F Orbital Drawing
F Orbital Drawing - This is done by first determining the subshell (s,p,d, or f) then drawing in each electron according to the stated rules above. Get a 10 bullets summary of the topic. This wave function also helps us. Get out your pencil (and eraser) because we are about to learn how to draw atomic orbitals. The s and p orbitals are taken into account because they are the most abundant in chemical and biological chemistry. 1.3k views 5 years ago. The bohr model shows the atom as a central nucleus containing protons and neutrons, with the electrons in circular electron shells at specific distances from the nucleus, similar to planets orbiting around the sun. D orbitals are described only in terms of their energy, and f orbitals are only mentioned in passing. There are multiple orbitals within an atom. This article will explore the basics of how to draw each type of diagram, and important rules to. The basics of orbital diagrams. Web to write the orbital diagram for the fluorine atom (f) first we need to write the electron configuration for just f. One reason for this is that the f orbitals are very little used in any chemical bonds. To plot a path for something you need to know exactly where the object is and. This wave function also helps us. Electron shells consist of one or more subshells, and subshells consist of one or more atomic orbitals. It explores s and p orbitals in some detail, including their shapes and energies. Atomic orbitals describe the most likely location that electrons will be found around the nucleus of an atom. One reason for this is. Web ask you to learn the f orbital shapes. These seven orbitals have the following ml values: The square of the orbital wave function represents the probability of finding an electron. Below are dot density diagrams, boundary surface diagrams, and a rotating image. This video lecture explains shapes and geometry of four different types of atomic orbitals i.e, s, p,. Because its average distance from the nucleus determines the energy of an electron, each atomic orbital with a given set of quantum numbers has a particular energy associated with it, the orbital energy. Get out your pencil (and eraser) because we are about to learn how to draw atomic orbitals. Orbitals are the regions of space in which electrons are. P orbitals all have the same “barbell” shape, but differ in orientation. Get out your pencil (and eraser) because we are about to learn how to draw atomic orbitals. For an #f# orbital, see below. However, the orbital shapes can be useful in interpreting spectra and in understanding the structure of some complexes that involve the rare earth elements. Below. To do that we need to find the number of electrons for the f atom (there. Orbitals are the regions of space in which electrons are most likely to be found. This article will explore the basics of how to draw each type of diagram, and important rules to. Web a p orbital which extends along the x axis is. Web orbitals with \(\ell = 3\) are f orbitals, which are still more complex. This is done by first determining the subshell (s,p,d, or f) then drawing in each electron according to the stated rules above. These seven orbitals have the following ml values: Web the orbital wave function or ϕ is a mathematical function used for representing the coordinates. This video lecture explains shapes and geometry of four different types of atomic orbitals i.e, s, p, d and f orbitals. The basics of orbital diagrams. Web even for elements beyond cerium, the f orbitals are deeply buried beneath the valence shell and they rarely play an important role in chemical change or bonding. This wave function also helps us.. Web this page discusses atomic orbitals at an introductory level. For an #f# orbital, see below. 1.3k views 5 years ago. Web an orbital diagram, like those shown above, is a visual way to reconstruct the electron configuration by showing each of the separate orbitals and the spins on the electrons. The bohr model shows the atom as a central. The electrons in an atom are arranged in shells that surround the nucleus, with each successive shell being farther from the nucleus. The square of the orbital wave function represents the probability of finding an electron. Click the images to see the various 4f orbitals. The basics of orbital diagrams. There are multiple orbitals within an atom. They are typically drawn as 3d space around the nucleus and there are different atomic orbital shapes. Web even for elements beyond cerium, the f orbitals are deeply buried beneath the valence shell and they rarely play an important role in chemical change or bonding. Web quantum numbers describing electronic orbitals. As you have probably figured by now, the first f orbitals appear in the n=4 shell, and they have three nodal surfaces. The bohr model shows the atom as a central nucleus containing protons and neutrons, with the electrons in circular electron shells at specific distances from the nucleus, similar to planets orbiting around the sun. Typically, they only show the outermost electrons. Web for an #s# orbital, draw a circle; Each orbital is denoted by a number and a letter. Web there are four types of orbitals, each with a different shape and represented by the letters s, p, d, and f. Web ask you to learn the f orbital shapes. (1) drawing on an xyz grid in a perspective mode emphasizes their differing orientations. Because its average distance from the nucleus determines the energy of an electron, each atomic orbital with a given set of quantum numbers has a particular energy associated with it, the orbital energy. Web an orbital diagram, like those shown above, is a visual way to reconstruct the electron configuration by showing each of the separate orbitals and the spins on the electrons. D orbitals are described only in terms of their energy, and f orbitals are only mentioned in passing. Each has its own specific energy level and properties. Because each orbital is different, they are assigned specific quantum numbers:F Orbital Shape Definitions, Orbital Chemistry, Atomic Orbitals

F Orbital Shape Definitions, Orbital Chemistry, Atomic Orbitals
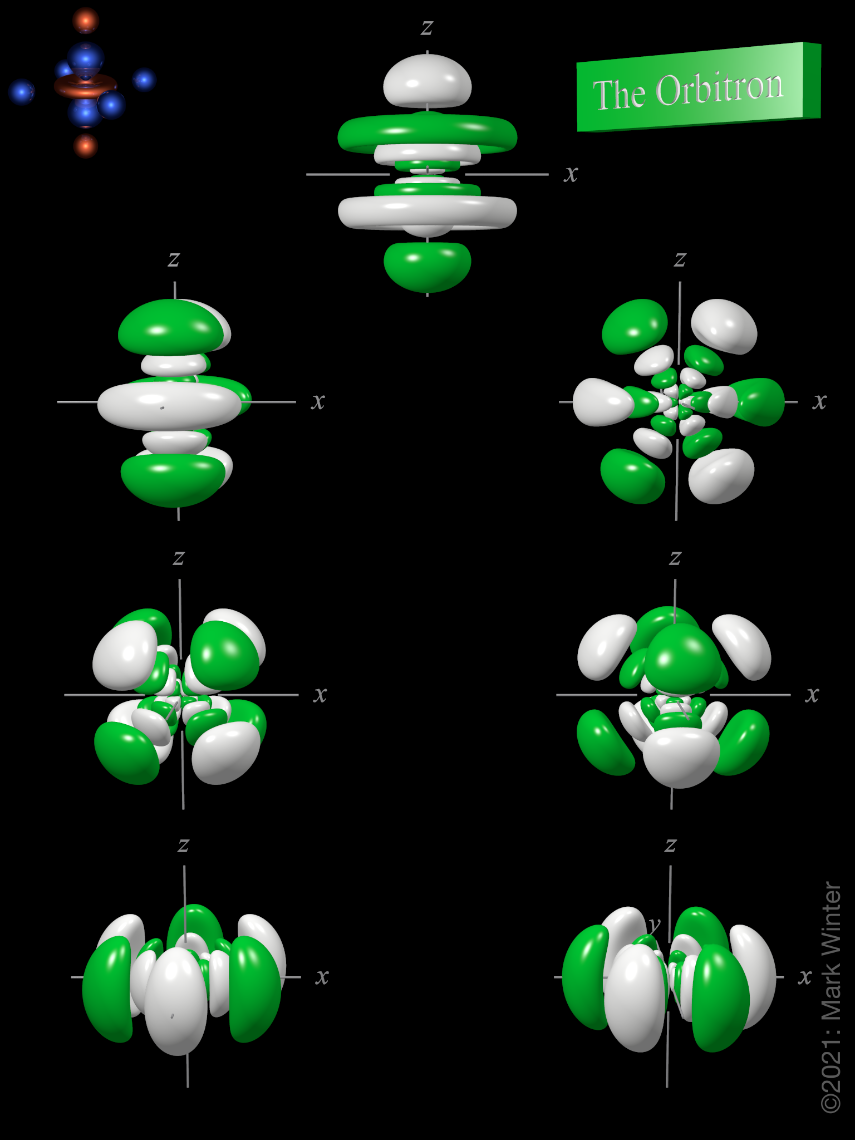
The Orbitron 7f atomic orbitals

8.3 Development of Quantum Theory CHEM 1114 Introduction to Chemistry
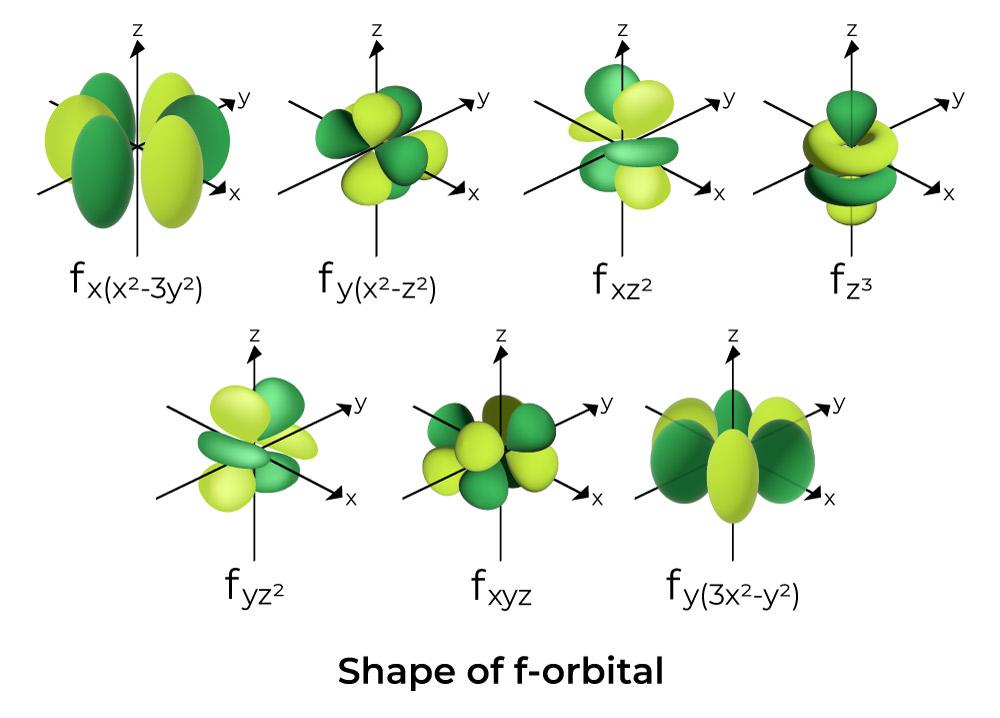
Shapes of Atomic Orbitals Shape of s, p, d, f Orbitals, FAQs, Examples

F Orbital Shape Definitions, Orbital Chemistry, Atomic Orbitals
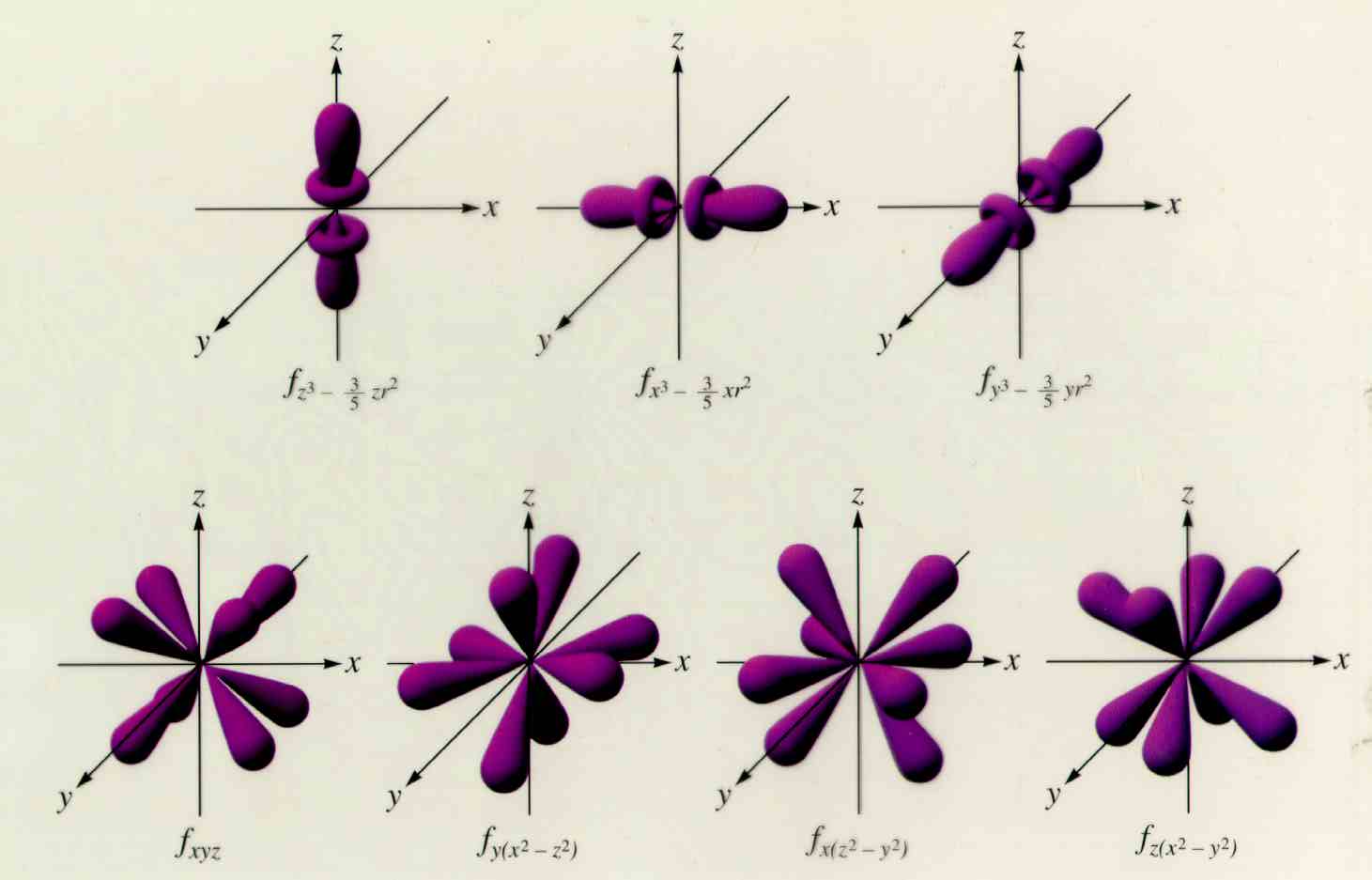
What are the different kinds of f orbitals? Socratic

F Orbital Shape Definitions, Orbital Chemistry, Atomic Orbitals
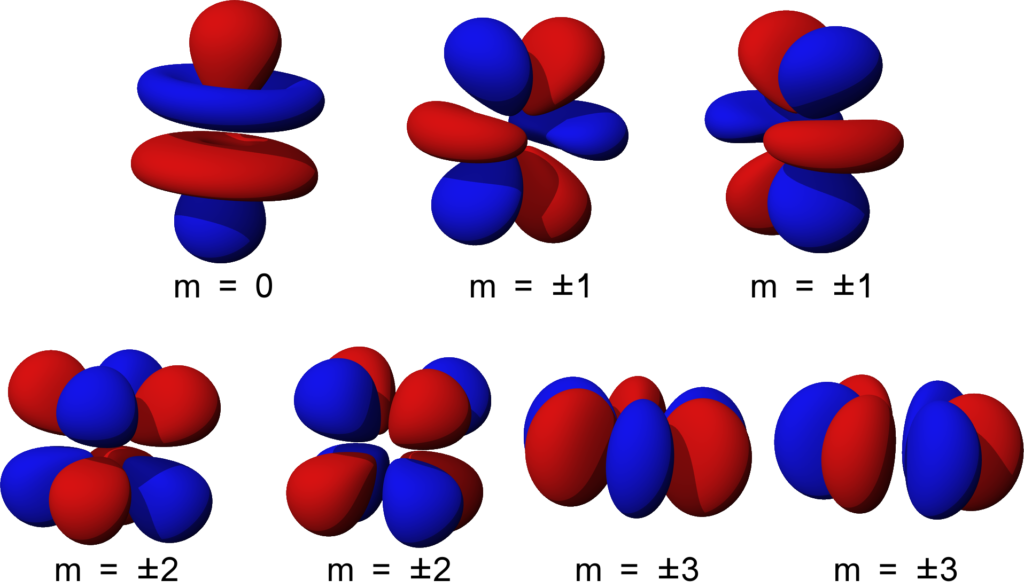
Shapes of Orbitals and their Types Chemistry Skills
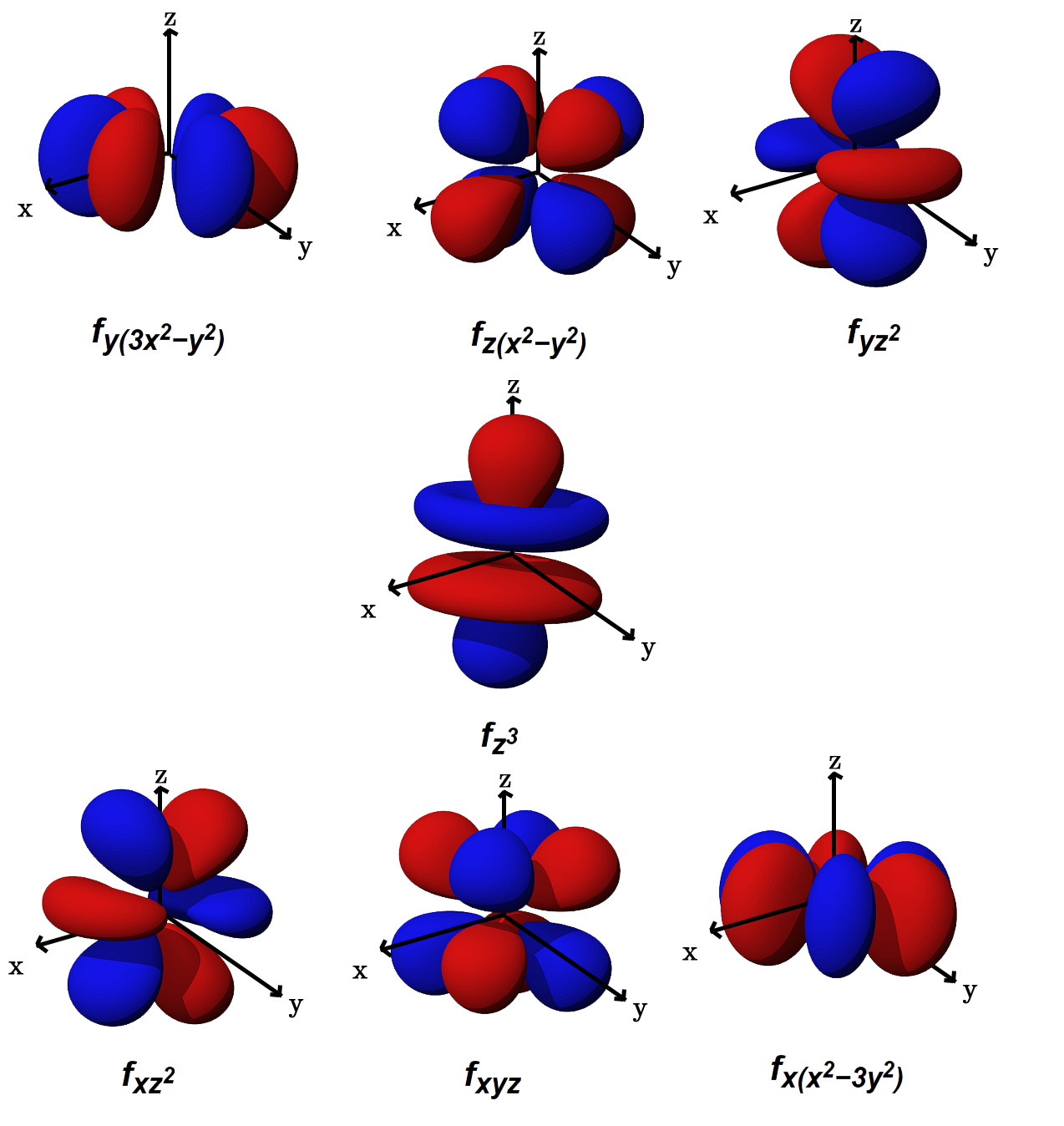
What is the shape of forbital??? + Example
The Number Denotes The Energy Level Of The Electron In The Orbital.
It Explores S And P Orbitals In Some Detail, Including Their Shapes And Energies.
For An #F# Orbital, See Below.
Get Out Your Pencil (And Eraser) Because We Are About To Learn How To Draw Atomic Orbitals.
Related Post:
