How Do You Draw A Tree Diagram
How Do You Draw A Tree Diagram - A coin and a dice are thrown at random. (iii) the product of the two numbers is at least 5. This calculates the probability of the bag containing a forbidden item (0.05) and not triggering the alarm (1 − 0.98 = 0.02). To add text to a shape, select the shape, and then type. Generate a tree diagram from text: We could then use the diagram to answer any question about probabilities involving two coins. Tree diagrams also help you find the root cause of a problem, break down large goals, and explain steps to others. We can use a tree diagram to help list all the possible outcomes. You and your team can work on the same tree diagram by saving it to a. This is done by multiplying each probability along the branches of the tree. (ii) the sum of the two numbers is even. · the probability of getting heads first and tails second is 0.5x0.5 = 0.25. You and your team can work on the same tree diagram by saving it to a. Web from this point, you can use your probability tree diagram to draw several conclusions such as: Fill in the probabilities. Web draw a tree diagram to represent the probabilities of drawing two consecutive balls of the same color. This means that the probability of tossing two heads is 25%. We give examples and also go through how to use a tree diag. Web about press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how youtube works test. A box contains 4 red and 2 blue chips. Web so p (h or 4) is 712. Web well, you could just count. Each of the ticked branches shows a way of achieving the desired outcome. Again, we can work this out from the tree diagram, by selecting every branch which includes a head or a 4: With smartdraw, anyone can quickly and easily create a tree diagram that looks like it was created by a professional. You are planning to go on a hike with a. Fill in the probabilities on the branches. You can also generate tree diagrams with plantuml and. A diagram used in strategic decision making, valuation or probability calculations. Web one card is removed at random from each box. Web select file > new > templates > general, and then open block diagram. (i) the sum of the numbers is 4. Web draw a tree diagram to represent the probabilities of drawing two consecutive balls of the same color. Web so p (h or 4) is 712. The probability the first bus will be late is 0.1 0.1 and the probability the second bus will be late is 0.3. P(h or 4) = p(h, 4) + p(h, not 4) + p(t, 4) = 1 12 + 5 12 + 1 12 = 7 12. B) getting a head or tail and an odd number. Notice that the. P (f) × p (¬a) = 0.05 × 0.02 = 0.001. Web so p (h or 4) is 712. (iii) the product of the two numbers is at least 5. For our example, 50% = 0.5, and 25% = 0.25. Web from this point, you can use your probability tree diagram to draw several conclusions such as: It's automated design does the drawing for you. A) let a denote the event of a head and an even number. (iii) two of the same color. This means that the probability of tossing two heads is 25%. (i) the sum of the numbers is 4. (i) at least one blue. · the probability of getting heads first and tails second is 0.5x0.5 = 0.25. Web it helps to draw a diagram to show the outcomes when looking at probability trees without replacement. (i) the sum of the numbers is 4. A coin and a dice are thrown at random. You and your team can work on the same tree diagram by saving it to a. Along the top path, we encounter heads and then heads again, or hh. B) calculate the probability of getting: You have two possible engines times four possible colors. A coin and a dice are thrown at random. Convert the percentages to decimals, and place those on the appropriate branch in the diagram. A coin and a dice are thrown at random. It's automated design does the drawing for you. Along the top path, we encounter heads and then heads again, or hh. The diagram starts at a single node, with branches emanating to additional nodes, which represent. To find the probability that a bag containing a forbidden item does not trigger the alarm, you multiply the probabilities together: · the probability of getting at least one tails from two consecutive flips is. (iii) two of the same color. P(h or 4) = p(h, 4) + p(h, not 4) + p(t, 4) = 1 12 + 5 12 + 1 12 = 7 12. A box contains 4 red and 2 blue chips. (iii) the product of the two numbers is at least 5. Again, we can work this out from the tree diagram, by selecting every branch which includes a head or a 4: (ii) one red and one blue. Tree diagrams can make some probability problems easier to visualize and solve. (when we take the 0.6 chance of sam being coach and include the 0.5 chance that sam will let you be goalkeeper we end up with an 0.3 chance.) The probability the first bus will be late is 0.1 0.1 and the probability the second bus will be late is 0.3.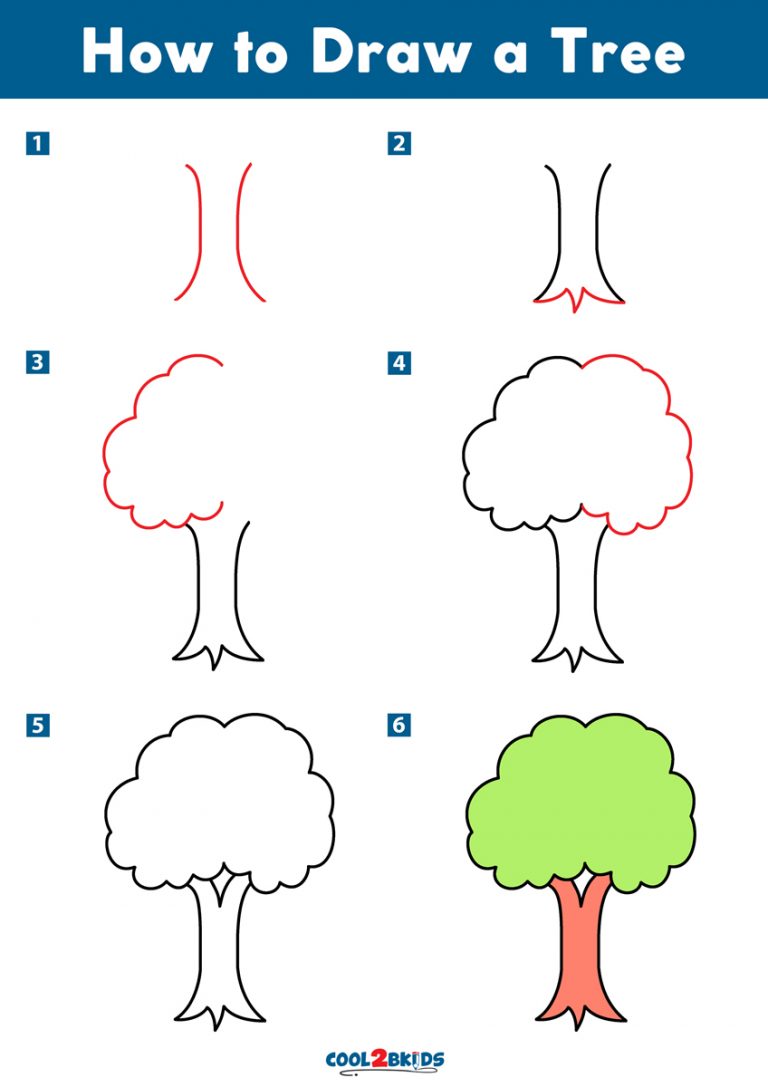
How to Draw a Tree Cool2bKids

Tree Diagrams no replacement version 2 Variation Theory

Easy How to Draw a Tree Tutorial Video and Tree Coloring Page
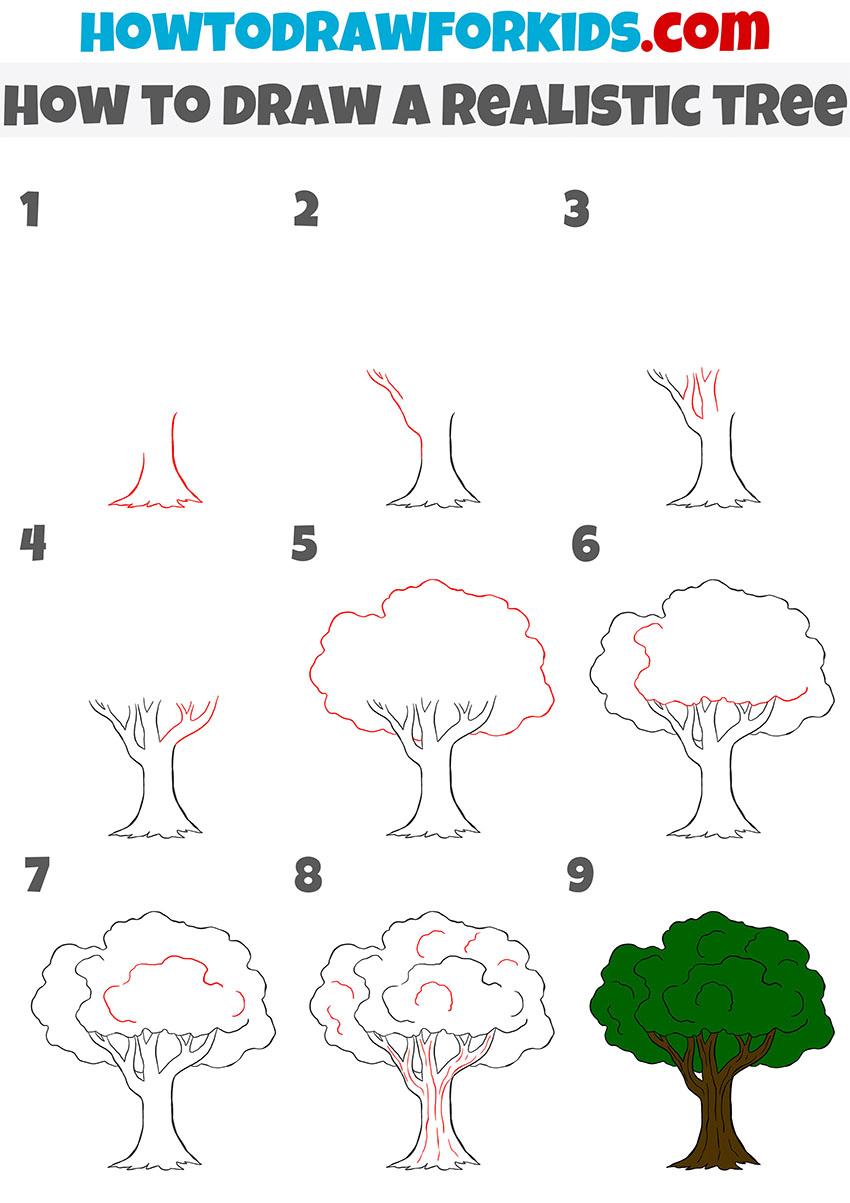
How to Draw a Realistic Tree Easy Drawing Tutorial For Kids

How To Construct, Make, Draw A Tree Diagram And What Is A Tree Diagram
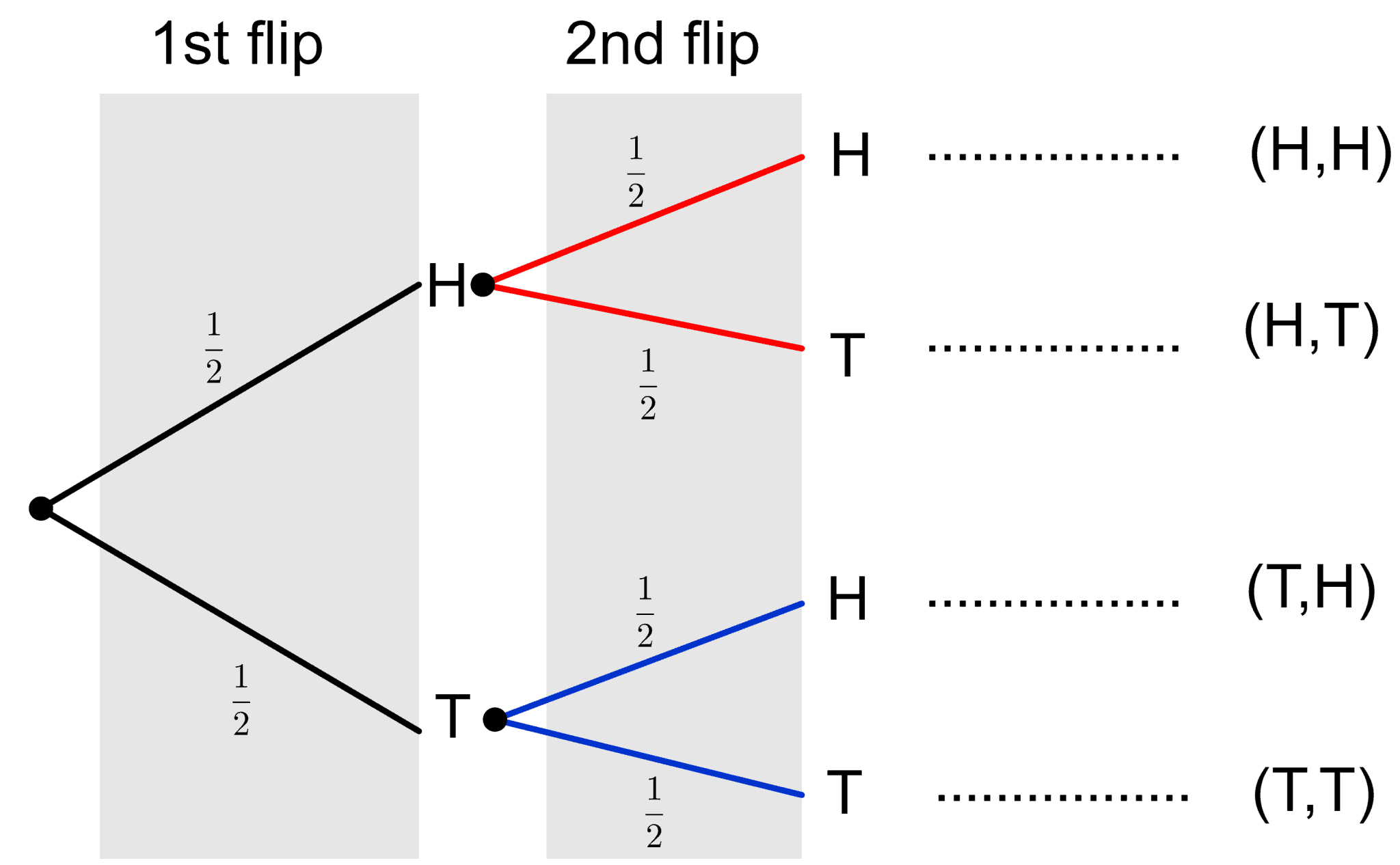
Finally, we can make a complete tree diagram of the two coin flips, as
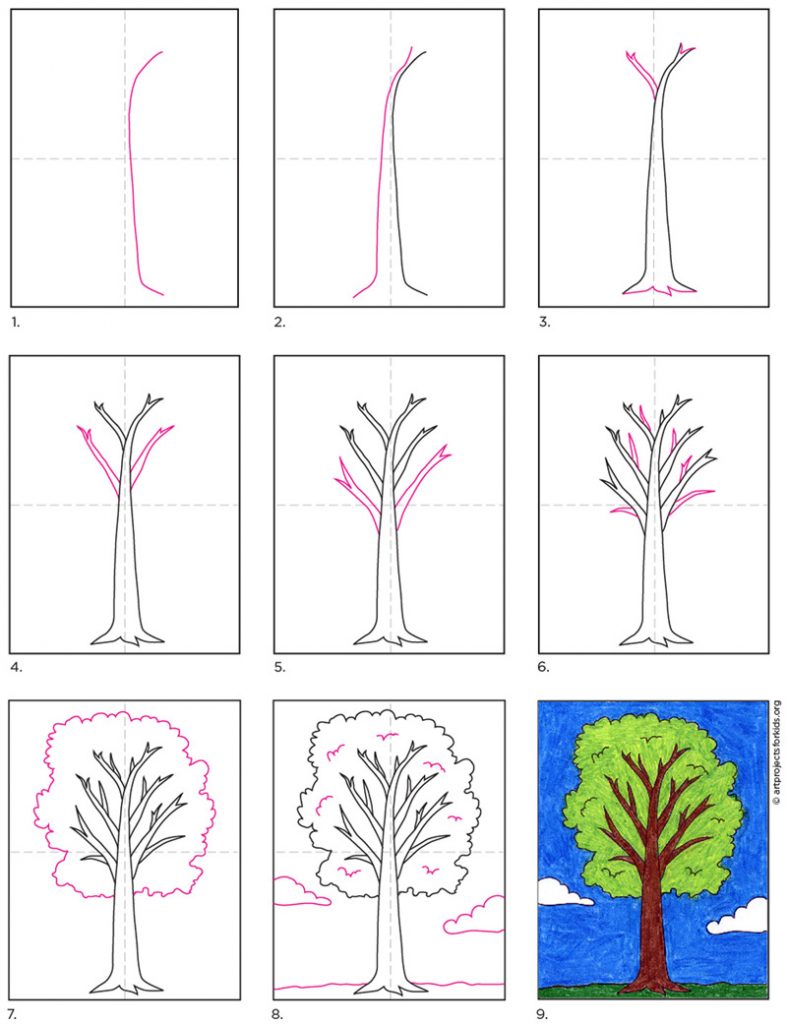
Easy How to Draw a Tree Tutorial Video and Tree Coloring Page
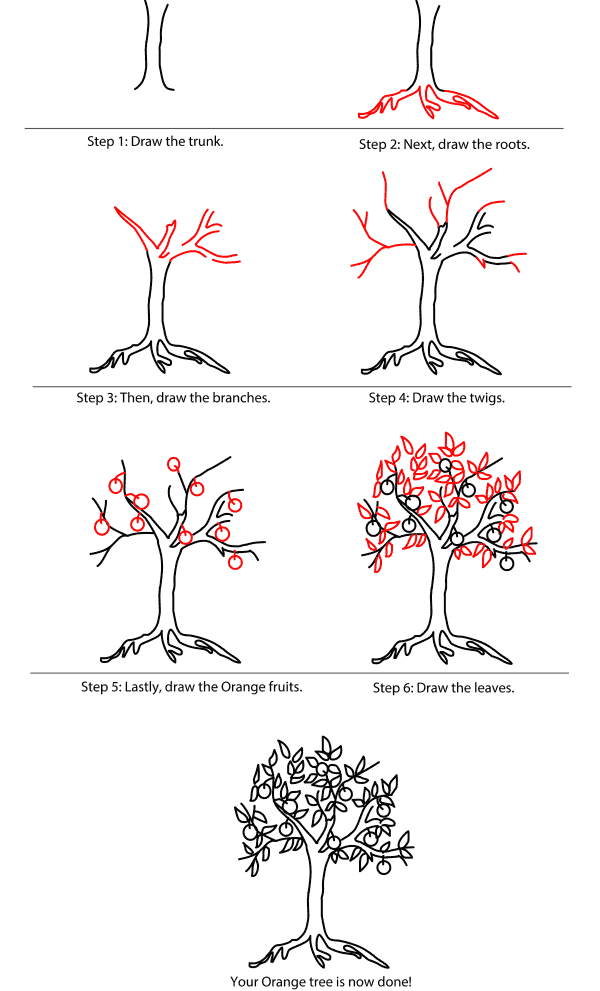
How To Draw A Tree (Step By Step Image Guides)

How Do You Draw A Tree Diagram
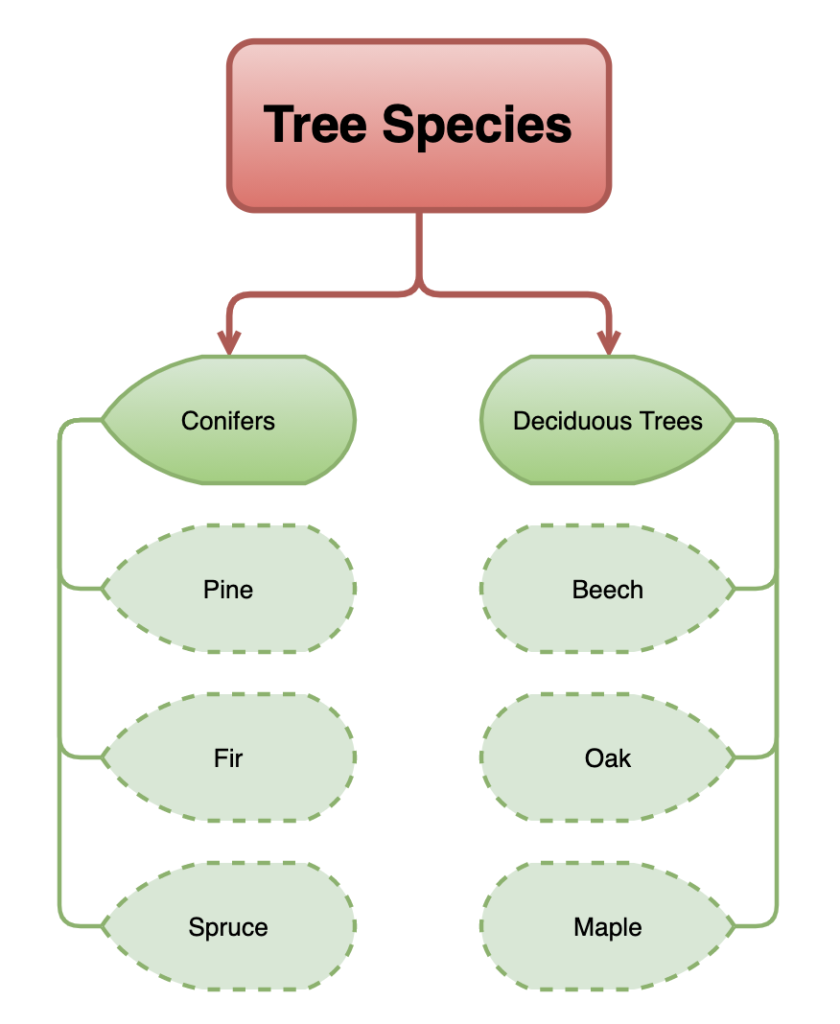
draw.io Training Exercise 5 Create a tree diagram draw.io
This Calculates The Probability Of The Bag Containing A Forbidden Item (0.05) And Not Triggering The Alarm (1 − 0.98 = 0.02).
Our Question Lists A B And C So That’s What We’ll Use Here.
For Example, On The Tree Diagram Above, Selecting A Red First Results In There Now Only Being 2 Red Marbles Left Out Of 9.
For Instance, In The First Draw, We Have $3$ Blue And $7$ Red Balls, So The Probability Of Drawing A Blue.
Related Post: