Ionic Energy Chart
Ionic Energy Chart - The first ionization energy, second ionization energy as well as third ionization energy of the elements are given in this chart below. First ionisation energy shows periodicity. 2nd in a periodic table cityscape style. First ionization energy, second ionization energy as well as third ionization energy of the elements are given in this chart. The size of that attraction will be governed by: At r0, the ions are more stable (have a lower potential energy) than they are at an infinite internuclear distance. Web explore how ionization energy changes with atomic number in the periodic table of elements via interactive plots. For a schematic overview of the periodic table of elements in chart form. Please report any accidental mistake in the above statistics on chemical elements. This form provides access to nist critically evaluated data on ground states and ionization energies of atoms and atomic ions. \(i\) is therefore the energy required for the reaction Web this list contains the 118 elements of chemistry. The 1st ionization energy of the element m is a measure of the energy required to remove one electron from one mole of the gaseous atoms m. The first ionization energy is quantitatively expressed as x(g) + energy x. First ionization energy,. At r0, the ions are more stable (have a lower potential energy) than they are at an infinite internuclear distance. First ionization energy, second ionization energy as well as third ionization energy of the elements are given in this chart. Web for each atom, the column marked 1 is the first ionization energy to ionize the neutral atom, the column. Please report any accidental mistake in the above statistics on chemical elements. A high value of ionization energy shows a high attraction between the electron and the nucleus. The 1st ionization energy of the element m is a measure of the energy required to remove one electron from one mole of the gaseous atoms m. This form provides access to. On the periodic table, first ionization energy generally increases as you move left to right across a period. Web chemists define the ionization energy (\(i\)) of an element as the amount of energy needed to remove an electron from the gaseous atom \(e\) in its ground state. Web nist atomic spectra database ionization energies form. Web ionization energy chart of. Web ionization energy can be shown by the equation: Web we summarize the important points about ionic bonding: Web the 2nd ionization energy of the element m is a measure of the energy required to remove one electron from one mole of the gaseous ion m + image showing periodicity of the chemical elements for ionization energy: Web the first. Please report any accidental mistake in the above statistics on chemical elements. Web this list contains the 118 elements of chemistry. Web we summarize the important points about ionic bonding: Web the values mentioned in the above periodic table is the first ionization energy and are given in electron volts (ev). Web the first 20 elements. At r0, the ions are more stable (have a lower potential energy) than they are at an infinite internuclear distance. Web the values mentioned in the above periodic table is the first ionization energy and are given in electron volts (ev). Web the first 20 elements. Please report any accidental mistake in the above statistics on chemical elements. First ionisation. Web table of polyatomic ions. Web chemists define the ionization energy (\(i\)) of an element as the amount of energy needed to remove an electron from the gaseous atom \(e\) in its ground state. Web this list contains the 118 elements of chemistry. That means that it varies in a repetitive way as you move through the periodic table. In. Web the values mentioned in the above periodic table is the first ionization energy and are given in electron volts (ev). The first ionization energy, second ionization energy as well as third ionization energy of the elements are given in this chart below. Web explore how ionization energy changes with atomic number in the periodic table of elements via interactive. Web in physics and chemistry, ionization energy (ie) is the minimum energy required to remove the most loosely bound electron of an isolated gaseous atom, positive ion, or molecule. Web nist atomic spectra database ionization energies form. For a schematic overview of the periodic table of elements in chart form. Web explore how ionization energy changes with atomic number in. For a schematic overview of the periodic table of elements in chart form. U can be calculated from the charges on the ions, the arrangement of the ions in the solid, and the internuclear distance. Web we summarize the important points about ionic bonding: Want to join the conversation? Image showing periodicity of the chemical elements for ionization energy: Use average covalent bond energies to estimate enthalpies of reaction When oppositely charged ions are brought together from r = ∞ to r = r0, the energy of the system is lowered (energy is released). The first ionization energy is quantitatively expressed as x(g) + energy x. Web explore how ionization energy changes with atomic number in the periodic table of elements via interactive plots. Web the lattice energy (u) of an ionic substance is defined as the energy required to dissociate the solid into gaseous ions; Web for each atom, the column marked 1 is the first ionization energy to ionize the neutral atom, the column marked 2 is the second ionization energy to remove a second electron from the +1 ion, the column marked 3 is the third ionization energy to remove a third electron from the +2 ion, and so on. 2nd in a periodic table cityscape style. First ionization energy, second ionization energy as well as third ionization energy of the elements are given in this chart. Web ionization energy can be shown by the equation: Want to join the conversation? In mehreren sprachenerfahrene journalistenmoderne plattformgenaue nachrichten
Calculate The Value Of The Third Ionization Energy Of Lithium How To
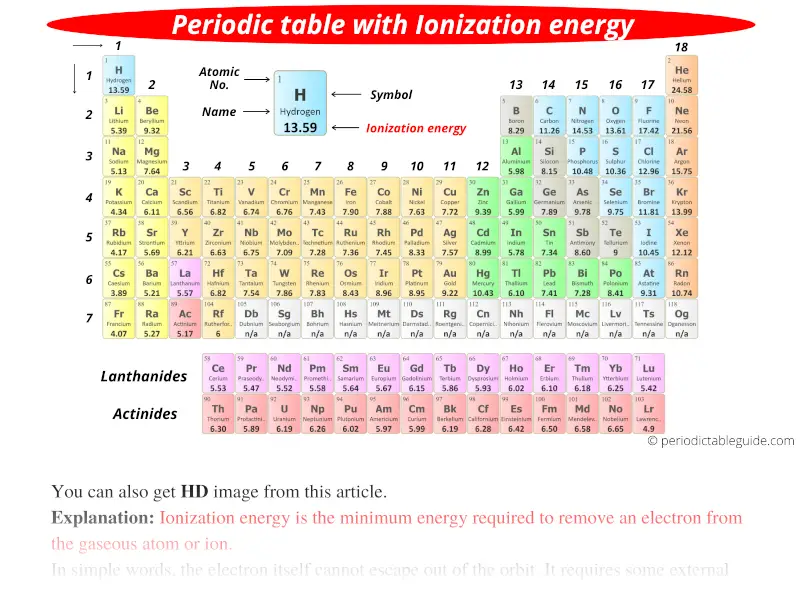
Periodic table with Ionization Energy Values (Labeled Image)
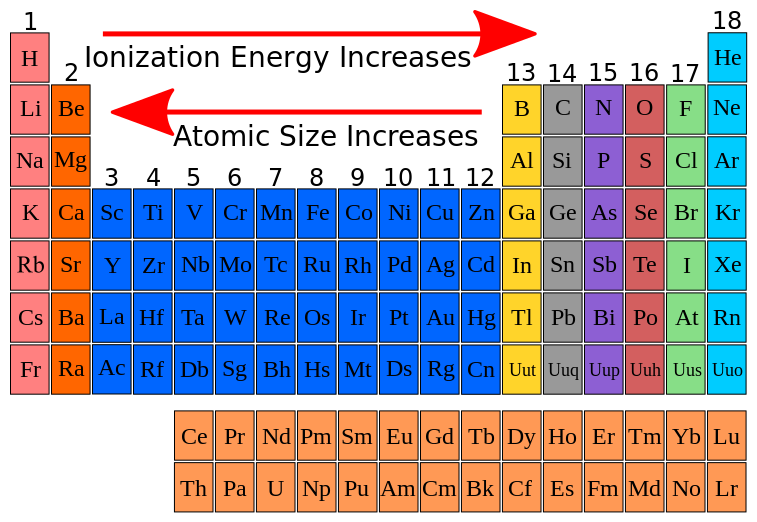
FileIonization energy atomic size.svg Wikimedia Commons
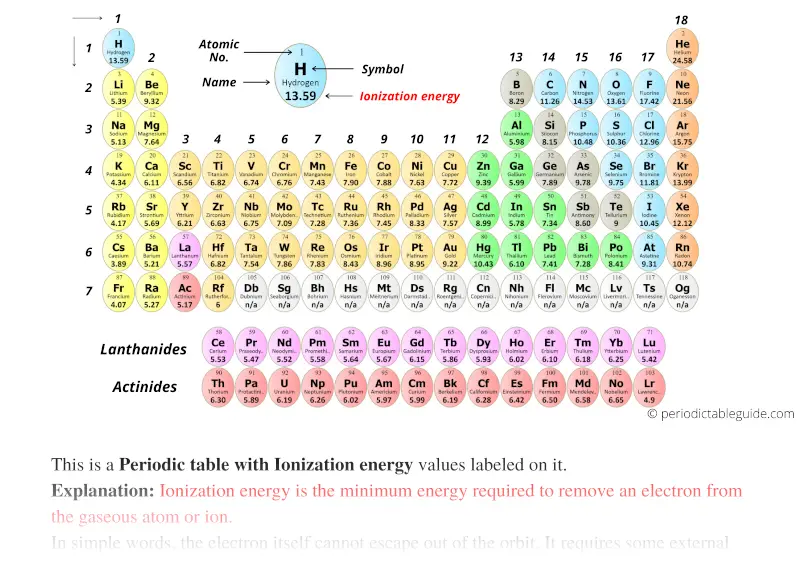
Periodic table with Ionization Energy Values (Labeled Image)
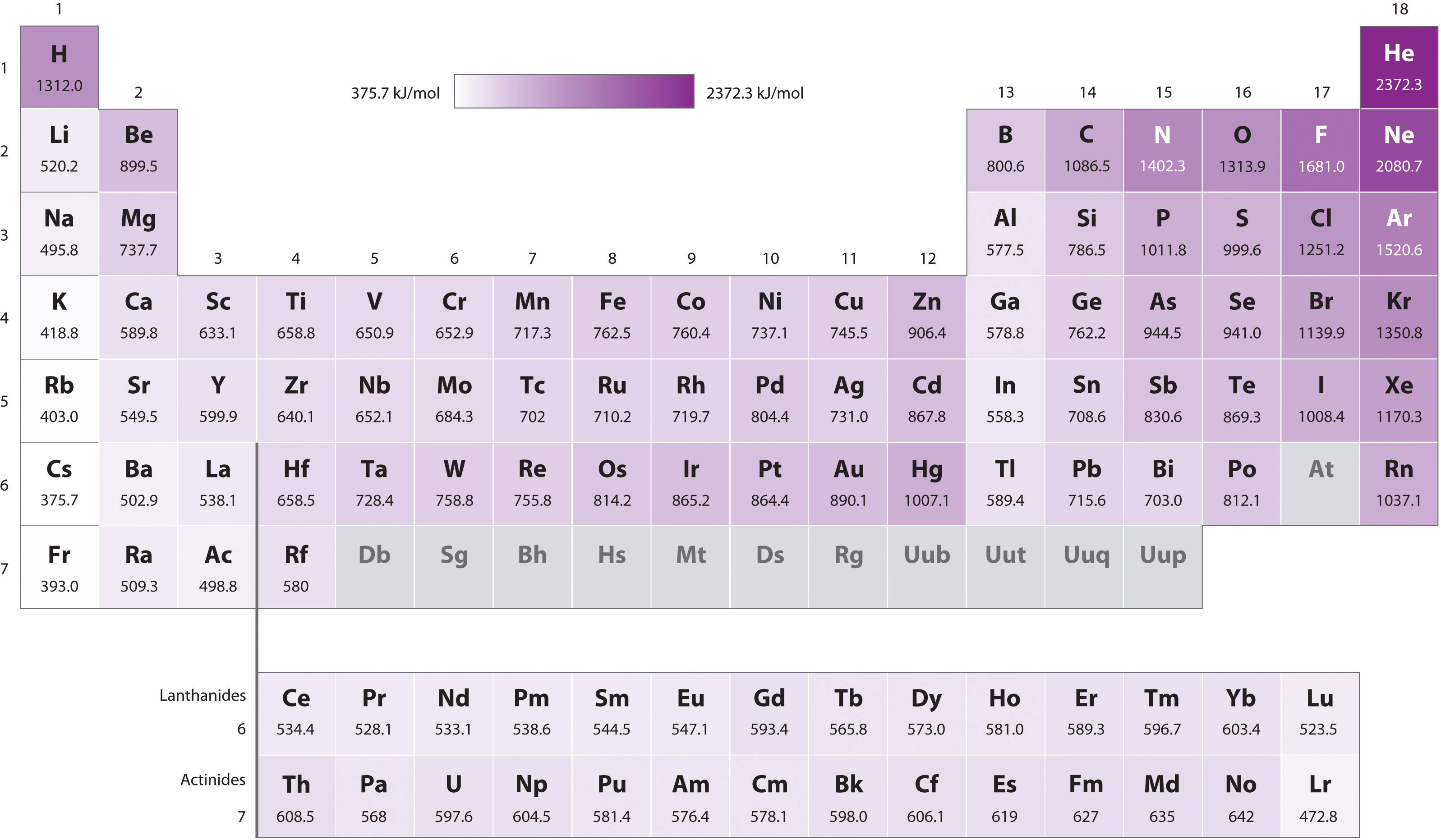
6.6 Ionization Energies Chemistry LibreTexts

Among the Following Which Element Has the Lowest Ionization Energy
Periodic Behavior Presentation Chemistry
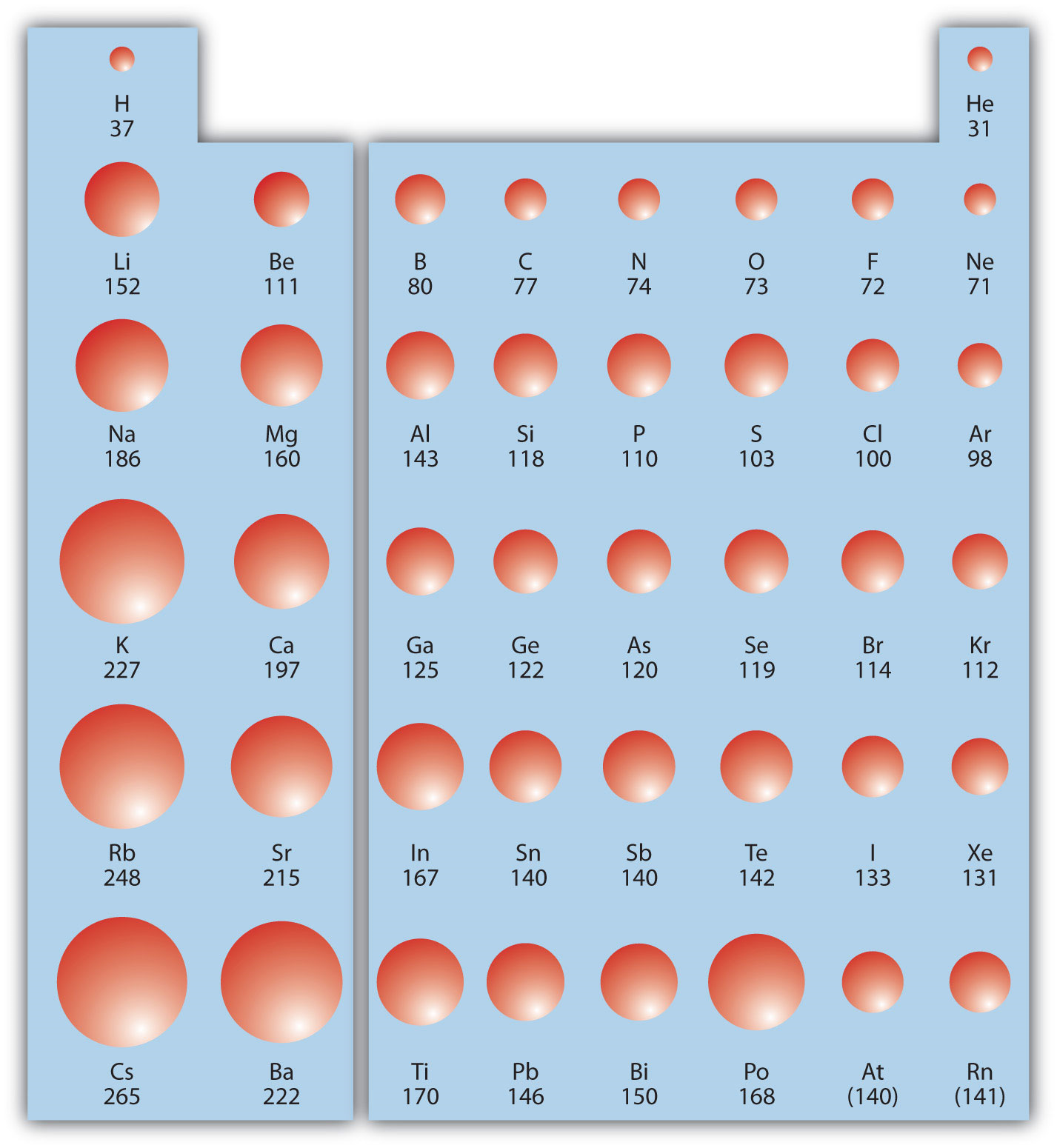
9.9 Periodic Trends Atomic Size, Ionization Energy, and Metallic
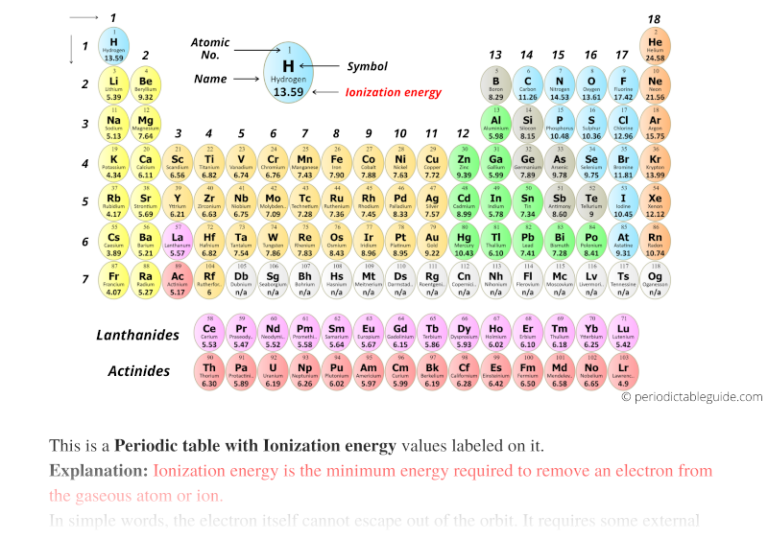
Periodic table with Ionization Energy Values (Labeled Image)
Periodic Trends in Ionization Energy CK12 Foundation
What Is Meant By “First” Ionization Energy?
That Means That It Varies In A Repetitive Way As You Move Through The Periodic Table.
Web From This Graph, We Can Determine The Equilibrium Bond Length (The Internuclear Distance At The Potential Energy Minimum) And The Bond Energy (The Energy Required To Separate The Two Atoms).
Web In Physics And Chemistry, Ionization Energy (Ie) Is The Minimum Energy Required To Remove The Most Loosely Bound Electron Of An Isolated Gaseous Atom, Positive Ion, Or Molecule.
Related Post:
.PNG)
