Igneous Rock Chart
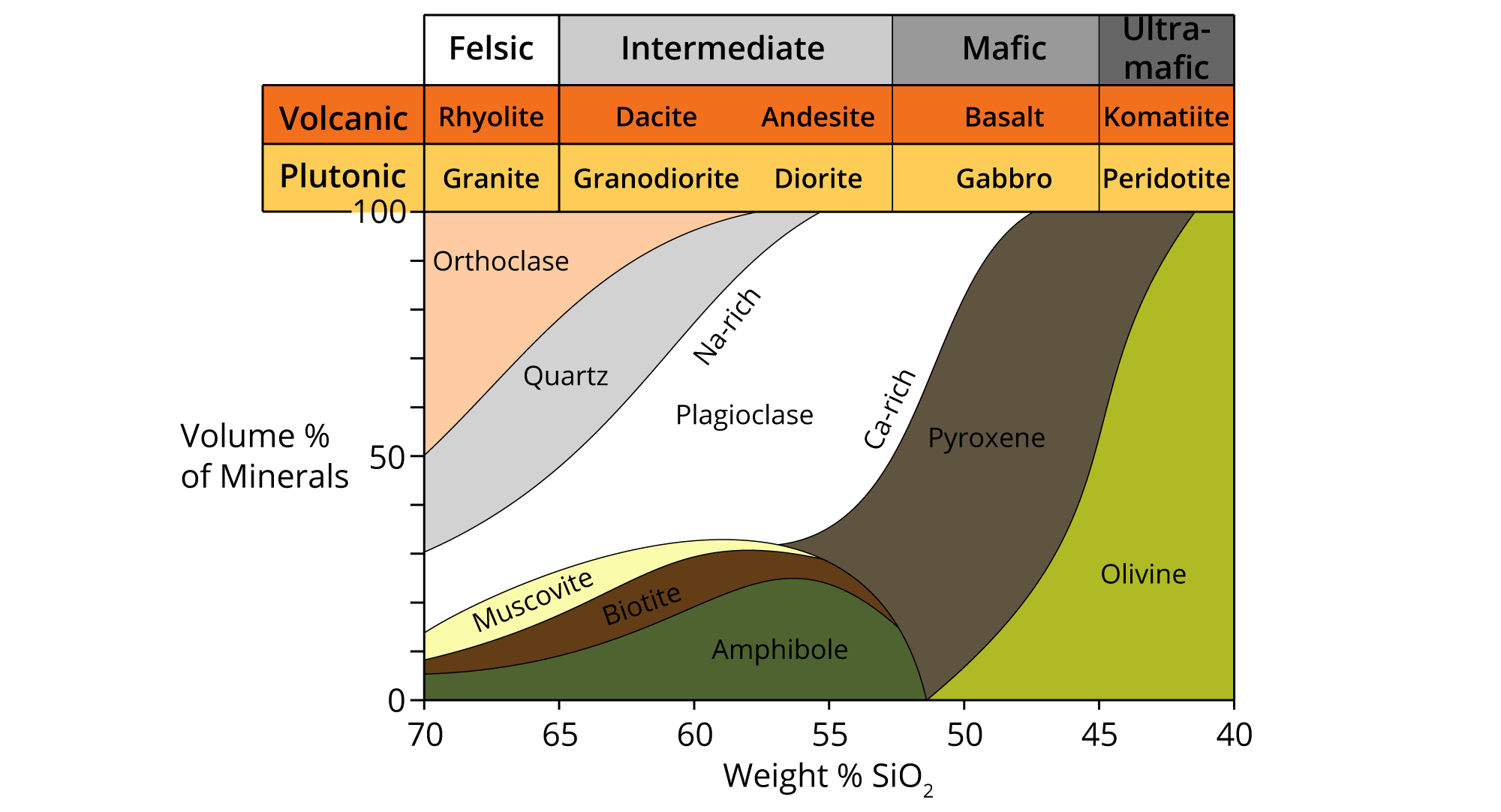
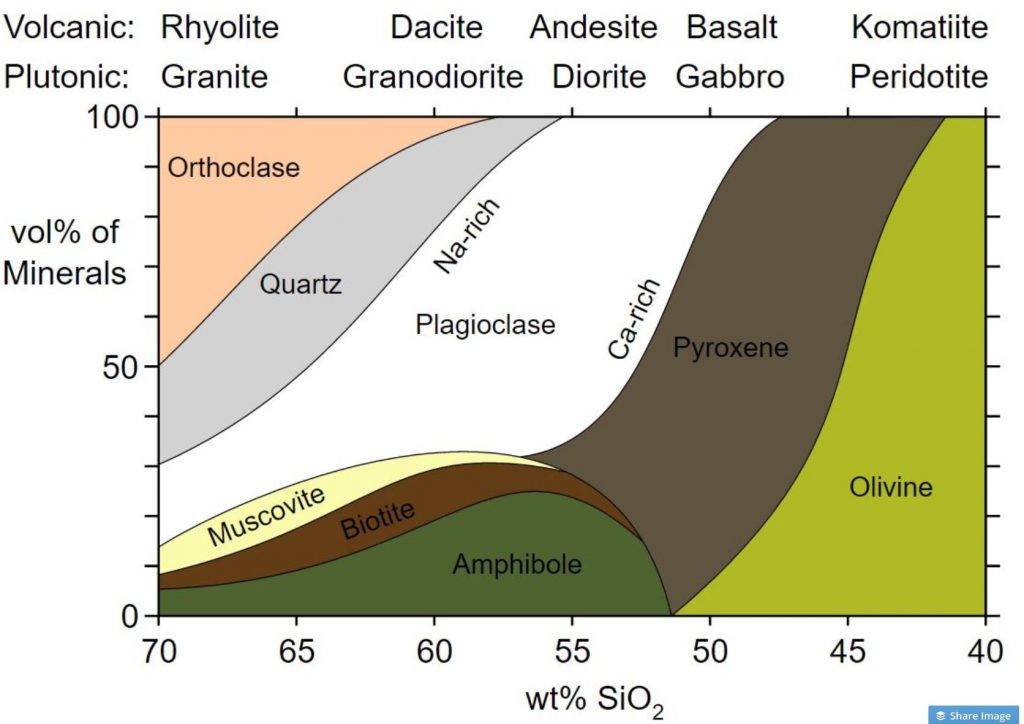
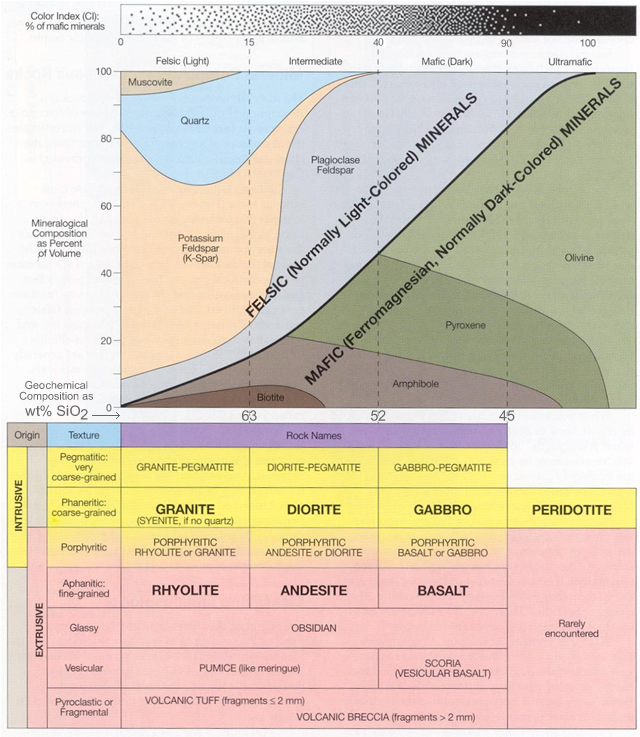
Igneous Rock Chart - Texture describes the physical characteristics of the minerals, such as grain size. Felsic, intermediate, mafic, and ultramafic, based on either their chemistry or their mineral composition. The diagram of bowen’s reaction series ( figure 7.7) shows that differences in chemical composition correspond to differences in the types of minerals within an igneous rock. This relates to the cooling history of the molten magma from which it came. Felsic, intermediate, mafic, and ultramafic. Properties and characteristics of igneous rocks. Web igneous rocks comprise one of the three principal classes of rocks, the others being metamorphic and sedimentary rocks. The diagram in figure 3.16 can be used to help classify igneous rocks by their mineral composition. Web igneous rocks are classified according to the relative abundances of minerals they contain. Composition refers to the rock’s specific mineralogy and chemical composition. Web igneous rocks are classified according to the relative abundances of minerals they contain. Felsic, intermediate, mafic, and ultramafic. Igneous rocks are typically hard and dense, resistant to weathering, and often exhibit a crystalline structure. In the mafic field, the arrows represent a rock containing 60% pyroxene and 40% olivine. Web in this study, we evaluated the fungal diversity present. Web once these two characteristics have been identified, the igneous rock identification chart is used to identify the rock name. Obsidian is an example of an extrusive igneous rock that is amorphous or lacks crystalline structure. Web igneous rock, any of various crystalline or glassy rocks formed by the cooling and solidification of molten earth material. Then, compare your observations. Igneous rocks are typically hard and dense, resistant to weathering, and often exhibit a crystalline structure. Web igneous rock composition is divided into four categories: Web as has already been described, igneous rocks are classified into four categories: Web igneous rocks form when magma (molten rock) cools and crystallizes, either at volcanoes on the surface of the earth or while. Felsic, intermediate, mafic, and ultramafic. The diagram in figure 3.4.1 can be used to help classify igneous rocks by their mineral composition. Igneous rocks constitute one of the three principal classes of rocks, the others being metamorphic and sedimentary. Web igneous rocks can be divided into four categories based on their chemical composition: Texture describes the physical characteristics of the. Mafic refers to the overall composition being high in concentrations of We detected 940,969 dna reads grouped into 198 amplicon sequence variants (asvs) representing the phyla ascomycota, basidiomycota, mortierellomycota, chytridiomycota, mucoromycota,. Web igneous rocks are classified based on texture and composition. A given rock is represented by a vertical line in the diagram. Andesite, basalt, dacite, obsidian, pumice, rhyolite, scoria,. This relates to the cooling history of the molten magma from which it came. Though they vary widely in composition, most igneous rocks consist of quartz, feldspars, pyroxenes, amphiboles, micas, olivines, nepheline, leucite, and apatite. Properties and characteristics of igneous rocks. Then, compare your observations to known igneous rock types. Felsic, intermediate, mafic, and ultramafic. Web igneous rocks comprise one of the three principal classes of rocks, the others being metamorphic and sedimentary rocks. Though they vary widely in composition, most igneous rocks consist of quartz, feldspars, pyroxenes, amphiboles, micas, olivines, nepheline, leucite, and apatite. For example, the arrows in the mafic field of the diagram represent a rock containing 48% pyroxene and 52% plagioclase. Classification chart for igneous rock lesson plan lab. Igneous rocks are typically hard and dense, resistant to weathering, and often exhibit a crystalline structure. For example, the arrows in the mafic field of the diagram represent a rock containing 48% pyroxene and 52% plagioclase feldspar. Web igneous rocks are classified according to the relative abundances of minerals they contain. The. Ultramafic, mafic, intermediate and felsic. A given rock is represented by a vertical line in the diagram. All magma develops underground, in the lower crust or upper mantle , because of the intense heat there. Web granite boulders at joshua tree national park, california. Web in this study, we evaluated the fungal diversity present associated with cores of oligocene rocks. The diagram of bowen’s reaction series ( figure 7.6 ) shows that differences in chemical composition correspond to differences in the types of minerals within an igneous rock. Web igneous rocks are classified based on texture and composition. Web as has already been described, igneous rocks are classified into four categories, based on either their chemistry or their mineral composition:. Texture describes the physical characteristics of the minerals, such as grain size. Web igneous rocks comprise one of the three principal classes of rocks, the others being metamorphic and sedimentary rocks. Web igneous rocks can be divided into four categories based on their chemical composition: Igneous rocks constitute one of the three principal classes of rocks, the others being metamorphic and sedimentary. Web in this study, we evaluated the fungal diversity present associated with cores of oligocene rocks using a dna metabarcoding approach. These categories refer to differing amounts of silica, potassium, sodium, calcium, iron, and magnesium found in the minerals that make up the rocks. Properties and characteristics of igneous rocks. Web examples include basalt, rhyolite, and andesite. The diagram of bowen’s reaction series ( figure 7.7) shows that differences in chemical composition correspond to differences in the types of minerals within an igneous rock. They are categorized based on their origin, texture, and mineral composition. Obsidian is an example of an extrusive igneous rock that is amorphous or lacks crystalline structure. Andesite, basalt, dacite, obsidian, pumice, rhyolite, scoria, and tuff. Web an igneous rock can be represented as a vertical line drawn through the diagram, and the vertical scale used to break down the proportion of each mineral it contains. Web igneous rock, any of various crystalline or glassy rocks formed by the cooling and solidification of molten earth material. Then, compare your observations to known igneous rock types. Web once these two characteristics have been identified, the igneous rock identification chart is used to identify the rock name.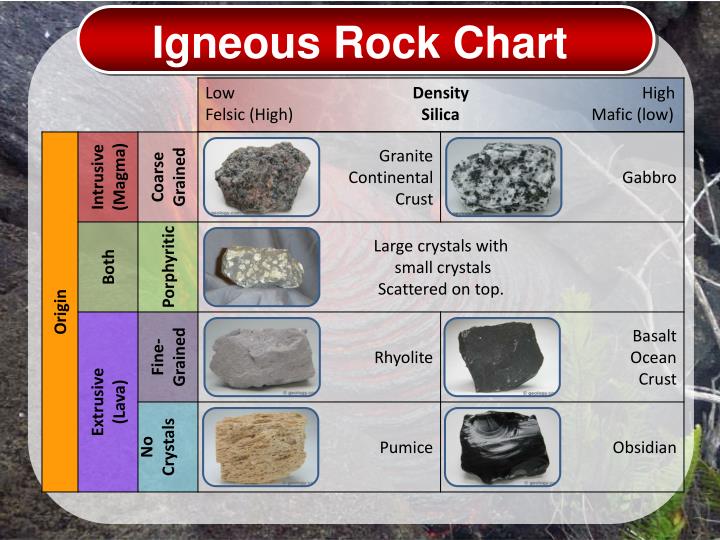
Igneous Rock Textures Chart

The GeoMessenger How to Write a Rock Description for Igneous
Igneous Rock Types Chart

General Classification of Igneous Rocks
4.1 Classification of Igneous Rocks Geosciences LibreTexts

Igneous Rock Chart
Part A
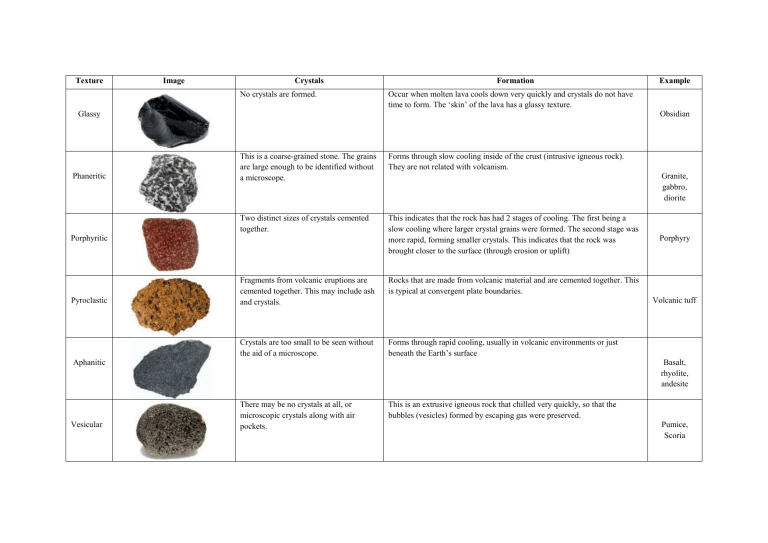
Igneous Rocks Texture Types
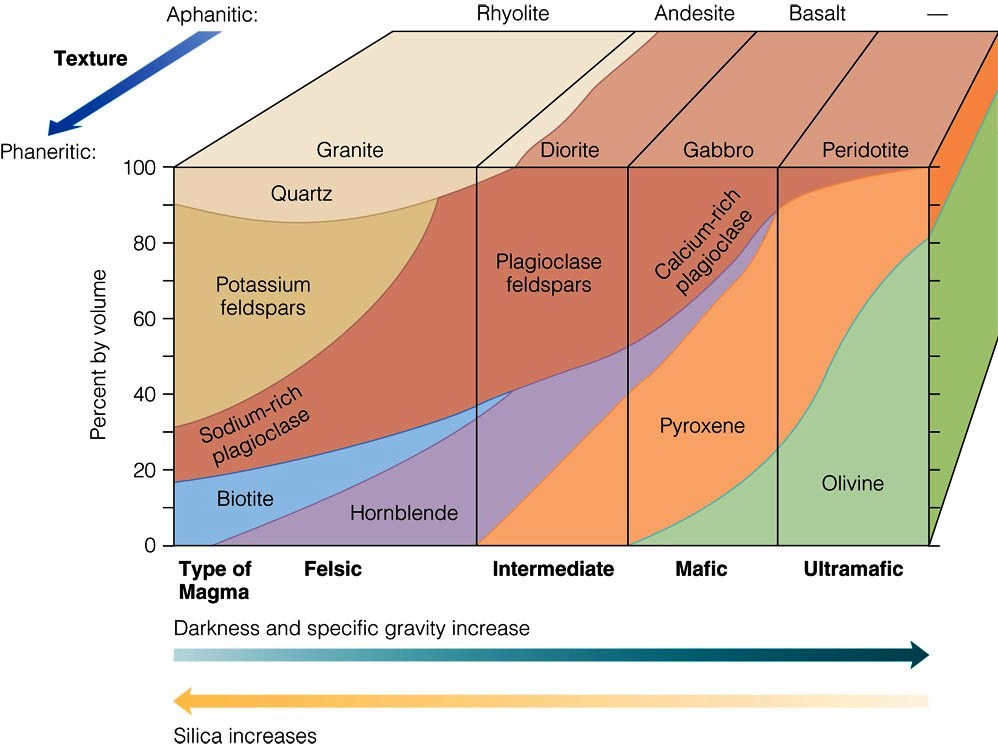
How Do Different Igneous Rocks Form From One Original Supply of Magma?

Igneous Rock Chart Flinn Scientific
Felsic, Intermediate, Mafic, And Ultramafic.
The Diagram Of Bowen’s Reaction Series ( Figure 7.6 ) Shows That Differences In Chemical Composition Correspond To Differences In The Types Of Minerals Within An Igneous Rock.
It Has A Composition That Is Intermediate Between Rhyolite And Andesite.
Web Igneous Rock Composition Is Divided Into Four Categories:
Related Post: