Fibrocartilage Drawing
Fibrocartilage Drawing - Web fibrocartilage is a hybrid between dense connective tissue and hyaline cartilage. The scattered hyaline cartilage cells (green arrows) produce matrix between the. White fibrocartilage consists of a mixture of white fibrous tissue and cartilaginous tissue in various proportions. Web fibrocartilage can be found in intervertebral discs, symphysis pubis, menisci, tendinous insertions, the glenohumeral/acetabular labrum, and the temporomandibular joint. Its abundant collagen bundles (black arrows) provide strength. Web fibrocartilage is primarily composed of type i collagen, and is located in areas like the intervertebral discs and the pubic symphysis. Its main function is to act as a cushion. Web fibrocartilage is a ubiquitous structure, present anywhere a tough but flexible material is required for biomechanical function. They have a fibrous appearance of mostly collagen fibers with interspersed areas of cartilage. The fibrous and cartilaginous components render this tissue extremely tough and resilient. Fibrocartilage, with its irregularly arranged fibers, is difficult to differentiate from dense irregular connective tissue. It is named so because of its triangular anatomic as well as its structural shape (figure 1). Web fibrocartilage forms a cushion between bones of the knee, where resistance to compression and to forces from multiple directions are needed. They have a fibrous appearance of. Fibrocartilage is reinforced with parallel bundles of collagen fibers, which in turn make it the strongest type of cartilage. Web fibrocartilage is a transition tissue that should be viewed as a blend between hyaline cartilage and dense fibrous connective tissue. It is found in intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, articular discs and menisci of joints. Web we will then take a. Note that the chondrocytes are surrounded by a matrix which helps differentiate fibrocartilage from dense connective tissue. The scattered hyaline cartilage cells (green arrows) produce matrix between the. Fibrocartilage is reinforced with parallel bundles of collagen fibers, which in turn make it the strongest type of cartilage. Its abundant collagen bundles (black arrows) provide strength. Web fibrocartilage is primarily composed. It is found predominantly in the intervertebral disks of the spine and at the insertions of ligaments and tendons. In elastic cartilage, chondrocytes are organised into elastic fibers , which make up a threadlike network or matrix. Web we will then take a closer look at the histological structure of fibrocartilage and finally, we will examine the role of fibrocartilage. They have a fibrous appearance of mostly collagen fibers with interspersed areas of cartilage. Under these conditions, collagen bundles are arranged irregularly, making this type of fibrocartilage easy to confuse with dense irregular connective tissue. Web a cartilaginous joint where the bones are joined by fibrocartilage is called a symphysis (“growing together”). Fibrocartilage, with its irregularly arranged fibers, is difficult. Web fibrocartilage is a transition tissue that should be viewed as a blend between hyaline cartilage and dense fibrous connective tissue. Web fibrocartilage is primarily composed of type i collagen, and is located in areas like the intervertebral discs and the pubic symphysis. Fibrocartilage, with its irregularly arranged fibers, is difficult to differentiate from dense irregular connective tissue. Fibrocartilage is. It is found predominantly in the intervertebral disks of the spine and at the insertions of ligaments and tendons. Fibrocartilage is reinforced with parallel bundles of collagen fibers, which in turn make it the strongest type of cartilage. It is a white, densely arranged, opaque, tufted tissue with a mixture of both chondrocytes and fibroblasts. In elastic cartilage, chondrocytes are. It is found predominantly in the intervertebral disks of the spine and at the insertions of ligaments and tendons. Web we will then take a closer look at the histological structure of fibrocartilage and finally, we will examine the role of fibrocartilage in embryonic development which has important clinical applications that we will also be covering here on this tutorial.. Rounded chondrocytes, frequently with visible cytoplasm and lacunae, differentiate fibrocartilage from connective tissue proper. Web fibrocartilage is a specialized form of connective tissue in which the ground substance is cartilage. Web fibrocartilage is a type of cartilage that should be viewed as a blend between hyaline cartilage and dense fibrous connective tissue. Fibrocartilage contains numerous bundles of thick collagen fibers,. Web fibrocartilage is primarily composed of type i collagen, and is located in areas like the intervertebral discs and the pubic symphysis. Web a cartilaginous joint where the bones are joined by fibrocartilage is called a symphysis (“growing together”). The scattered hyaline cartilage cells (green arrows) produce matrix between the. Web fibrocartilage is a supportive connective tissue that is extremely. Web fibrocartilage forms a cushion between bones of the knee, where resistance to compression and to forces from multiple directions are needed. Web the triangular fibrocartilage complex (tfcc) is an incredibly complex structure that provides intrinsic stability to the distal radioulnar joint and the ulnocarpal aspect of the wrist. Web fibrocartilage, type of connective tissue that provides structural support for the musculoskeletal system. The main type of cell found in fibrocartilage is chondrocytes (mature cartilage cells) which exist in a tiny space known as a lacuna. Fibrocartilage, with its irregularly arranged fibers, is difficult to differentiate from dense irregular connective tissue. After reading this post, you will differentiate among three types of cartilage histology features based on slide pictures. It is named so because of its triangular anatomic as well as its structural shape (figure 1). The scattered hyaline cartilage cells (green arrows) produce matrix between the. Web fibrocartilage is a ubiquitous structure, present anywhere a tough but flexible material is required for biomechanical function. Web we will then take a closer look at the histological structure of fibrocartilage and finally, we will examine the role of fibrocartilage in embryonic development which has important clinical applications that we will also be covering here on this tutorial. Web elastic cartilage, sometimes referred to as yellow fibrocartilage, is a type of cartilage that provides both strength and elasticity to certain parts of the body, such as the ears. Web fibrocartilage is a mixture of dense regular connective tissue and hyaline cartilage. It is a white, densely arranged, opaque, tufted tissue with a mixture of both chondrocytes and fibroblasts. Web fibrocartilage is a type of cartilage that should be viewed as a blend between hyaline cartilage and dense fibrous connective tissue. It is a white, densely arranged, opaque, tufted tissue with a mixture of both chondrocytes and fibroblasts. The fibrous and cartilaginous components render this tissue extremely tough and resilient.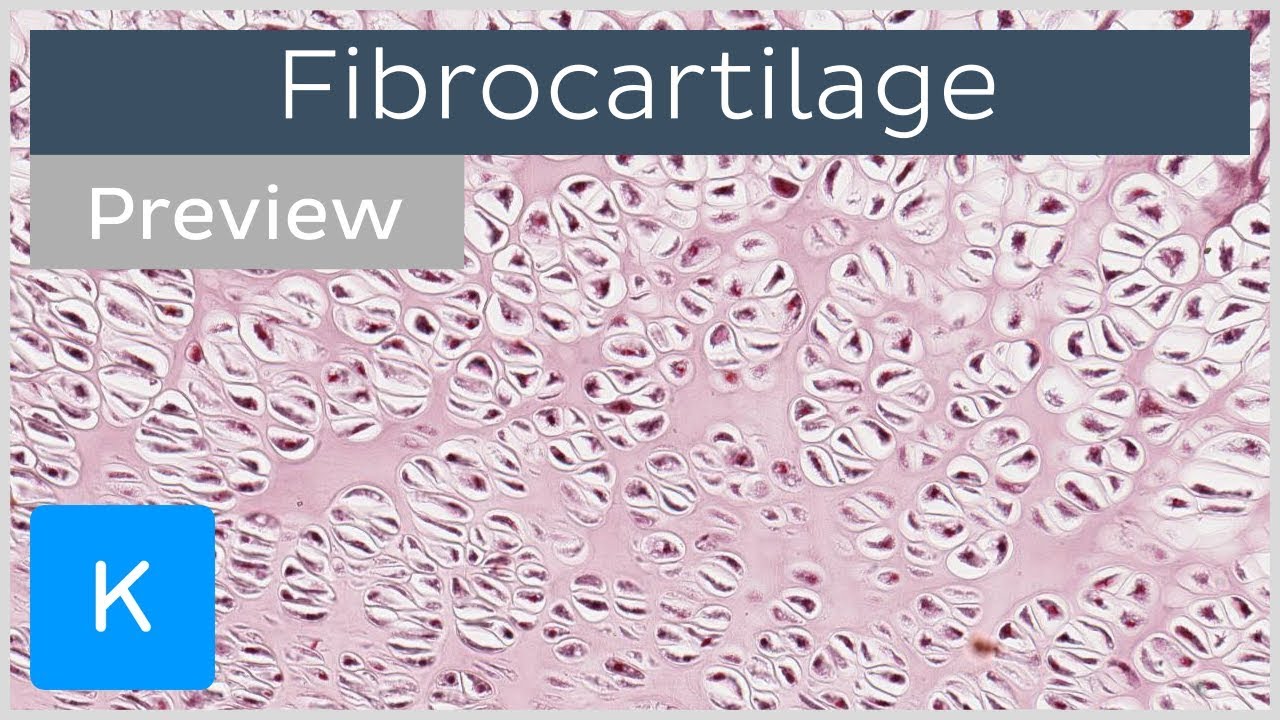
Fibrocartilage location and tissue function (preview) Human
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/chondrocytes-2/VE1RFpkfhfwCTypLMrguAg_Chondrocytes.png)
Fibrocartilage Under Microscope Labeled Micropedia

Perichondrium as hyaline, fibrous and elastic cartilage membrane

Fibrocartilage Connective Tissue Fibrocartilage Cell Biology

White Fibrocartilage ClipArt ETC
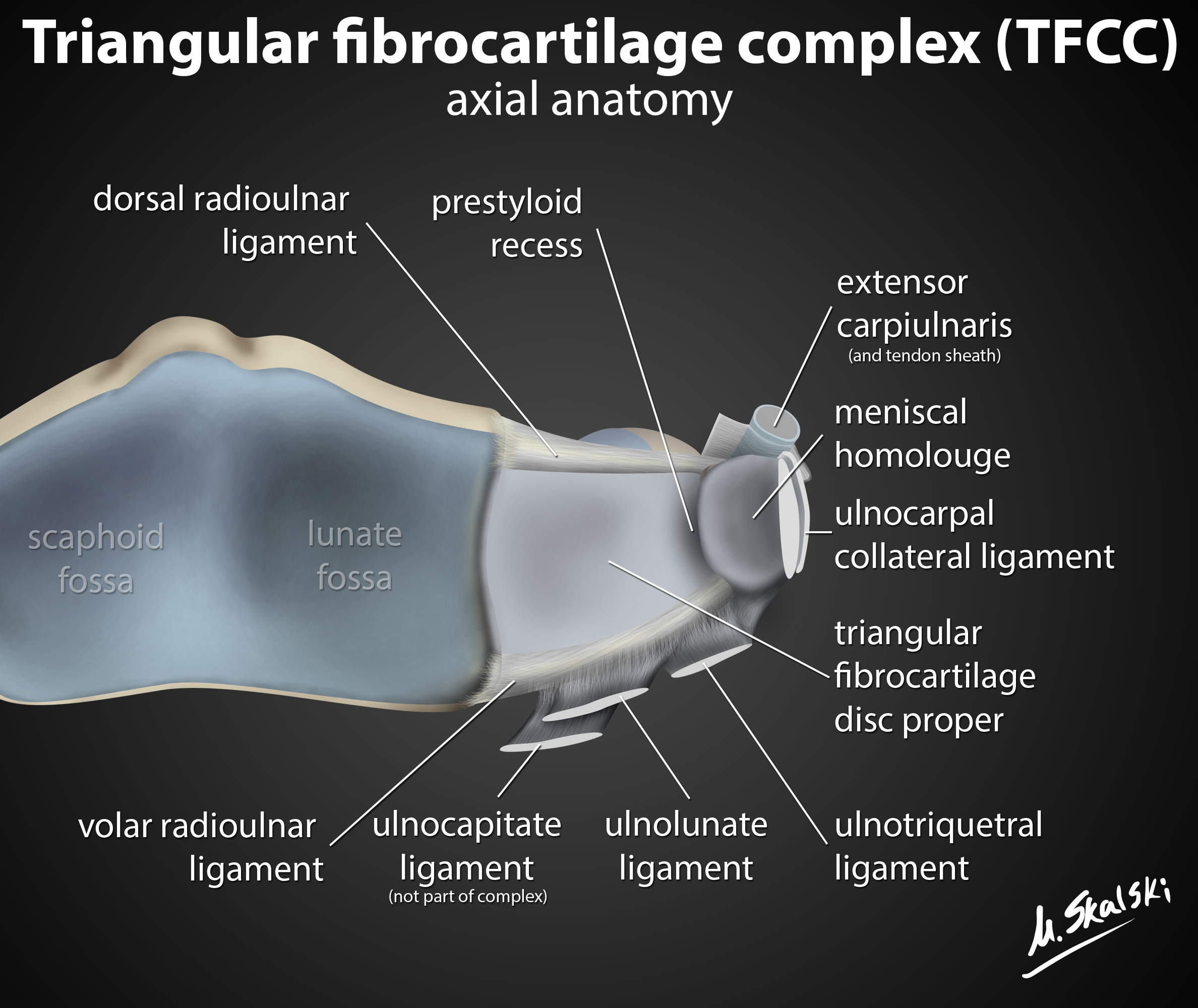
Radiopaedia Drawing Triangular fibrocartilage complex English

Fibrocartilage Cartilage Under Microscope Micropedia

How to draw histology of fibrocartilage ? YouTube

Cartilage Basic Science Orthobullets

Hyaline , elastic and fibrocartilage how to identify under microscope
It Is Found In Intervertebral Discs, Pubic Symphysis, Articular Discs And Menisci Of Joints.
It Is Found Predominantly In The Intervertebral Disks Of The Spine And At The Insertions Of Ligaments And Tendons.
Web A Cartilaginous Joint Where The Bones Are Joined By Fibrocartilage Is Called A Symphysis (“Growing Together”).
They Have A Fibrous Appearance Of Mostly Collagen Fibers With Interspersed Areas Of Cartilage.
Related Post: