Foot Anatomy Chart
Foot Anatomy Chart - Identification of compression syndromes requires a very good understanding of the anatomy of the nerves and vessels of the foot and ankle. These bones give structure to the foot and allow for all foot movements like flexing the toes and ankle, walking, and running. Major (2nd most important) medial arch support. And the forefoot, which includes the metatarsals and phalanges. Learn more about foot bones and foot anatomy here. Web the anatomy of feet: Web the foot muscles are divided into nine compartments encompassed by fascia, although past studies on the exact divisions of the foot have varied considerably. It will also look at some of the common conditions that affect the foot and their possible treatment options. The hindfoot, midfoot, and forefoot. Web in humans, the foot is one of the most complex structures in the body. Identification of compression syndromes requires a very good understanding of the anatomy of the nerves and vessels of the foot and ankle. Upper ankle joint (tibiotarsal), talocalcaneonavicular, and subtalar joints. The osseous components of the ankle joint include the distal tibia, distal fibula, and talus. Web the many bones, ligaments, and tendons of the foot help you move, but they. The osseous components of the ankle joint include the distal tibia, distal fibula, and talus. [3] [4] this article discusses the key anatomical structures of the foot. This article will give an overview of foot anatomy and foot problems that come from overuse, injury, and normal wear and tear of the foot. Web it consists of 28 bones, which can. Web the many bones, ligaments, and tendons of the foot help you move, but they can also be injured and limit your mobility. [1] [2] the medial compartment contains the abductor hallucis, flexor hallicus brevis, and. There are ten intrinsic muscles located in the plantar aspect (sole) of the foot. Web the foot is divided into three parts: Web there. Web the many bones, ligaments, and tendons of the foot help you move, but they can also be injured and limit your mobility. The osseous components of the ankle joint include the distal tibia, distal fibula, and talus. They are complex structures with 26 bones. [3] [4] this article discusses the key anatomical structures of the foot. Web now that. [1] [2] the medial compartment contains the abductor hallucis, flexor hallicus brevis, and. This article will give an overview of foot anatomy and foot problems that come from overuse, injury, and normal wear and tear of the foot. And the forefoot, which includes the metatarsals and phalanges. These will be reviewed in the sections of this chapter. It is made. Ebraheim’s educational animated video describes anatomical structures of the foot and ankle, the bony anatomy, the joints, ligaments, and the compartments, in a simple and easy way. The ankle or tibiotalar joint constitutes the junction of the lower leg and foot. Like the fingers, the toes have flexor and extensor muscles that power. It is made up of three joints:. The ankle joint, also known as the talocrural joint, allows dorsiflexion and plantar flexion of the foot. Web it consists of 28 bones, which can be divided functionally into three groups, referred to as the tarsus, metatarsus and phalanges. Bones of the foot and ankle. Web the foot muscles are divided into nine compartments encompassed by fascia, although past studies. Web in humans, the foot is one of the most complex structures in the body. They are complex structures with 26 bones. This article will give an overview of foot anatomy and foot problems that come from overuse, injury, and normal wear and tear of the foot. These bones are divided into three main regions: Web the many bones, ligaments,. A clinician's ability to understand the anatomical structures of the foot is crucial for assessment and treatment, especially for clinicians working with clients with musculoskeletal conditions. The osseous components of the ankle joint include the distal tibia, distal fibula, and talus. There are ten intrinsic muscles located in the plantar aspect (sole) of the foot. Web the foot is divided. The ankle joint, also known as the talocrural joint, allows dorsiflexion and plantar flexion of the foot. The osseous components of the ankle joint include the distal tibia, distal fibula, and talus. Web the many bones, ligaments, and tendons of the foot help you move, but they can also be injured and limit your mobility. Web there are a variety. The hindfoot, midfoot, and forefoot. They are complex structures with 26 bones. And the forefoot, which includes the metatarsals and phalanges. The midfoot, containing the navicular, cuboid, and cuneiforms; Web there are a variety of anatomical structures that make up the anatomy of the foot and ankle (figure 1) including bones, joints, ligaments, muscles, tendons, and nerves. Learn more about foot bones and foot anatomy here. Web now that you’ve measured your foot size, compare the measurements against a nike size chart to find the best shoe size for you. There are ten intrinsic muscles located in the plantar aspect (sole) of the foot. Web the anatomy of the foot. The ankle joint, also known as the talocrural joint, allows dorsiflexion and plantar flexion of the foot. Upper ankle joint (tibiotarsal), talocalcaneonavicular, and subtalar joints. Web in humans, the foot is one of the most complex structures in the body. [3] [4] this article discusses the key anatomical structures of the foot. Base of the 5th metatarsal (lateral band), plantar plate and bases of the five proximal phalanges. Web the many bones, ligaments, and tendons of the foot help you move, but they can also be injured and limit your mobility. [1] [2] the medial compartment contains the abductor hallucis, flexor hallicus brevis, and.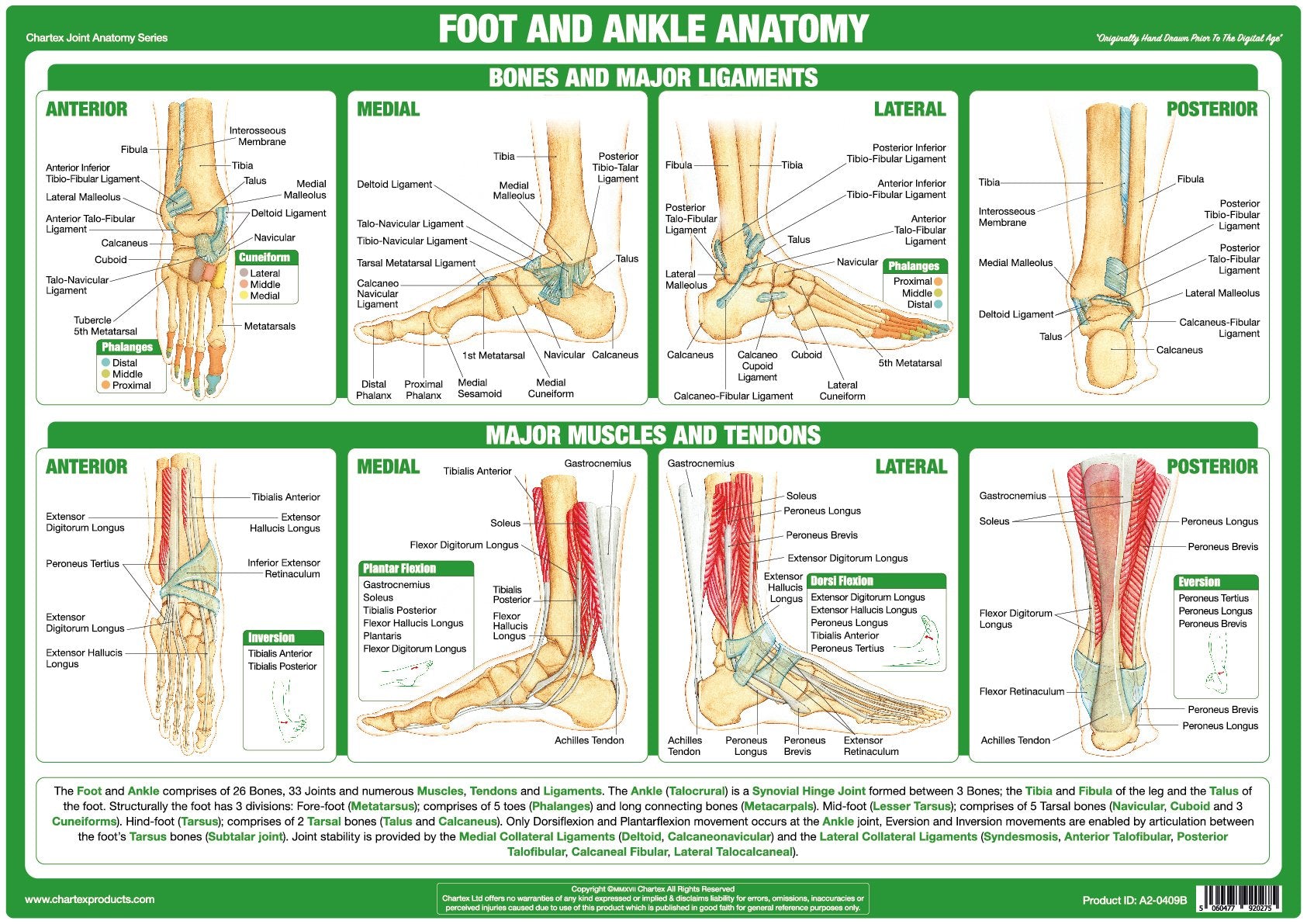
hand bone anatomy joints

Foot & Ankle Anatomy Chart Feet Poster Anatomical Chart
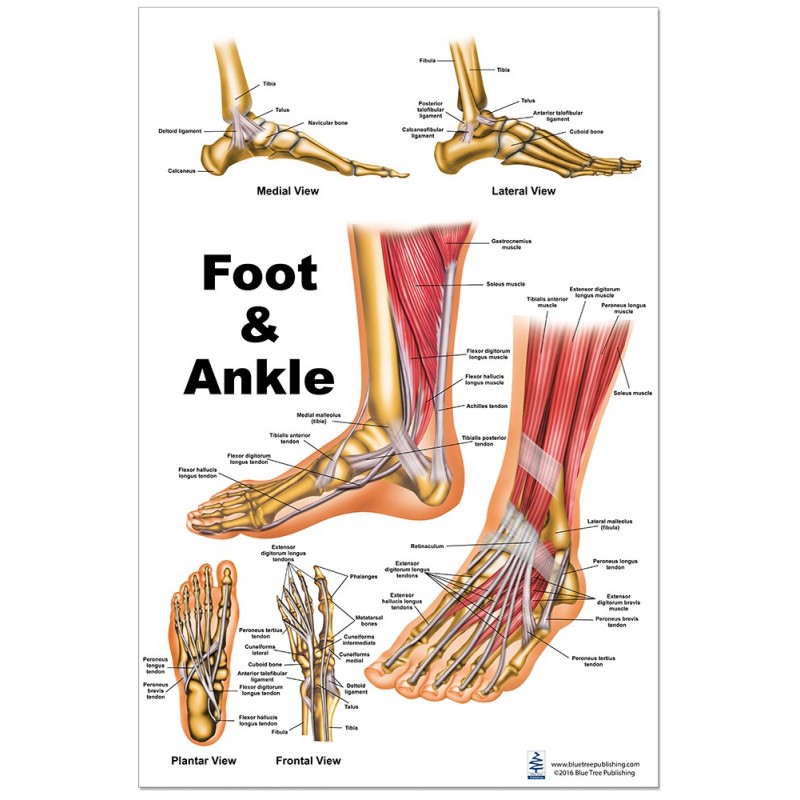
Foot Muscles Anatomy lupon.gov.ph

Foot Anatomy 101 A Quick Lesson From a New Hampshire Podiatrist Nagy

Understanding the Foot and Ankle 1004 Anatomical Parts & Charts

This chart shows foot and ankle bone and ligament anatomy, normal
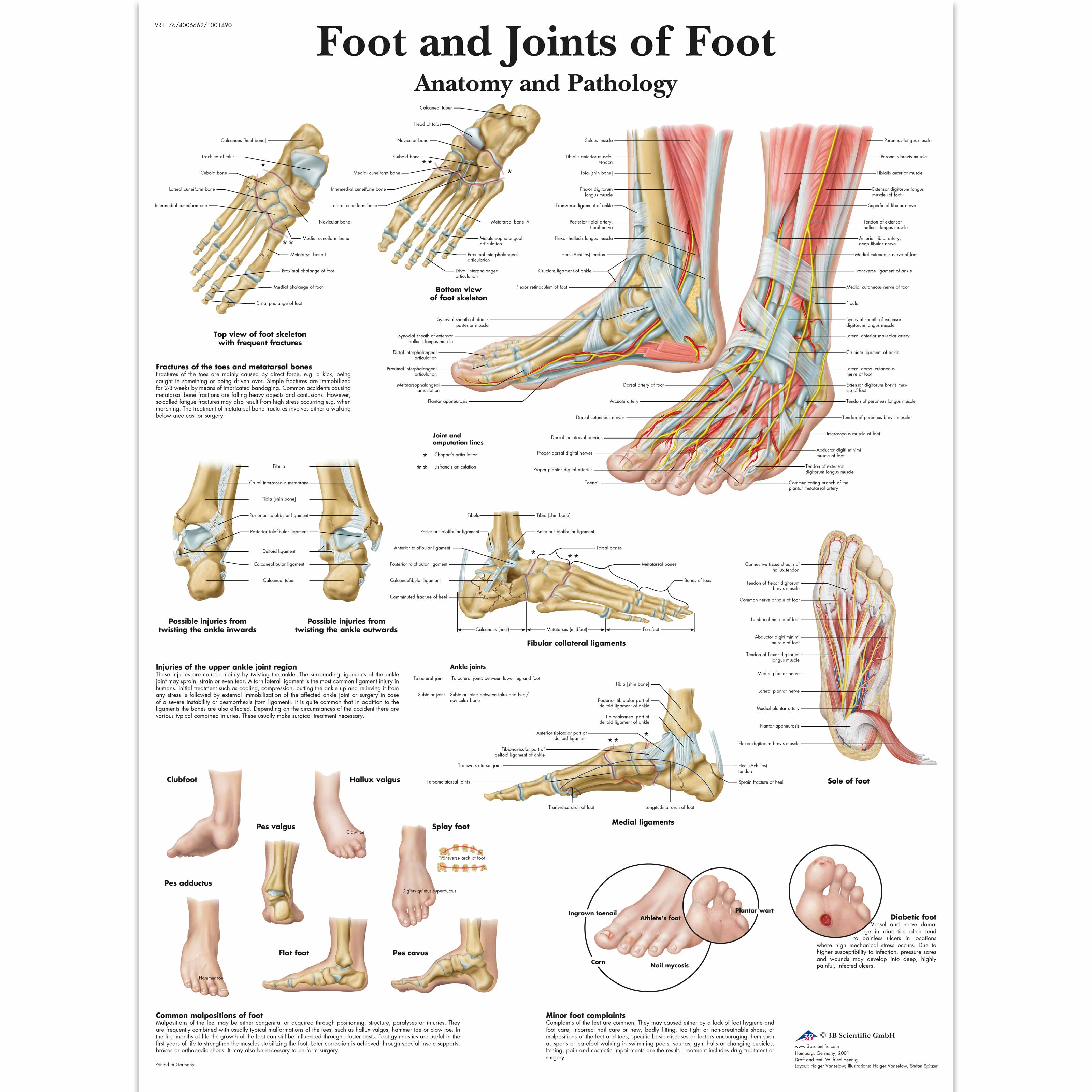
Anatomical Charts and Posters Anatomy Charts Foot and Ankle
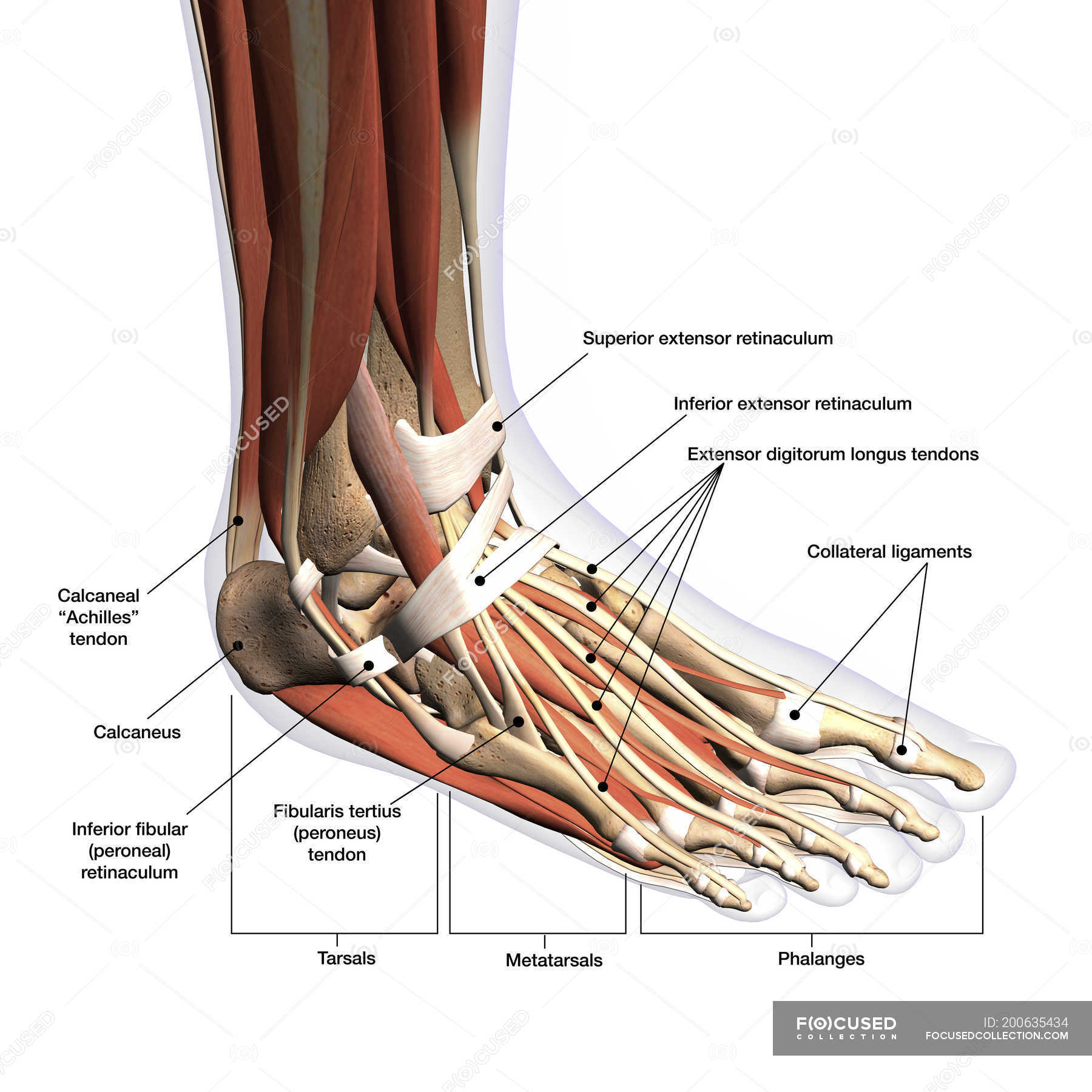
Anatomy of human foot with labels on white background — ankle, leg

hand bone and tendon chart Artist The Dorsal Foot How Do I Love
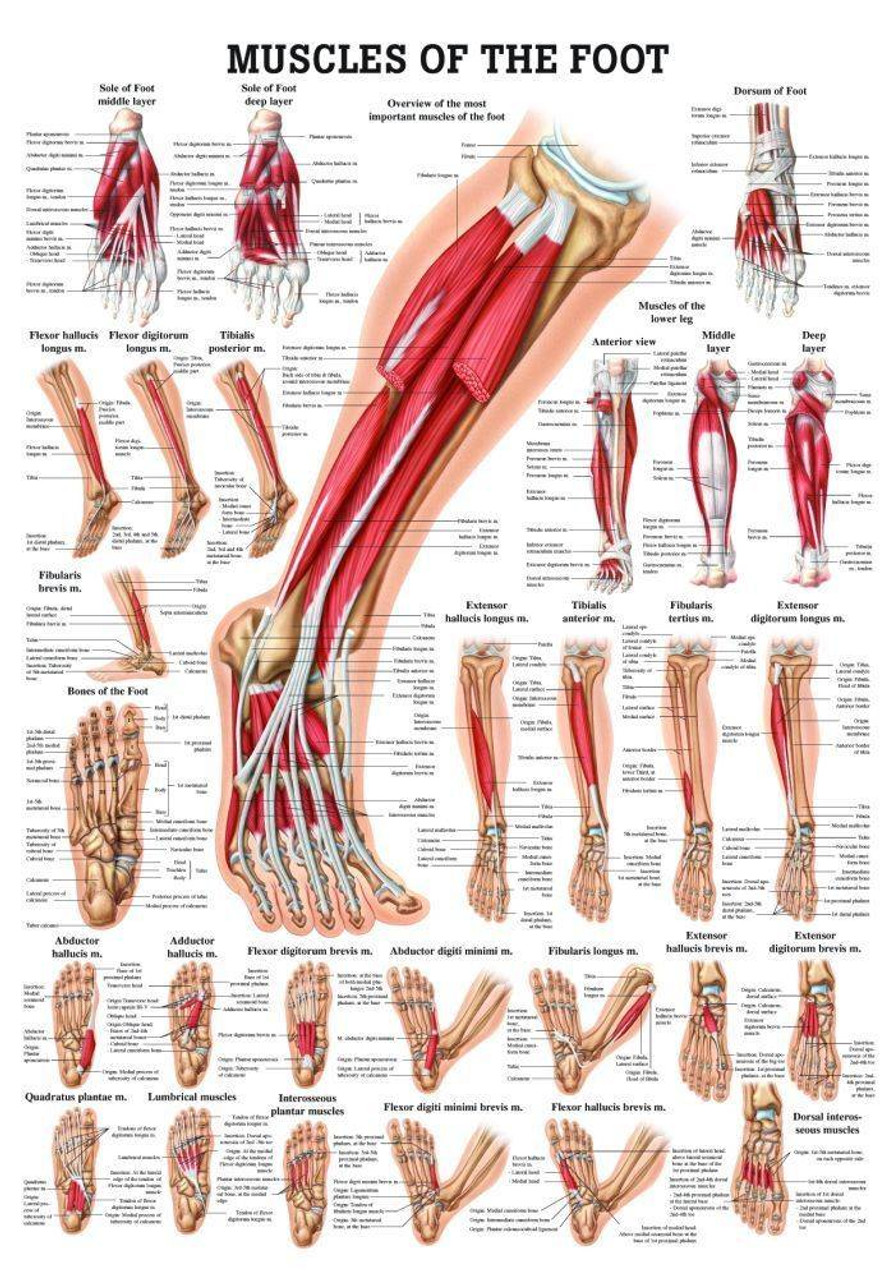
Foot Ankle Anatomy Chart Poster Laminated ubicaciondepersonas.cdmx.gob.mx
The Anatomic Structures Below The Ankle Joint Comprise The Foot, Which Includes:
These Bones Give Structure To The Foot And Allow For All Foot Movements Like Flexing The Toes And Ankle, Walking, And Running.
The Dorsal Layer Of Foot Muscles.
This Article Will Give An Overview Of Foot Anatomy And Foot Problems That Come From Overuse, Injury, And Normal Wear And Tear Of The Foot.
Related Post: