Earth Layers Chart
Earth Layers Chart - Study of the physical history of the earth, its. Structure of the earth’s interior. Scale used by geologists used to divide the earth's 4.6 billion year history into units of time. By mechanical properties such as rheology, or chemically. Web the four layers of the earth are the inner core, outer core, mantle, and crust. Discover how scientists study them using earthquake waves, density, magnetism and more. Earth’s atmosphere has five major and several secondary layers. Web this animation by earthquide shows the layers by composition and by mechanical properties. The crust, the mantle, the outer core, and the inner core. Web earth's atmosphere is composed of a series of layers, each with its own specific traits. Explore the detailed layer model of. Structure of the earth’s interior. Web the four layers of the earth are the inner core, outer core, mantle, and crust. Web each layer has its own properties, composition, and characteristics that affects many of the key processes of our planet. Troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, and thermospherethe thermosphere is subdivided to include the ionosphere and. By mechanical properties such as rheology, or chemically. Earth’s atmosphere has five major and several secondary layers. Structure of the earth interactive diagram. Web as shown in the diagram, the earth's three primary layers consist of the crust, mantle, and core. Crust and lithosphere earth’s outer surface is its crust; Moving upward from ground level, these layers are called the troposphere, stratosphere,. Earth’s atmosphere has five major and several secondary layers. The planet, and the layer of gas round it, is alive in a geological sense. Explore how tectonic plates, earth's. Web earth's atmosphere is composed of a series of layers, each with its own specific traits. Scale used by geologists used to divide the earth's 4.6 billion year history into units of time. Diagram of the layers within earth’s atmosphere. Explore the detailed layer model of. By mechanical properties such as rheology, or chemically. Nomenclature cards (color & bw) print all these. See images and facts about each layer, from. Troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, and thermospherethe thermosphere is subdivided to include the ionosphere and the outer most layer that is. Mechanically, it can be divided into lithosphere,. Study of the physical history of the earth, its. Each layer has a unique chemical composition, physical. Study of the physical history of the earth, its. Crust and lithosphere earth’s outer surface is its crust; See images and facts about each layer, from. Web earth's atmosphere is composed of a series of layers, each with its own specific traits. In the layers of the earth diagram above, you can see each distinct layer is visually represented. Study of the physical history of the earth, its. Web learn about the four main layers of the earth (crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core) and their properties and characteristics. Explore the detailed layer model of. Discover how scientists study them using earthquake waves, density, magnetism and more. Explore how tectonic plates, earth's. The crust is the outermost layer and the layer humans are most. Explore the detailed layer model of. From lowest to highest, the. The planet, and the layer of gas round it, is alive in a geological sense. The structure of earth can be defined in two ways: Diagram of the layers within earth’s atmosphere. Web layers of the earth. Study of the physical history of the earth, its. Moving upward from ground level, these layers are called the troposphere, stratosphere,. From lowest to highest, the. Web the four layers of the earth are the inner core, outer core, mantle, and crust. Explore the detailed layer model of. The average thickness of the crust is about 35 km. Explore how tectonic plates, earth's. Scale used by geologists used to divide the earth's 4.6 billion year history into units of time. The average thickness of the crust is about 35 km. By mechanical properties such as rheology, or chemically. Earth’s atmosphere has five major and several secondary layers. In the layers of the earth diagram above, you can see each distinct layer is visually represented. Nomenclature cards (color & bw) print all these. The planet, and the layer of gas round it, is alive in a geological sense. Web learn about the four main layers of the earth (crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core) and their properties and characteristics. The structure of earth can be defined in two ways: Study of the physical history of the earth, its. From lowest to highest, the. See images and facts about each layer, from. Scale used by geologists used to divide the earth's 4.6 billion year history into units of time. Troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, and thermospherethe thermosphere is subdivided to include the ionosphere and the outer most layer that is. Web as shown in the diagram, the earth's three primary layers consist of the crust, mantle, and core. Moving upward from ground level, these layers are called the troposphere, stratosphere,. Web earth's atmosphere is composed of a series of layers, each with its own specific traits.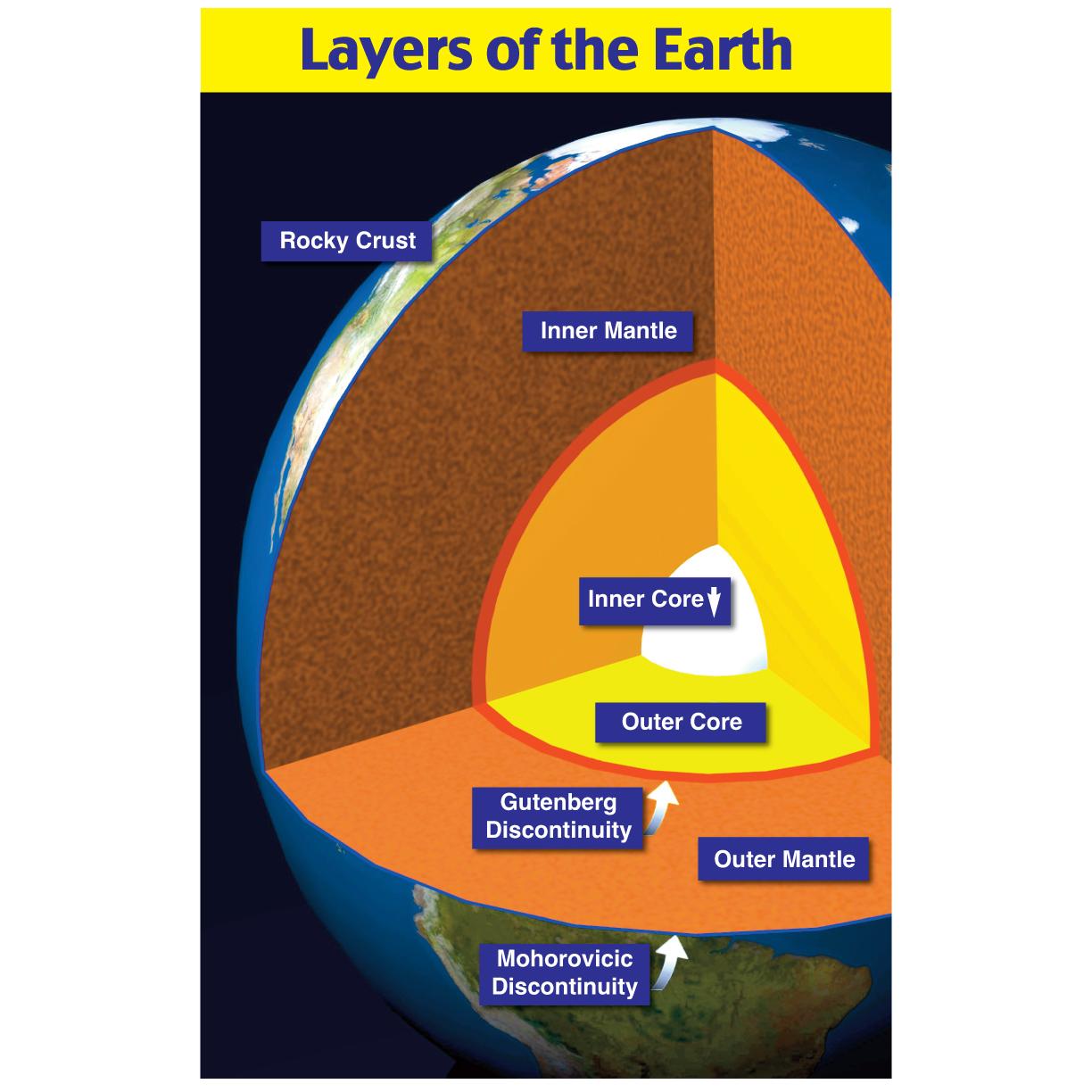
Layers of the Earth Educational Laminated Chart
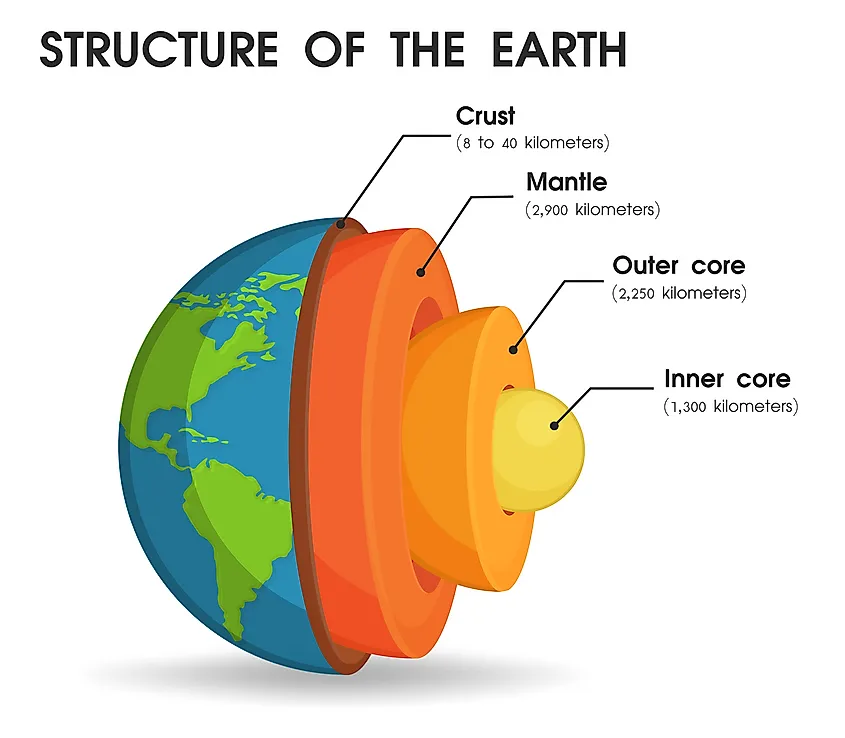
Earth WorldAtlas

Earth's interior Layers of the earth Geography4u read geography
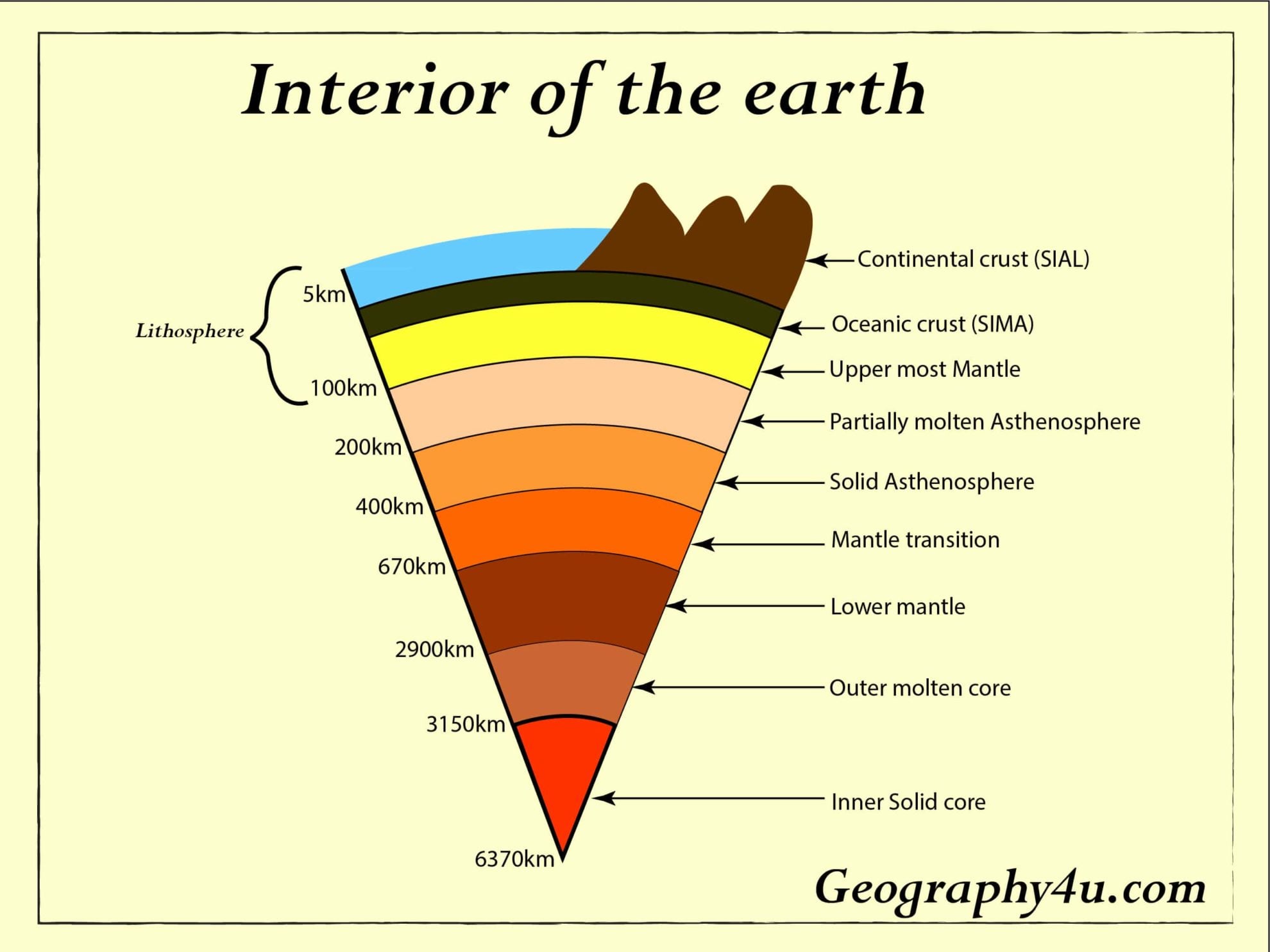
Earth's interior Layers of the earth Geography4u read geography

Earth's interior Layers of the earth Geography4u read geography
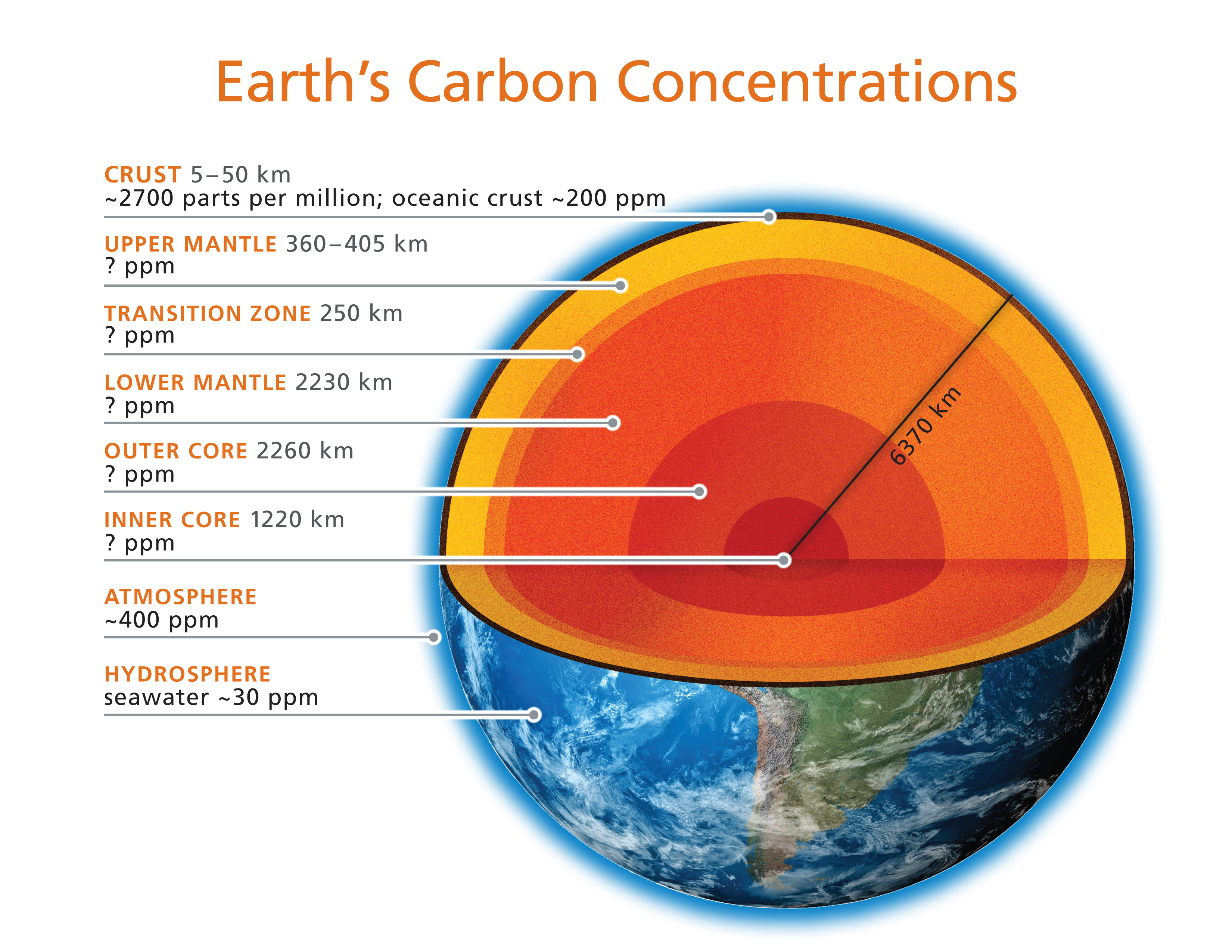
the structure of the earth. The relief — Steemkr
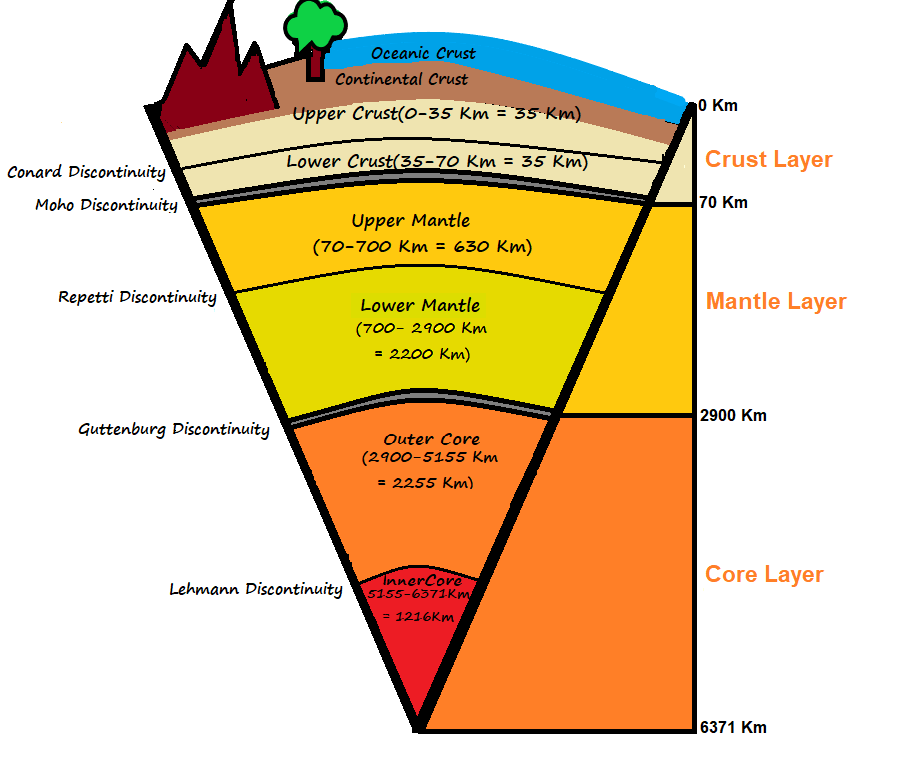
What are the layers of the earth
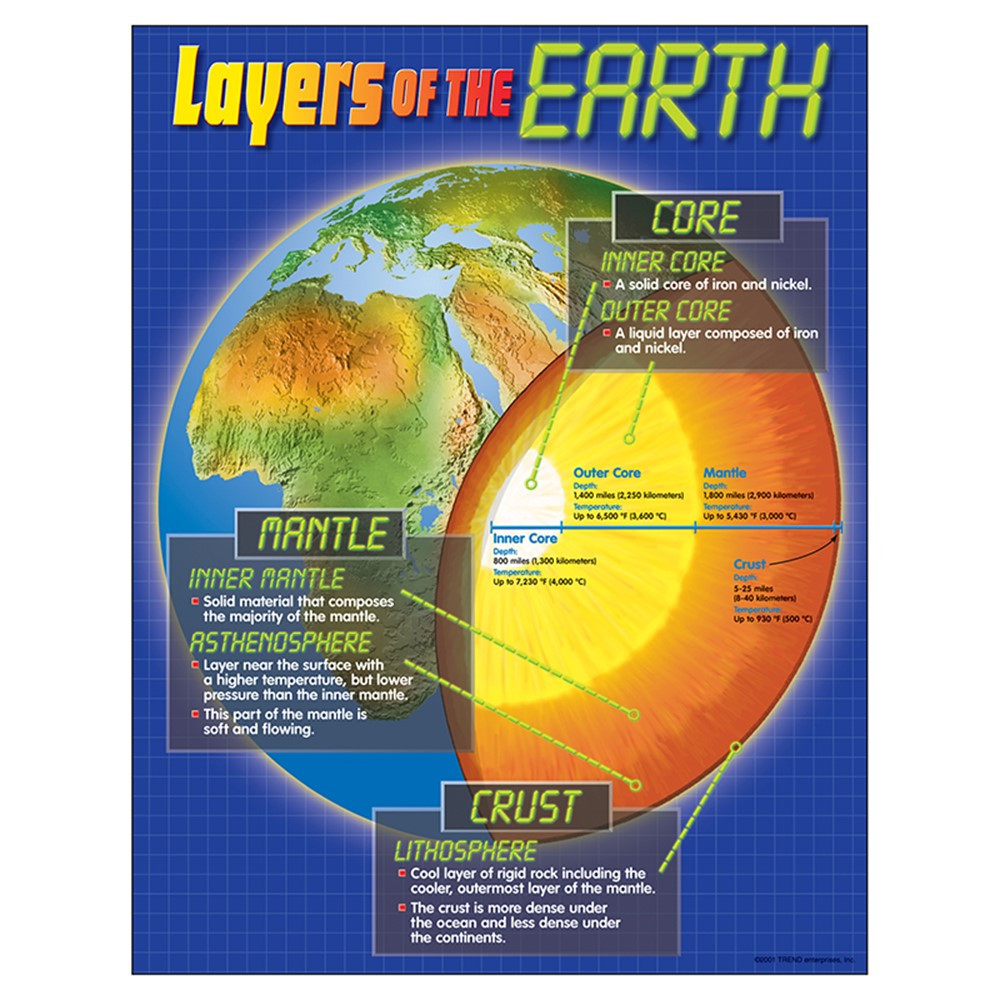
Layers of the Earth Learning Chart T38087 Trend Enterprises Inc.

Schematic showing and labeling earth layers Structure of the earth
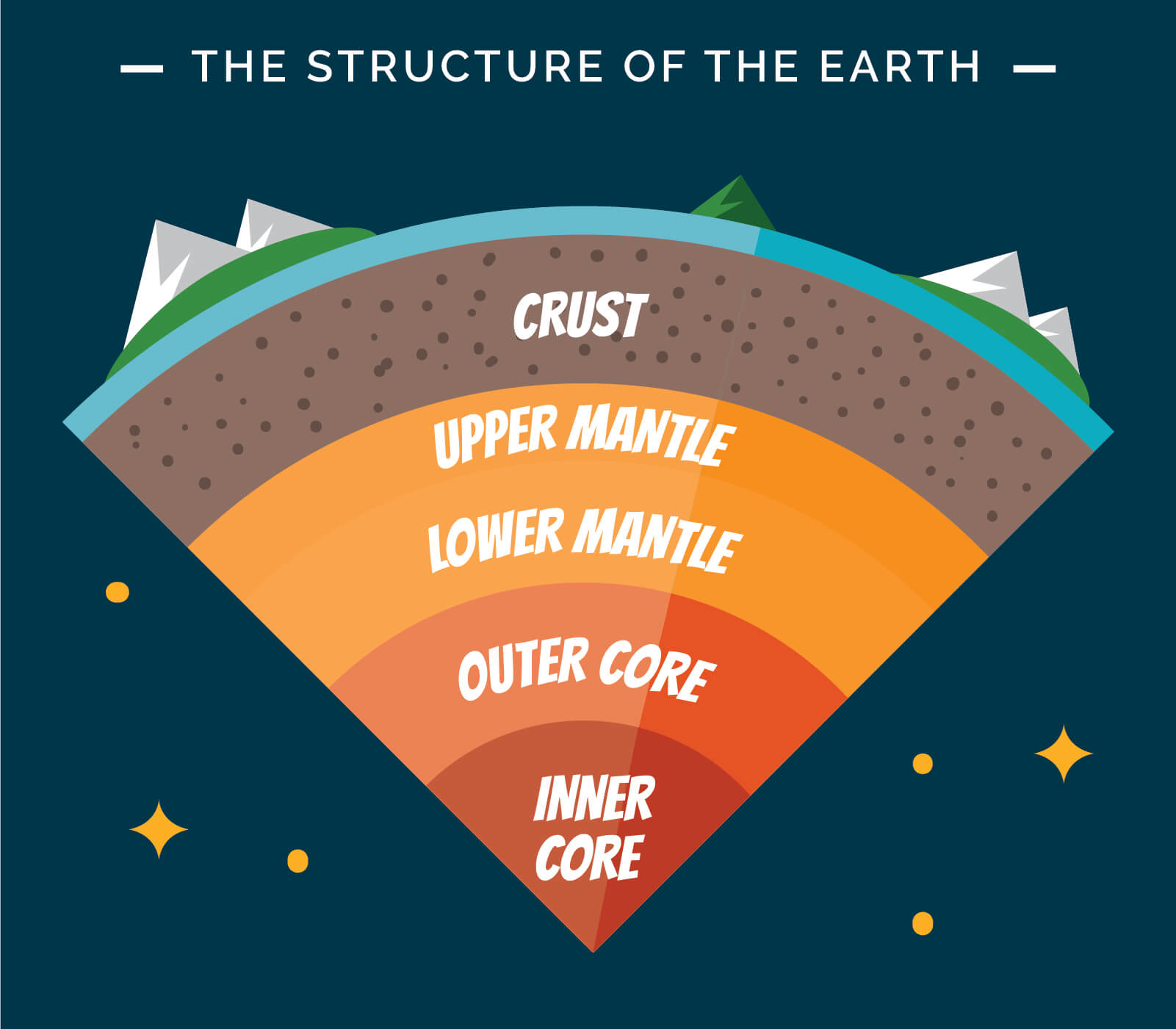
Structure of the earth infographic 217614 Vector Art at Vecteezy
Web The Structure Of The Earth Is Divided Into Four Major Components:
Web Layers Of The Earth.
The Crust Is The Outermost Layer And The Layer Humans Are Most.
Explore The Detailed Layer Model Of.
Related Post: