Electrocardiogram Drawing
Electrocardiogram Drawing - • describe ekg characteristics of atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, The interpretation algorithm presented below is easy to follow and it can be carried out by anyone. The greater the number of leads used, the more information the ecg provides. Web about the book. The electrocardiogram paper is a graph paper where for every five small (1 mm) squares you can find a heavier line forming a larger 5 mm square. Web • draw and label the normal ekg waveform, p to u and explain each part of the wave. Right axis deviation = qrs axis greater than +90°. This applet lets you draw a typical ecg, given information about blood pressure and volume at corresponding times in the cardiac cycle. With each beat, an electrical impulse (or “wave”) travels through the heart. Web a systematic approach to ecg interpretation: This electrical wave causes the muscle to squeeze and pump blood from the heart. The ecg must always be interpreted systematically. The pr interval is assessed in order to determine whether impulse conduction from the. Web ecg (ekg) waveform explained and labeled in only 4 minutes. The applet is divided into four zones, each corresponding to a different segment of. Web careful analysis of the ecg reveals a detailed picture of both normal and abnormal heart function and is an indispensable clinical diagnostic tool. Web an electrocardiogram (ecg or ekg) is a quick test to check the heartbeat. It is printed on grid paper called the ecg strip or ecg tracing. The interpretation algorithm presented below is easy to follow. It is simple test, a graphic record produced by an electrocardiograph provides details about one’s heart rate and rhythm and depicts if the heart has enlarged due to hypertension or evidence of myocardial infarction (if any). Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. Web drawing of the ekg, with labels. The interpretation algorithm presented below is easy to follow and it can be carried out by anyone. • describe ekg characteristics of atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, Web electrocardiogram (ecg) an electrocardiogram (ecg) is a graphic representation of the electrical activity of the heart plotted against time. The standard electrocardiograph uses 3, 5, or 12 leads. Electrocardiograms are simple, inexpensive, noninvasive,. Ecg machines can be found in medical offices, hospitals, operating rooms and ambulances. Web ecg (ekg) waveform explained and labeled in only 4 minutes. Luckily, it is almost always possible to draw conclusions about the conduction system based on the visible ecg waveforms and rhythm. Web electrocardiogram (ecg) an electrocardiogram (ecg) is a graphic representation of the electrical activity of. Web drawing of the ekg, with labels of intervals p=p wave, pr=pr segment, qrs=qrs complex, qt=qt interval, st=st segment, t=t wave. Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. Web electrocardiogram (ecg) an electrocardiogram (ecg) is a graphic representation of the electrical activity of the heart plotted against time. Web (usmle. • discuss how different leads represent the heart. Electrocardiogram of a healthy man, 21 years old. Electrocardiogram, commonly known as ecg or ekg is a medical test report indicating the heart’s electrical activity and rhythm during repeated cardiac cycles. It is printed on grid paper called the ecg strip or ecg tracing. • outline 9 steps in interpreting the ekg. In 1902, the dutch physician einthovan invented ecg, and his tremendous input in clinical. The word ecg derives from the german language. The applet is divided into four zones, each corresponding to a different segment of the ecg. Note that in paediatric ecg interpretation, the cardiac axis lies between +30 to +190 degrees at birth and moves leftward with age.. Elektrokardiogram człowieka zdrowego (mężczyzna, lat 21), na wydruku zaznaczony jest wdech i wydech. When performing ecg / ekg interpretation and analyzing heart rhythms, it is important to know the. The interpretation algorithm presented below is easy to follow and it can be carried out by anyone. Some personal devices, such as. The term “lead” may be used to refer to. Web an electrocardiogram (ecg or ekg) is a quick test to check the heartbeat. Find more information about electrocardiography: The word ecg derives from the german language. It records the electrical signals in the heart. Web an ecg is used to check how the heart is functioning. When performing ecg / ekg interpretation and analyzing heart rhythms, it is important to know the. Web electrocardiogram (ecg) is defined as a recording of the heart’s electrical activity. Click on the screen where. It mainly records how often the heart beats (heart rate) and how regularly it beats ( heart rhythm ). It is printed on grid paper called the ecg strip or ecg tracing. The interpretation algorithm presented below is easy to follow and it can be carried out by anyone. • outline 9 steps in interpreting the ekg. The standard electrocardiograph uses 3, 5, or 12 leads. Adhesive electrodes are affixed to the skin surface allowing measurement of cardiac impulses from many angles. The greater the number of leads used, the more information the ecg provides. Failure to perform a systematic interpretation of the ecg may be detrimental. Web an ecg is used to check how the heart is functioning. With each beat, an electrical impulse (or “wave”) travels through the heart. Web careful analysis of the ecg reveals a detailed picture of both normal and abnormal heart function and is an indispensable clinical diagnostic tool. • describe ekg characteristics of atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, Some personal devices, such as.
The Electrocardiogram explained What is an ECG?

A Basic Guide to ECG/EKG Interpretation First Aid for Free
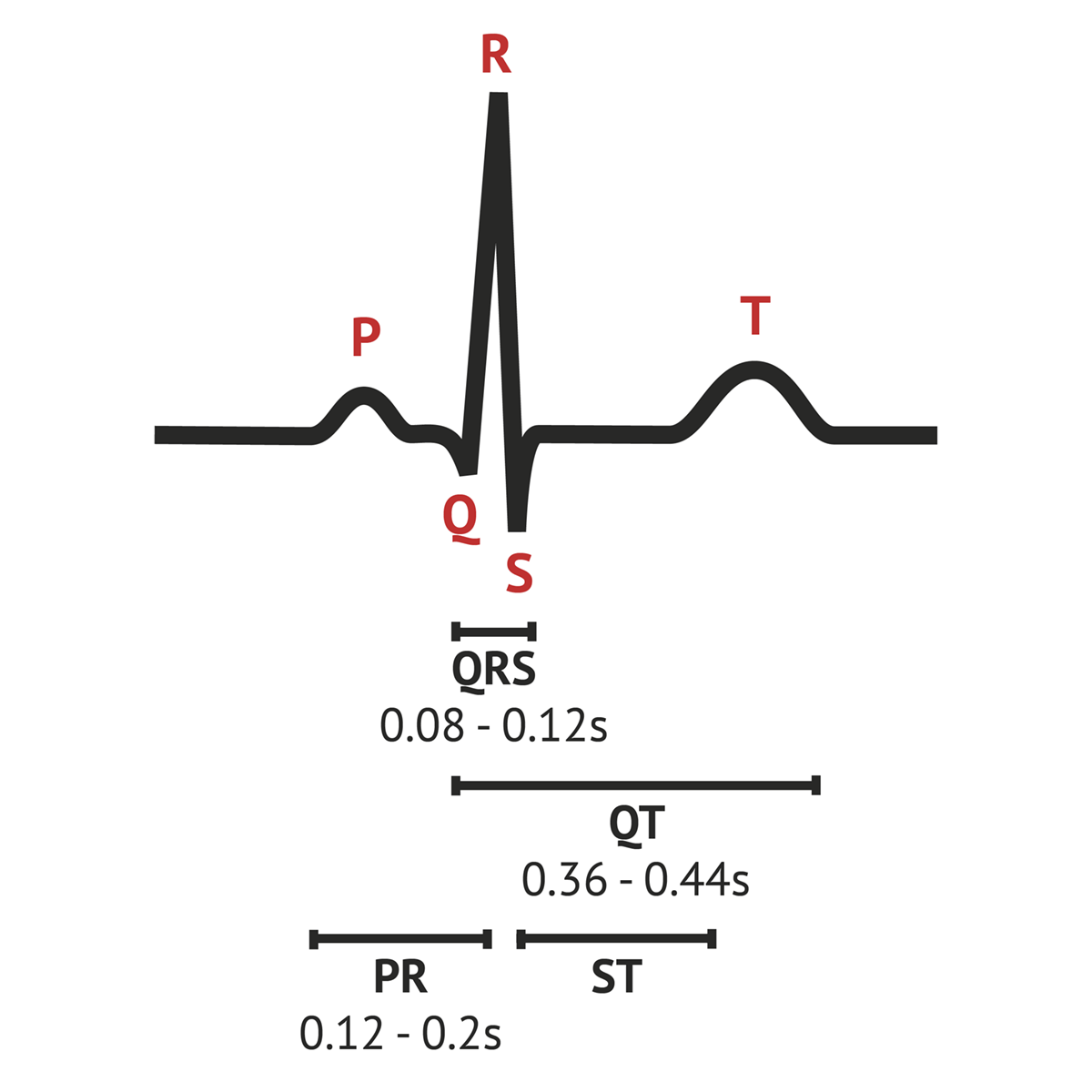
The Normal ECG Trace ECG Basics MedSchool
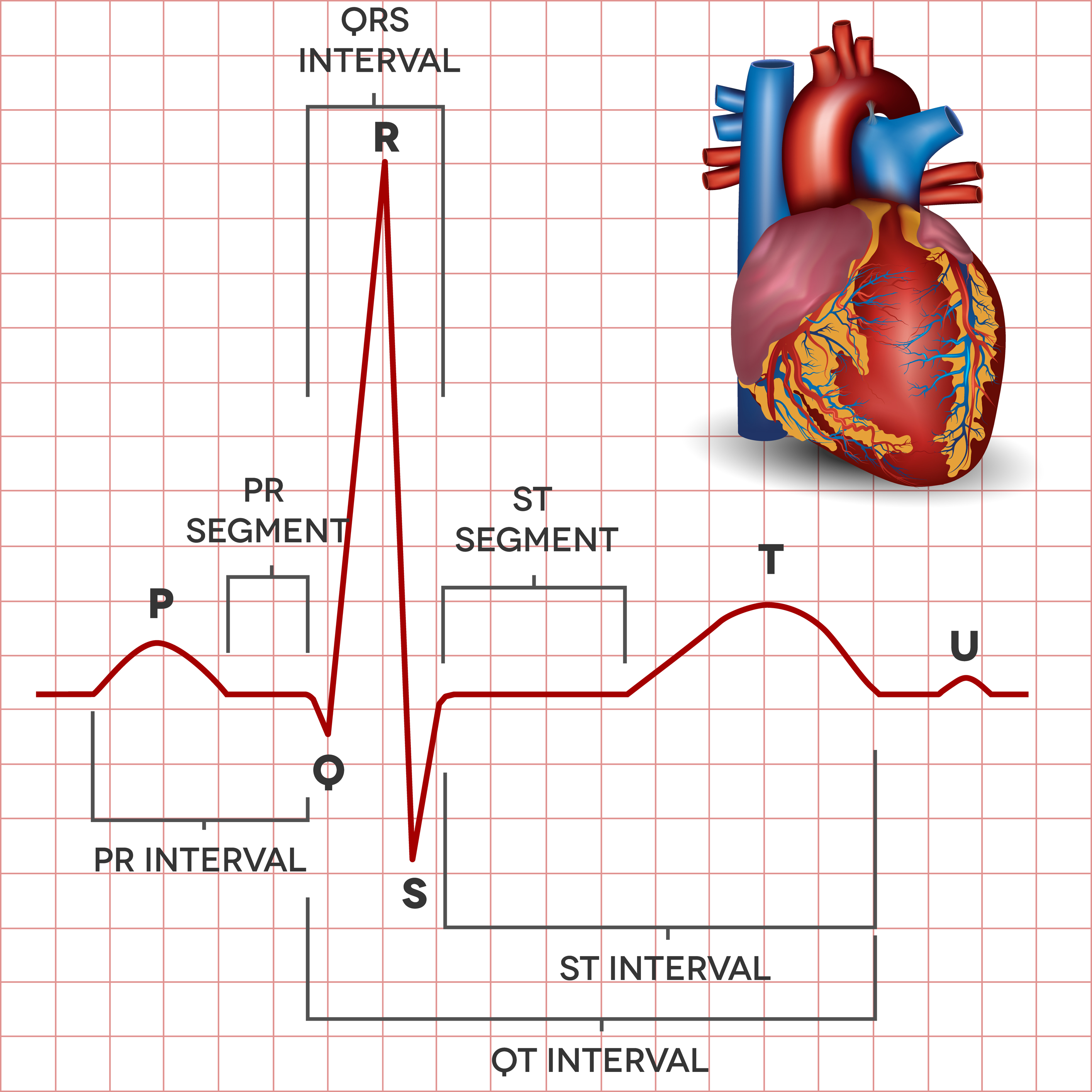
The Electrocardiogram explained What is an ECG?

5Lead ECG Interpretation (Electrocardiogram) Tips for Nurses FRESHRN

Normal electrocardiogram tracing Waves, intervals and segments

Diagram of Standard ECG How to draw Heart Beat Biology Diagram

HOW TO DRAW AN ECG. TRACE HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY BODY FLUIDS AND
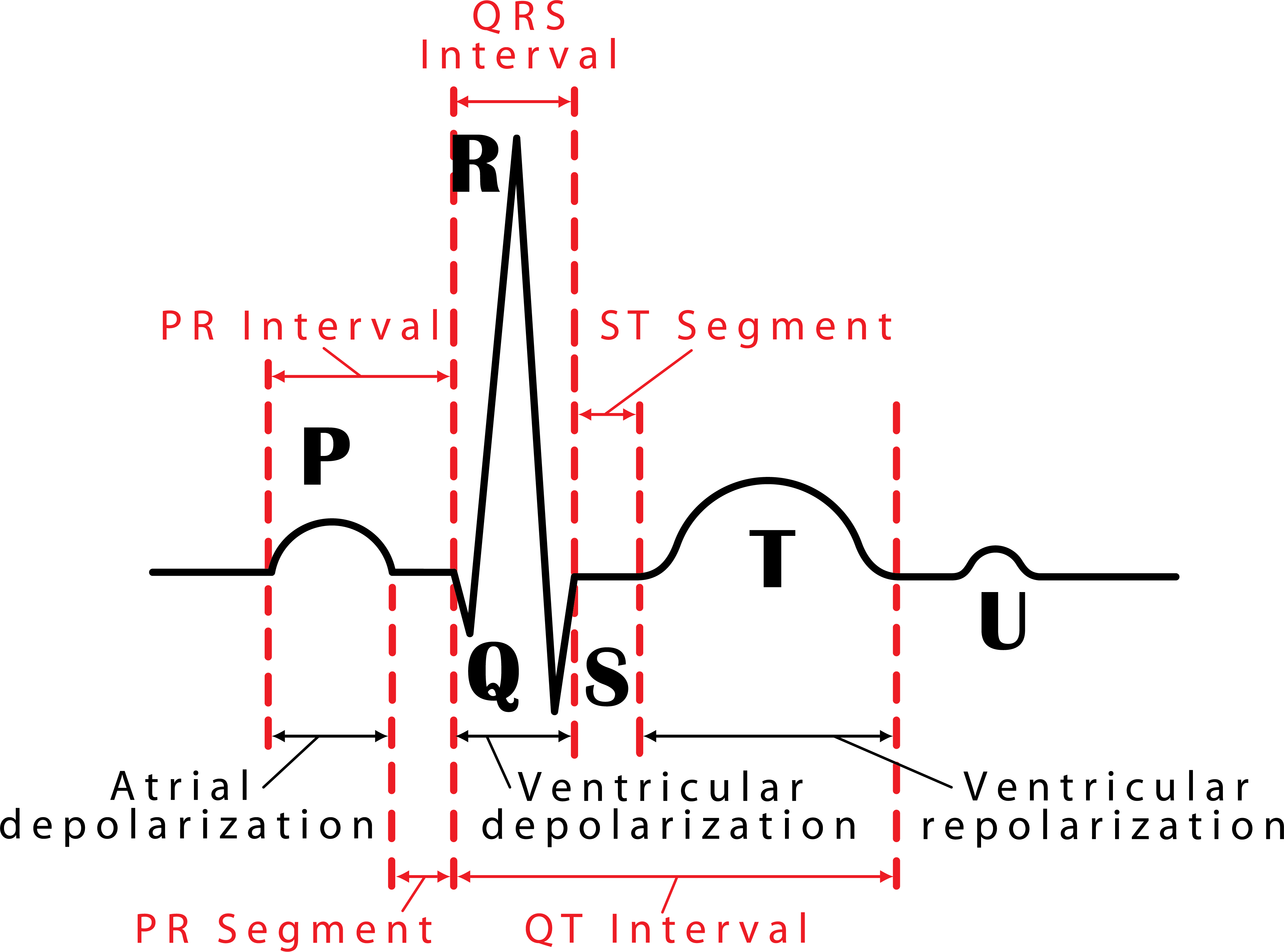
048 How to Read an Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) Interactive Biology
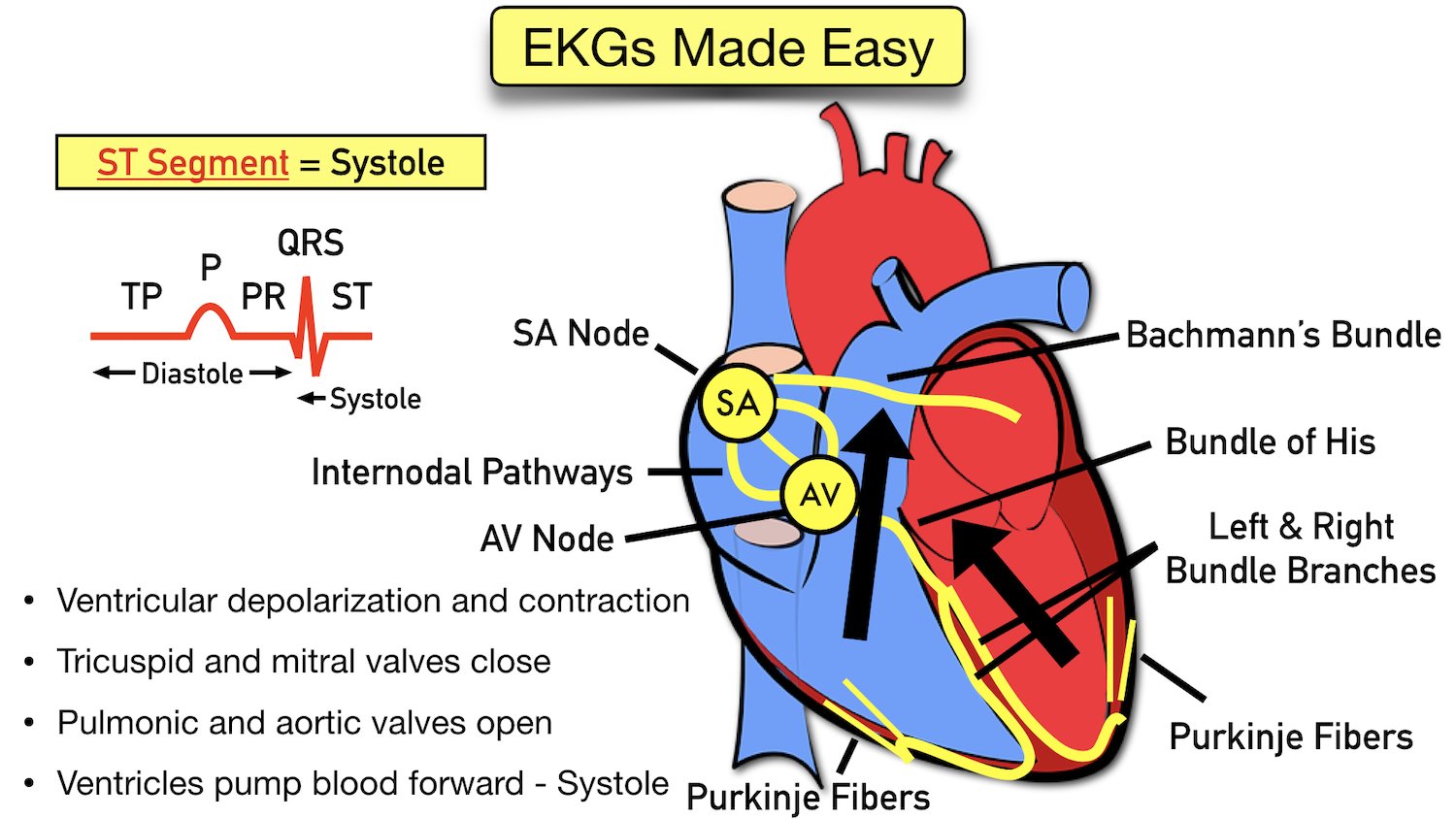
ECG Waveform Explained EKG Labeled Diagrams and Components — EZmed
Test Results Can Help Diagnose Heart Attacks And Irregular Heartbeats, Called Arrhythmias.
Find More Information About Electrocardiography:
Right Axis Deviation = Qrs Axis Greater Than +90°.
Electrocardiograms Are Simple, Inexpensive, Noninvasive, And Readily Obtained.
Related Post: