Element Radius Chart
Element Radius Chart - Elements in the periodic table are organized into periods and groups. Click on radio button atomic radius. Web the periodic table of the elements by webelements. Pdf without crop marks | pdf with crop marks. Slater are an empirical set of atomic radii derived by the careful comparison of bond lengths in over 1200 bond types in ionic, metallic, and covalent crystals and molecules (reference 1). Web the simplest answer is that potassium has higher valence energy level (energy level 4) than lithium (energy level 2), which has greater distance from the nuclear thus has bigger radius. The relative size of the atoms follows a set of trends on the periodic table. Web the atomic radius of a chemical element is the distance from the center of the nucleus to the outermost shell of an electron. 1 å = 1 × 10−10 m = 100 pm. Many references give table of atomic radii. Web click on periodic table push button. The relative size of the atoms follows a set of trends on the periodic table. This special periodic table shows the relative size of atoms of periodic table elements based on atomic radius data. If the two atoms are of the same kind, then the covalent radius is simply one half of the. Web the latest release of the periodic table (dated 4 may 2022) includes the most recent abridged standard atomic weight values released by the iupac commission on isotopic abundances and atomic weights ( ciaaw ), compiled as part of the 2021 table of standard atomic weights 2021. Sometimes in text books and other sources, the rather vague term atomic radius. Many references give table of atomic radii. Going across a period, the main group elements tend to decrease in atomic radius due to the increased nuclear charge. In general, atomic radius or atom size decreases as you move from left to right. This atomic radius (calculated) table gives the atomic radius (calculated) of all the elements of periodic table in. Explore the chemical elements through this periodic table. Web the periodic table of the elements by webelements. Web the latest release of the periodic table (dated 4 may 2022) includes the most recent abridged standard atomic weight values released by the iupac commission on isotopic abundances and atomic weights ( ciaaw ), compiled as part of the 2021 table of. These values derived by j.c. Web explore how atomic radius changes with atomic number in the periodic table of elements via interactive plots. Pdf without crop marks | pdf with crop marks. Going across a period, the main group elements tend to decrease in atomic radius due to the increased nuclear charge. Web atomic radii (clementi) gallery of images. In general, atomic radius or atom size decreases as you move from left to right. These values derived by j.c. Web this table shows how the atom size, and atomic radius values change as you move horizontally and vertically across the periodic table. This special periodic table shows the relative size of atoms of periodic table elements based on atomic. Below mentioned radii are the van der waals radius in picometer (pm)). Web the covalent atomic radius (r cov) is half the internuclear distance in a molecule with two identical atoms bonded to each other, whereas the metallic atomic radius (r met) is defined as half the distance between the nuclei of two adjacent atoms in a metallic element. Slater. Visualize trends, 3d orbitals, isotopes, and mix compounds. Pdf without crop marks | pdf with crop marks. The relative size of the atoms follows a set of trends on the periodic table. This special periodic table shows the relative size of atoms of periodic table elements based on atomic radius data. Click on radio button atomic radius. The periodic table is an arrangment of the chemical elements ordered by atomic number so that periodic properties of the elements (chemical periodicity) are made clear. The relative size of the atoms follows a set of trends on the periodic table. Slater are an empirical set of atomic radii derived by the careful comparison of bond lengths in over 1200. Web the simplest answer is that potassium has higher valence energy level (energy level 4) than lithium (energy level 2), which has greater distance from the nuclear thus has bigger radius. Web the periodic table of the elements (including atomic radius) element name. When clicking the radio button (3) the atomic radius of all the elements will be viewed simultaniously. Atoms consist of a nucleus with positively charged protons and neutral neutrons surrounded by shells of electrons. Look up chemical element names, symbols, atomic masses and other properties, visualize trends, or even test your elements knowledge by playing a periodic table game! This is due to the way electrons form shells around the nucleus. (a) the covalent atomic radius, rcov, is half the distance between the nuclei of two like atoms joined by a covalent bond in the same molecule, such as cl 2. This atomic radius (calculated) table gives the atomic radius (calculated) of all the elements of periodic table in pm. Web click on periodic table push button. How many electrons are filled out in each subshell? Many references give table of atomic radii. When clicking the radio button (3) the atomic radius of all the elements will be viewed simultaniously in the text fields located above the symbols. Web the periodic table of the elements (including atomic radius) element name. Web the covalent atomic radius (r cov) is half the internuclear distance in a molecule with two identical atoms bonded to each other, whereas the metallic atomic radius (r met) is defined as half the distance between the nuclei of two adjacent atoms in a metallic element. 1 å = 1 × 10−10 m = 100 pm. If the two atoms are of the same kind, then the covalent radius is simply one half of the bond length. Atomic radius is the measure of the distance from the centre of the nucleus to the outer electron. Web explore how atomic radius changes with atomic number in the periodic table of elements via interactive plots. Web the periodic table contains nist’s latest critically evaluated data for atomic properties of the elements.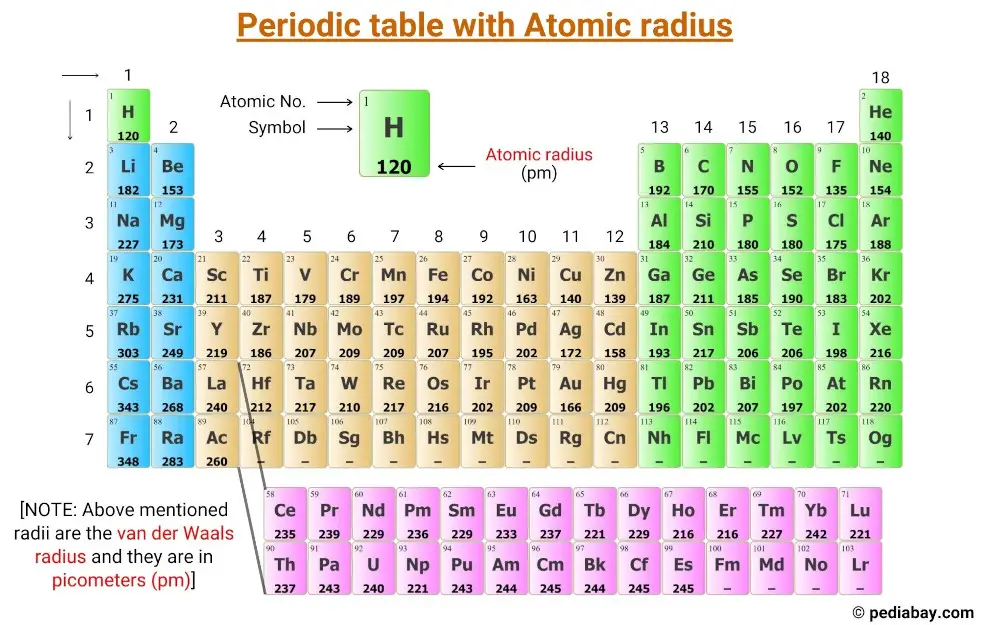
Atomic Radius of Elements (With Periodic table Chart) Pediabay

Atomic Radius of Elements

Elements, Atomic Radii and the Periodic Radii
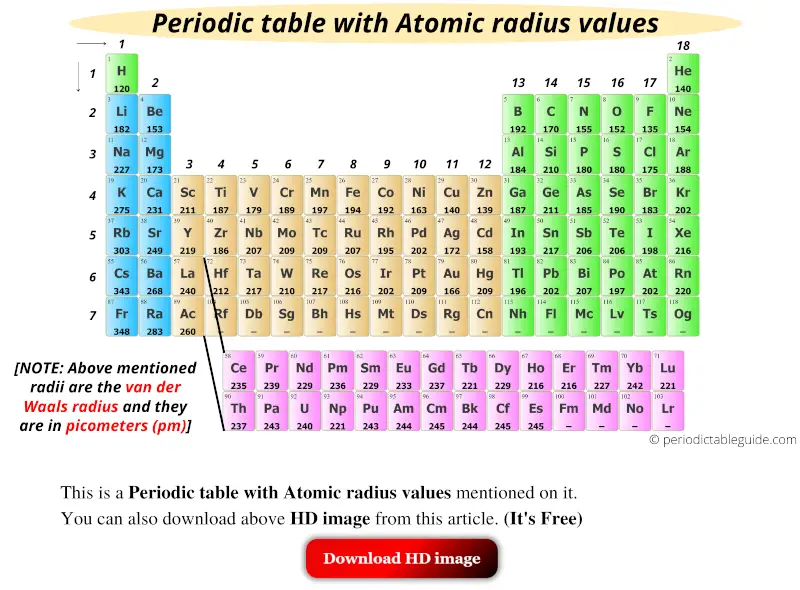
Get the Periodic table with Atomic radius values (Img+Chart)

Atomic Radius and Ionic Radius

This periodic table chart shows the relative sizes of each element
.png)
Periodic Table Of The Elements Atomic Radius vrogue.co
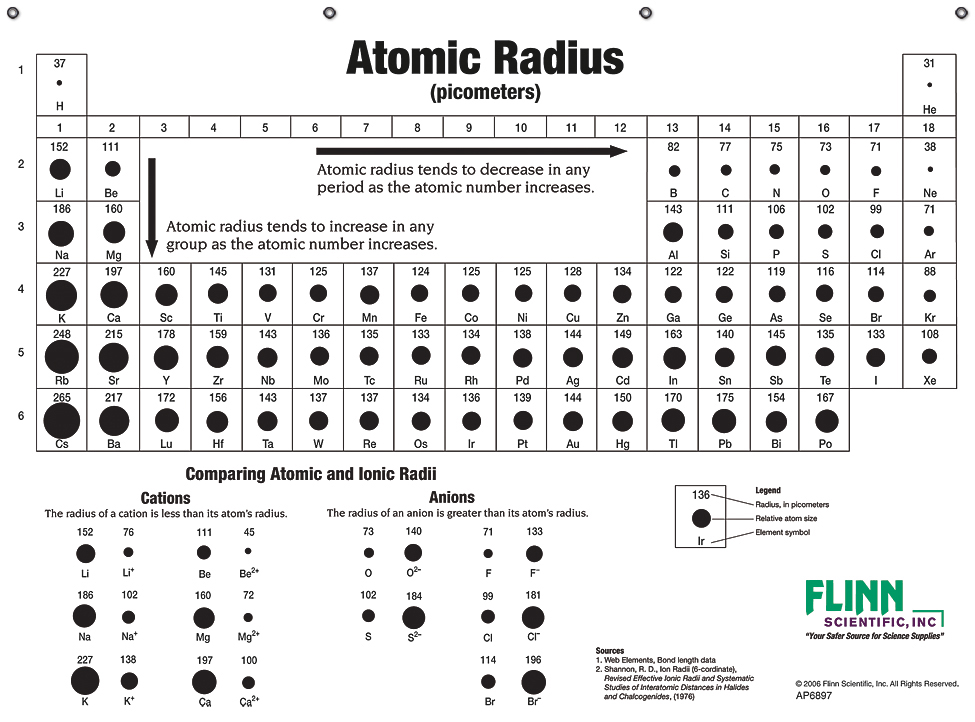
Atomic Sizes and Radii Charts for Chemistry
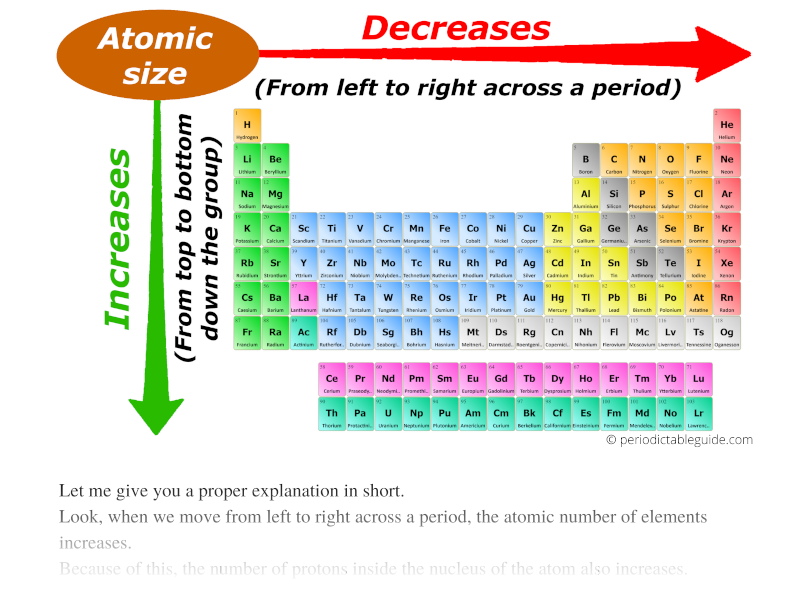
Periodic Table Showing Atomic Radius

Atomic Radius of Elements The Periodic Table
Web The Atomic Radius Of A Chemical Element Is A Measure Of The Size Of Its Atom, Usually The Mean Or Typical Distance From The Center Of The Nucleus To The Outermost Isolated Electron.
Web The Atomic Radius Of A Chemical Element Is The Distance From The Center Of The Nucleus To The Outermost Shell Of An Electron.
Slater Are An Empirical Set Of Atomic Radii Derived By The Careful Comparison Of Bond Lengths In Over 1200 Bond Types In Ionic, Metallic, And Covalent Crystals And Molecules (Reference 1).
Web The Simplest Answer Is That Potassium Has Higher Valence Energy Level (Energy Level 4) Than Lithium (Energy Level 2), Which Has Greater Distance From The Nuclear Thus Has Bigger Radius.
Related Post: