Eye Anatomical Chart
Eye Anatomical Chart - Anatomy and physiology of the eye. The outermost layer, known as the fibrous tunic , is composed of the cornea and sclera , which provide shape to the eye and support the deeper structures. Web human eye, specialized sense organ in humans that is capable of receiving visual images, which are relayed to the brain. Read an overview of general eye anatomy to learn how the parts of the eye work together. It is responsible for producing fine detail in central vision, the part you use when you look directly at something. The chart covers general anatomy of the eye with colorful detailed renderings all fully labeled. Web here are descriptions of some of the main parts of the eye: Each photoreceptor is linked to a nerve fiber. Below, find an explanation of each anatomical part from the above video with physiologic and pathologic correlates. The macula is a small highly sensitive part of the retina. It contains the fovea, the area of your eye which produces the sharpest images of all. Web the optic nerve carries signals of light, dark, and colors to a part of the brain called the visual cortex, which assembles the signals into images and produces vision. The opening in the middle of the iris through which light passes to the. Anatomy warehouse provides a comprehensive selection of human eye models and charts, each displaying the inner structures of the eye. Ein problem mit diesem produkt melden. They are placed within the orbits, two cavities in the upper face, in the anterior surface of the head. Web the eye is made up of three coats, or layers, enclosing various anatomical structures.. The pupil is the opening at the center of the iris. Anatomy and physiology of the eye. Abhängig von der lieferadresse kann die ust. The nerve fibers from the photoreceptors are bundled together to form the optic nerve. Anatomical eye models and charts for optometrists and patient education. Mandy helton bas, rvtg, vts(ecc) function of the eye. The iris is the colored part of the eye that regulates the amount of light entering the eye. Web read on for a basic description and explanation of the structure (anatomy) of your eyes and how they work (function) to help you see clearly and interact with your world. Ein problem. The iris is the colored part of the eye that regulates the amount of light entering the eye. The anatomy of the eye includes auxiliary structures, such as the bony eye socket and extraocular muscles, as well as the structures of the eye itself, such as the lens and the retina. The back part of the eye's interior. Web overview. Web selecting or hovering over a box will highlight each area in the diagram. The macula is a small highly sensitive part of the retina. Web eye anatomy (16 parts of the eye & what they do) the following are parts of the human eyes and their functions: They are placed within the orbits, two cavities in the upper face,. The cornea is the clear outer part of the eye’s focusing system located at the front of the eye. Größe 50,8 x 66 cm. Web the eye is made up of three coats, or layers, enclosing various anatomical structures. Web human eye, specialized sense organ in humans that is capable of receiving visual images, which are relayed to the brain.. These citations have been automatically generated based on the information we have and it may not be 100% accurate. The lens is a clear part of the eye behind the iris that helps to The iris adjusts the size of the pupil and controls the amount of light that can enter the eye. Ein problem mit diesem produkt melden. The. They are placed within the orbits, two cavities in the upper face, in the anterior surface of the head. Here is a tour of the eye starting from the outside, going in through the front and working to the back. Web to understand the diseases and conditions that can affect the eye, it helps to understand basic eye anatomy. This. The anatomy of the eye includes auxiliary structures, such as the bony eye socket and extraocular muscles, as well as the structures of the eye itself, such as the lens and the retina. The outermost layer, known as the fibrous tunic , is composed of the cornea and sclera , which provide shape to the eye and support the deeper. Web 6 min read. Web the eye is made up of three coats, or layers, enclosing various anatomical structures. A diagram to learn about the parts of the eye and what they do. The lens is a clear part of the eye behind the iris that helps to Reflexes produced by the streak retinoscope. Web the optic nerve carries signals of light, dark, and colors to a part of the brain called the visual cortex, which assembles the signals into images and produces vision. The cornea is the clear outer part of the eye’s focusing system located at the front of the eye. The opening in the middle of the iris through which light passes to the back of the eye. Near the centre of the retina is the macula. Anatomy & embryology of the eye. Anatomy of the extraocular muscles. •acknowledgement of surroundings •communication •help with food acquisition (hunting) •navigation •recognition of friend and foe. The conjunctiva is the membrane covering the sclera (white portion of your eye). Web selecting or hovering over a box will highlight each area in the diagram. The retina converts light into electrical impulses that are sent to the brain through the optic nerve. The iris adjusts the size of the pupil and controls the amount of light that can enter the eye.
Understanding The Eye Anatomy Health Life Media

Human eye anatomy Royalty Free Vector Image VectorStock
/GettyImages-1128675065-e4bac15b0f39449dba31f25f1020bc8a.jpg)
Eye Anatomy Poster
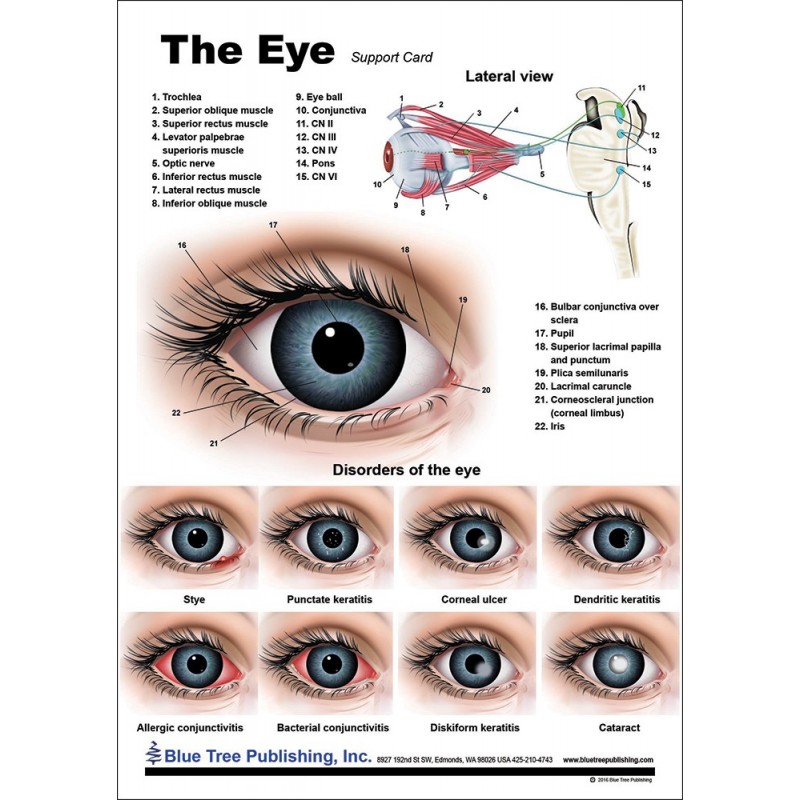
Eye Anatomical Chart
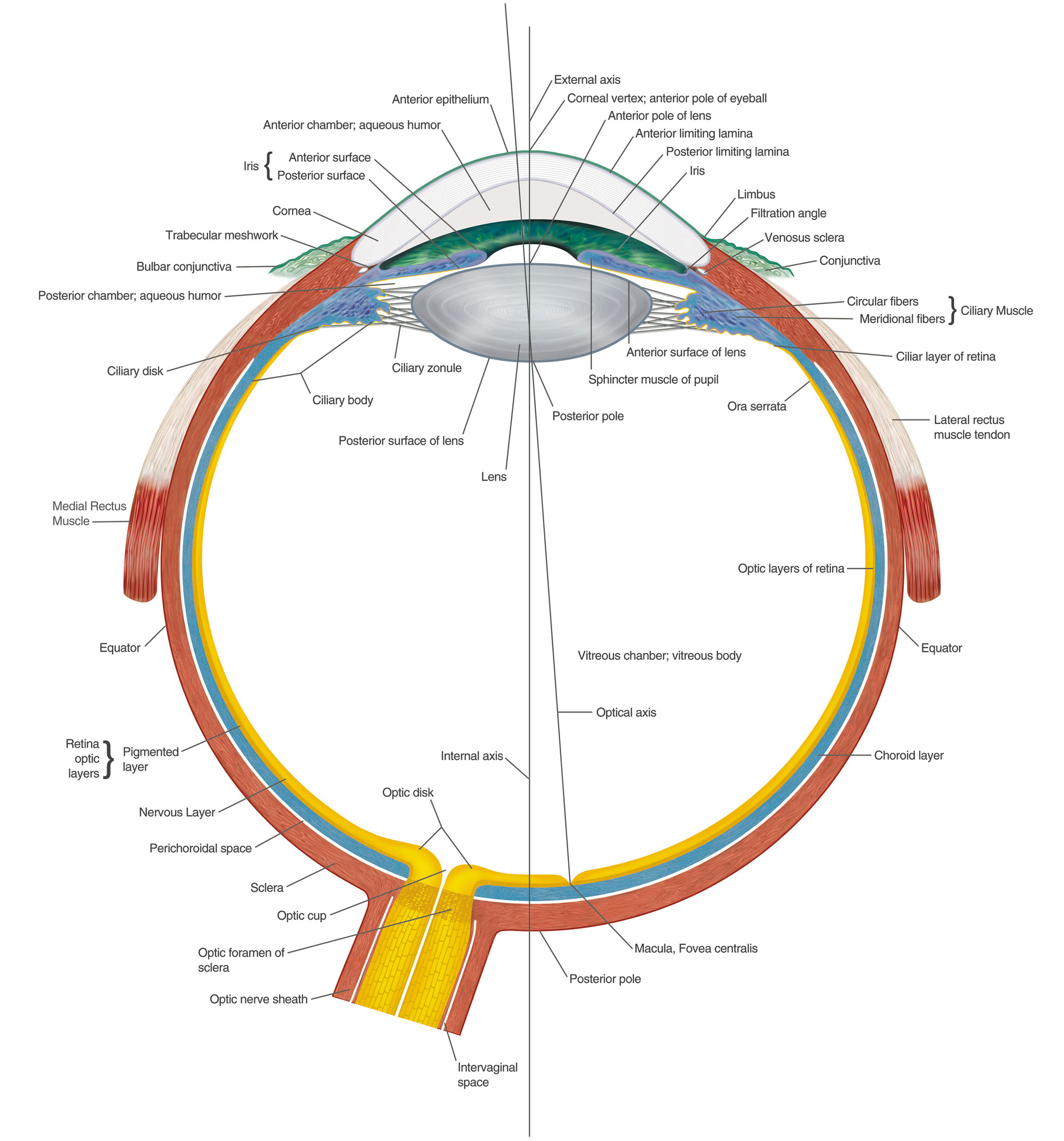
Eye Anatomy Chart B
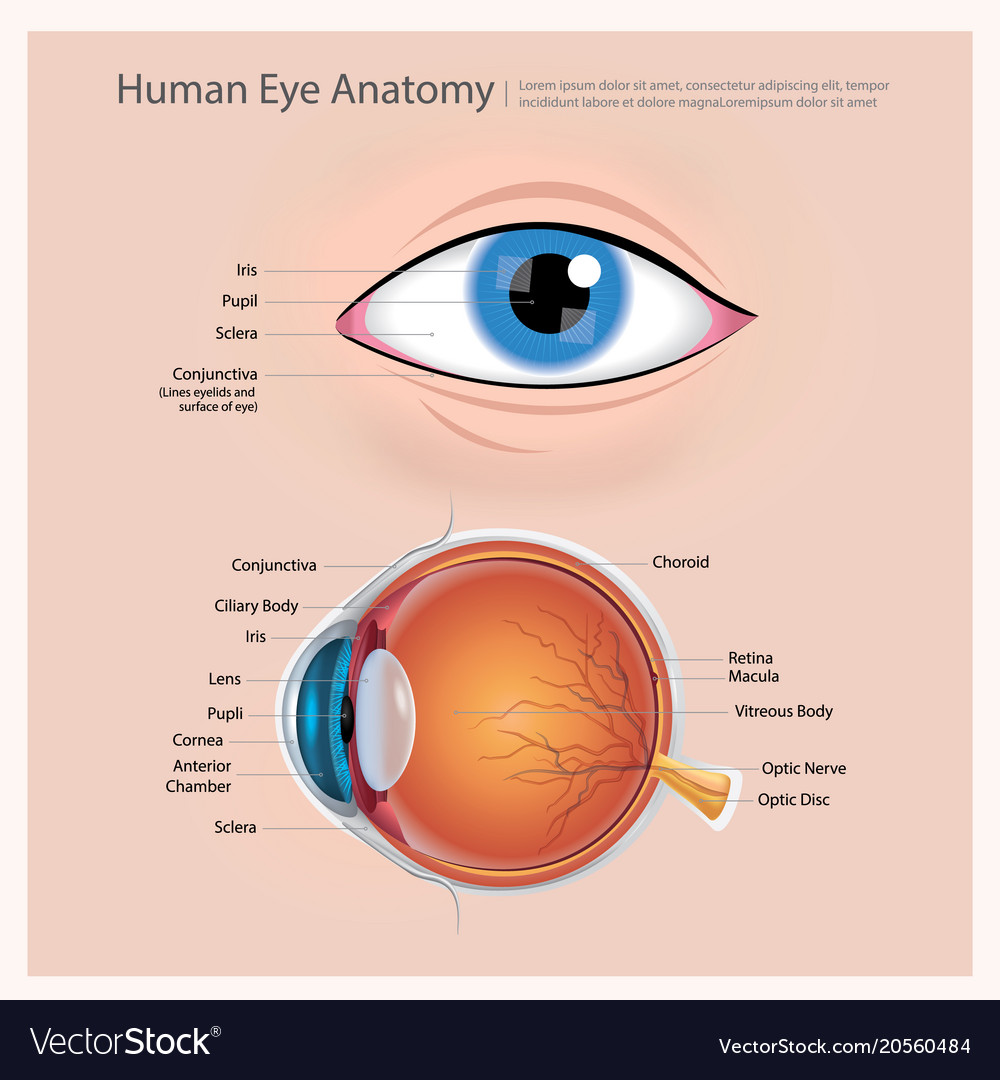
Eye Anatomy Poster
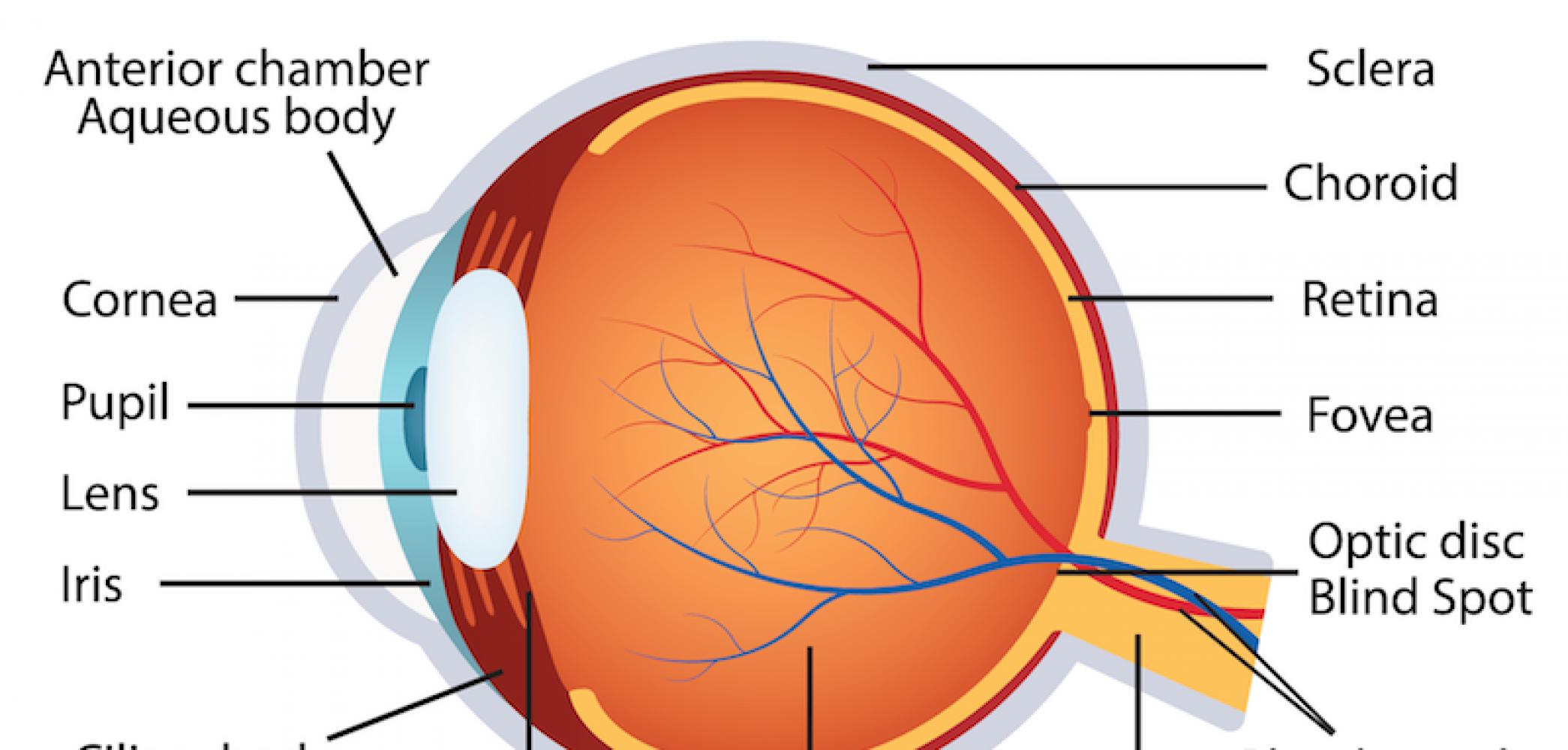
humaneyeanatomy La Pine Eyecare Clinic

Eye Diagram Vector Art, Icons, and Graphics for Free Download
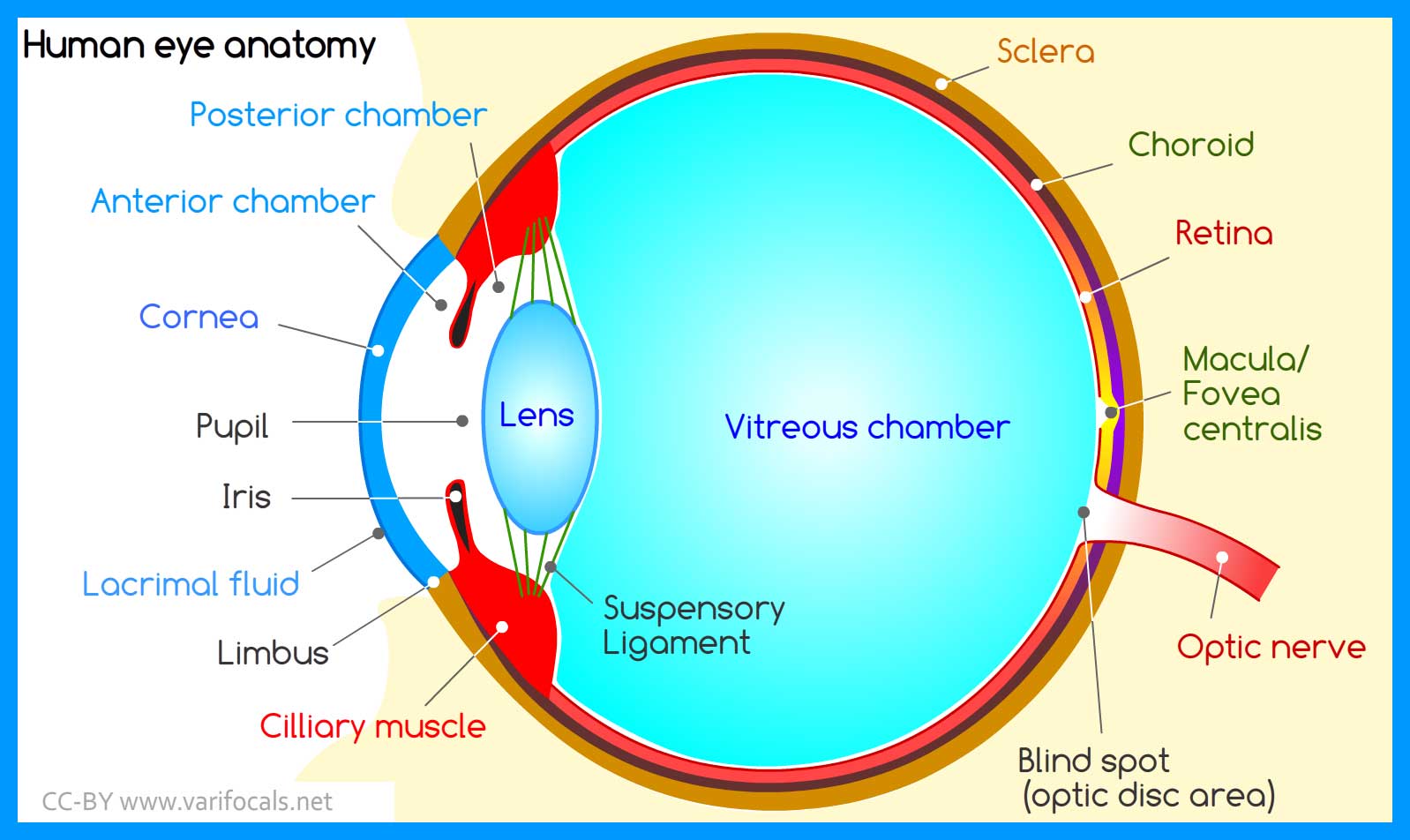
Labeled Diagram Of Eye
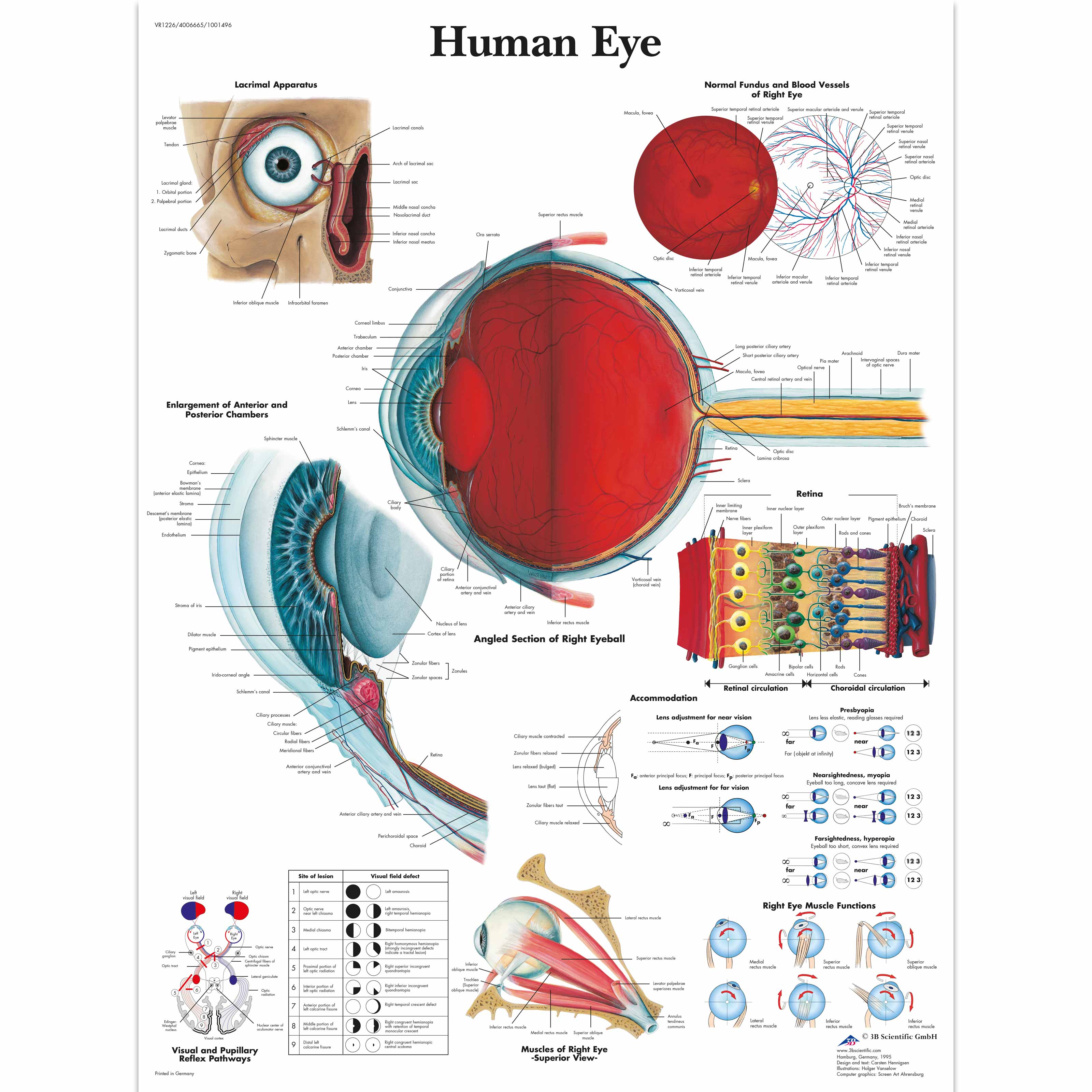
Human Eye Chart 1001496 3B Scientific VR1226L Ophthalmology
Mandy Helton Bas, Rvtg, Vts(Ecc) Function Of The Eye.
The Chart Covers General Anatomy Of The Eye With Colorful Detailed Renderings All Fully Labeled.
Clear And Flexible, The Lens Changes Shape To Focus Light On The Retina.
The Front Part (What You See In The Mirror) Includes:
Related Post: