes or corrodes. This can help you in the selection of the best materials for your application where galvanic corrosion is a concern. Web corrosion, with the use of charts depicting the galvanic (or electromotive force) series in different environments. As a rule of thumb, if the wetted area of the corroding metal is 10 times the wetted area of the noble metal, then galvanic When dissimilar metals are used together in the presence of an electrolyte, separate them with a dielectric material such as insulation, paint or similar surface coating. The table, however, must be interpreted not only Such tables are of significant value in drawing the attention of designers to the dangers of unintended galvanic corrosion. Below, we have provided a galvanic series corrosion chart showcasing the metal combinations that carry the highest risk. The chart below shows how different plating materials react to one another with regard to their galvanic potential. Web the galvanic series chart below shows metals and their electrochemical voltage range (relative activity in flowing sea water). Web galvanic corrosion (also called bimetallic corrosion or dissimilar metal corrosion) is an electrochemical process in which one metal corrodes preferentially when it is in electrical contact with another, in the presence of an electrolyte. This chart is designed to assist in broadly assessing the risk of galvanic corrosion associated with a given metal coming into contact with another metal. Learn how to identify, avoid, and prevent galvanic corrosion with a chart of metal reactivity and examples of common scenarios. What are the causes of galvanic corrosion?
Dielectric Chart
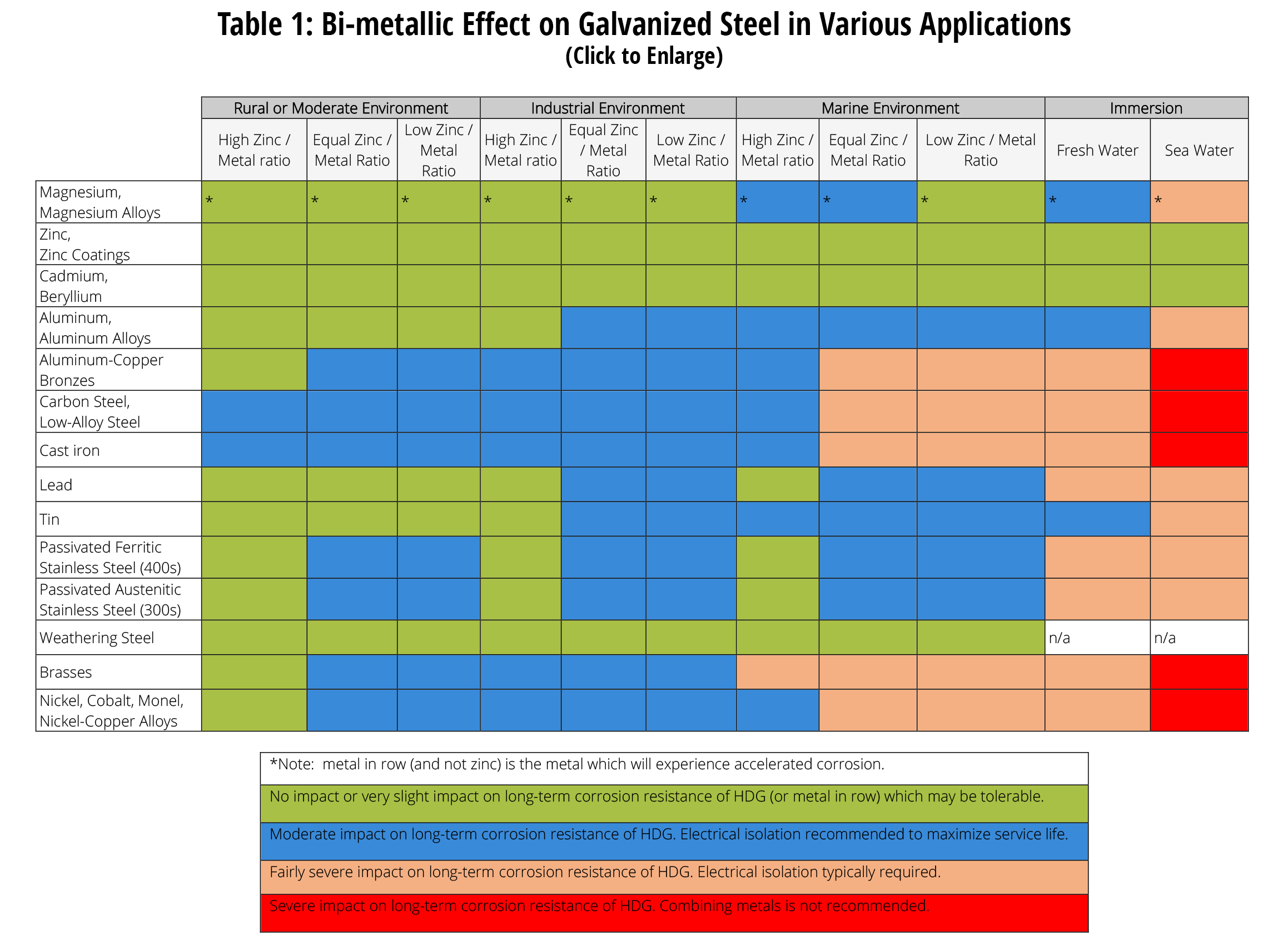
Dissimilar Metal Corrosion with… American Galvanizers Association

The 5 W’s of Isolation Gaskets Triangle Fluid Controls Ltd.
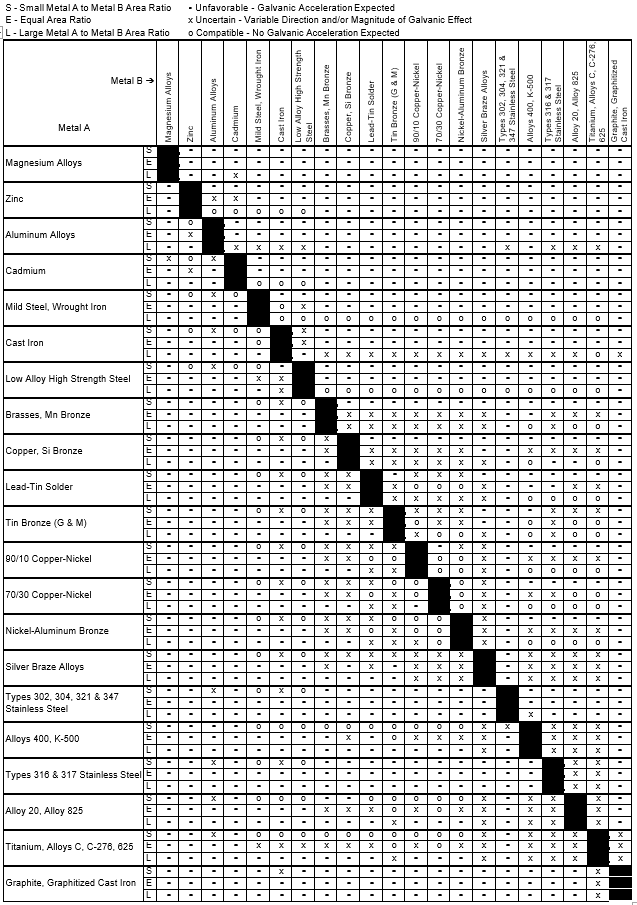
Dielectric Corrosion Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master

Stainless Steel Galvanic Corrosion Chart

Corrosion charts Graphite Technology
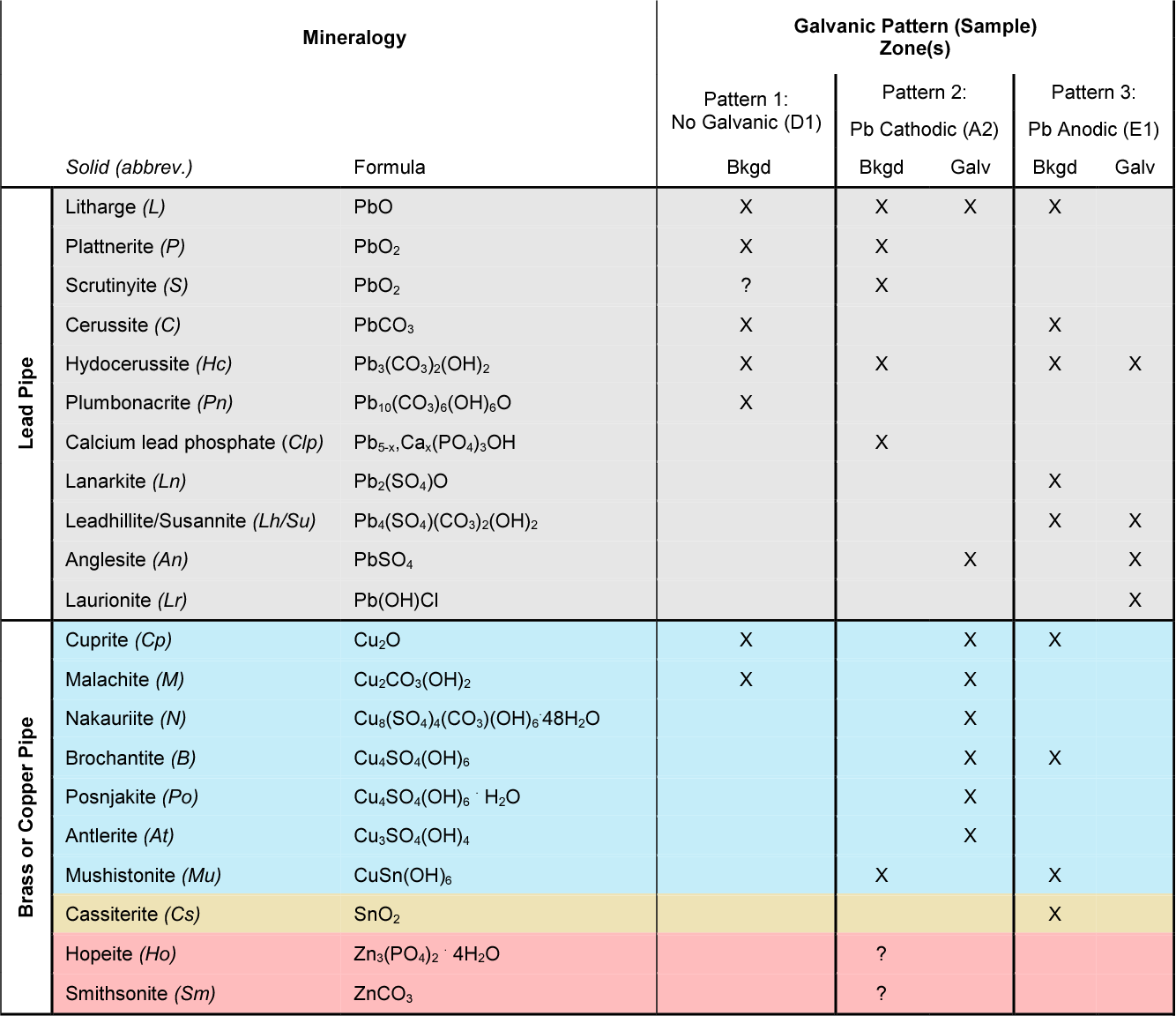
Dielectric Corrosion Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master
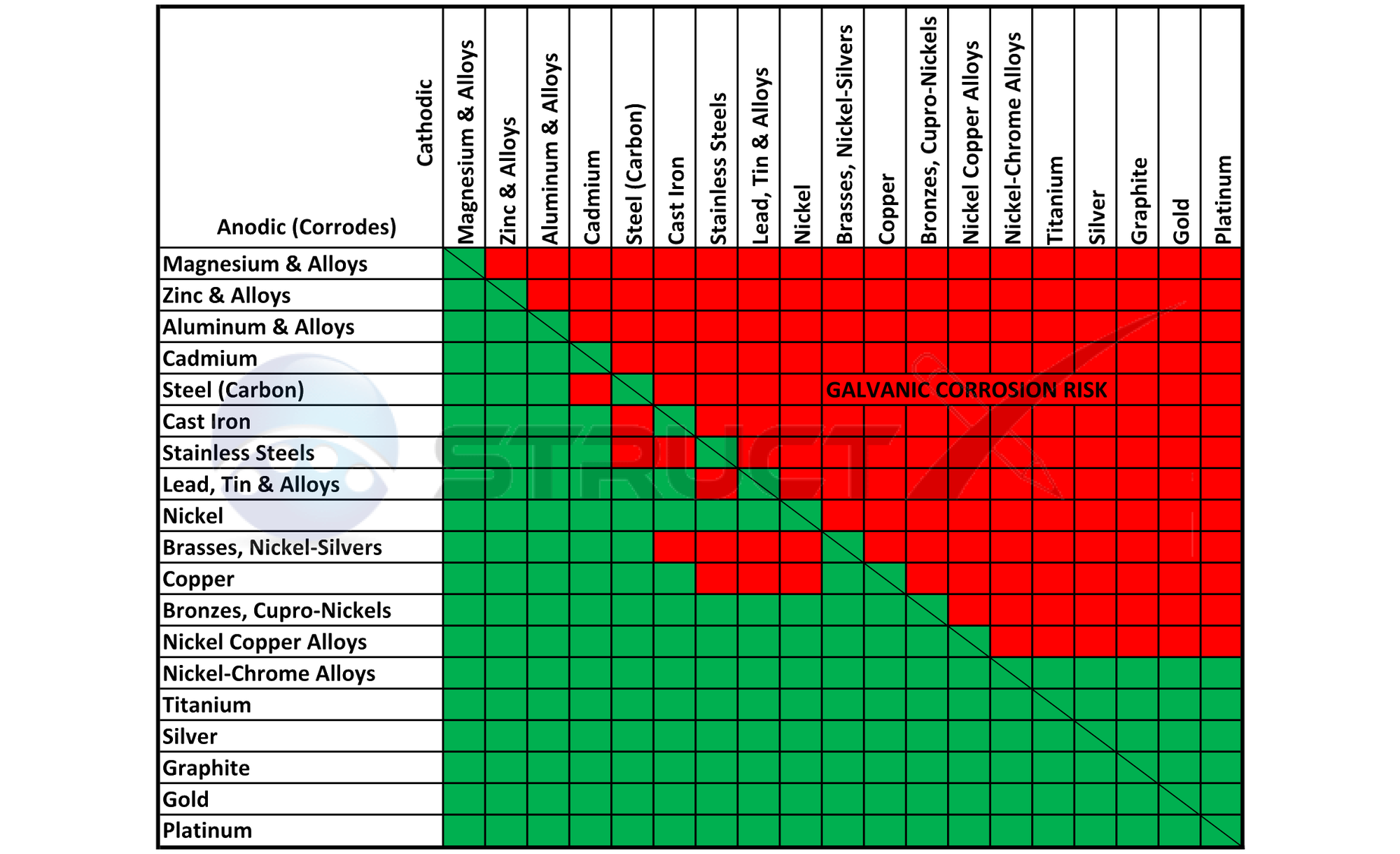
Aluminum Corrosion Resistance Chart
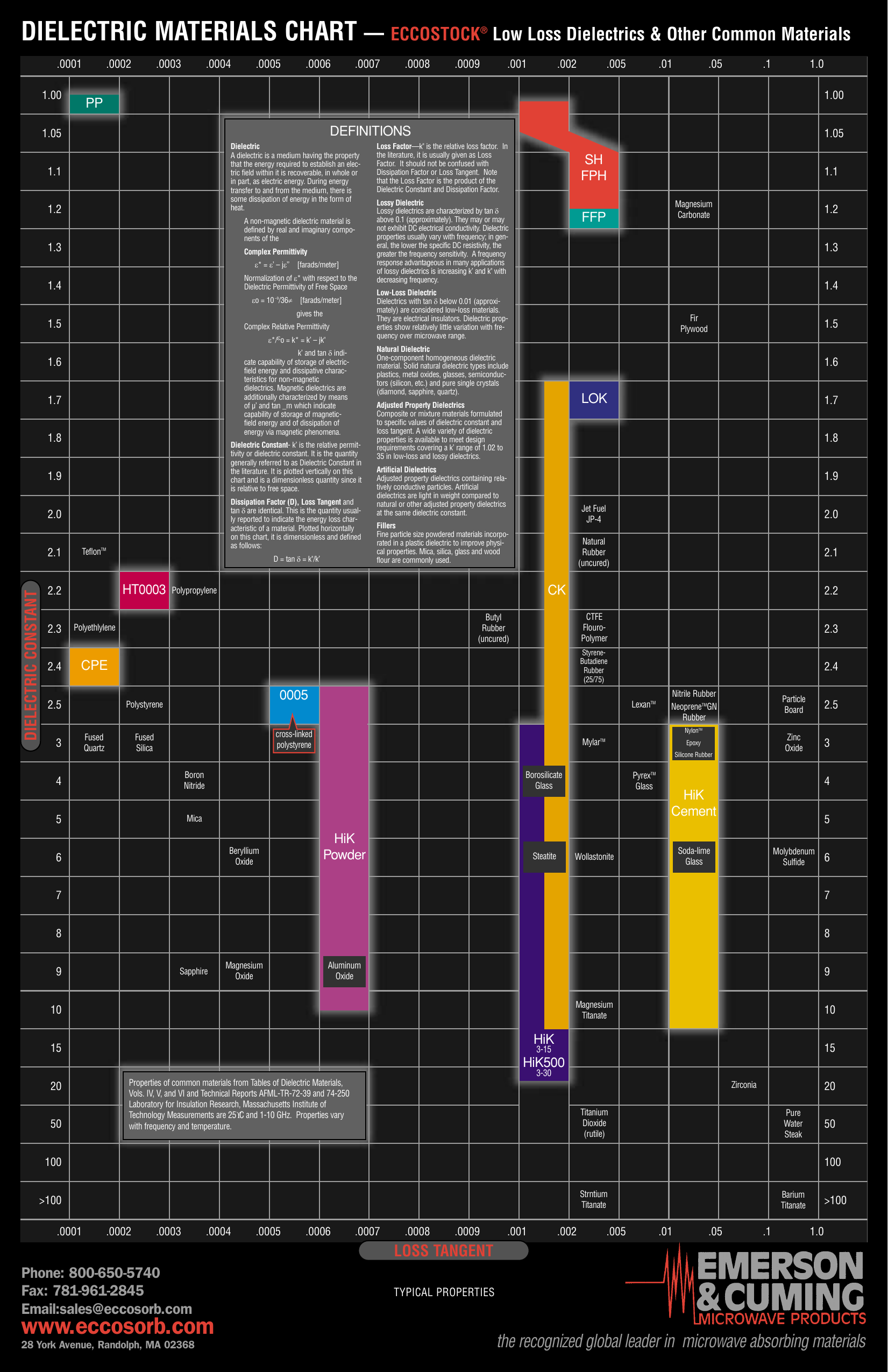
Dielectric Chart
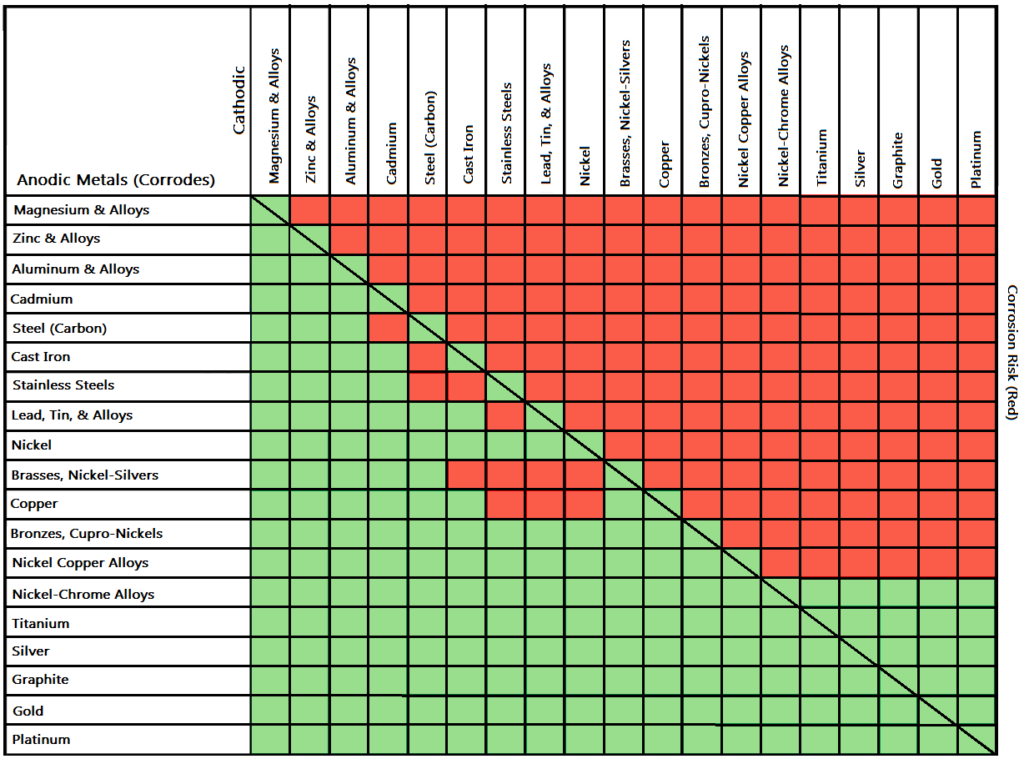
Architectural Metals Archives Monarch Metal
Passive) Under Conditions Which Provide Sufficient Oxygen To The Surface.
They Help To Create A Barrier Between The Two Metals, Which.
Web Find Out How Different Metals Will Corrode When Placed Together In An Assembly Based On Their Galvanic Corrosion Potential.
Web This Slide Includes A Chart Of Galvanic Corrosion Potential Between Common Construction Metals.
Related Post: