Draw A Diastereomer For Each Of The Following Compounds
Draw A Diastereomer For Each Of The Following Compounds - Draw a diastereomer for each of the following compounds:. Stereoisomers are two types, diastereomers and enantiomers. Draw a diastereomer for each of the following compounds: Draw a diastereomer of the following compound. Web here are the diastereomers for each compound: Here’s the best way to solve it. Web consider the following compounds: Web draw one enantiomer and one diastereomer for each of the following compounds. Here’s an example when you switch only the first chiral center (in red). Web draw one enantiomer and one diastereomer for each of the following compounds. Web by definition, they are diastereomers of each other. Web consider the following compounds: Be sure to answer all parts. Web they are stereoisomers, yet they aren’t enantiomers. Draw one enantiomer and one diastereomer for each of the. Web they are stereoisomers, yet they aren’t enantiomers. Here’s an example when you switch only the first chiral center (in red). First, we need to identify the asymmetric centers in the given compounds. Web by definition, they are diastereomers of each other. Draw a diastereomer for each of the following compounds: Draw the enantiomer and a diastereomer for the following compound. Here’s an example when you switch only the first chiral center (in red). Oh oh draw all the stereoisomers of the following compounds ho oh. 2.1 polar covalent bonds and electronegativity; Web by definition, they are diastereomers of each other. Ch3 h oh ch3 ci ci hw ch ch3ch2 ch3 h3c ch3 с с ch. > diastereomers are stereoisomers that are not superimposable and are not mirror images. Web draw one enantiomer and one diastereomer for each of the following compounds. Stereoisomers are two types, diastereomers and enantiomers. In a pair of diastereomers, some of the chiral centers are the. Draw a diastereomer for each of the following compounds: Draw a diastereomer for each of the following compounds: Web draw one enantiomer and one diastereomer for each of the following compounds. Web draw a diastereomer for each of the following compounds: Stereoisomers are two types, diastereomers and enantiomers. Stereoisomers are two types, diastereomers and enantiomers. Web here are the diastereomers for each compound: Web draw a diastereomer for each of the following compounds: Draw a diastereomer of the following compound. Draw a diastereomer for each of the following compounds: Is the structure chiral or achiral? You change the configuration of one of the chiral centres. The four possible combination are ss, rr, sr and rs (figure 1). 2.1 polar covalent bonds and electronegativity; Web draw one enantiomer and one diastereomer for each of the following compounds. Oh oh draw all the stereoisomers of the following compounds ho oh. Web diastereomers only occur in compounds containing more than one chiral center. Here’s an example when you switch only the first chiral center (in red). You change the configuration of one of the chiral centres. Web here are the diastereomers for each compound: Web here are the diastereomers for each compound: Web consider the following compounds: Draw a diastereomer for each of the following compounds: Here’s an example when you switch only the first chiral center (in red). Notice that compounds c and b also have a diastereomeric relationship, by the same definition. Web draw a diastereomer for each of the following compounds: Here’s the best way to solve it. Draw a diastereomer for each of the following compounds: > diastereomers are stereoisomers that are not superimposable and are not mirror images. First, we need to identify the asymmetric centers in the given compounds. Part a draw the molecule on the canvas by choosing buttons. Web they are stereoisomers, yet they aren’t enantiomers. Here’s the best way to solve it. Web draw one enantiomer and one diastereomer for each of the following compounds. Draw a diastereomer of the following compound. Draw a diastereomer for each of the following compounds:. Web diastereomers only occur in compounds containing more than one chiral center. Is the structure chiral or achiral? Notice that compounds c and b also have a diastereomeric relationship, by the same definition. > diastereomers are stereoisomers that are not superimposable and are not mirror images. You change the configuration of one of the chiral centres. Web here are the diastereomers for each compound: Web draw one enantiomer and one diastereomer for each of the following compounds. Draw a diastereomer for each of the following compounds: Draw a diastereomer for each of the following compounds: To describe such a relationship, we need a new term— diastereomer.Solved Draw a diastereomer for each of the following
Solved Draw a diastereomer for each of the following
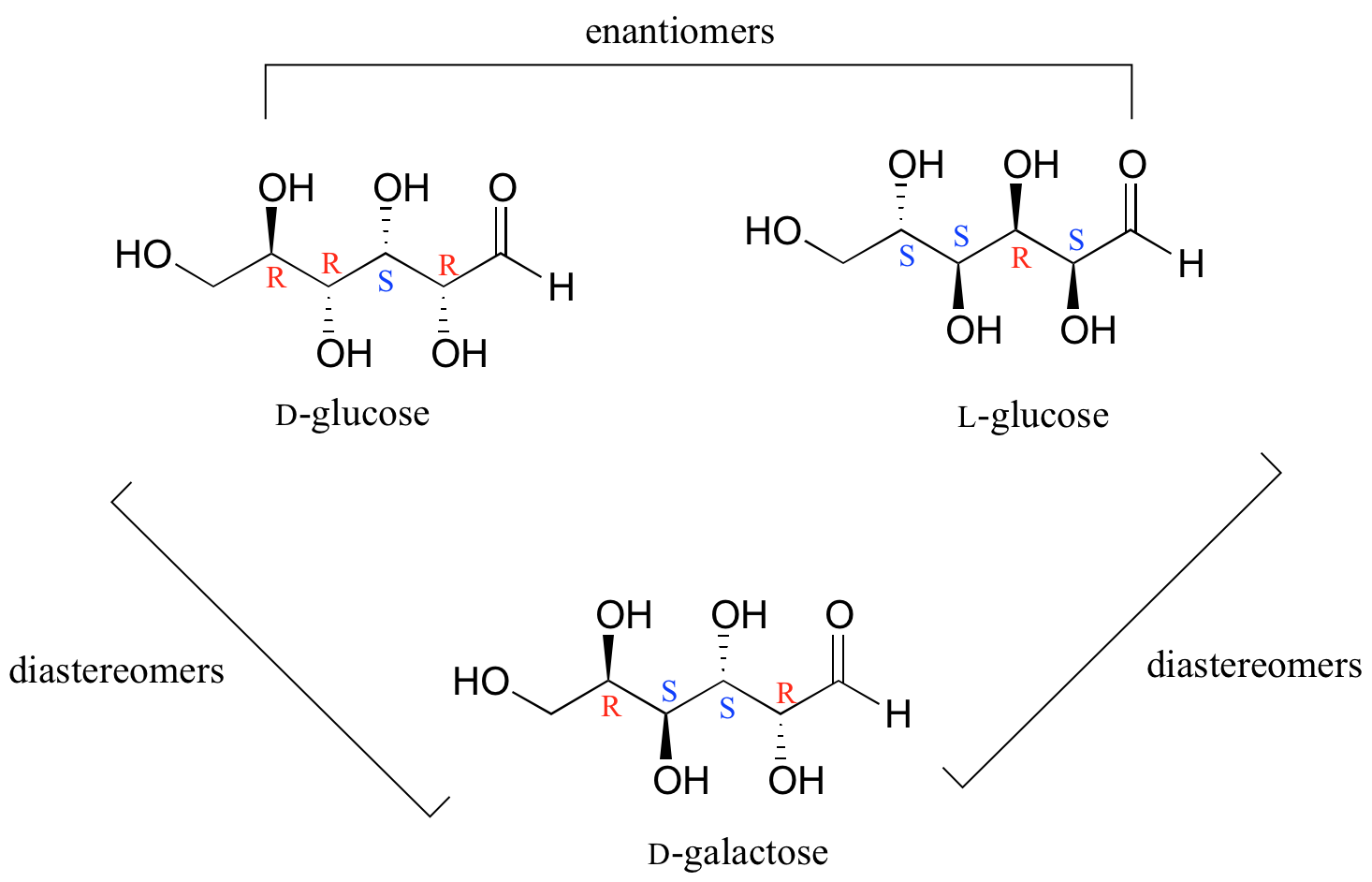
draw a diastereomer for each of the following compounds
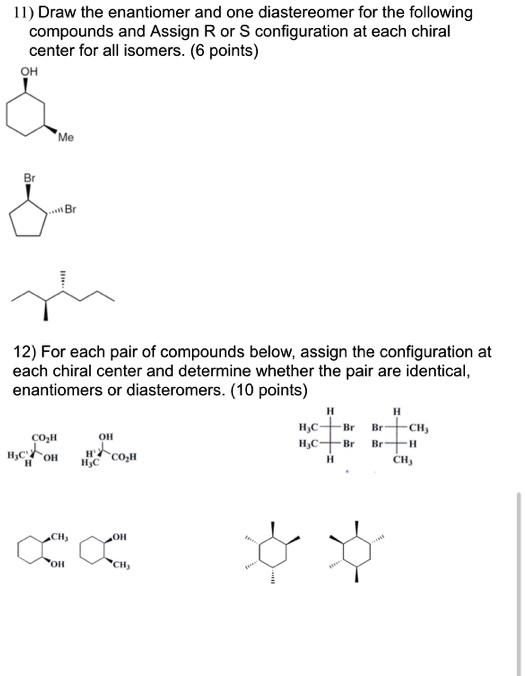
draw a diastereomer for each of the following compounds
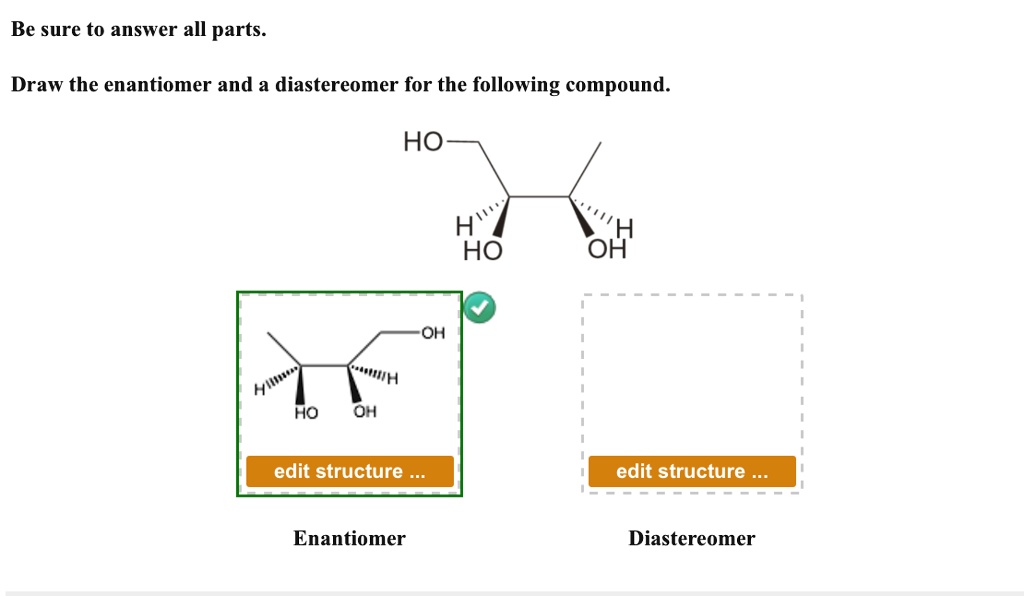
SOLVED Be sure to answer all parts Draw the enantiomer and a
[Solved] Organic Chemistry7a) Draw Draw a diastereomer for
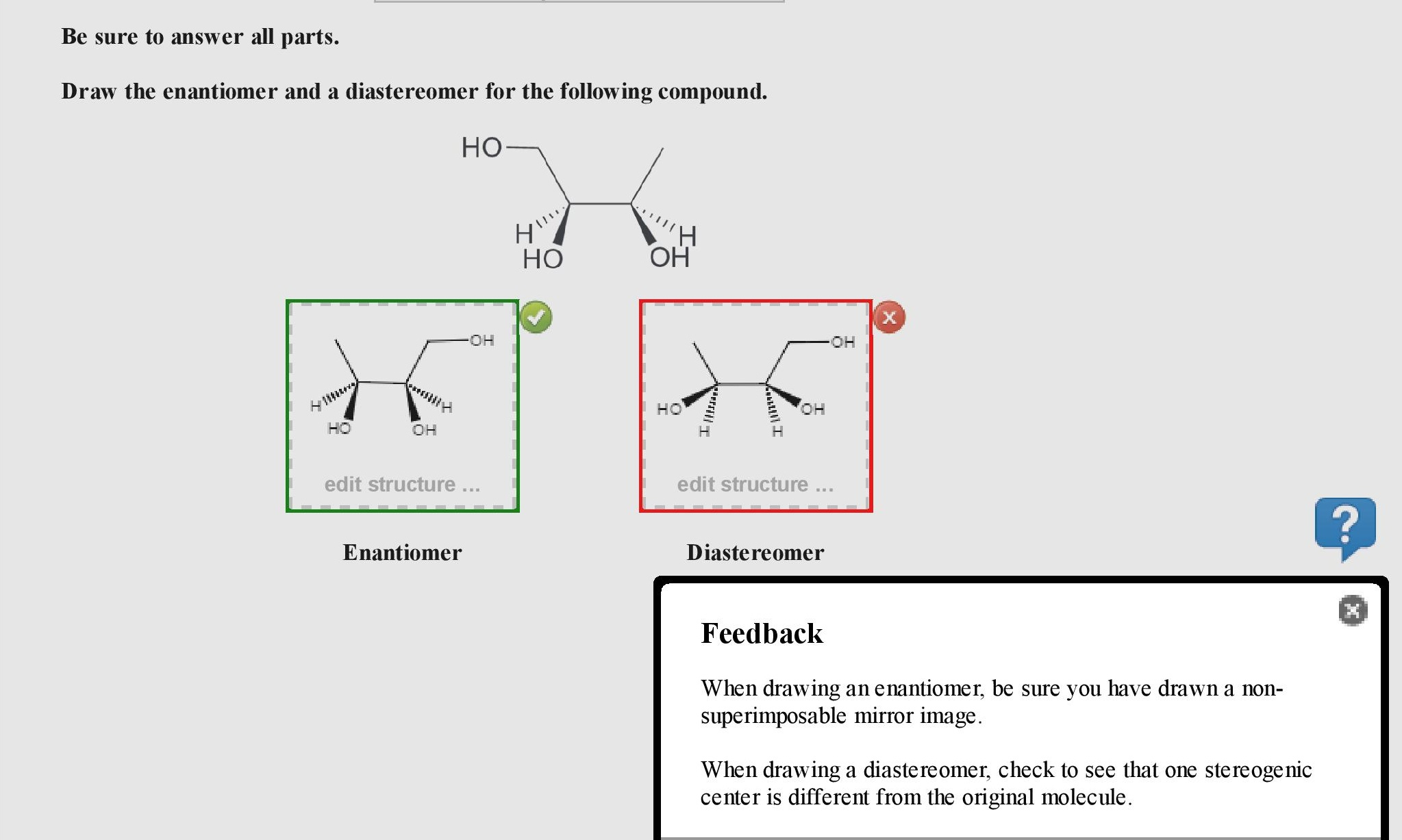
draw a diastereomer for each of the following compounds
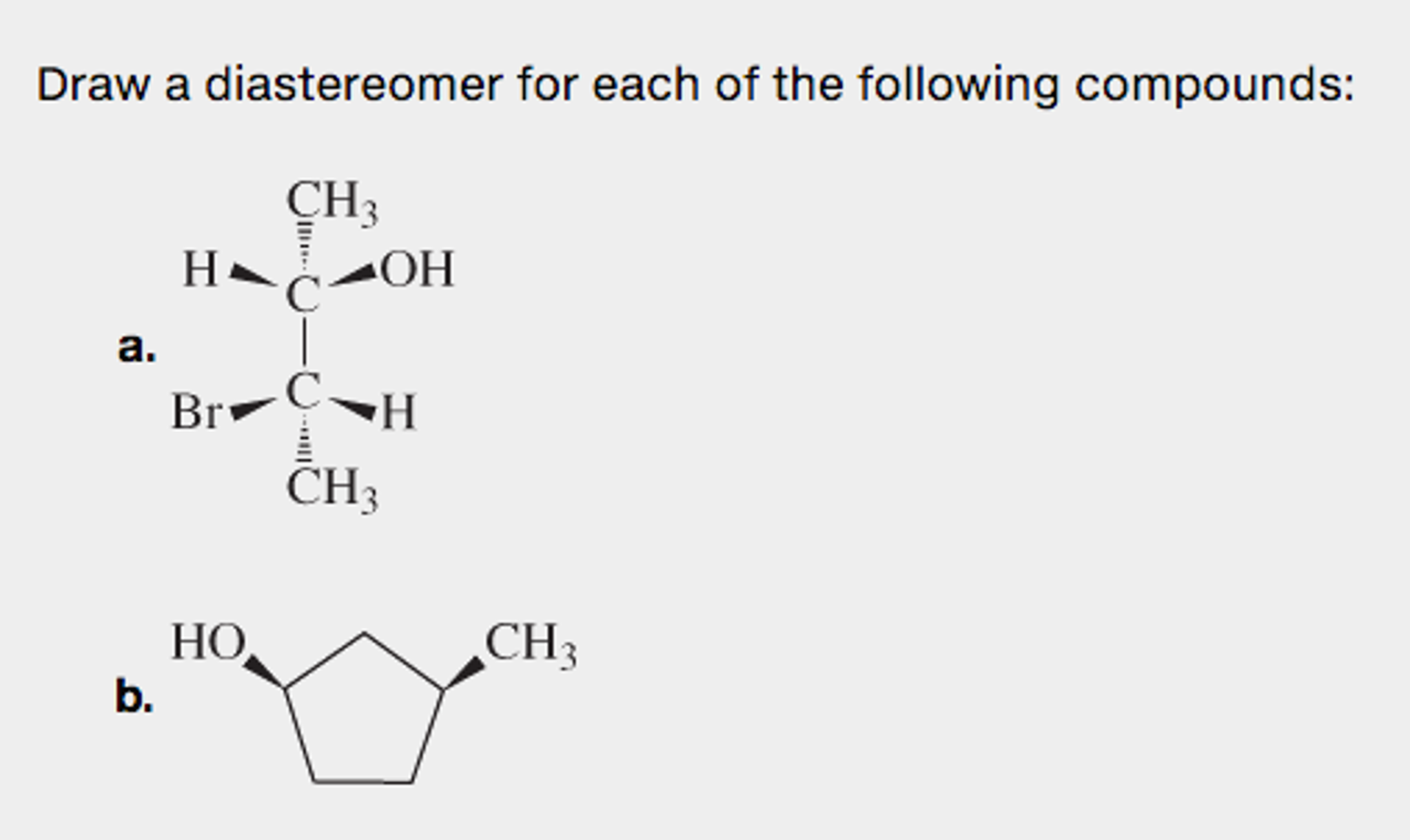
Draw A Diastereomer For Each Of The Following Compounds
draw a diastereomer for each of the following compounds
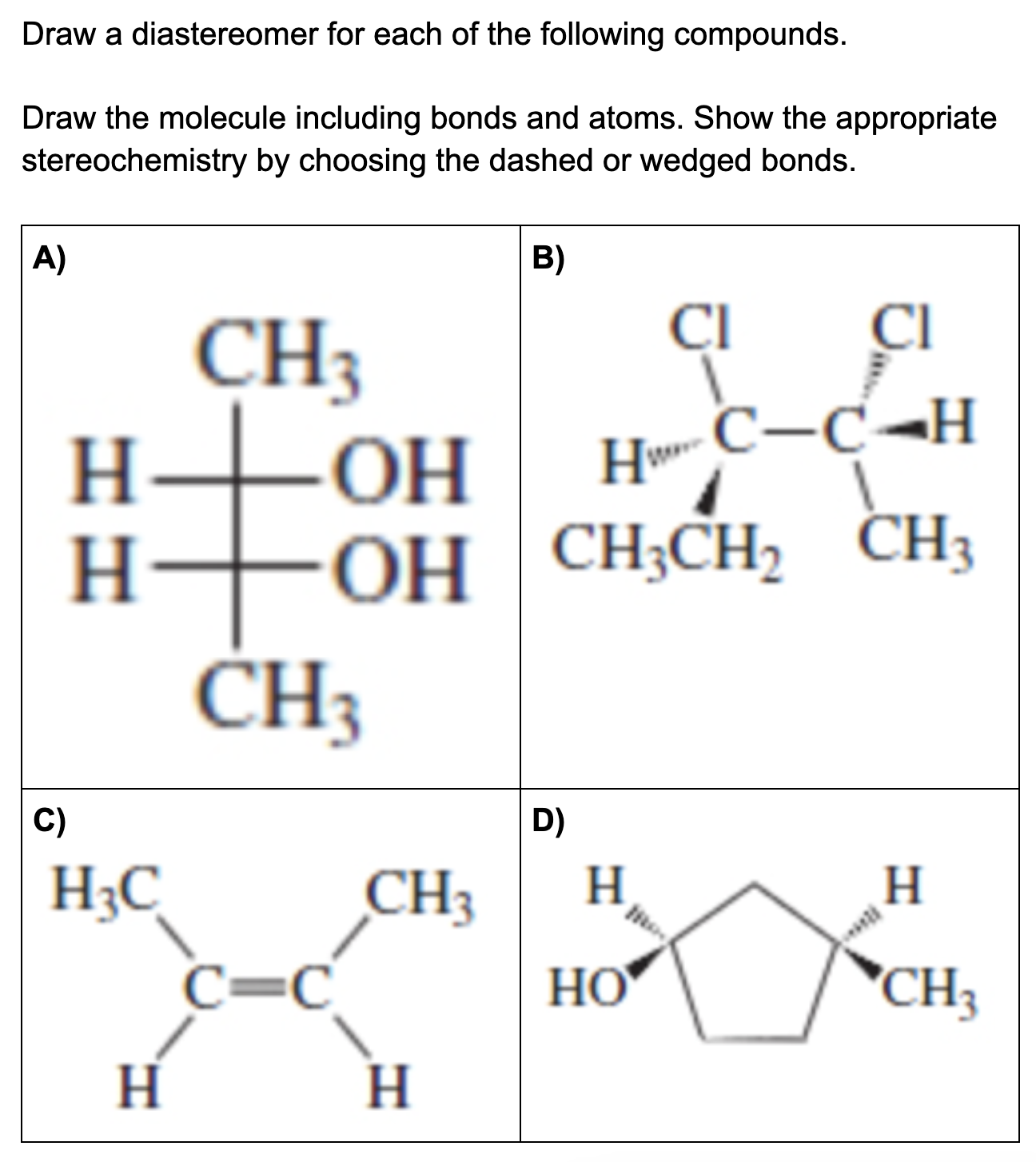
Solved Draw a diastereomer for each of the following
Web Consider The Following Compounds:
The Four Possible Combination Are Ss, Rr, Sr And Rs (Figure 1).
Web Draw A Diastereomer For Each Of The Following Compounds:
Stereoisomers Are Two Types, Diastereomers And Enantiomers.
Related Post:
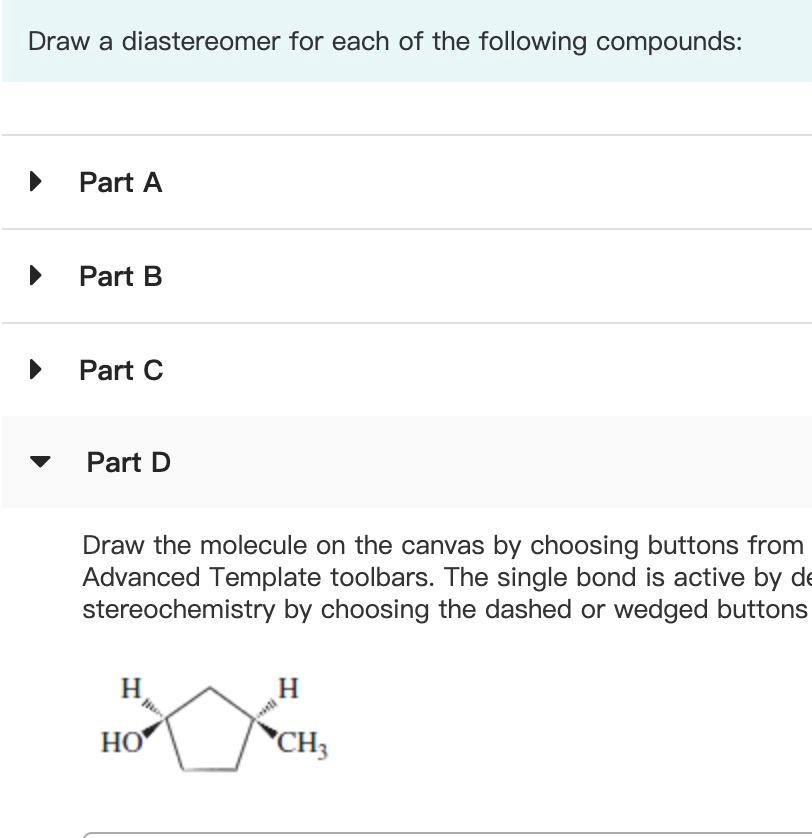
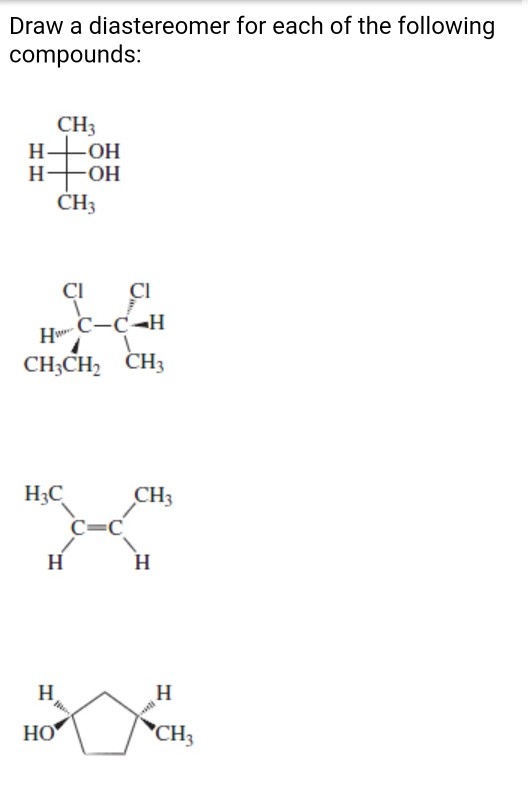
![[Solved] Organic Chemistry7a) Draw Draw a diastereomer for](https://media.cheggcdn.com/media/eab/eab310d9-cc56-4151-aa61-3c549f878aa2/phpmQS7za)
