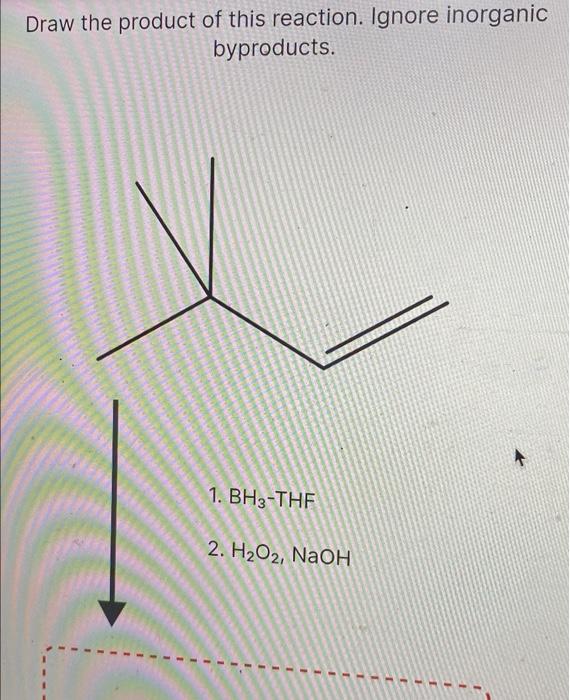
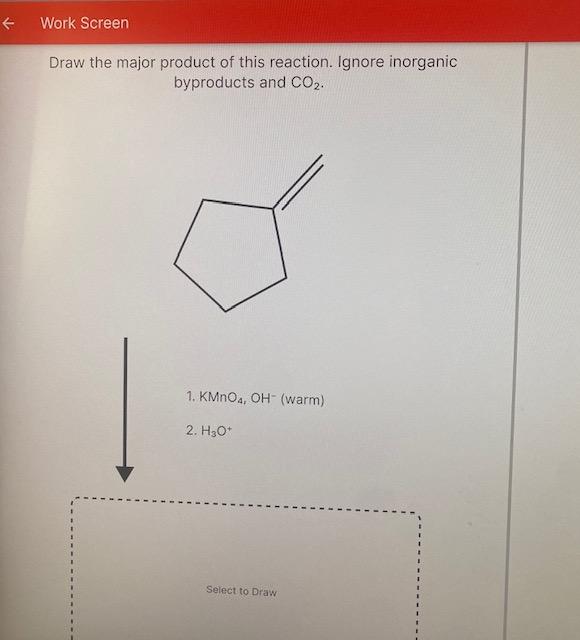
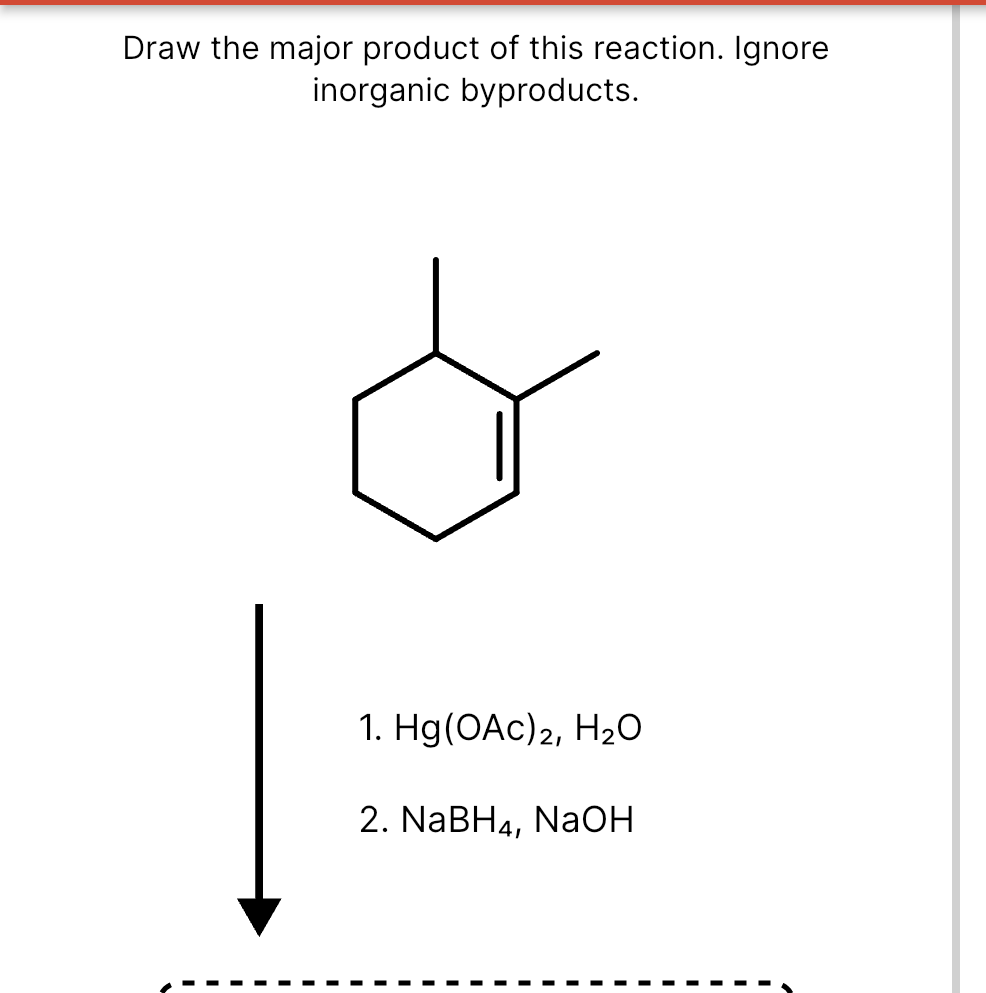
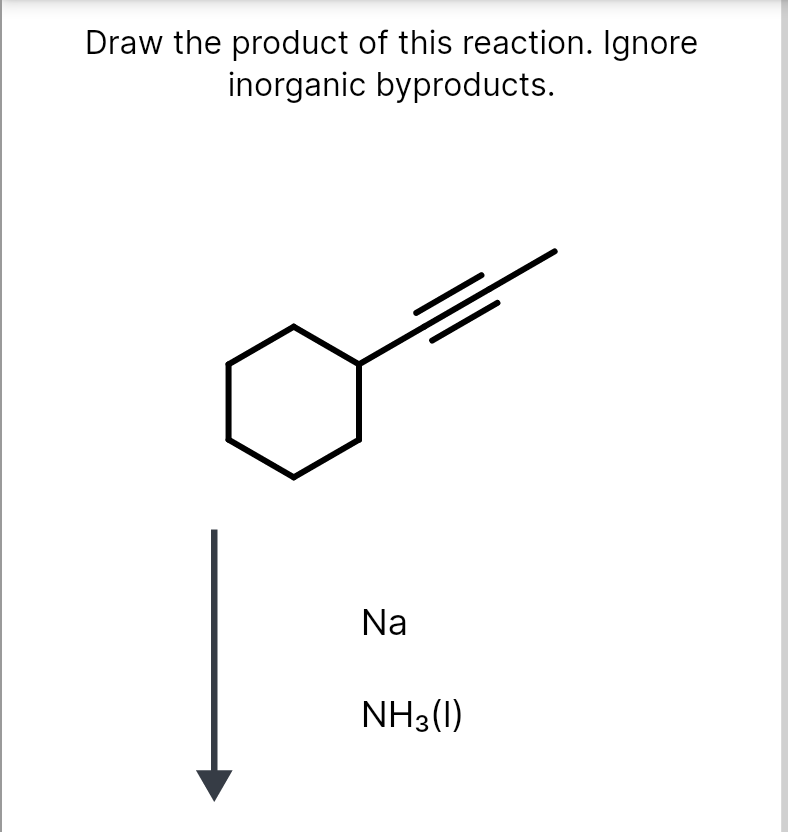
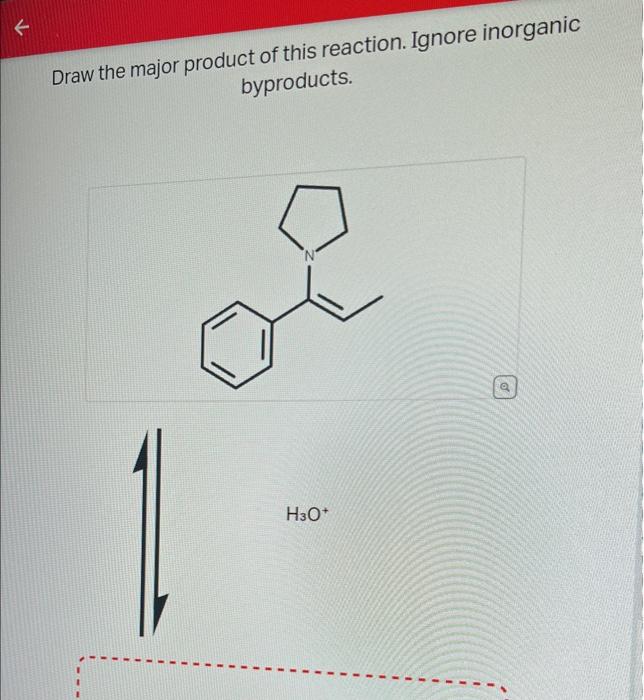
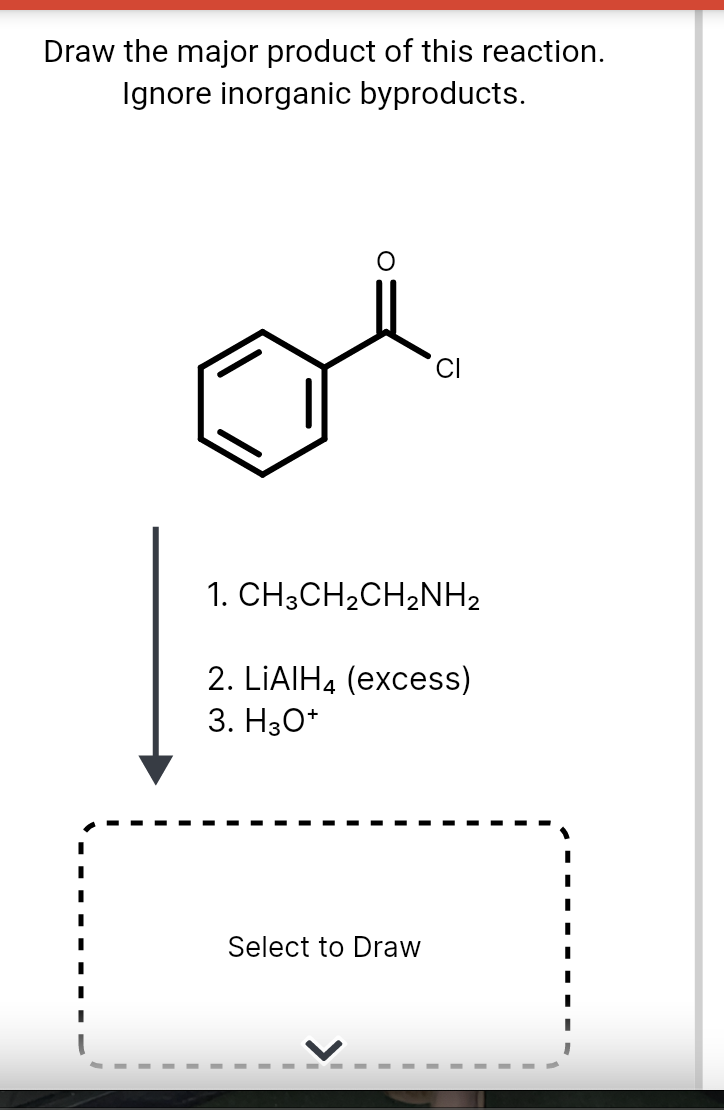
Draw The Product Of This Reaction Ignore Inorganic Byproducts
Draw The Product Of This Reaction Ignore Inorganic Byproducts - Draw the major product of this reaction. Sodium goes from a 0 to +1 oxidation state while chlorine goes from a 0 to a − 1 oxidation state. This problem has been solved! O 2 \mathrm{o_2} o 2 Finally, the addition of h3o+ will protonate the negatively charged carbon, resulting in the final product. So, the product of this reaction will be a molecule with two. Web ignore any inorganic byproducts. Therefore, the product of this reaction is \textbf{nh3}. Web 2na(s) + cl 2(g) → 2nacl(s) this reaction can also be classified as a redox reaction due to the changes in oxidation states. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Sodium goes from a 0 to +1 oxidation state while chlorine goes from a 0 to a − 1 oxidation state. Web 2na(s) + cl 2(g) → 2nacl(s) this reaction can also be classified as a redox reaction due to the changes in oxidation states. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core. Web ignore any inorganic byproducts. Finally, the addition of h3o+ will protonate the negatively charged carbon, resulting in the final product. Web hbr (1 equiv) select to draw draw the product of this reaction. Draw the major product of this reaction. This problem has been solved! The product of this reaction is nh3. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Draw the major product of this reaction. Draw a terminal alkene that would lead to this as the major product under these conditions. The balanced chemical equation for the reaction is: O 2 \mathrm{o_2} o 2 The product of this reaction is nh3. Web ignore any inorganic byproducts. Br2 (2 equiv) select to draw draw the starting structure that would produce this product under these conditions. Web hbr (1 equiv) select to draw draw the product of this reaction. Finally, the addition of h3o+ will protonate the negatively charged carbon, resulting in the final product. The product of this reaction is nh3. Web 2na(s) + cl 2(g) → 2nacl(s) this reaction can also be classified as a redox reaction due to the changes in oxidation states. O 2 \mathrm{o_2} o 2 Web ignore any inorganic byproducts. This problem has been solved! Draw a terminal alkene that would lead to this as the major product under these conditions. So, the product of this reaction will be a molecule with two. Br2 (2 equiv) select to draw draw the starting structure that would produce this product under these conditions. Web hbr (1 equiv) select to draw draw the. O 2 \mathrm{o_2} o 2 The product of this reaction is nh3. This problem has been solved! Web hbr (1 equiv) select to draw draw the product of this reaction. Draw the major product of this reaction. The product of this reaction is nh3. Draw a terminal alkene that would lead to this as the major product under these conditions. O 2 \mathrm{o_2} o 2 Finally, the addition of h3o+ will protonate the negatively charged carbon, resulting in the final product. Br2 (2 equiv) select to draw draw the starting structure that would produce this product under. Br2 (2 equiv) select to draw draw the starting structure that would produce this product under these conditions. Web 2na(s) + cl 2(g) → 2nacl(s) this reaction can also be classified as a redox reaction due to the changes in oxidation states. Web hbr (1 equiv) select to draw draw the product of this reaction. Draw a terminal alkene that. Br2 (2 equiv) select to draw draw the starting structure that would produce this product under these conditions. Sodium goes from a 0 to +1 oxidation state while chlorine goes from a 0 to a − 1 oxidation state. This problem has been solved! Web hbr (1 equiv) select to draw draw the product of this reaction. So, the product. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Web 2na(s) + cl 2(g) → 2nacl(s) this reaction can also be classified as a redox reaction due to the changes in oxidation states. Therefore, the product of this reaction is \textbf{nh3}. Web hbr (1 equiv) select to draw draw the product of this reaction. Web ignore any inorganic byproducts. Draw the major product of this reaction. Finally, the addition of h3o+ will protonate the negatively charged carbon, resulting in the final product. The product of this reaction is nh3. Br2 (2 equiv) select to draw draw the starting structure that would produce this product under these conditions. Draw a terminal alkene that would lead to this as the major product under these conditions. O 2 \mathrm{o_2} o 2 The balanced chemical equation for the reaction is:Solved Draw the product of this reaction. Ignore
Solved Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore

How do i solve this? Draw the product of this reaction. Ignore
[Solved] . Draw the product of this reaction. Ignore
Solved Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore
Solved Draw the product of this reaction. Ignore

draw the major product of this reaction. ignore byproducts
Solved Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore
[Solved] . Draw the product of this reaction. Ignore
Solved Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore
Sodium Goes From A 0 To +1 Oxidation State While Chlorine Goes From A 0 To A − 1 Oxidation State.
This Problem Has Been Solved!
So, The Product Of This Reaction Will Be A Molecule With Two.
Draw The Starting Structure That Would Lead To The Major Product Shown Under The Provided Conditions.
Related Post: