Disaccharide Drawing
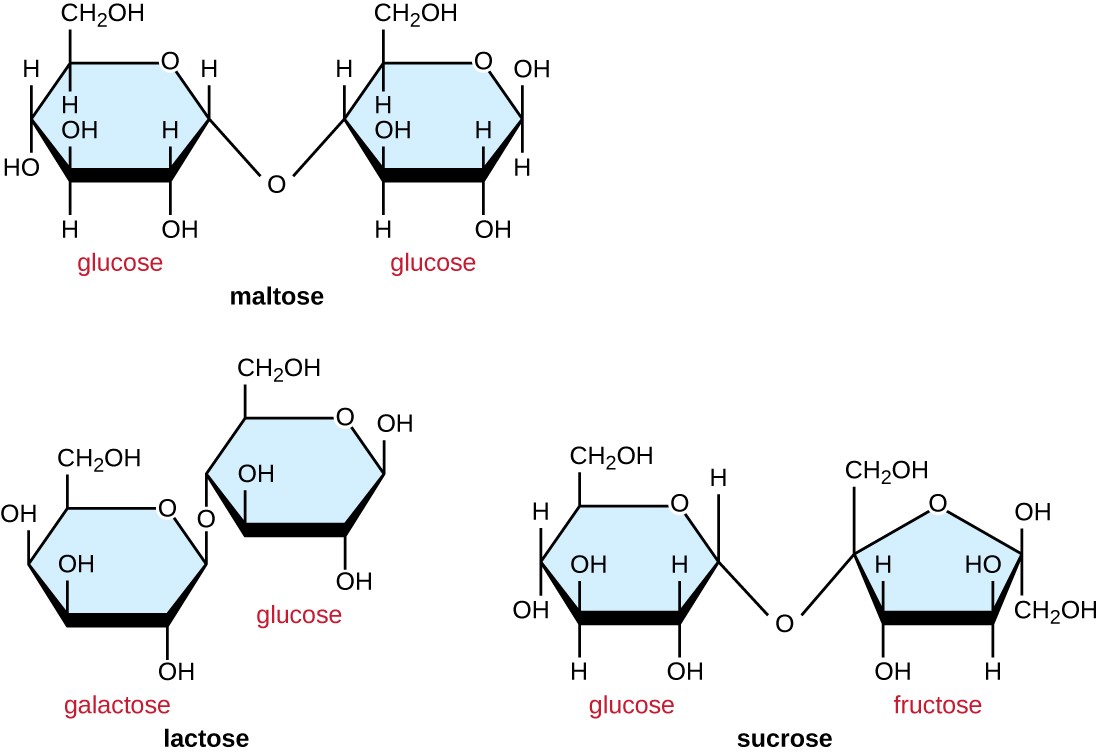
Disaccharide Drawing - Some commonly known examples of disaccharides include sucrose, lactose, and maltose. If the alcohol is itself a sugar, the glycosidic product is a. When the alcohol component of a glycoside is provided by a hydroxyl function on another monosaccharide, the compound is called a disaccharide. When determining the orientation of the ohs on each c, orient the wedge and dash drawing in your mind so that the c atoms adjacent to the one of interest are pointing down. Identify the type of glycoside link (e.g., 1,4′‑ β) present in a given disaccharide structure. Web about press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how youtube works test new features nfl sunday ticket press copyright. Know common disaccharides' structures, sources, and properties, including maltose, cellobiose, lactose, and sucrose. Here is a look at how disaccharides form, examples, and properties. This linkage is formed from the reaction of the anomeric carbon of one cyclic monosaccharide with the oh group of a second monosaccharide. Identify the type of glycoside link (e.g., 1,4′‑ β) present in a given disaccharide structure. The general chemical formula of a disaccharide is c 12 h 22 o 11. Four examples of disaccharides composed of two glucose units are shown in the following diagram. Web to fully establish the structure of a disaccharide, we must determine (1) the identity of the component monosaccharides; Some commonly known examples of disaccharides include sucrose, lactose, and maltose. So. Four examples of disaccharides composed of two glucose units are shown in the following diagram. Here is a look at how disaccharides form, examples, and properties. They act as a source of monosaccharides. Click for even more information. Common examples of disaccharides are sucrose, maltose, and lactose. Web disaccharides are the carbohydrates that are made up of two monosaccharide subunits. If the alcohol is itself a sugar, the glycosidic product is a. Some commonly known examples of disaccharides include sucrose, lactose, and maltose. Draw the structure of a specific disaccharide, given the structure of the monosaccharide units and. When the alcohol component of a glycoside is provided. They act as a source of monosaccharides. The general chemical formula of a disaccharide is c 12 h 22 o 11. (2) the type of ring junction, furanose or pyranose, in each monosaccharide, as it exists in the disaccharide; Draw the structure of a specific disaccharide, given the structure of the monosaccharide units and. We have di, which means two,. Common examples of disaccharides are sucrose, maltose, and lactose. Web to fully establish the structure of a disaccharide, we must determine (1) the identity of the component monosaccharides; They have 12 carbon atoms, and their chemical formula is c 12 h 22 o 11. Draw the structure of a specific disaccharide, given the structure of the monosaccharide units and. Web. Be able to draw and name the glycosidic linkage in disaccharides. Know common disaccharides' structures, sources, and properties, including maltose, cellobiose, lactose, and sucrose. A disaccharide, also called a double sugar, is a molecule formed by two monosaccharides, or simple sugars. In this video, we will be looking at the. This linkage is formed from the reaction of the anomeric. Four examples of disaccharides composed of two glucose units are shown in the following diagram. Draw the structure of a specific disaccharide, given the structure of the monosaccharide units and the type of glycoside link involved. Web for those, draw a wedge and dash line drawing of the molecule. Identify the type of glycoside link (e.g., 1,4′‑ β) present in. We have di, which means two, and saccharide, which means sugar. Learn which monosaccharide is commonly found in all disaccharides, disaccharide structure, function with examples at byju's. Web about press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how youtube works test new features nfl sunday ticket press copyright. Web identify the two monosaccharide units in a. Web disaccharides are the carbohydrates that are made up of two monosaccharide subunits. Identify the type of glycoside link (e.g., 1,4′‑ β) present in a given disaccharide structure. Remember, this is the anomeric carbon. Know common disaccharides' structures, sources, and properties, including maltose, cellobiose, lactose, and sucrose. (2) the type of ring junction, furanose or pyranose, in each monosaccharide, as. Click for even more information. Now, with disaccharides, most commonly the glycosidic linkage forms between the anomaric carbon, or c1. 14k views 2 years ago chemistry. Web identify the two monosaccharide units in a given disaccharide. Remember, this is the anomeric carbon. 14k views 2 years ago chemistry. Draw the structure of a specific disaccharide, given the structure of the monosaccharide units and the type of glycoside link involved. Click for even more information. Web identify the two monosaccharide units in a given disaccharide. Web to fully establish the structure of a disaccharide, we must determine (1) the identity of the component monosaccharides; Four examples of disaccharides composed of two glucose units are shown in the following diagram. A disaccharide, also called a double sugar, is a molecule formed by two monosaccharides, or simple sugars. Learn which monosaccharide is commonly found in all disaccharides, disaccharide structure, function with examples at byju's. Draw the structure of a specific disaccharide, given the structure of the monosaccharide units and. This linkage is formed from the reaction of the anomeric carbon of one cyclic monosaccharide with the oh group of a second monosaccharide. Some commonly known examples of disaccharides include sucrose, lactose, and maltose. Overview of carbohydrates, including structure and properties of monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. (2) the type of ring junction, furanose or pyranose, in each monosaccharide, as it exists in the disaccharide; They act as a source of monosaccharides. Identify the type of glycoside link (e.g., 1,4′‑ β) present in a given disaccharide structure. Be able to draw and name the glycosidic linkage in disaccharides.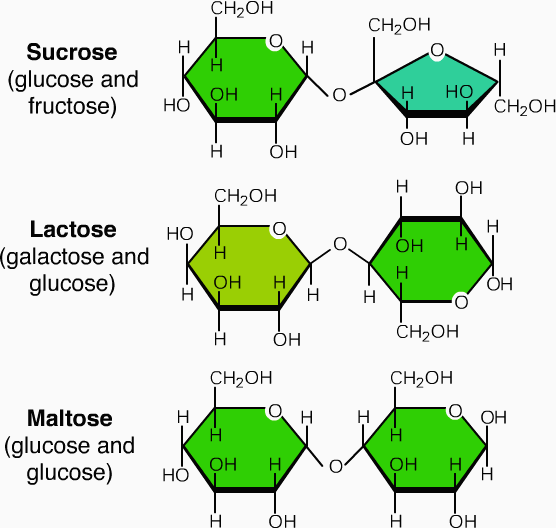
Disaccharides

Disaccharide Examples What Is a Disaccharide?
7.2 Carbohydrates Microbiology 201
/GettyImages-121842928-56b8d9e85f9b5829f83fcc3d.jpg)
List of Types of Disaccharides

Chemical structures main disaccharides Royalty Free Vector

Glucose and Disaccharides Biological Molecules Ep 7 Zoë Huggett

16.6 Disaccharides The Basics of General, Organic, and Biological

Biochemistry Glossary Disaccharides Draw It to Know It

Disaccharides Definition, Function, Structure & Examples
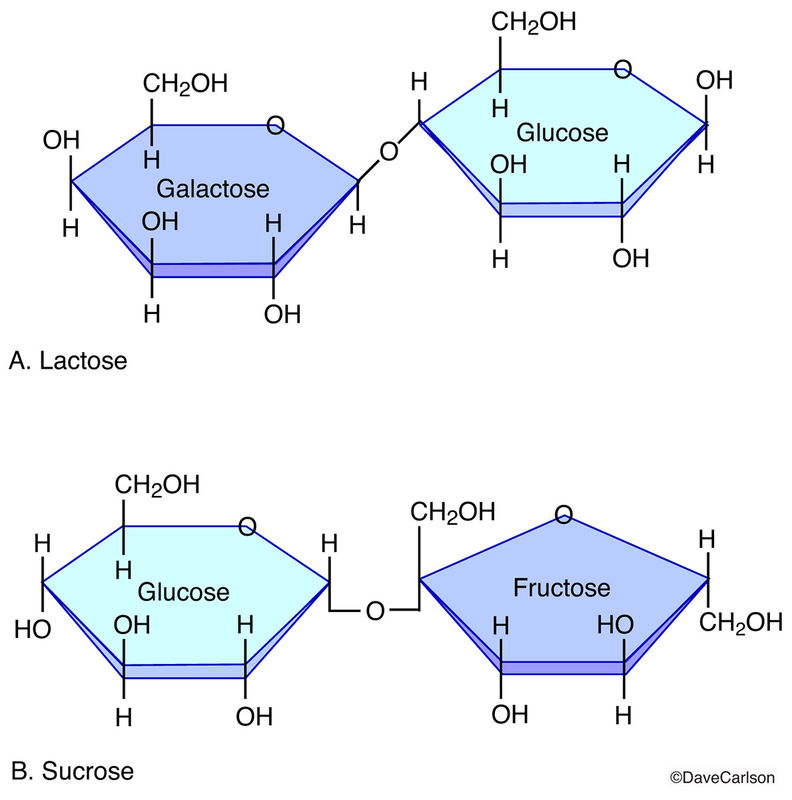
Disaccharide Molecules Carlson Stock Art
The General Chemical Formula Of A Disaccharide Is C 12 H 22 O 11.
Examples Include Sucrose, Maltose, And Lactose.my Website:
Identify The Type Of Glycoside Link (E.g., 1,4′‑ Β) Present In A Given Disaccharide Structure.
When Determining The Orientation Of The Ohs On Each C, Orient The Wedge And Dash Drawing In Your Mind So That The C Atoms Adjacent To The One Of Interest Are Pointing Down.
Related Post: