Draw Glycolysis
Draw Glycolysis - But i'm just going to focus on the carbon backbone. And glucose, we know its formula. The following equation well summarizes the process of glycolysis: Web glycolysis is the first and common step for aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration. However, it is also known that ecs are heterogeneous, and their phenotypic features depend on the vascular bed. Adp and nad stand for adenosine diphosphate and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, respectively. This is the first step of the preparatory phase where glucose is activated by the involvement of the enzyme called hexokinase and converted into glucose 6 phosphate. In preparatory phase glucose molecule is activated for breakdown and energy is invested in the process of phosphorylation of glucose. Web glycolysis is the process by which one molecule of glucose is converted into two molecules of pyruvate, two hydrogen ions and two molecules of water. Web glycolysis, which translates to splitting sugars, is the process of releasing energy within sugars. It can be used as an energy source through the pathways of glycolysis and aerobic respiration. And glucose, we know its formula. Web so glycolysis, or really cellular respiration, it starts off with glucose. Web figure 7.7 glycolysis begins with an energy investment phase which requires 2 atp to phosphorylate the starting glucose molecule. Fad + 2 e − +. In preparatory phase glucose molecule is activated for breakdown and energy is invested in the process of phosphorylation of glucose. Through this process, the 'high energy' intermediate molecules of atp and nadh are synthesised. In this phase, the starting molecule of glucose gets rearranged, and two phosphate groups are. Web background it is generally accepted that endothelial cells (ecs), primarily. Web glycolysis also produces two nadh, which can help power the electron transport chain (fourth animation), and two atp, which are used for many cellular processes (sixth animation). Web glycolysis is the primary step of cellular respiration, which occurs in all organisms. Hexokinase requires mg 2+ to catalyze the reaction. The first five reactions constitutes the preparatory phase. Web glycolysis. Web glycolysis is the catabolic process in which glucose is converted into pyruvate via ten enzymatic steps. Indira rajagopal (oregon state university) 9.1: Web equation of glycolysis. Fad + 2 e − + 2 h + → fadh 2. In the absence of oxygen, the cells make small amounts of atp as glycolysis is followed by fermentation. In the absence of oxygen, the cells make small amounts of atp as glycolysis is followed by fermentation. Web the video focuses on one of the most important metabolic pathway, glycolysis. Web glycolysis is a series of reactions that take place in the cell cytoplasm. The first five reactions constitutes the preparatory phase. But i'm just going to draw it. This is the first step of the preparatory phase where glucose is activated by the involvement of the enzyme called hexokinase and converted into glucose 6 phosphate. Web glycolysis is the process by which one molecule of glucose is converted into two molecules of pyruvate, two hydrogen ions and two molecules of water. Web equation of glycolysis. This multistep process. So it is a ring, or can be a ring. Hexokinase requires mg 2+ to catalyze the reaction. Web glycolysis is the process by which one molecule of glucose is converted into two molecules of pyruvate, two hydrogen ions and two molecules of water. Web about this video.in this video lecture you will learn basic concept of glycolysisglycolysis is the. Web glycolysis is the first and common step for aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration. Web glycolysis takes place in the cytosol of a cell, and it can be broken down into two main phases: Indira rajagopal (oregon state university) 9.1: Hexokinase requires mg 2+ to catalyze the reaction. An enzyme that carries hydrogen. Web glycolysis occurs in ten steps. Indira rajagopal (oregon state university) 9.1: But i'm just going to draw it as six carbons in a row. Hexokinase requires mg 2+ to catalyze the reaction. And then the first step is, it gets phosphorylated and we have a whole video on the phosphorylation of glucose, and all of these steps are facilitated. The video covers the stoichiometry and energetics of the glycolysis. Adp and nad stand for adenosine diphosphate and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, respectively. Three possible catabolic fates of the pyruvate formed in glycolysis. So it is a ring, or can be a ring. Glycolysis is followed by the krebs cycle during aerobic respiration. An atp molecule is used during this step as a phosphate donor. Glycolysis is followed by the krebs cycle during aerobic respiration. It involves the oxidation of glucose into pyruvate (a 3 carbon compound), that produces (overall) atp and reduced nad: Web background it is generally accepted that endothelial cells (ecs), primarily rely on glycolysis for atp production, despite having functional mitochondria. Adp and nad stand for adenosine diphosphate and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, respectively. And glucose, we know its formula. So it is a ring, or can be a ring. Glycolysis consists of series of 10 enzyme catalyzed reactions which are divided into two phases. This multistep process yields two atp molecules containing free energy, two pyruvate molecules, two high energy, electron. Short bursts of anaerobic respiration can also be sustained in animals that convert pyruvate into lactate. Web glycolysis also produces two nadh, which can help power the electron transport chain (fourth animation), and two atp, which are used for many cellular processes (sixth animation). Web figure 7.7 glycolysis begins with an energy investment phase which requires 2 atp to phosphorylate the starting glucose molecule. Fad + 2 e − + 2 h + → fadh 2. Web glycolysis occurs in ten steps. In aerobic organisms, the pyruvate is then moved to the mitochondria where it is oxidized into the. Web glycolysis is the primary step of cellular respiration, which occurs in all organisms.
HonorChemistry 2017 Biochemistry Glycolysis

Glycolysis Chart
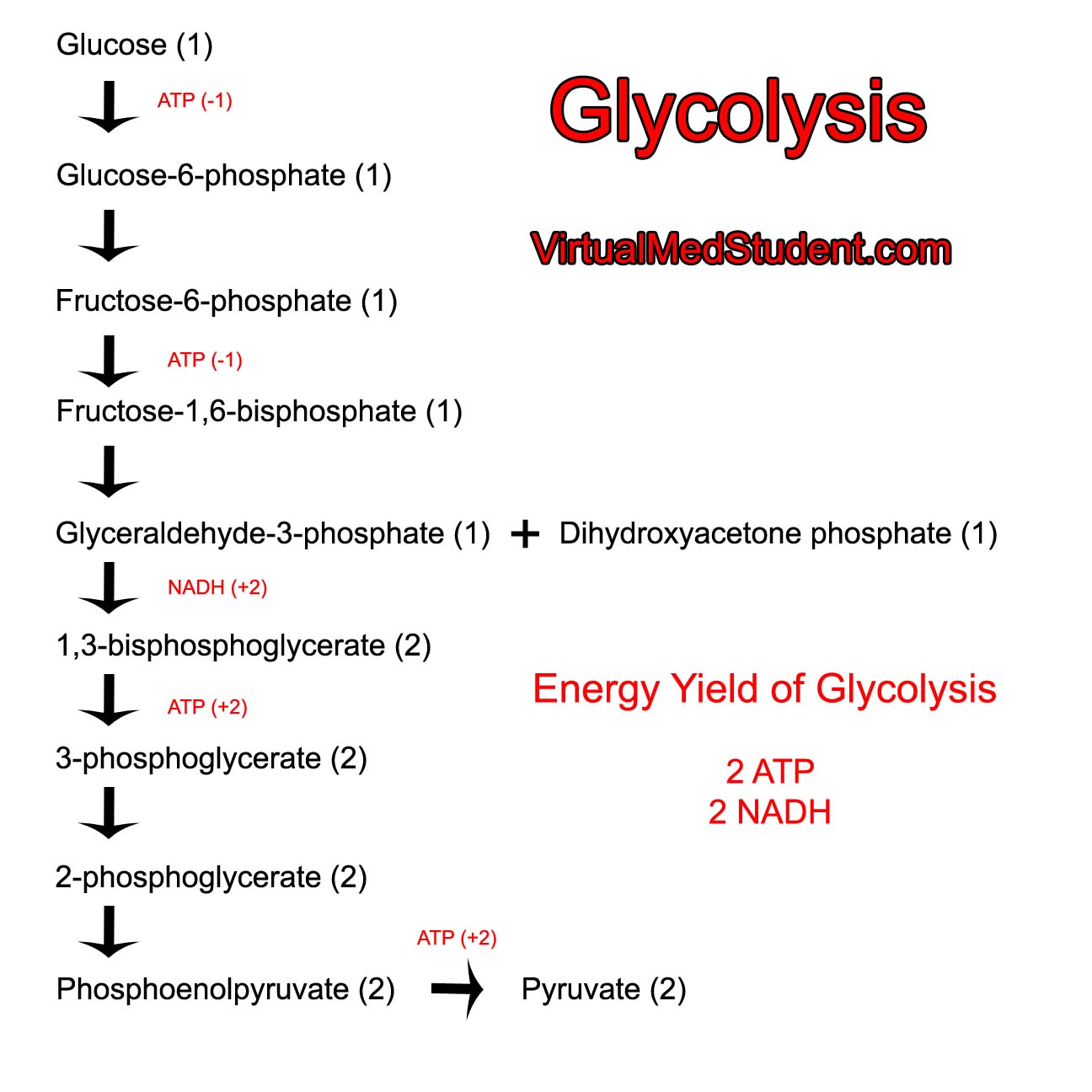
Sugar Strip Down Glycolysis and Energy Formation

What is Glycolysis? Superprof

Biochemistry Glossary Glycolysis Draw It to Know It
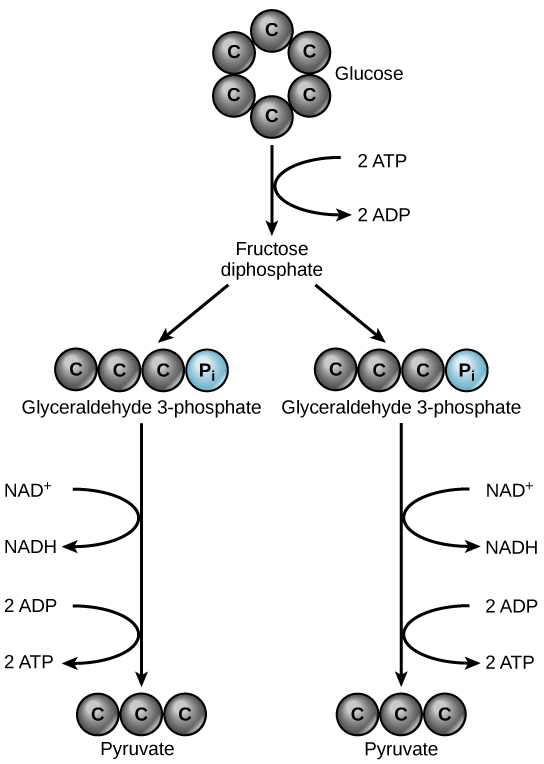
Glycolysis MHCC Biology 112 Biology for Health Professions

Stages of Glycolysis Science Decoder
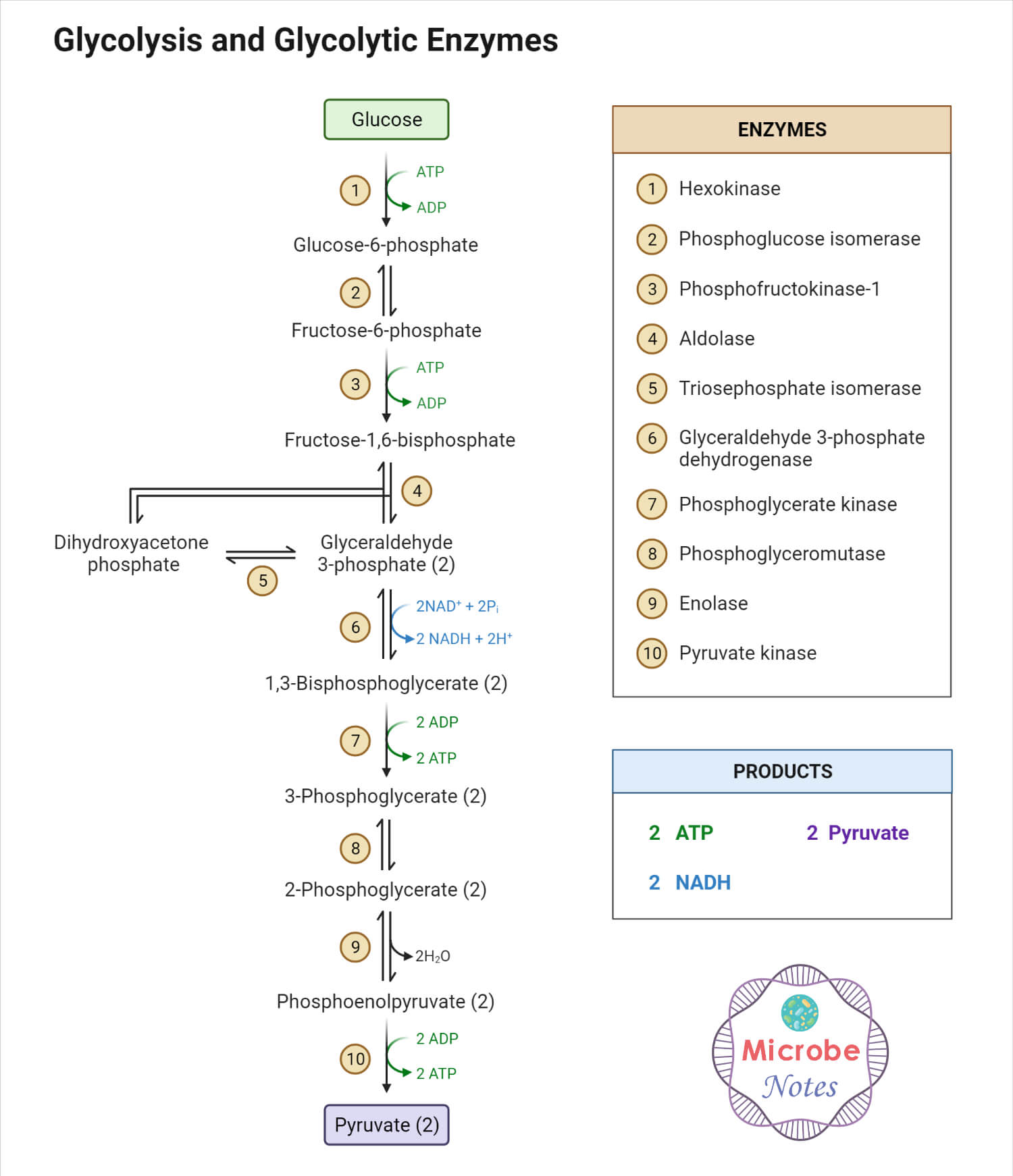
Glycolysis 10 Steps with Diagram and ATP Formation
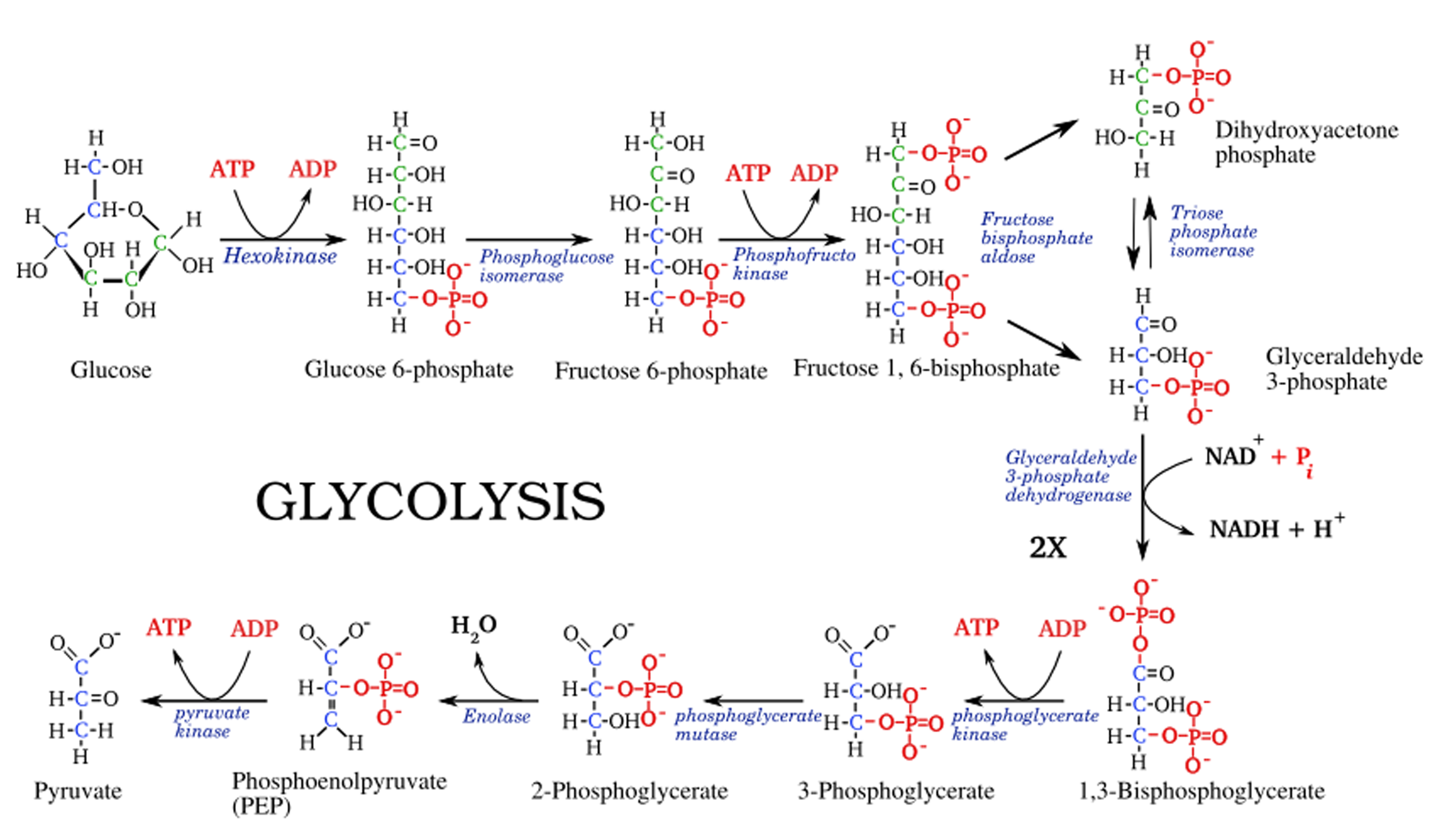
Glycolysis steps, diagram and enzymes involved Online Biology Notes
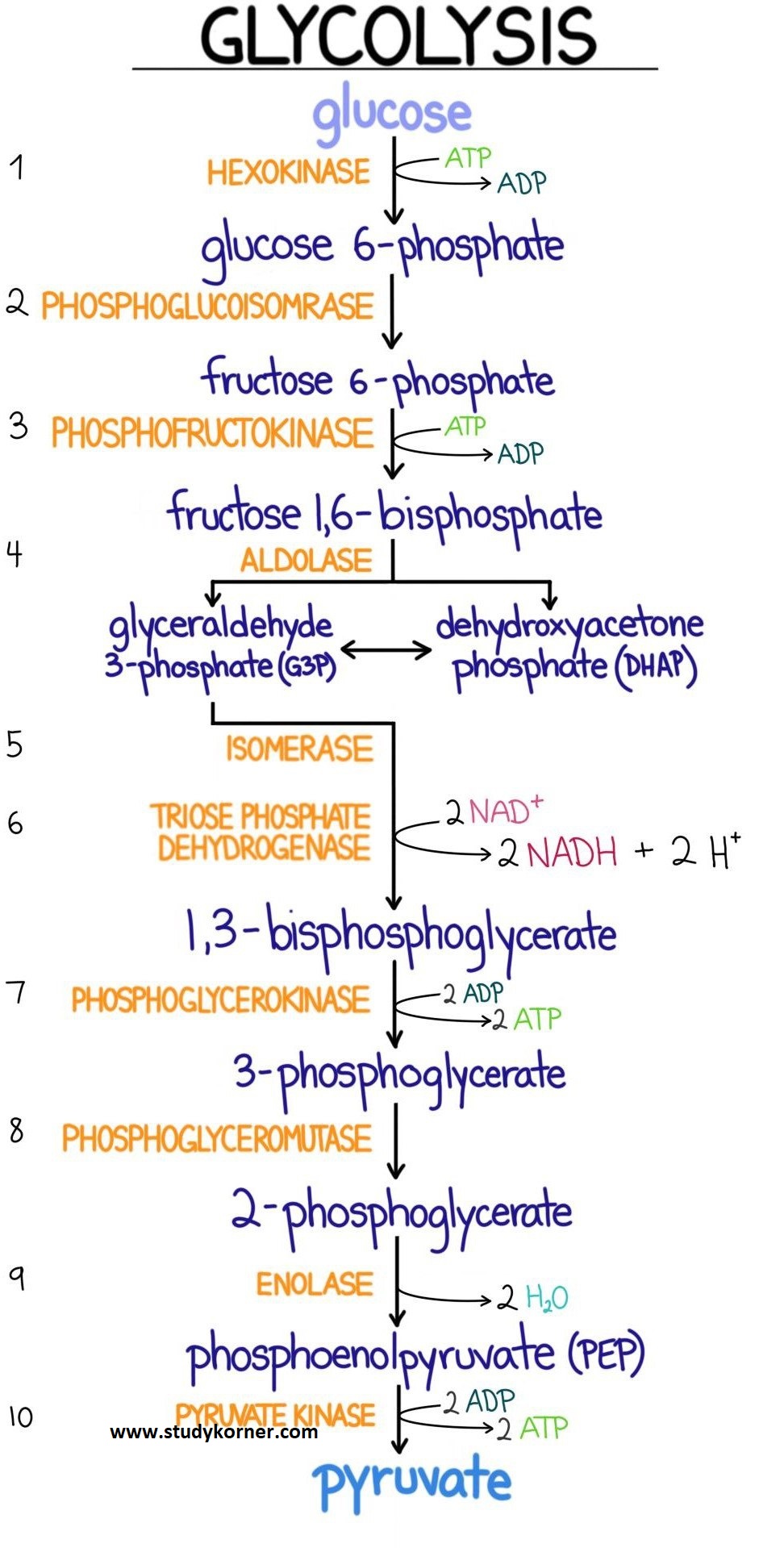
Glycolysis Flow Chart Introduction Pathway Diagram & Summary StudyPK
There Are Three Regulatory Steps, Each Of Which Is Highly Regulated.
So, It Can Be Defined As A Metabolic Process Where A Glucose Molecule Gets Broken Down Under The Influence Of Several Enzymes.
Pyruvate Also Serves As A Precursor In Many Anabolic Reactions, Not Shown Here.
Web Glycolysis Is The First And Common Step For Aerobic And Anaerobic Cellular Respiration.
Related Post: