Immune Response Flow Chart
Immune Response Flow Chart - Their role is to fight infections and get rid of debris. An adaptive response is specific to the particular type of pathogen that has invaded the body or to cancerous cells. Web the immune system responds to antigens by producing cells that directly attack the pathogen, or by producing special proteins called antibodies. Helper t cells, or th cells, coordinate immune responses by communicating with other cells. Web the adaptive immune system is activated if pathogens successfully enter the body and manage to evade the general defenses of the innate immune system. The adaptive immune system identifies and attacks specific germ invaders. It includes barriers to infection, phagocytes, mast cells, and inflammation. Leukocytes are white blood cells. Web the innate immune system is a general defense mechanism that protects you from the time your body is exposed to harmful germs until the time the second part of the immune response — the adaptive immune system — kicks in. A third mechanism used by antibodies to eradicate viruses, is the activation of phagocytes. Abnormal regulation of the various effector mechanisms can lead to chronic or acute. Web the adaptive immune system is activated if pathogens successfully enter the body and manage to evade the general defenses of the innate immune system. Web the immune system responds to antigens by producing cells that directly attack the pathogen, or by producing special proteins called antibodies.. Web agglutinated viruses make an easier target for immune cells than single viral particles. These mechanisms work together, and the fully integrated immune response draws elements from many effector systems in order to tailor a response to the specific invading pathogen. Leukocytes are white blood cells. Web t cells contribute to immune defenses in two major ways: Others directly attack. Web the chemicals that trigger an inflammatory response attract leukocytes to the site of injury or infection. A third mechanism used by antibodies to eradicate viruses, is the activation of phagocytes. Web unlike the innate immune system, which attacks only based on the identification of general threats, the adaptive immunity is activated by exposure to pathogens, and uses an immunological. Web by integrating our interactome with expression data, we identified trends in the dynamics of immune interactions and constructed a reductionist mathematical model that predicts cellular. Web the chemicals that trigger an inflammatory response attract leukocytes to the site of injury or infection. Web • the innate immune response is the body’s first line of defense. Web the innate immune. Antibodies attach to an antigen and attract cells that will engulf and destroy the pathogen. Others directly attack infected or cancerous cells. Web innate immune responses are activated rapidly but do not hold a molecular memory. Adaptive immunity retains memory, providing protection against subsequent insult by the same pathogen. Their role is to fight infections and get rid of debris. Web the adaptive immune system is activated if pathogens successfully enter the body and manage to evade the general defenses of the innate immune system. Web • the innate immune response is the body’s first line of defense. Web t cells contribute to immune defenses in two major ways: It includes t cells, b cells, and antibodies. Web innate immune. Abnormal regulation of the various effector mechanisms can lead to chronic or acute. T and b lymphocytes (t and b cells) are part of the adaptive immune system. Web the immune system responds to antigens by producing cells that directly attack the pathogen, or by producing special proteins called antibodies. The adaptive immune system identifies and attacks specific germ invaders.. Helper t cells, or th cells, coordinate immune responses by communicating with other cells. Web unlike the innate immune system, which attacks only based on the identification of general threats, the adaptive immunity is activated by exposure to pathogens, and uses an immunological memory to learn about the threat and. Web innate immune responses are activated rapidly but do not. Web • the innate immune response is the body’s first line of defense. Web the innate immune system is a general defense mechanism that protects you from the time your body is exposed to harmful germs until the time the second part of the immune response — the adaptive immune system — kicks in. • the adaptive immune response takes. Some direct and regulate immune responses; Leukocytes are white blood cells. Adaptive immunity retains memory, providing protection against subsequent insult by the same pathogen. Helper t cells, or th cells, coordinate immune responses by communicating with other cells. These mechanisms work together, and the fully integrated immune response draws elements from many effector systems in order to tailor a response. The adaptive immune system identifies and attacks specific germ invaders. Web • the innate immune response is the body’s first line of defense. Adaptive immunity retains memory, providing protection against subsequent insult by the same pathogen. Web agglutinated viruses make an easier target for immune cells than single viral particles. Web the innate immune system is a general defense mechanism that protects you from the time your body is exposed to harmful germs until the time the second part of the immune response — the adaptive immune system — kicks in. Some direct and regulate immune responses; Leukocytes are white blood cells. Web by integrating our interactome with expression data, we identified trends in the dynamics of immune interactions and constructed a reductionist mathematical model that predicts cellular. Web the immune system responds to antigens by producing cells that directly attack the pathogen, or by producing special proteins called antibodies. Web the immune system uses many mechanisms to combat infection by microbes. Web the chemicals that trigger an inflammatory response attract leukocytes to the site of injury or infection. Web t cells contribute to immune defenses in two major ways: It includes t cells, b cells, and antibodies. Web the adaptive immune system is activated if pathogens successfully enter the body and manage to evade the general defenses of the innate immune system. Their role is to fight infections and get rid of debris. Web the innate immune system works to fight off pathogens before they can start an active infection.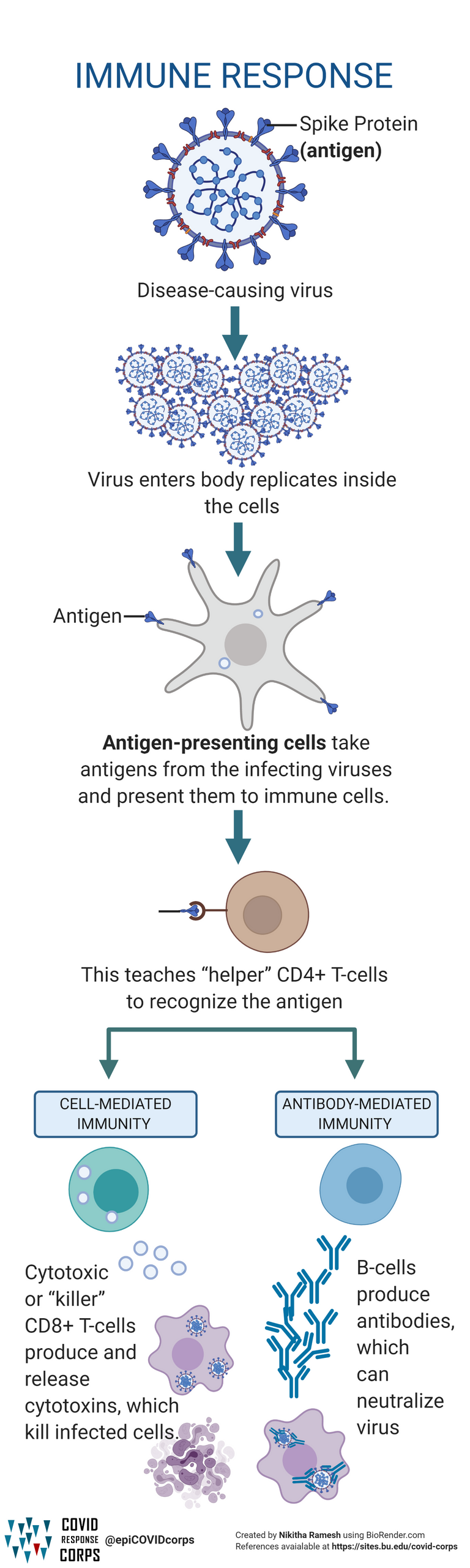
Types of Vaccines Infographics Epidemiology COVID19 Response Corps

Adaptive Immunity · Concepts of Biology

Innate and Adaptive Immunity in the Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis
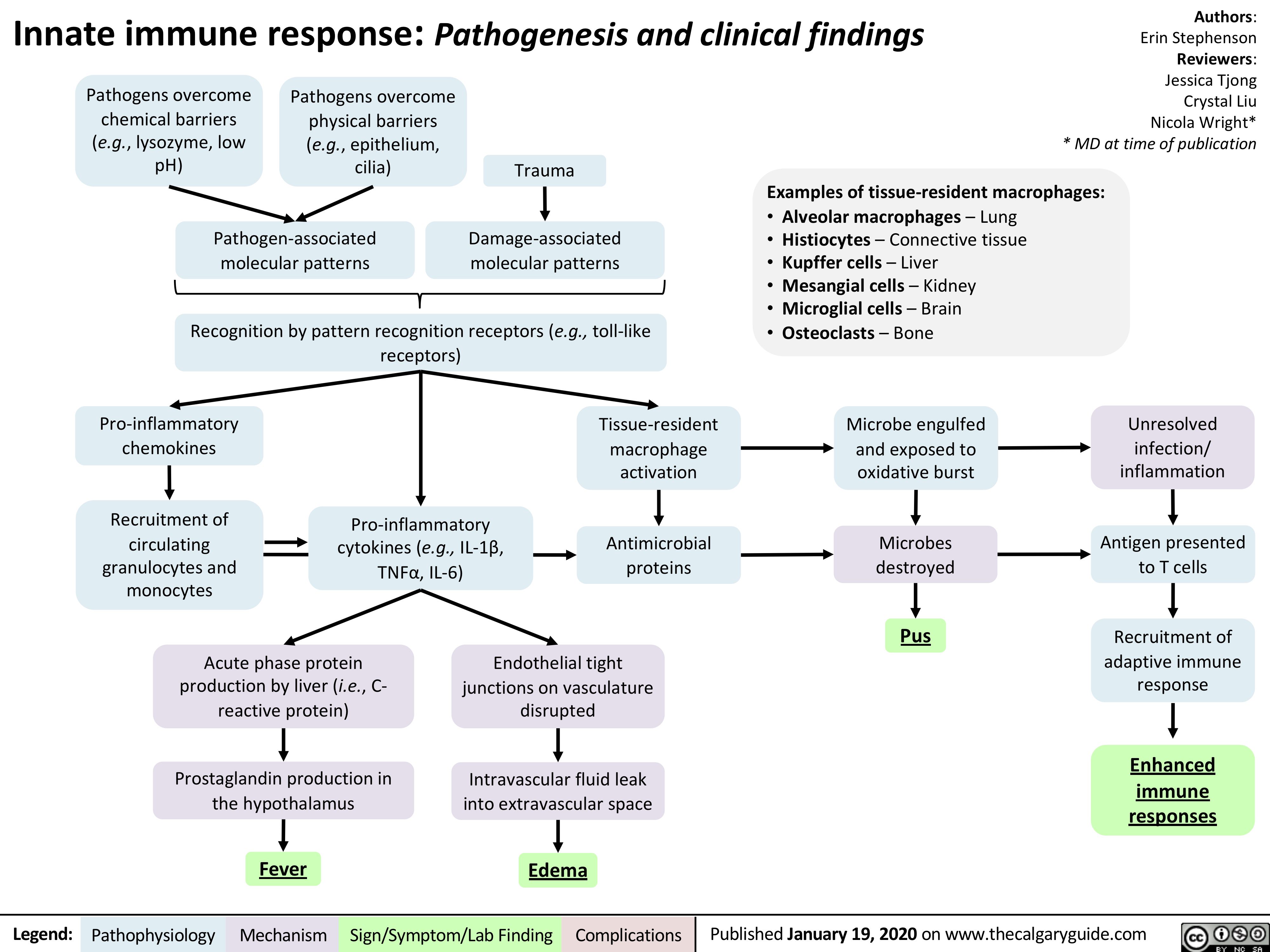
Innate Immune Response Calgary Guide
Innate and Acquired Immunity / What's LPS / Macrophi Inc. LPS

Understanding Immunological Memory
Innate Immune Response Boundless Biology

Barrier Defenses and the Innate Immune Response · Anatomy and Physiology
A level Biology Immunity Overview Diagram Teaching Resources

Innate versus Adaptive Beckman Coulter
Helper T Cells, Or Th Cells, Coordinate Immune Responses By Communicating With Other Cells.
Others Directly Attack Infected Or Cancerous Cells.
T And B Lymphocytes (T And B Cells) Are Part Of The Adaptive Immune System.
Web Innate Immune Responses Are Activated Rapidly But Do Not Hold A Molecular Memory.
Related Post:

