Glaucoma Cup To Disc Ratio Chart
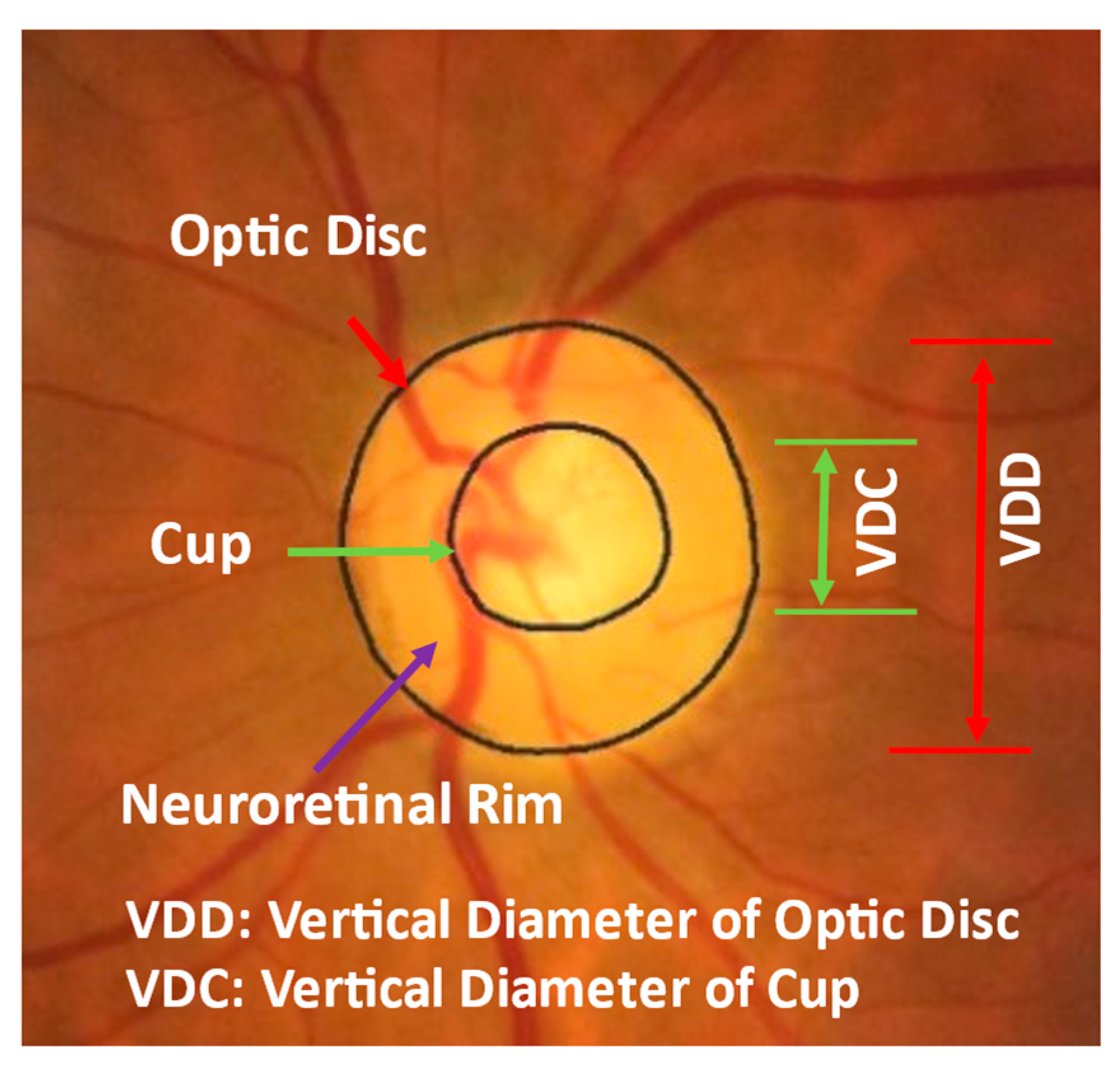
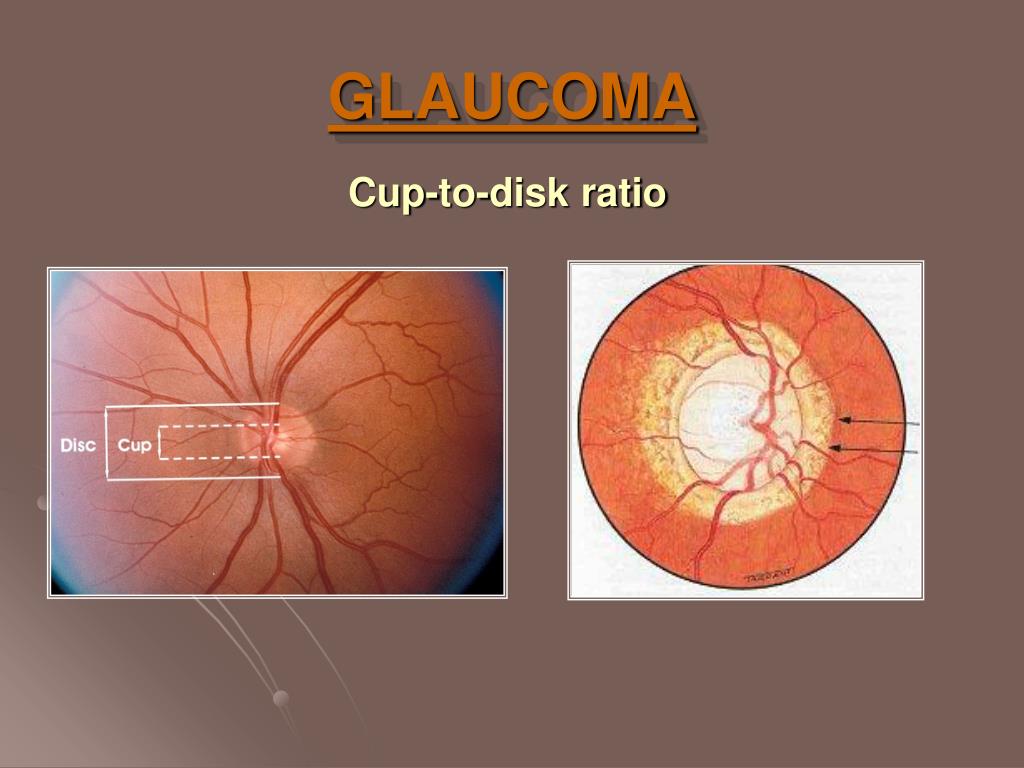
Glaucoma Cup To Disc Ratio Chart - If it fills 7/10 of the disc, the ratio is 0.7. The changes in peripapillary region. • if cup to disc ratio size is more than >0.5 mm then this is called case of glaucoma. The normal cup to disc ratio (the diameter of the cup divided by the diameter of the whole nerve head or disc) is about 1/3 or 0.3. Fig 1 shows some cases of glaucoma visible on the retinal. There were poor correlations between cdr and iop ( r = 0.18; To evaluate the relative diagnostic strength of cup to disc (c/d) ratio, clinical disc damage likelihood scale (ddls), a new clinical method of documenting glaucomatous. Image license and citation guidelines. However, a general rule of thumb is that ~0.6 or greater is suspicious. The shape and configuration of the vessels in the onh; If it fills 7/10 of the disc, the ratio is 0.7. • if cup to disc ratio size is more than. Web comprehensive ophthalmology, glaucoma. The normal cup to disc ratio (the diameter of the cup divided by the diameter of the whole nerve head or disc) is about 1/3 or 0.3. Web how is optic nerve damage detected? Web comprehensive ophthalmology, glaucoma. The presence of the laminar dot sign in the cup; • if cup to disc ratio size is more than >0.5 mm then this is called case of glaucoma. The shape and configuration of the vessels in the onh; Web if the cup fills 1/10 of the disc, the ratio will be 0.1. There were poor correlations between cdr and iop ( r = 0.18; • if cup to disc ratio size is more than. The shape and configuration of the vessels in the onh; Web if the cup fills 1/10 of the disc, the ratio will be 0.1. Web the average cup to disc ratio is about 0.4, and ratios of 0.7. P = 0.000209) and cdr and age ( r = 0.21; • if cup to disc ratio size is more than >0.5 mm then this is called case of glaucoma. Image license and citation guidelines. The normal cup to disc ratio (the diameter of the cup divided by the diameter of the whole nerve head or disc) is about 1/3. The presence of the laminar dot sign in the cup; Image license and citation guidelines. Through periodic photographs of the optic nerve, the ratio of the cup to the. In glaucoma, the inferior and superior rims are affected first. Web a cup to disc ratio greater than 0.6 [1] in the scale of 0 to 1 is generally considered to. The normal cup to disc ratio (the diameter of the cup divided by the diameter of the whole nerve head or disc) is about 1/3 or 0.3. Through periodic photographs of the optic nerve, the ratio of the cup to the. Web has pressure its cup/disc ratio may vary from 0.1 to 0.9. • if cup to disc ratio size. Web has pressure its cup/disc ratio may vary from 0.1 to 0.9. The presence of the laminar dot sign in the cup; Web a cup to disc ratio greater than 0.6 [1] in the scale of 0 to 1 is generally considered to be suspicious for glaucoma. If it fills 7/10 of the disc, the ratio is 0.7. In glaucoma,. There is not a specific c/d ratio that is diagnostic of glaucoma. Web comprehensive ophthalmology, glaucoma. In glaucoma, the inferior and superior rims are affected first. Web how is optic nerve damage detected? The shape and configuration of the vessels in the onh; Web in order to detect progression of glaucomatous damage, we use clinical, structural and functional examination of the optic nerve. The normal cup to disc ratio (the diameter of the cup divided by the diameter of the whole nerve head or disc) is about 1/3 or 0.3. • if cup to disc ratio size is more than. To evaluate the. There were poor correlations between cdr and iop ( r = 0.18; The changes in peripapillary region. Web has pressure its cup/disc ratio may vary from 0.1 to 0.9. Web the average cup to disc ratio is about 0.4, and ratios of 0.7 or greater happen only 2.5% of the time, so cups this big raise our suspicion that glaucoma. However, a general rule of thumb is that ~0.6 or greater is suspicious. Web comprehensive ophthalmology, glaucoma. The shape and configuration of the vessels in the onh; Through periodic photographs of the optic nerve, the ratio of the cup to the. There is not a specific c/d ratio that is diagnostic of glaucoma. • if cup to disc ratio size is more than >0.5 mm then this is called case of glaucoma. • if cup to disc ratio size is more than. The changes in peripapillary region. Fig 1 shows some cases of glaucoma visible on the retinal. There were poor correlations between cdr and iop ( r = 0.18; Image license and citation guidelines. The normal cup to disc ratio (the diameter of the cup divided by the diameter of the whole nerve head or disc) is about 1/3 or 0.3. Web this study aims to determine the risk of acg and open angle glaucoma. Web how is optic nerve damage detected? Web in order to detect progression of glaucomatous damage, we use clinical, structural and functional examination of the optic nerve. Web has pressure its cup/disc ratio may vary from 0.1 to 0.9.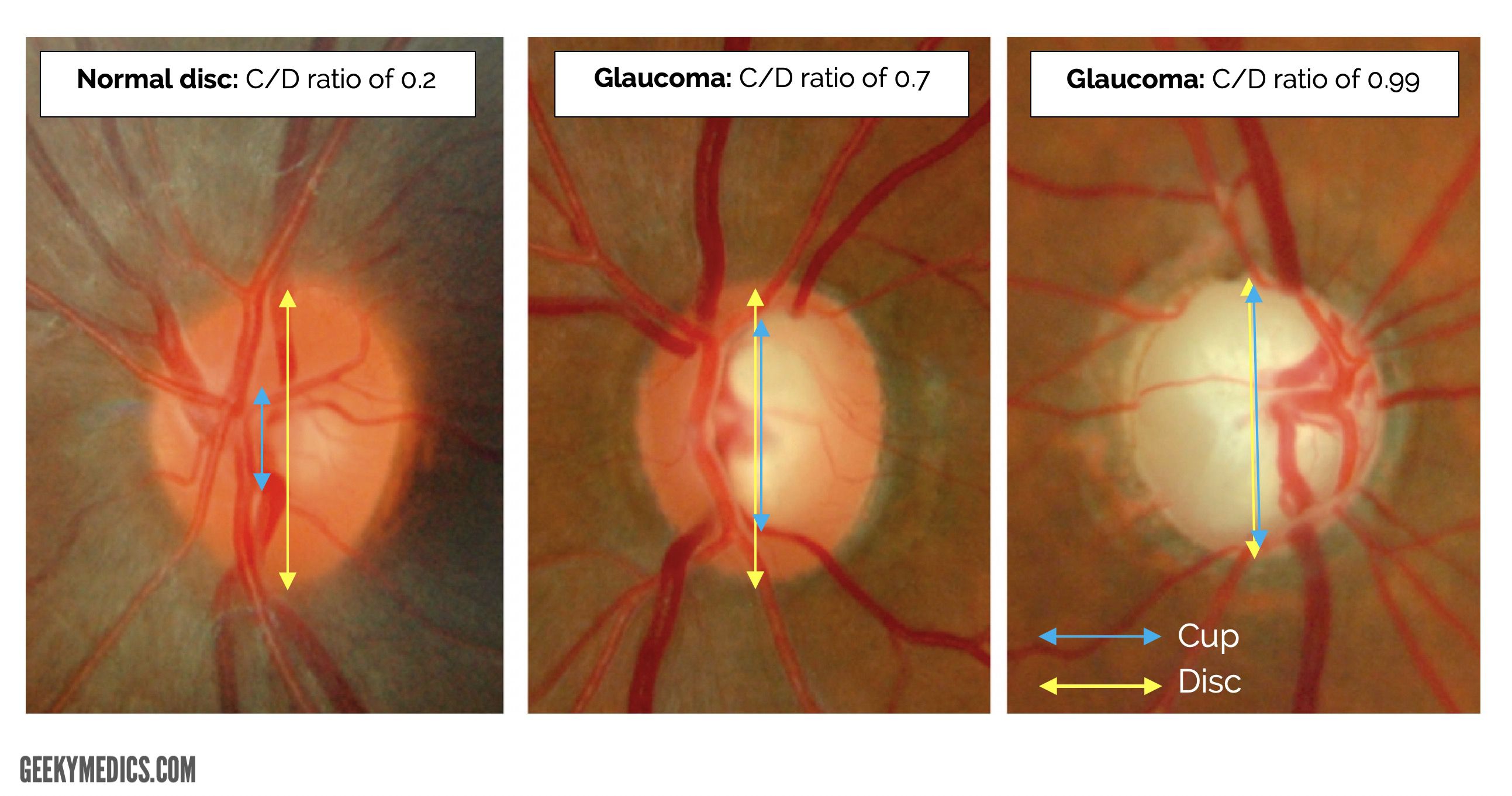
Fundoscopic Appearances of Retinal Pathologies Geeky Medics
Diagnostics Free FullText Identifying Those at Risk of A
Optic Disc Staging Systems Effective in Grading Advanced

Optician

시신경유두비증가, 유두함몰비증가, C/D ratio 및 시신경유두테패임, notching

image processing Detecting an ellipse in a photo

Automated determination of cuptodisc ratio for classification of

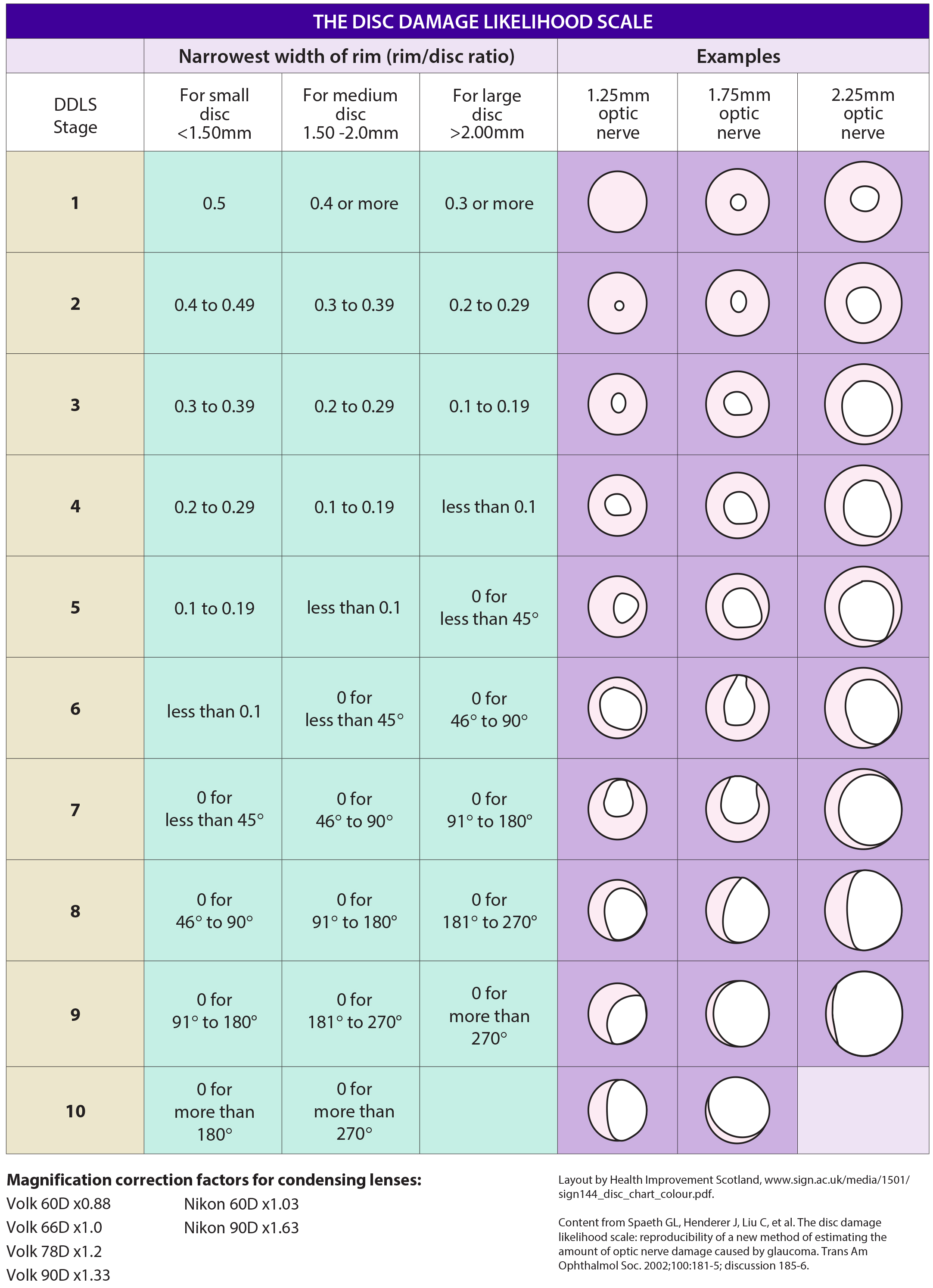
Comparison of disc damage likelihood scale, cup to disc ratio, and
PPT PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID177697

Automated determination of cuptodisc ratio for classification of
The Presence Of The Laminar Dot Sign In The Cup;
To Evaluate The Relative Diagnostic Strength Of Cup To Disc (C/D) Ratio, Clinical Disc Damage Likelihood Scale (Ddls), A New Clinical Method Of Documenting Glaucomatous.
Web If The Cup Fills 1/10 Of The Disc, The Ratio Will Be 0.1.
In Glaucoma, The Inferior And Superior Rims Are Affected First.
Related Post: