Harmonic Progression Chart
Harmonic Progression Chart - Web in tonal harmonic function, three core regions dictate the tonal balance: Web this page titled 9: Web an authentic cadence (v → i) or (viio → i) is the strongest way to approach a i chord. The strongest of all progressions involves the root of the chord moving down a fifth (or up a fourth), especially dominant (v) to tonic (i or i). I'll add this up here too. Ask yourself what happens after this melodic idea: These categories are traditionally called tonic (t), subdominant (s — also called predominant, p or pd), and dominant (d). Composers from the 1600s through the 1800s favored certain strong progressions. Strong progressions are the most common ones in tonal music and they often signal structurally important spots in a piece. The way in which the chords are arranged in a harmonic progression can have a significant impact on the overall feel and mood of a piece of music. These categories are traditionally called tonic (t), subdominant (s — also called predominant, p or pd), and dominant (d). 9.1 the circle of fifths progression. The only difference between the two is in the seventh degree. Web the harmonic minor scale is very similar to the natural minor scale. Each of these functions has their own characteristic scale degrees. Web in tonal harmonic function, three core regions dictate the tonal balance: The progression of harmonic functions in music is cyclical in nature: A detailed edit history is available upon request. The terms of a harmonic series are of the form 1/a, 1/(a + d), 1/(a + 2d), 1/(a + 3d),. I'll add this up here too. These categories are traditionally called tonic (t), subdominant (s — also called predominant, p or pd), and dominant (d). Web this page titled 9: Ask yourself what happens after this melodic idea: Web an authentic cadence (v → i) or (viio → i) is the strongest way to approach a i chord. Composers from the 1600s through the 1800s favored. Web expand into this chart of strong harmonic progressions (not including those in minor). Web the ultimate harmonic mixing & composing chart is a visual aid for musicians, producers, composers and djs to easily create music that always has harmonic chord progressions. Each of these functions has their own characteristic scale degrees. Web in this chapter we will look at. Web the chord chart below lists the common traid and four note extended chords belonging to the key of a harmonic minor. The only difference between the two is in the seventh degree. Web harmonic function is the tendency of chords to rest or progress to other chords. 9.1 the circle of fifths progression. The strongest of all progressions involves. The strongest way to approach viio is a circle progression from iv. Ask yourself what happens after this melodic idea: This sheet is now widely used worldwide as a teaching and practical tool in music and dj schools and has been downloaded hundreds of thousands of times. The progression of harmonic functions in music is cyclical in nature: In minor,. The progression of harmonic functions in music is cyclical in nature: These categories are traditionally called tonic (t), subdominant (s — also called predominant, p or pd), and dominant (d). In minor, doing chromatic alterations of at least the 7th scale degree is the basic thing to do. Web the ultimate harmonic mixing & composing chart is a visual aid. The strongest way to approach viio is a circle progression from iv. In harmonic progression, any term in the sequence is considered as the harmonic means of its two neighbours. In minor, doing chromatic alterations of at least the 7th scale degree is the basic thing to do. Harmonic progression and harmonic function is shared under a gnu free documentation. Web this page titled 9: The terms of a harmonic series are of the form 1/a, 1/(a + d), 1/(a + 2d), 1/(a + 3d),. A sequence is a pattern immediately repeated in the same voice that begins on a different pitch class. Web the ultimate harmonic mixing & composing chart is a visual aid for musicians, producers, composers and. In this text, we will discuss four. Composers from the 1600s through the 1800s favored certain strong progressions. Web in this chapter we will look at common harmonic progressions and examine the principle of harmonic function that underlies progressions. 9.1 the circle of fifths progression. Many texts on music theory enumerate three harmonic functions. The triad and extended (four voice) chord sequence derived from the harmonic minor scale are as follows. Web the circle of fifths progression has a feeling of inevitability about it because it consists of harmonic sequences. Ask yourself what happens after this melodic idea: The progression of harmonic functions in music is cyclical in nature: These categories are traditionally called tonic (t), subdominant (s — also called predominant, p or pd), and dominant (d). Web the harmonic minor scale is very similar to the natural minor scale. Each of these functions has their own characteristic scale degrees. Chord progressions are the foundation of harmony in western musical tradition from the common practice era of classical music to the 21st century. Strong progressions are the most common ones in tonal music and they often signal structurally important spots in a piece. On the natural minor scale, the seventh degree is minor, while in the harmonic minor scale, the seventh degree is major. Web in a musical composition, a chord progression or harmonic progression (informally chord changes, used as a plural) is a succession of chords. A detailed edit history is available upon request. Web the chart to the left shows natural progressions and patterns in diatonic chords from a major scale. Composers from the 1600s through the 1800s favored certain strong harmonic progressions. Many texts on music theory enumerate three harmonic functions. A sequence is a pattern immediately repeated in the same voice that begins on a different pitch class.
Harmonic Progression Music Theory
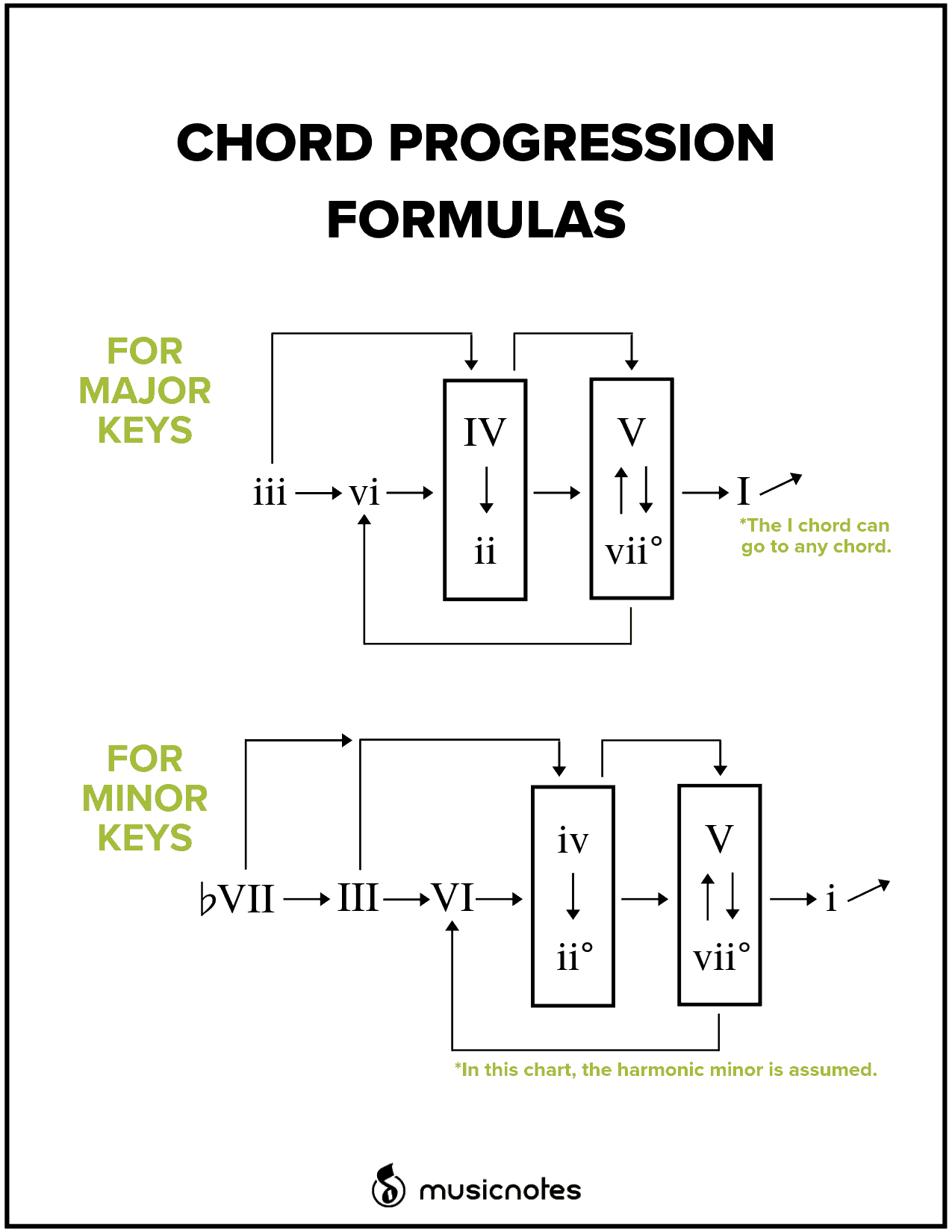
How to Use Chord Progression Formulas in Music — Musicnotes Now
Harmonic Progression Brilliant Math & Science Wiki

The Harmonic Minor Scale on Piano (Free Chart + Pictures

Practicing Functional Harmony with Dice Henry Flurry

Printable Guitar Harmonic Minor Scale Chart Guitar Scales Guitar Images

Harmonic Progression Music theory guitar, Music theory, Music theory
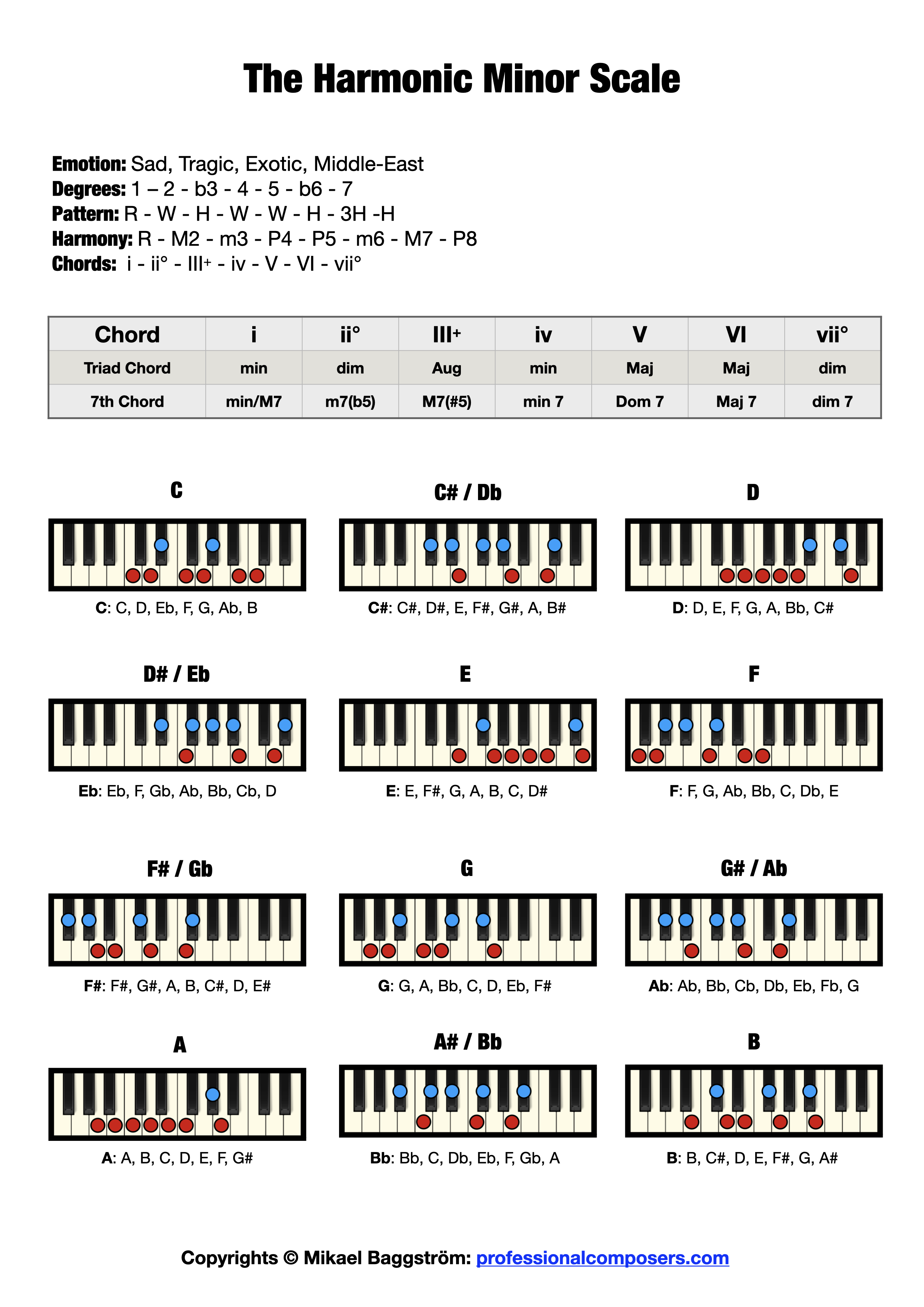
The Harmonic Minor Scale on Piano (Free Chart + Pictures
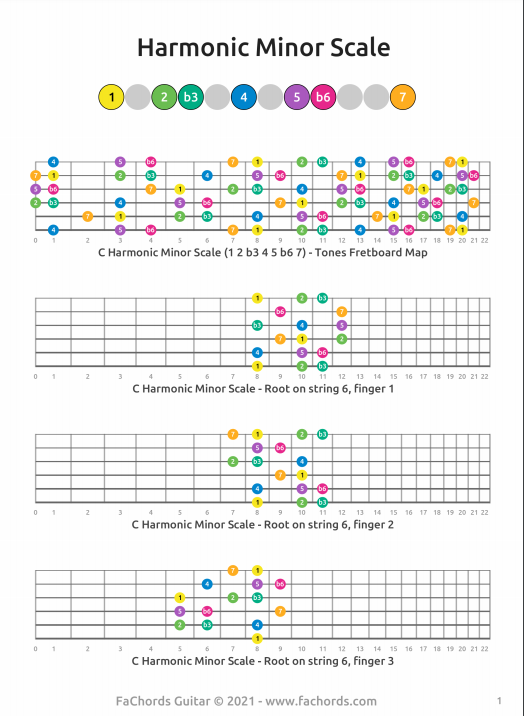
The Harmonic Minor Scale How To Play This Scale On Guitar (2022)
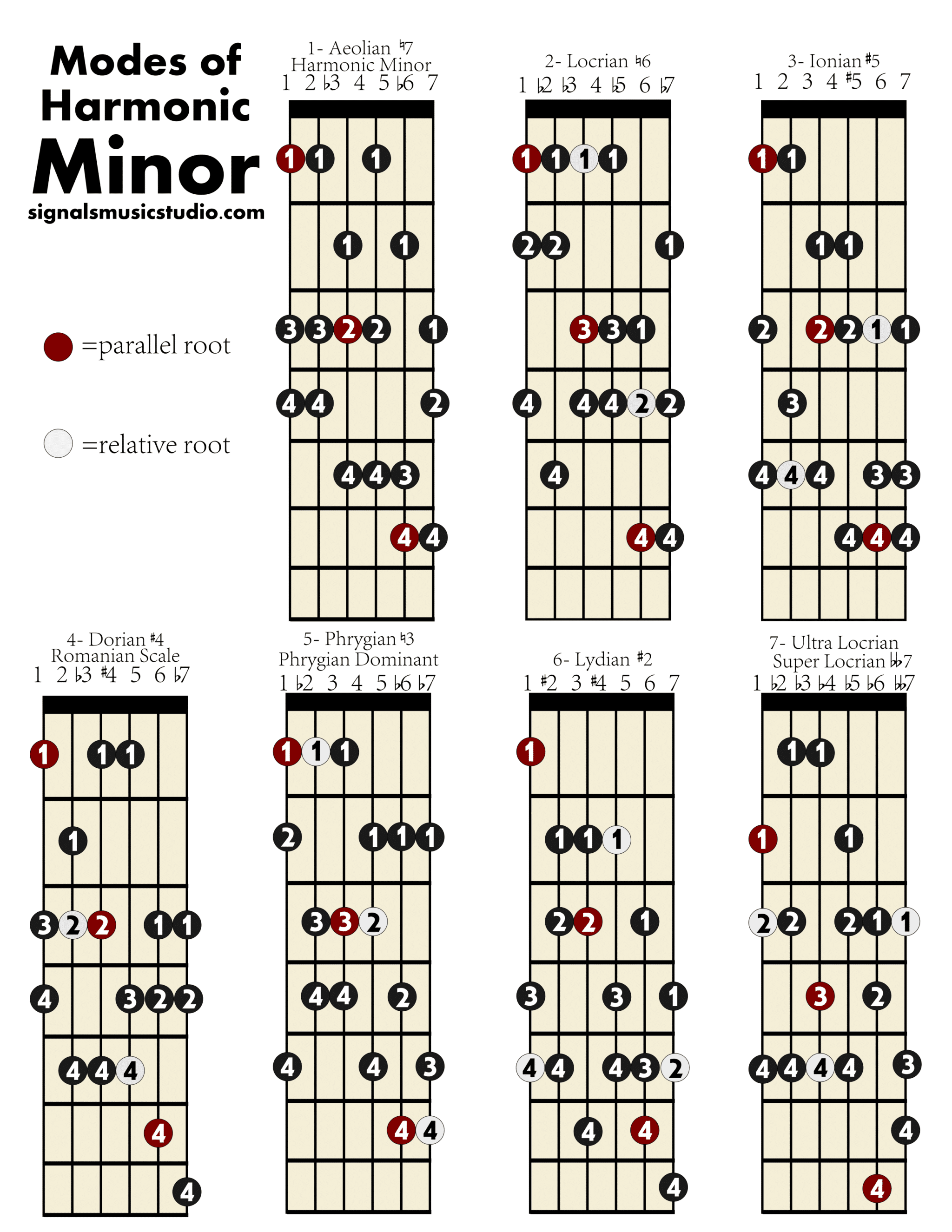
HARMONIC MINOR MODES PNG Files Signals Music Studio
9.1 The Circle Of Fifths Progression.
Web A Harmonic Progression (Hp) Is Defined As A Sequence Of Real Numbers Which Is Determined By Taking The Reciprocals Of The Arithmetic Progression That Does Not Contain 0.
To Understand Harmonic Sequence We Will First Look At Melodic Sequences, Since The Bass Line Is The “Melody” In A Harmonic Sequence.
Web The Chord Chart Below Lists The Common Traid And Four Note Extended Chords Belonging To The Key Of A Harmonic Minor.
Related Post:
