Foot Anatomical Chart
Foot Anatomical Chart - The midfoot, containing the navicular, cuboid, and cuneiforms; Web the first foot pain diagram looks at the front and top of the foot, the second foot pain identifier looks underneath and at the back of the foot. It's so easy to revise with! These bones are divided into three main regions: Additionally, the lower leg often refers to the area between the knee and the ankle and this area is critical to the functioning of the foot. Web last updated march 1, 2024 • 47 revisions •. Web now that you’ve measured your foot size, compare the measurements against a nike size chart to find the best shoe size for you. Learn more about foot bones and foot anatomy here. They are complex structures with 26 bones. There are 29 muscles associated with the human foot: A clinician's ability to understand the anatomical structures of the foot is crucial for assessment and treatment, especially for clinicians working with clients with musculoskeletal conditions. Web the 26 bones of the foot consist of eight distinct types, including the tarsals, metatarsals, phalanges, cuneiforms, talus, navicular, and cuboid bones. This foot pain diagram shows common problems that cause pain on. Extrinsic muscles arise from the anterior, posterior and lateral compartments of the leg. It's so easy to revise with! The foot is crucial to human locomotion and postural stability, and the muscles associated with the foot are therefore involved principally in this function. Web last updated march 1, 2024 • 47 revisions •. Web the foot is traditionally divided into. Web the foot is the lowermost point of the human leg. Web this article will give an overview of foot anatomy and foot problems that come from overuse, injury, and normal wear and tear of the foot. Web from the large, strong muscles of the buttocks and legs to the tiny, fine muscles of the feet and toes, these muscles. It will also look at some of the common conditions that affect the foot and their possible treatment options. Web foot and ankle anatomy consists of 33 bones, 26 joints and over a hundred muscles, ligaments and tendons. The hindfoot, midfoot, and forefoot. [3] [4] this article discusses the key anatomical structures of the foot. These bones give structure to. Web the anatomy of the foot. Web foot and ankle anatomical chart. Web the foot is divided into three parts: And the forefoot, which includes the metatarsals and phalanges. Extrinsic muscles arise from the anterior, posterior and lateral compartments of the leg. [3] [4] this article discusses the key anatomical structures of the foot. Web our lower limb muscle chart contains tables with the attachments, innervations and functions of every muscle. Learn more about foot bones and foot anatomy here. The dorsal fascia of the foot is the continuation of the deep fascia of. A clinician's ability to understand the anatomical structures. The last two together are called the lower ankle joint. These bones are divided into three main regions: A clinician's ability to understand the anatomical structures of the foot is crucial for assessment and treatment, especially for clinicians working with clients with musculoskeletal conditions. Upper ankle joint (tibiotarsal), talocalcaneonavicular, and subtalar joints. While other shoe brands may use similar size. It is made up of three joints: A clinician's ability to understand the anatomical structures of the foot is crucial for assessment and treatment, especially for clinicians working with clients with musculoskeletal conditions. Web now that you’ve measured your foot size, compare the measurements against a nike size chart to find the best shoe size for you. The midfoot, containing. The hindfoot, the midfoot, and the forefoot (figure 2). Our foot and ankle chart is one of our best selling charts, perfect for learning and explaining the major bony. The hindfoot, midfoot, and forefoot. Web foot and ankle anatomical chart. Web last updated march 1, 2024 • 47 revisions •. Upper ankle joint (tibiotarsal), talocalcaneonavicular, and subtalar joints. The dorsal fascia of the foot is the continuation of the deep fascia of. There are 29 muscles associated with the human foot: Learn more about foot bones and foot anatomy here. It is made up of three joints: The hindfoot, the midfoot, and the forefoot (figure 2). Web the feet support the human body when standing, walking, running, and more. Extrinsic muscles arise from the anterior, posterior and lateral compartments of the leg. The last two together are called the lower ankle joint. These bones are divided into three main regions: Web the first foot pain diagram looks at the front and top of the foot, the second foot pain identifier looks underneath and at the back of the foot. The ankle joint, also known as the talocrural joint, allows dorsiflexion and plantar flexion of the foot. Web this article will give an overview of foot anatomy and foot problems that come from overuse, injury, and normal wear and tear of the foot. Web from the large, strong muscles of the buttocks and legs to the tiny, fine muscles of the feet and toes, these muscles can exert tremendous power while constantly making small adjustments for balance — whether the body is at rest or in motion. A clinician's ability to understand the anatomical structures of the foot is crucial for assessment and treatment, especially for clinicians working with clients with musculoskeletal conditions. This foot pain diagram shows common problems that cause pain on top of the foot at the front. While other shoe brands may use similar size scales, it’s best to check out a shoe brand’s size charts before purchasing a new pair of shoes from them, as each brand’s exact approach to size and fit may vary. And the forefoot, which includes the metatarsals and phalanges. Upper ankle joint (tibiotarsal), talocalcaneonavicular, and subtalar joints. There are 29 muscles associated with the human foot: Web the anatomy of feet: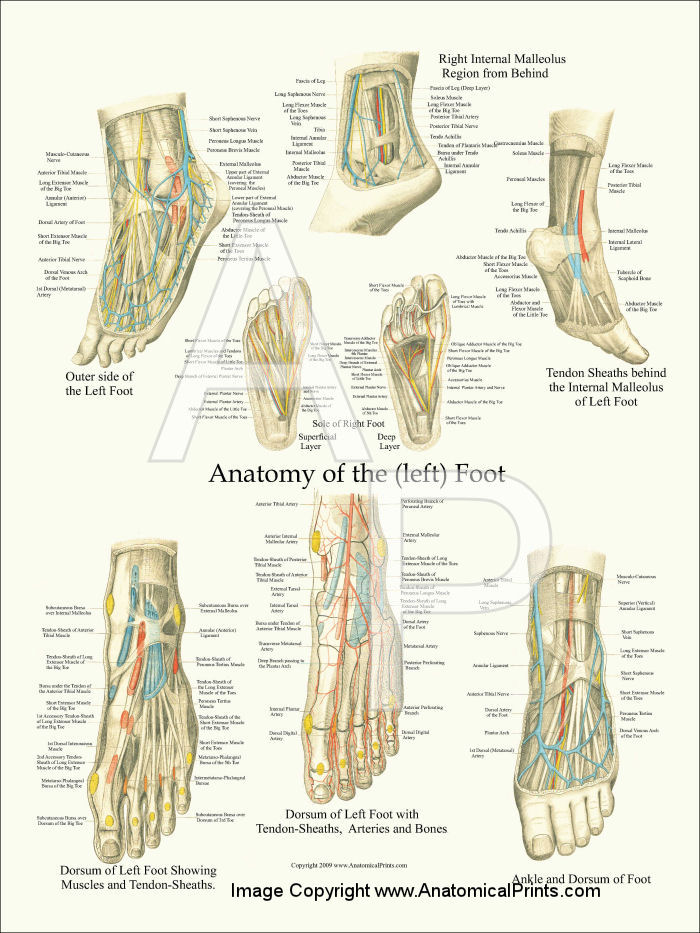
Foot Anatomy Poster
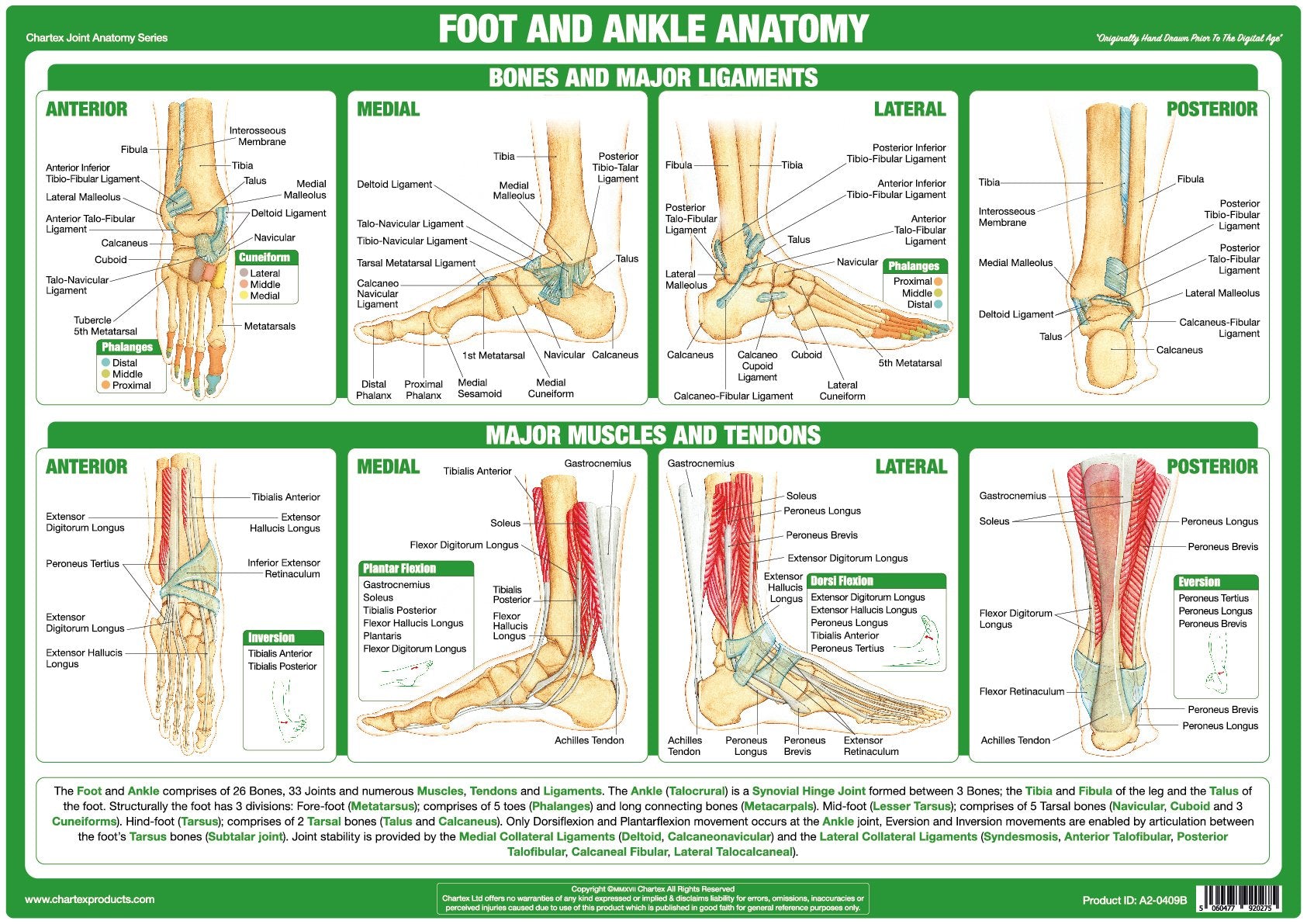
Chartex Foot and Ankle Joint Anatomy Chart
.jpg?response-content-disposition=attachment)
Foot Anatomy Chart
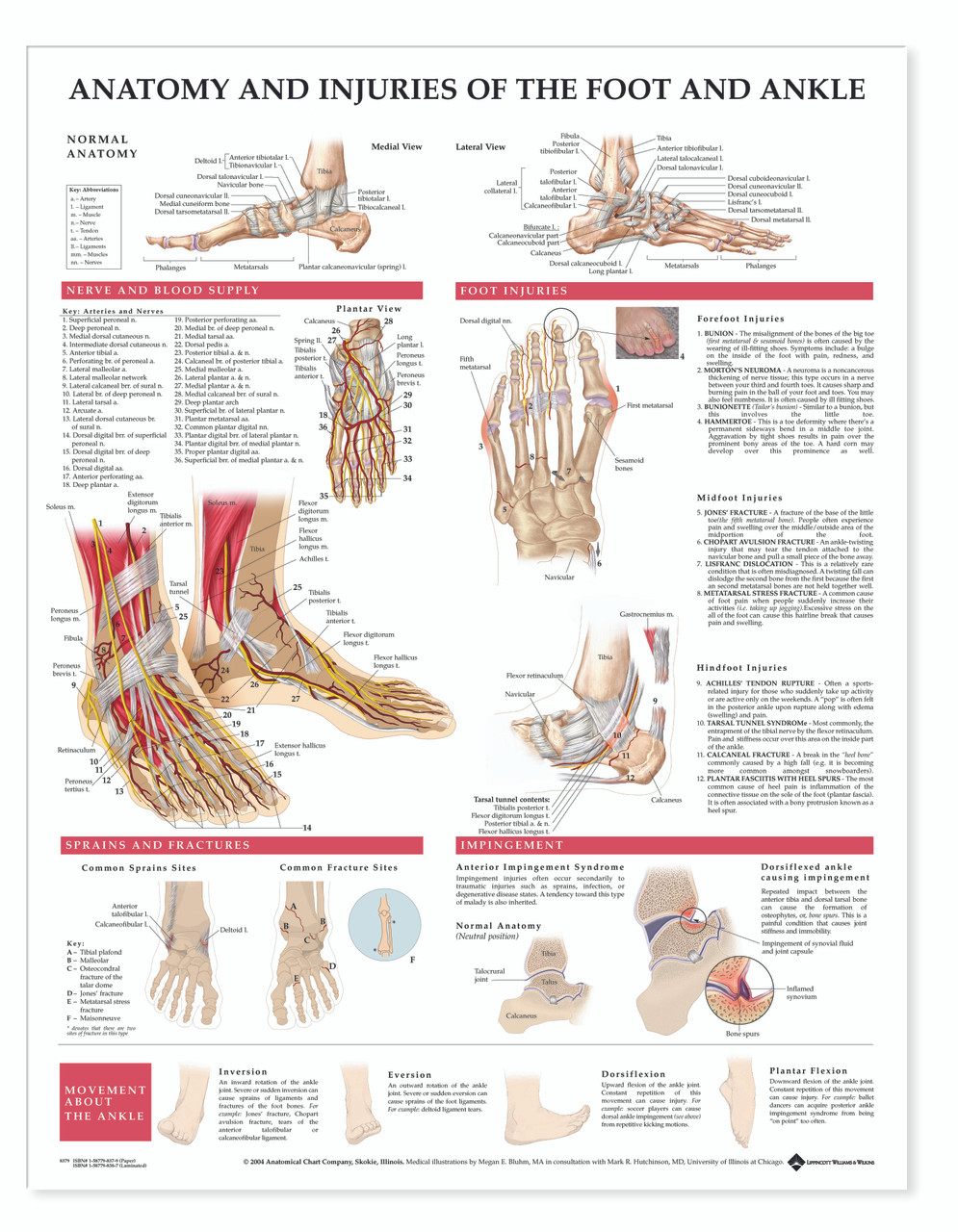
Foot Ankle Anatomy Chart Poster Laminated
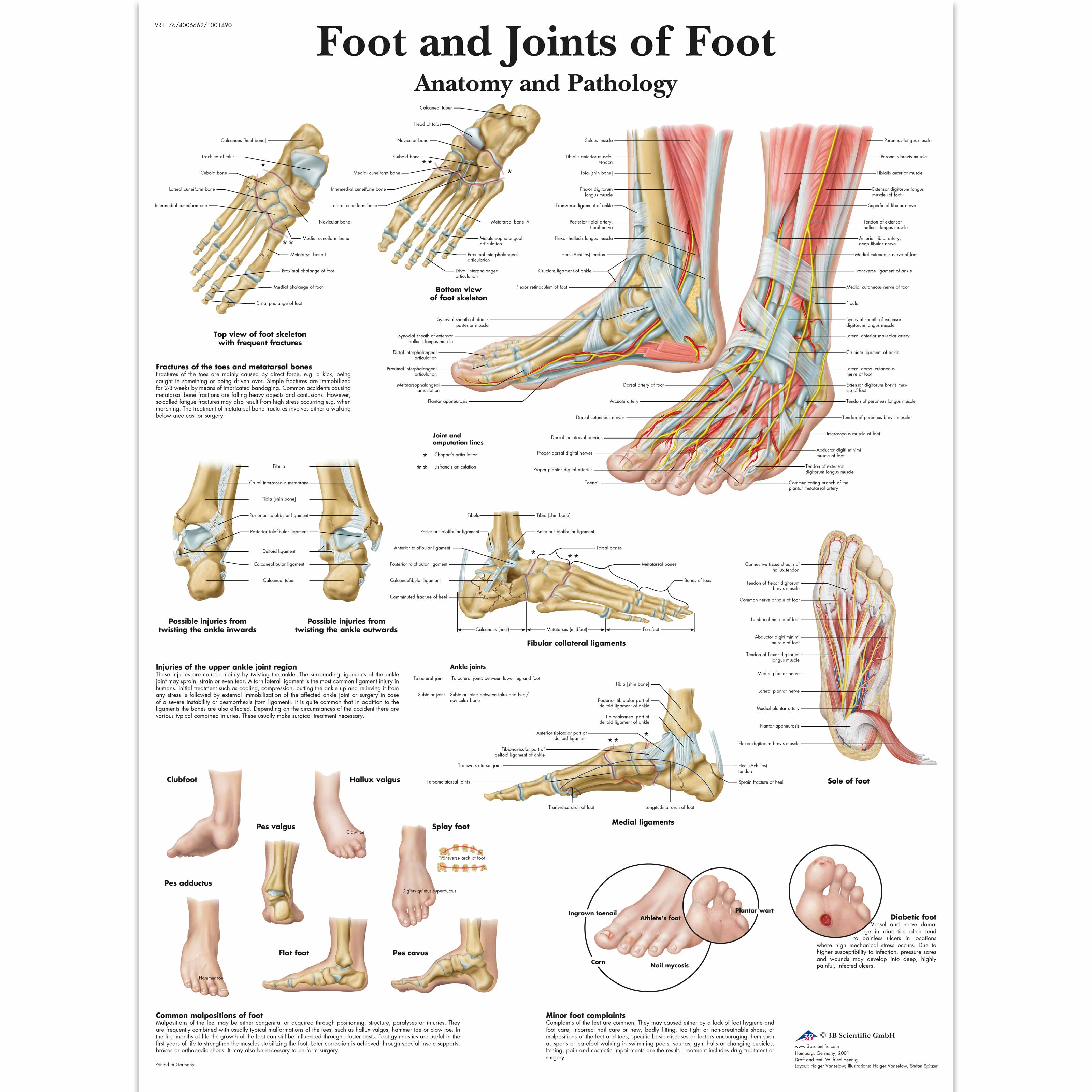
Anatomical Charts and Posters Anatomy Charts Foot and Ankle

This chart shows foot and ankle bone and ligament anatomy, normal
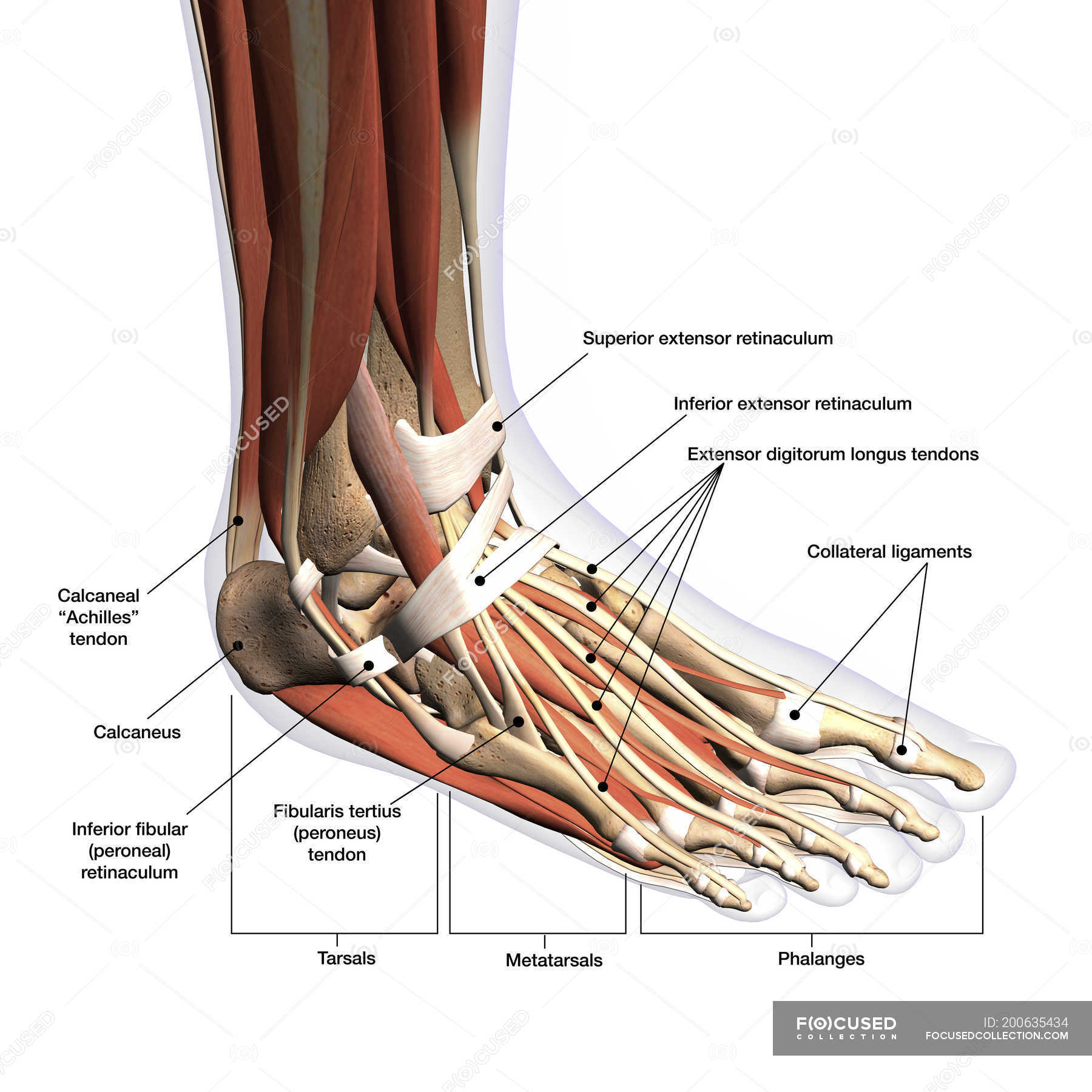
Anatomy of human foot with labels on white background — ankle, leg
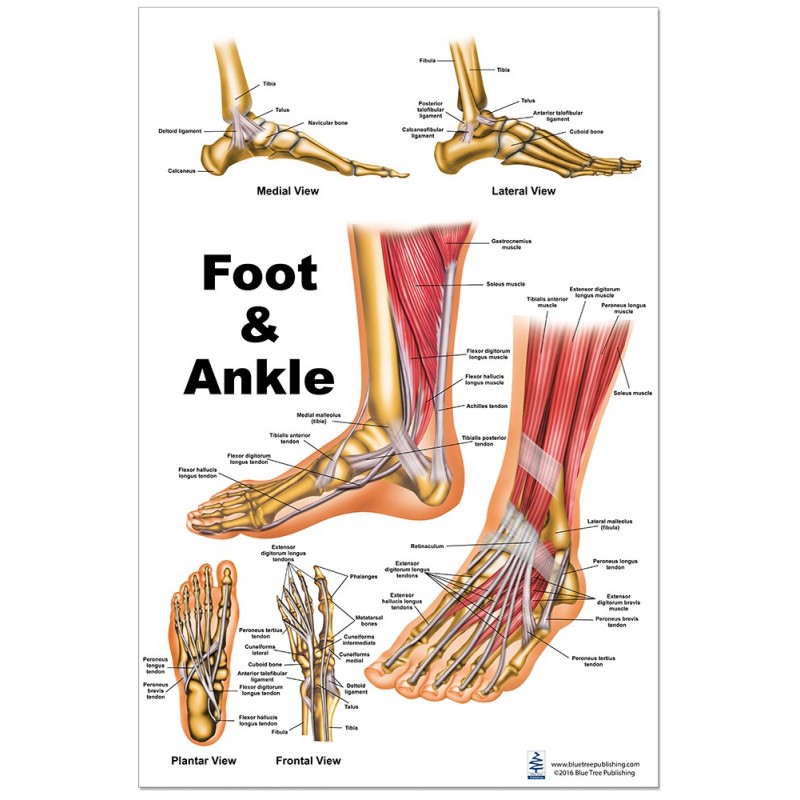
ankle and foot anatomy

Foot Anatomy 101 A Quick Lesson From a New Hampshire Podiatrist Nagy

Understanding the Foot and Ankle 1004 Anatomical Parts & Charts
Additionally, The Lower Leg Often Refers To The Area Between The Knee And The Ankle And This Area Is Critical To The Functioning Of The Foot.
The Midfoot, Containing The Navicular, Cuboid, And Cuneiforms;
Web Our Lower Limb Muscle Chart Contains Tables With The Attachments, Innervations And Functions Of Every Muscle.
Web The Foot Is Traditionally Divided Into Three Regions:
Related Post: