Drawing Histograms
Drawing Histograms - Web using a ruler, draw out the basic axes. The histogram above shows a frequency distribution for time to. These graphs take your continuous measurements and place them into ranges of values known as bins. Label the marks so that the scale is clear and give a name to the horizontal axis. Open the data and bins folder to add data and/or adjust your bins manually. In a histogram, the data is visualized in groups. Use the information in the table to draw a histogram. You can add as many as you like, mixing and matching types and arranging them into subplots. Type your data into columns in minitab. The histogram provides a visual representation of. Calculate the frequency density for each class interval. Bar heights are approximately as follows. Drawing and interpreting histograms features comparisons to bar charts and clear visual explanations. Choose a suitable scale to represent weights on the horizontal axis. The area of the bar represents the frequency, so to find the height of the bar, divide frequency by the class. If you have trouble making the right angle where the axes meet, go ahead and cheat: A bar’s height indicates the frequency of data points with a value within the corresponding bin. Choose a scale for the vertical axis that will accommodate the class with the highest frequency. Click on the + button above to add a trace. A histogram. These are the vertical and horizontal lines that form basic outline of the histogram. You will need to adjust the window yourself. When you draw the vertical line down the center of the histogram, and the two sides are identical in size and shape, the histogram is said to be symmetric. A histogram plots number of drives, versus driving distance,. Click “graph” and then click “histogram.”. Open the data and bins folder to add data and/or adjust your bins manually. If you have trouble making the right angle where the axes meet, go ahead and cheat: Make charts and dashboards online from csv or excel data. 2 n is the number of the value (no mathematical meaning). Count the number of data points that fall within each bin. This might range from test results to population distribution. Choose the type of histogram you want to make. You can add as many as you like, mixing and matching types and arranging them into subplots. Draw a bar for each interval so its height matches the number of drives. Web a histogram is a chart that plots the distribution of a numeric variable’s values as a series of bars. Bar heights are approximately as follows. Collect your data and decide on the number and size of bins (categories) you want to divide your data into. Histograms are very similar to bar graphs, but there are some differences. In most. This is the highest value in the range, subtracting the lowest. First we need to calculate the class width for each row. Bar heights are approximately as follows. Assume you get the following test scores: Drawing and interpreting histograms features comparisons to bar charts and clear visual explanations. Web a video explaining how to draw a histogram from a grouped frequency table suitable for gcse higher maths.exam question booklets:📝🔗exam question edexcel sty. A frequency histogram is a special graph that uses vertical columns to show frequencies (how many times each score. Web the process of making a histogram using the given data is described below: This might range. Web traces of various types like bar and line are the building blocks of your figure. First we need to calculate the class width for each row. Then draw the bars corresponding to each of the given weights using their frequencies. Type your data into columns in minitab. If you have trouble making the right angle where the axes meet,. Choose a suitable scale to represent the frequencies on the vertical axis. Taller bars show that more data falls in that range. Draw a bar for each interval so its height matches the number of drives in that interval. These graphs take your continuous measurements and place them into ranges of values known as bins. Draw a vertical line just. The area of the bar represents the frequency, so to find the height of the bar, divide frequency by the class. Make charts and dashboards online from csv or excel data. First we need to calculate the class width for each row. It is a type of bar chart that shows the frequency or number of observations within different numerical ranges, called bins. Web courses on khan academy are always 100% free. Each bin has a bar that represents the count or percentage of observations that fall within that bin. The histogram provides a visual representation of. Web histograms are a great way to show results of continuous data, such as: Then draw the bars corresponding to each of the given weights using their frequencies. In a histogram, the data is visualized in groups. A bar’s height indicates the frequency of data points with a value within the corresponding bin. Using histograms looks at calculating proportions of the population, including the median. Draw a bar for each interval so its height matches the number of drives in that interval. The vertical axis gives us the freque. Bar heights are approximately as follows. Remember that the horizontal axis represents the values of the variables.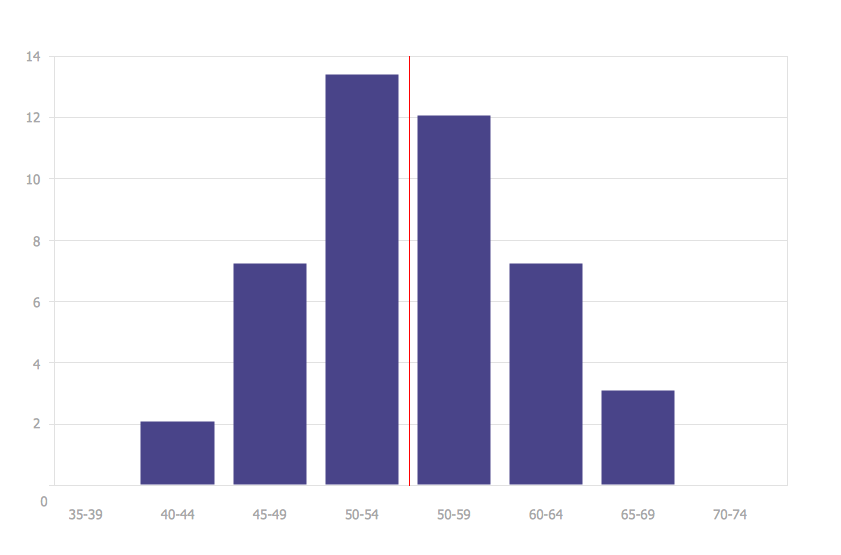
How To Draw a Histogram

How to make a Histogram with Examples Teachoo Histogram

3 Ways to Draw a Histogram wikiHow

What Is a Histogram? Expii
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Histogram2-3cc0e953cc3545f28cff5fad12936ceb.png)
How To Draw A Histogram By Hand

How To Draw A Histogram And Frequency Polygon
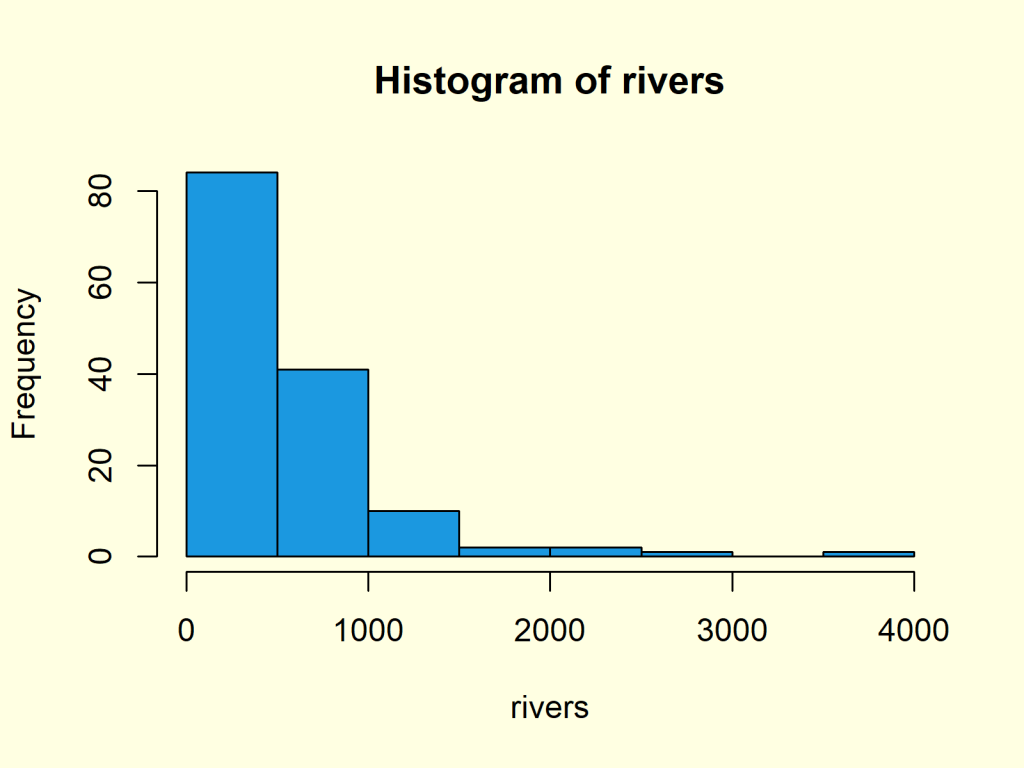
Create a Histogram in Base R (8 Examples) hist Function Tutorial
Best How To Draw A Histogram of all time The ultimate guide drawimages4

How to Draw a Histogram by Hand YouTube
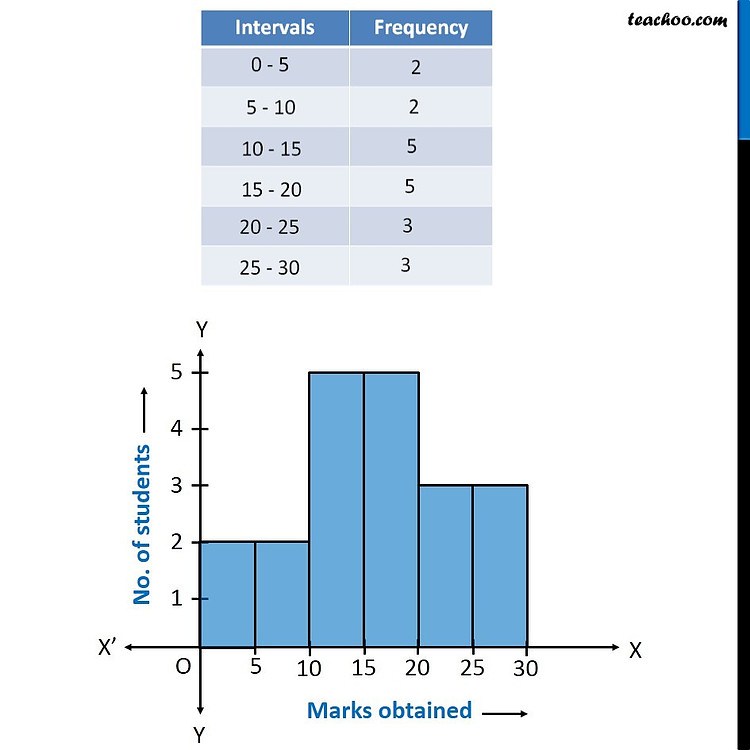
How to make a Histogram with Examples Teachoo Types of Graph
You Can Add As Many As You Like, Mixing And Matching Types And Arranging Them Into Subplots.
Draw A Vertical Line Just To The Left Of The Lowest Class.
You Will Need To Adjust The Window Yourself.
Open The Data And Bins Folder To Add Data And/Or Adjust Your Bins Manually.
Related Post: