Flow Chart Of Blood Clotting
Flow Chart Of Blood Clotting - Web blood clotting (technically “blood coagulation”) is the process by which (liquid) blood is transformed into a solid state. The blood clotting process or coagulation is an important process that. Narrowed or blocked arteries can limit blood flow to the. Web the diagram below shows red blood cells, white blood cells of different types (large, purple cells), and platelets. Blood vessels damaged by high blood pressure can narrow, break or leak. Vascular factors of hemostasis |. Coagulation, or blood clotting, is a physiological process in our bodies. Web a thrombus that breaks loose and flows to another location in a person’s body is known as an embolus. Web blood clotting, or coagulation, is an important process that prevents excessive bleeding when a blood vessel is injured. Prevention of bleeding or haemorrhage. The blood clotting process or coagulation is an important process that. Web this sequence of reactions comprises the classic intrinsic pathway of coagulation, the mechanism for initiating thrombin generation and clot formation in the activated partial thromboplastin time (aptt) assay universally used as a clinical measure for the integrity of plasma coagulation [ 8 ]. Blood clotting prevents continued /.. Narrowed or blocked arteries can limit blood flow to the. Web the coagulation process is characterised by a cascade of events which lead to the formation of a blood clot. Web write a flow chart showing major events taking place in the clotting of blood. This capability is essential to keep you alive, particularly with significant injuries. Through vasoconstriction, adhesion,. Web the diagram below shows red blood cells, white blood cells of different types (large, purple cells), and platelets. When an injury causes a blood vessel wall to break, platelets are activated. In the following diagram, the process of blood clotting. They also interact with other blood proteins to form fibrin. Web clotting is a process in which liquid blood. Through vasoconstriction, adhesion, activation, and aggregation, the contributors form a transient plug to act as the cork to the leaking. Web the coagulation process is characterised by a cascade of events which lead to the formation of a blood clot. When activated, these factors trigger the conversion of other factors in the coagulation cascade resulting in secondary haemostasis. They change. Web this sequence of reactions comprises the classic intrinsic pathway of coagulation, the mechanism for initiating thrombin generation and clot formation in the activated partial thromboplastin time (aptt) assay universally used as a clinical measure for the integrity of plasma coagulation [ 8 ]. Vascular factors of hemostasis |. Acute venous and arterial thromboses are the most common cause of. Narrowed or blocked arteries can limit blood flow to the. When an injury causes a blood vessel wall to break, platelets are activated. A picture showing clotting of blood cells. Through vasoconstriction, adhesion, activation, and aggregation, the contributors form a transient plug to act as the cork to the leaking. Platelets (a type of blood cell) and proteins in your. Did this video help you? When an injury causes a blood vessel wall to break, platelets are activated. The clot will dissolve after the damage heals. Web clotting is a process in which liquid blood is converted into a gelatinous substance that eventually hardens. Web blood clotting, or coagulation, is an important process that prevents excessive bleeding when a blood. Web hematology and oncology / hemostasis / overview of hemostasis. The clot will dissolve after the damage heals. This capability is essential to keep you alive, particularly with significant injuries. The aim is to stop the flow of blood from a vessel. Web blood flows through the blood vessels to deliver the needed oxygen and nutrients to the different cells. Proteins called clotting factors initiate reactions which activate more clotting factors. This process occurs via two pathways which unite downstream to form the common pathway. The formation of a clot is the result. Web this sequence of reactions comprises the classic intrinsic pathway of coagulation, the mechanism for initiating thrombin generation and clot formation in the activated partial thromboplastin time. A picture showing clotting of blood cells. They change shape from round to spiny, stick to the broken vessel wall and each other, and begin to plug the break. Platelets and clotting factors work together to seal the site of the injury. When activated, these factors trigger the conversion of other factors in the coagulation cascade resulting in secondary haemostasis.. When activated, these factors trigger the conversion of other factors in the coagulation cascade resulting in secondary haemostasis. Embolism is the medical name for a blocked artery caused by an embolus. They also interact with other blood proteins to form fibrin. This reaction stops bleeding and allows your body to start repairs on the injury. Web blood clotting, or coagulation, is an important process that prevents excessive bleeding when a blood vessel is injured. Web blood clotting (technically “blood coagulation”) is the process by which (liquid) blood is transformed into a solid state. Prevention of bleeding or haemorrhage. Web clotting is a process in which liquid blood is converted into a gelatinous substance that eventually hardens. Platelets and clotting factors work together to seal the site of the injury. The clots can block blood flow, raising the risk of a stroke. High blood pressure also can cause blood clots to form in the arteries leading to the brain. Did this video help you? They change shape from round to spiny, stick to the broken vessel wall and each other, and begin to plug the break. Acute venous and arterial thromboses are the most common cause of death in developed countries. The coagulation cascade is a series of reactions, catalysed by protein enzymes known as coagulation ‘factors’. The clot will dissolve after the damage heals.
Blood Clotting Cascade Diagram
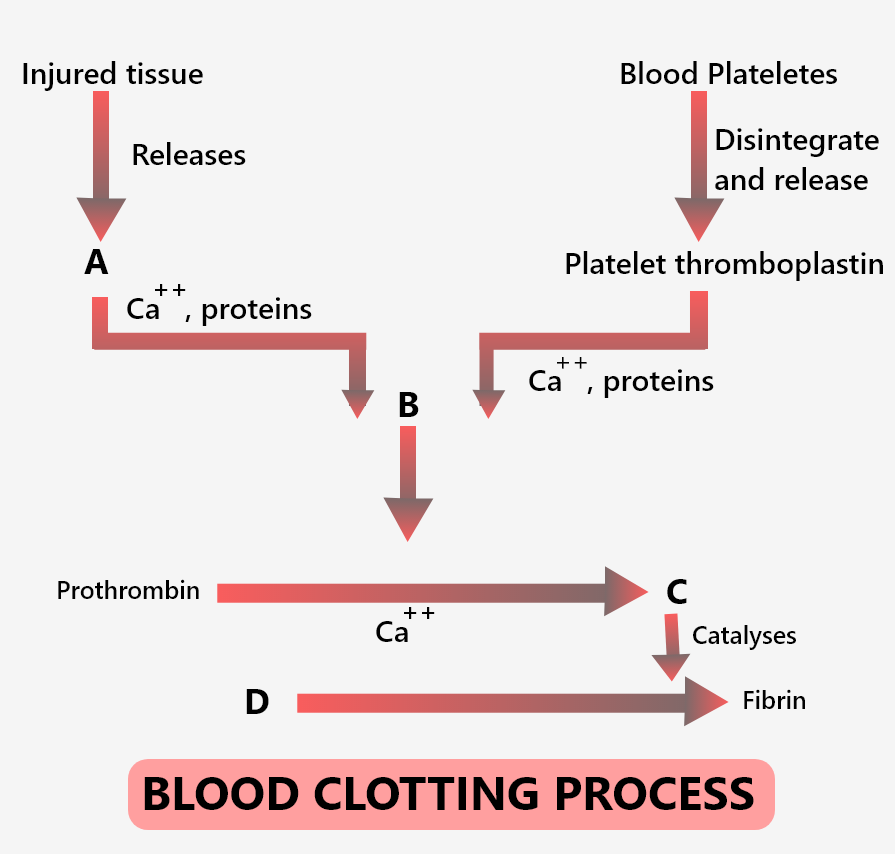
In the extrinsic clotting pathway, the active factor VII activates

Flow Chart Blood Clotting Process Diagram
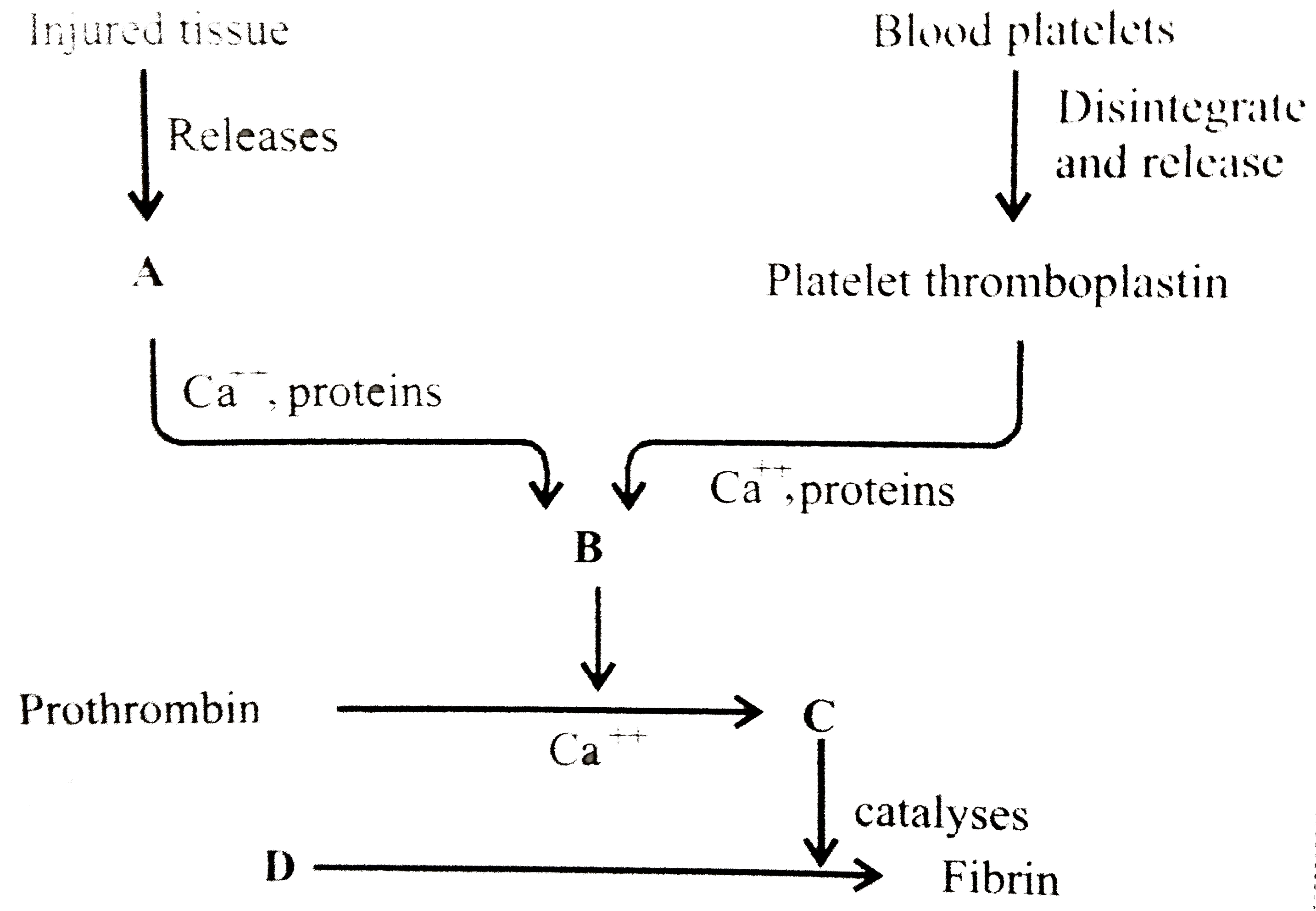
Describe the process of blood clotting.

Hemostasis · Anatomy and Physiology

Blood clotting (Edexcel Alevel Biology B) Teaching Resources
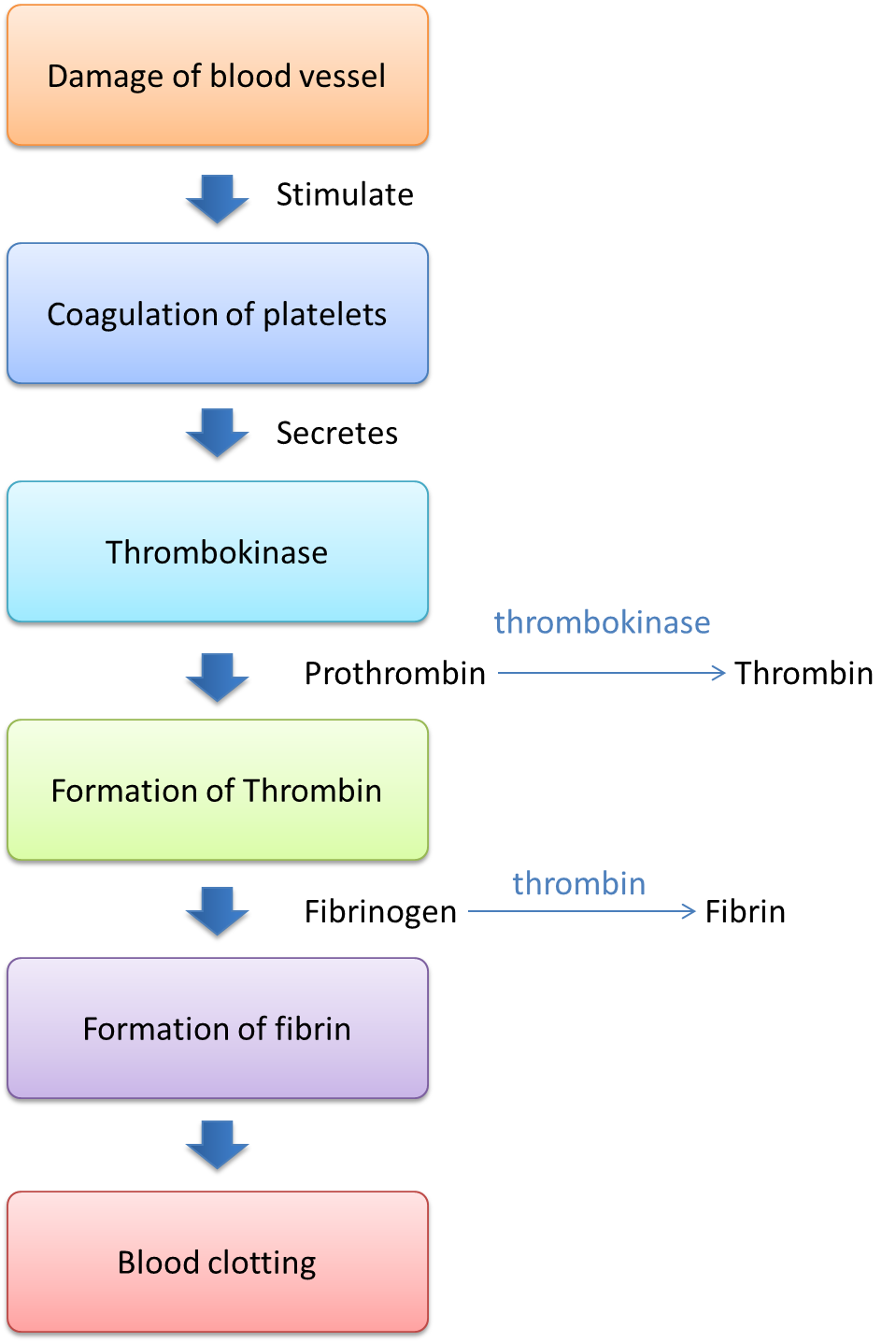
1.3.1 Mechanism of Blood Clotting SPM Biology

Blood Clotting Cascade Diagram

The Clotting Cascade Made Easy! Nurse Your Own Way
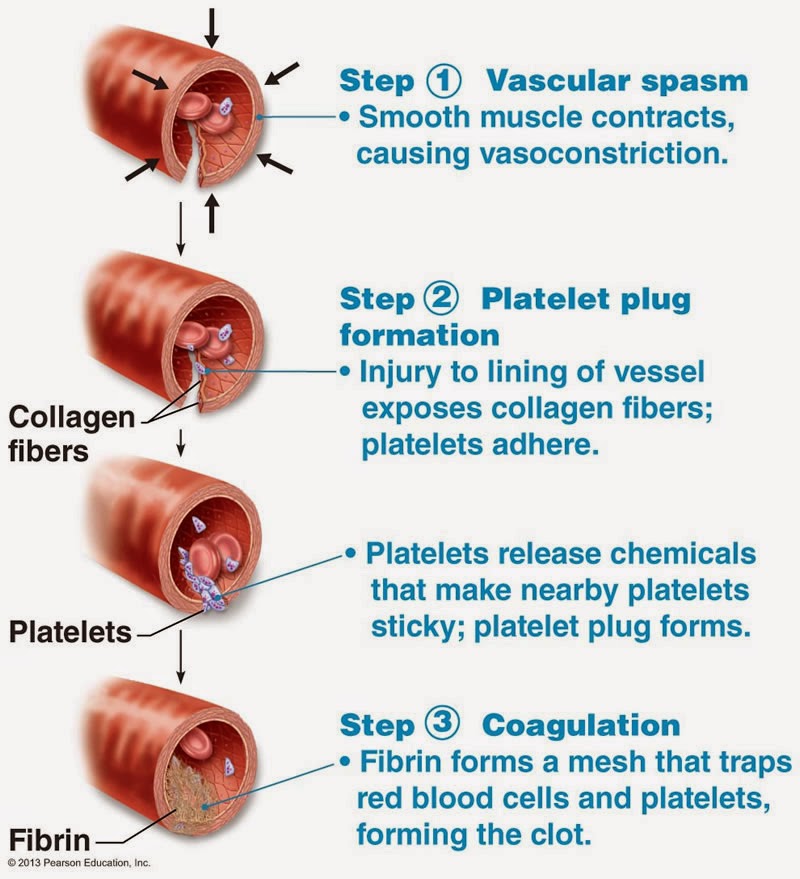
Bio Geo Nerd Blood Clotting
Web Hemostasis Is Your Body’s Normal Reaction To An Injury That Causes Bleeding.
Platelets (A Type Of Blood Cell) And Proteins In Your Plasma (The Liquid Part Of Blood) Work Together To Stop The Bleeding By Forming A Clot Over The Injury.
Narrowed Or Blocked Arteries Can Limit Blood Flow To The.
A Picture Showing Clotting Of Blood Cells.
Related Post: