Drawing Of Hydrogen Atom
Drawing Of Hydrogen Atom - Two hydrogen atoms can combine by donating each of their electrons into a single covalent bond, depicted on the right as the area where the gray clouds around each hydrogen atom overlap. Web since such a sphere or circle encloses most of (but not all) the electron density, it is about as close as one can come to drawing a boundary which encloses the atom. Explain the difference between the absorption spectrum and the emission spectrum of radiation. Its nucleus consists of a single proton (red) and no neutrons. The first step, however, is to teach them how to draw basic models of atoms. Web one carbon atom forms four covalent bonds with four hydrogen atoms by sharing a pair of electrons between itself and each hydrogen (h) atom. Quantum numbers for the first four shells. Increasing ease of removal of the hydrogen atom shown in bold) and justify your answer. Atomic hydrogen constitutes about 75% of the baryonic mass of the universe. In the covalent bond, the electron pair is shared between the two hydrogen atoms. Web the hydrogen atom (h) contains only one proton, one electron, and no neutrons. We all know that electrons in an atom or a molecule absorb energy and get excited, they jump from a lower energy level to a higher energy level, and they emit radiation when they come back to their original states. 5.5k views 8 years ago. The. The schrödinger wave equation for the hydrogen atom. The periodic table, electron shells, and orbitals. He described it as a positively charged nucleus, comprised of protons and neutrons, surrounded by a negatively charged electron cloud. The electronegativity value for carbon (c) and hydrogen (h) is 2.55 and 2.1 respectively, so the difference in their electronegativity values is only 0.45 (<0.5. Its nucleus consists of a single proton (red) and no neutrons. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the coulomb force. Web the hydrogen atom (h) contains only one proton, one electron, and no neutrons. Lithium is the first element in which an additional. E (. The most common element in the universe is hydrogen, a gas that makes up about 99% of the universe’s known mass 1. Bohr’s model of the hydrogen atom. Therefore, if we make a proton the size of the picture above, 1000 pixels across, then the electron orbiting this proton is located 50,000,000 pixels to the right (but could be found. 1), the most common isotope of the element hydrogen. Lithium is the first element in which an additional. We all know that electrons in an atom or a molecule absorb energy and get excited, they jump from a lower energy level to a higher energy level, and they emit radiation when they come back to their original states. Hydrogen is. Web figure 7.3.5 the emission spectra of elements compared with hydrogen. Web the electrons in an atom are arranged in shells that surround the nucleus, with each successive shell being farther from the nucleus. In the covalent bond, the electron pair is shared between the two hydrogen atoms. H ν = δ e = ( 1 n l o w. Web one carbon atom forms four covalent bonds with four hydrogen atoms by sharing a pair of electrons between itself and each hydrogen (h) atom. Distinguish between the bohr and schrödinger models of the atom. The diameter of a hydrogen atom is roughly 100,000 times larger than a proton. For \(e \geq 0\), the energy is a continuum, since the. Increasing ease of removal of the hydrogen atom shown in bold) and justify your answer. Niels bohr introduced the atomic hydrogen model in 1913. This can be determined using the atomic number and the mass number of the element (see the concept on atomic numbers and mass numbers). Bohr’s model of the hydrogen atom. He described it as a positively. By the end of this section, you will be able to: Web describe the hydrogen atom in terms of wave function, probability density, total energy, and orbital angular momentum. Bohr’s model of the hydrogen atom. Memorization over the winter break. These images show (a) hydrogen gas, which is atomized to hydrogen atoms in the discharge tube; Web elements are shown from atomic number 1 (hydrogen) up to 94 (plutonium). The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the coulomb force. Niels bohr introduced the atomic hydrogen model in 1913. Web a neutral hydrogen atom, shown left, contains one electron. Web the hydrogen atom. Quantum numbers for the first four shells. Bohr’s model of the hydrogen atom. Identify the physical significance of each of the quantum numbers ( n, l, m) of the hydrogen atom. Web solution for (a) arrange k to o in order of increasing acidity (i.e. The first step, however, is to teach them how to draw basic models of atoms. The electrons are thus equally. Hydrogen is the main component of stars, and a star is,. The electronegativity value for carbon (c) and hydrogen (h) is 2.55 and 2.1 respectively, so the difference in their electronegativity values is only 0.45 (<0.5 criteria); For \(e \geq 0\), the energy is a continuum, since the electron is in fact a free particle. Hydrogen is the most abundant of all elements in the universe. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the coulomb force. Distinguish between the bohr and schrödinger models of the atom. The quantum mechanical model of the atom. Web since such a sphere or circle encloses most of (but not all) the electron density, it is about as close as one can come to drawing a boundary which encloses the atom. Two hydrogen atoms can combine by donating each of their electrons into a single covalent bond, depicted on the right as the area where the gray clouds around each hydrogen atom overlap. 5.5k views 8 years ago.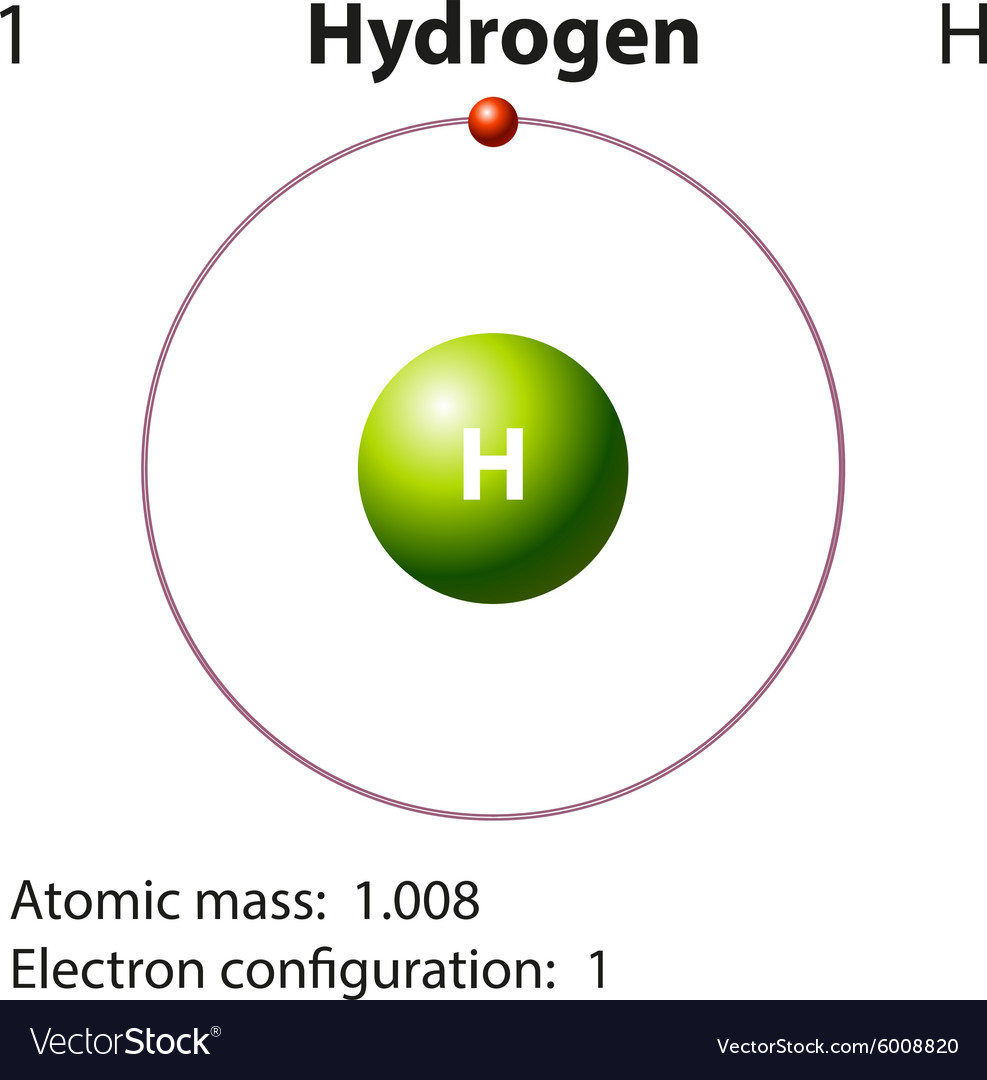
Diagram representation of the element hydrogen Vector Image

Hydrogen Molecule Diagram

How to Learn About the Chemistry of the Hydrogen Atom 12 Steps
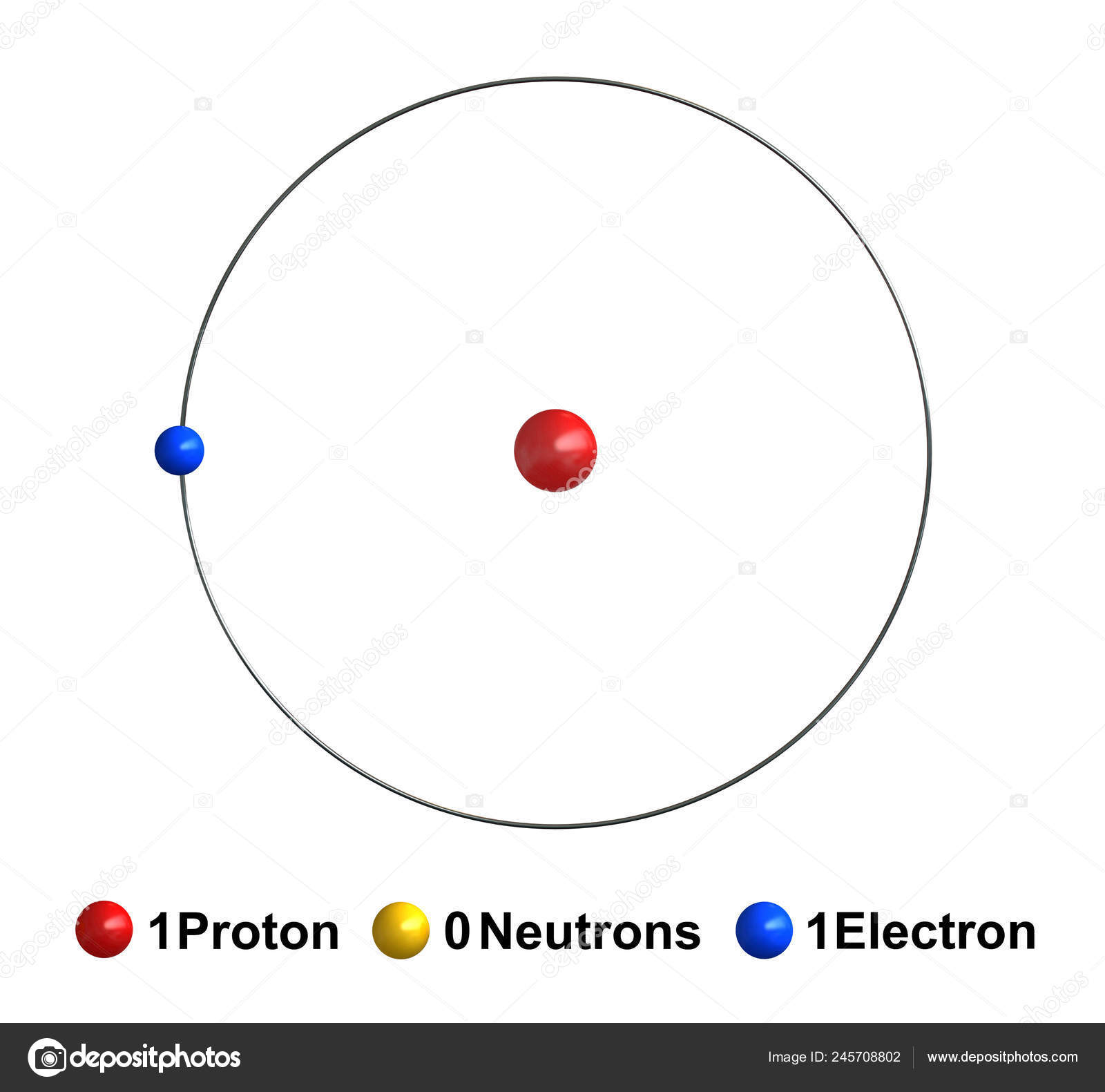
Render Atom Structure Hydrogen Isolated White Backgroun Stock Photo by
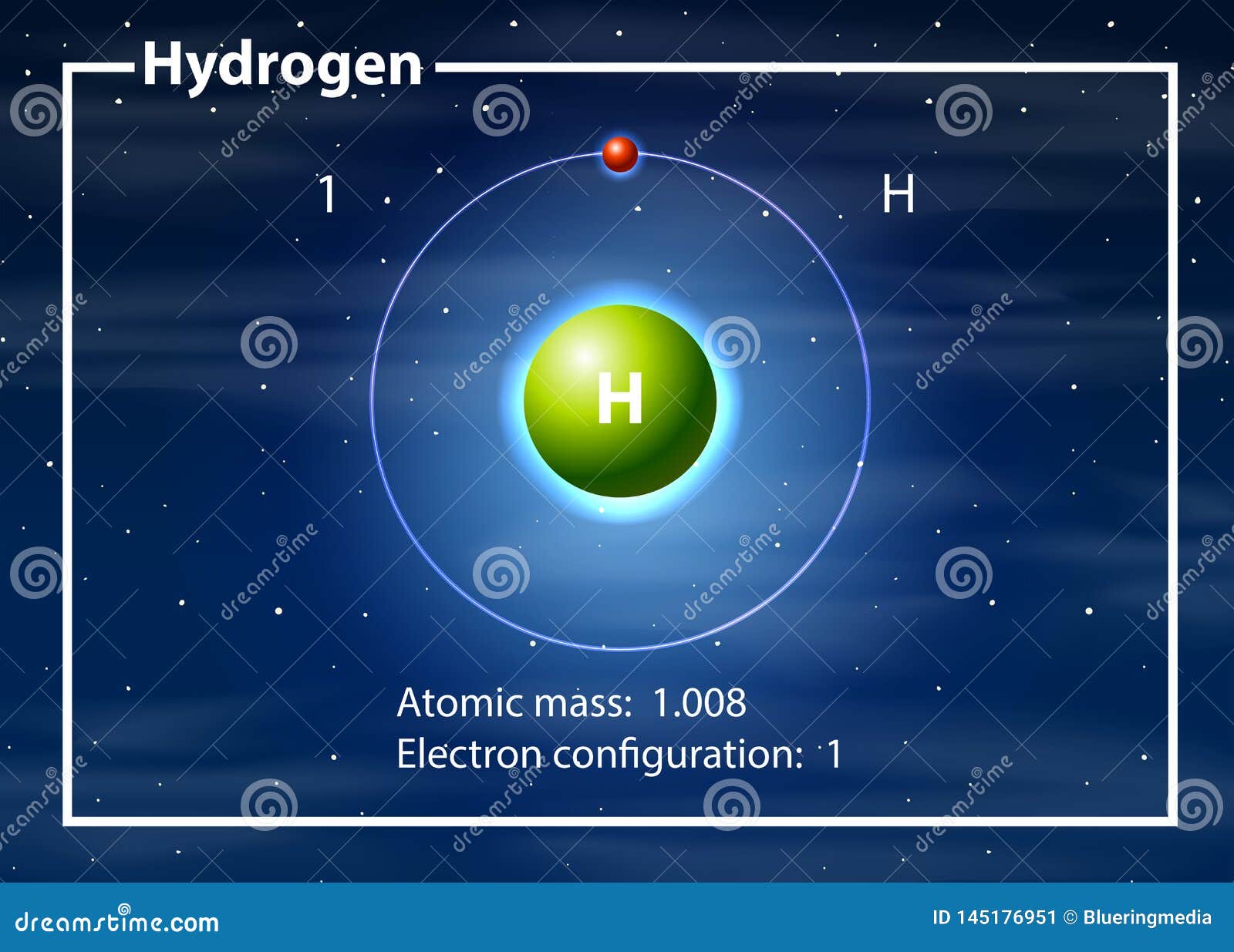
Hydrogen Atom Diagram Concept Stock Vector Illustration of abstract
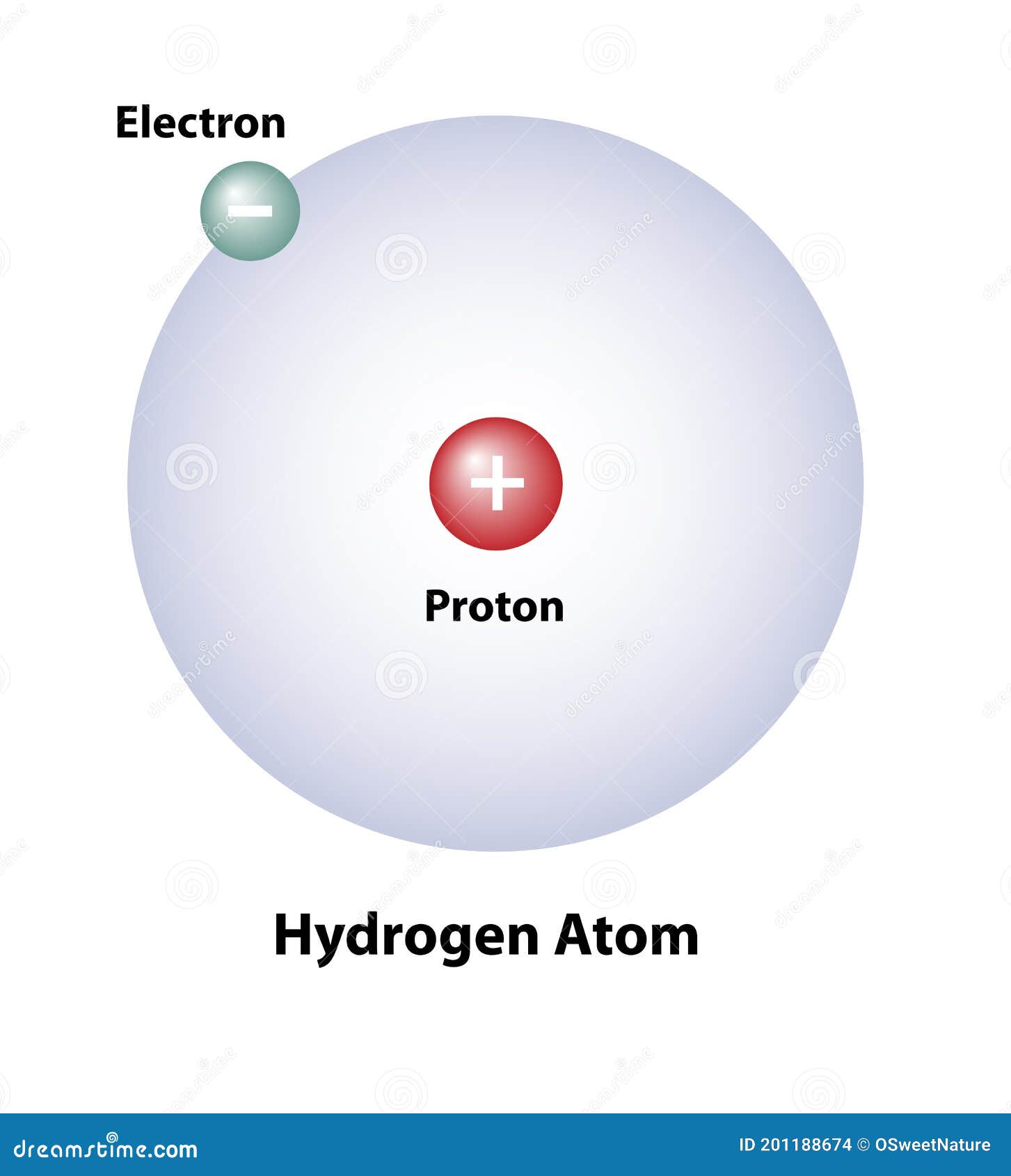
Molecular Structure of a Hydrogen Atom Stock Vector Illustration of

Hydrogen, atomic structure Stock Image C018/3682 Science Photo
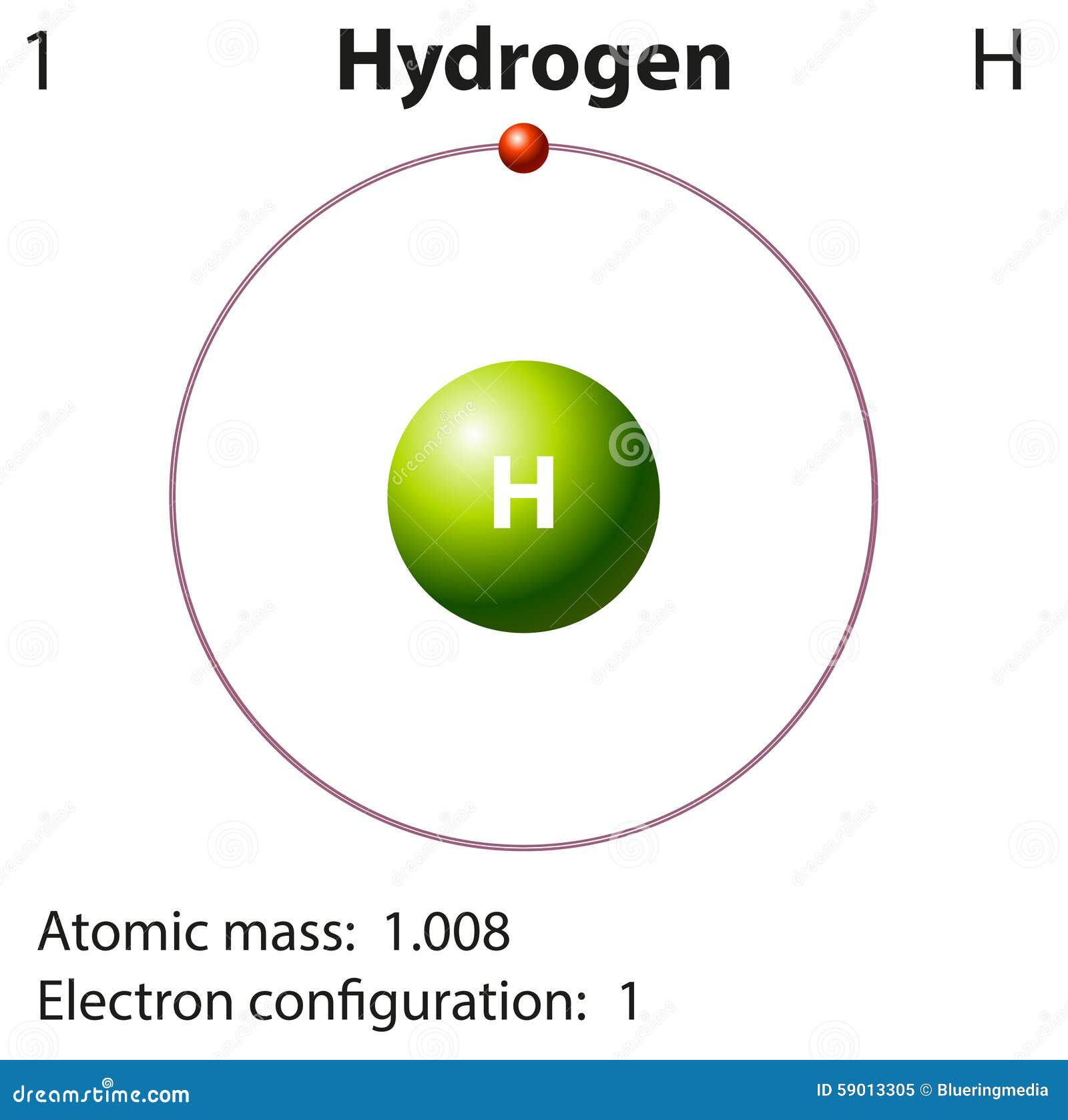
Diagram Representation Of The Element Hydrogen Stock Vector Image

Bohr Model Hydrogen Atom Electron Structure Stock Vector (Royalty Free

Hydrogen atom diagram concept illustration Stock Vector Image & Art Alamy
E ( N) = − 1 N 2 ⋅ 13.6 Ev.
Its Nucleus Consists Of A Single Proton (Red) And No Neutrons.
In The Covalent Bond, The Electron Pair Is Shared Between The Two Hydrogen Atoms.
Web The Electrons In An Atom Are Arranged In Shells That Surround The Nucleus, With Each Successive Shell Being Farther From The Nucleus.
Related Post: