Kingdom Characteristics Chart
Kingdom Characteristics Chart - (unicellular / multicellular) cell structure. Web classification and its types. Web organisms are traditionally classified into six kingdoms (archaebacteria, eubacteria, protista, fungi, plantae, and animalia) based on characteristics like cell type, nutrient acquisition, and reproduction. Web eukaryotic, multicellular, no cell wall, heterotroph. Examples include elephants, whales, and humans. These organisms are prokaryotic and unicellular. Each kingdom includes a set of organisms that share similar characteristics. All animals are members of the kingdom animalia (also called metazoa). What are the kingdoms of life? 1 classification of living things and naming of organisms. Web the plant kingdom has the following characteristic features: Web discover which kingdom you belong to and what characteristics you’d have if you fell into one of the other five kingdoms. 5 phylogeny, cladistics, and cladograms. The organisms in each kingdom are considered biologically distinct from the others. Characteristics of the 5 kingdoms of life. Web fill in the chart below, listing the distinctive characteristics of each kingdom. How do the three domains of life differ from each other? Web in biology, a kingdom of life is a taxonomy rank that is below domain and above phylum. Web organisms are traditionally classified into six kingdoms (archaebacteria, eubacteria, protista, fungi, plantae, and animalia) based on characteristics. 1 classification of living things and naming of organisms. The plant cell contains the outer cell wall and a large central vacuole. Web discover which kingdom you belong to and what characteristics you’d have if you fell into one of the other five kingdoms. Remember for each kingdom your want to find: They make their own food and hence are. Once you know about the six kingdoms of life, you’ll be a classification king… or queen! Web the five kingdoms are: (cell wall / no cell wall) mobility. Web discover which kingdom you belong to and what characteristics you’d have if you fell into one of the other five kingdoms. This classification was based upon certain characters like mode of. It is estimated that around 9 or 10 million species of animals inhabit the earth. Web 6 kingdoms of life chart kingdom cell type body form cell structure nutrition habitat distinguishing characteristics examples animalia plantae fungi protista eubacteria archaebacteria. Examples include elephants, whales, and humans. Distinguishing features of the five kingdoms. Web list the features that distinguish the kingdom animalia. Heffley, scott f created date: Web the five kingdoms are: This kingdom contains all living and extinct animals. They make their own food and hence are called autotrophs. Web fill in the chart below, listing the distinctive characteristics of each kingdom. Kingdoms are divided into smaller groups called phylum. In biology, a kingdom is the second highest taxonomic rank, just below domain. Phyla) is the largest formal major grouping within plant taxonomy below kingdom. They reproduce asexually by vegetative propagation or sexually. Web in biology, a kingdom of life is a taxonomy rank that is below domain and above phylum. Kingdoms are divided into smaller groups called phylum. Web list the features that distinguish the kingdom animalia from other kingdoms; A domain contains one or more kingdoms. Animals come in all kinds of sizes and shapes. They reproduce asexually by vegetative propagation or sexually. In other words, it is a broad classification of organisms according to their characteristics. They make their own food and hence are called autotrophs. Examples include elephants, whales, and humans. Animals come in all kinds of sizes and shapes. This form of kingdom classification includes five kingdoms monera, protista, fungi, plantae and animalia. Remember for each kingdom your want to find: Explain the processes of animal reproduction and embryonic development; Archaebacteria, eubacteria, fungi, protista, plants and animals. Animals come in all kinds of sizes and shapes. Web all land plants share the following characteristics: Web classification and its types. How organisms in that kingdom are important to us. Archaebacteria, eubacteria, fungi, protista, plants and animals. 6 classification of living things practice questions. 5 phylogeny, cladistics, and cladograms. Web list the features that distinguish the kingdom animalia from other kingdoms; Web in biology, a kingdom of life is a taxonomy rank that is below domain and above phylum. Examples include elephants, whales, and humans. Web here is a list of the classifications found in the modern hierarchy, their groups and characteristics from highest to lowest taxonomic rank. This kingdom contains all living and extinct animals. Phyla) is the largest formal major grouping within plant taxonomy below kingdom. How are organisms classified into kingdoms? Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free. In botany, the equivalent of a phylum is called a division. Once you know about the six kingdoms of life, you’ll be a classification king… or queen! How do the three domains of life differ from each other?
Kingdom Comparison Chart Science lesson activities, Homeschool life

Characteristics of the 6 Kingdoms Taxonomy, Prokaryotes, Eubacteria

Six Kingdom Classification System
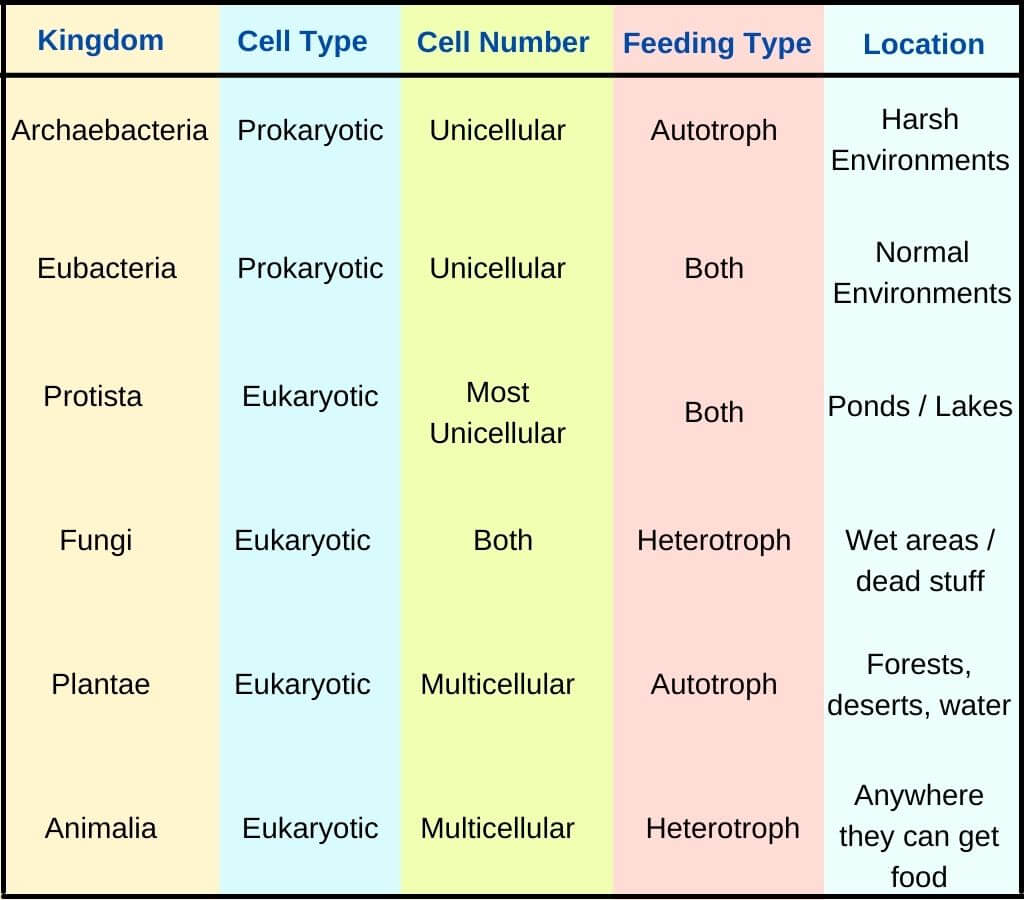
A Simple Explanation of the 6 Kingdoms of Life
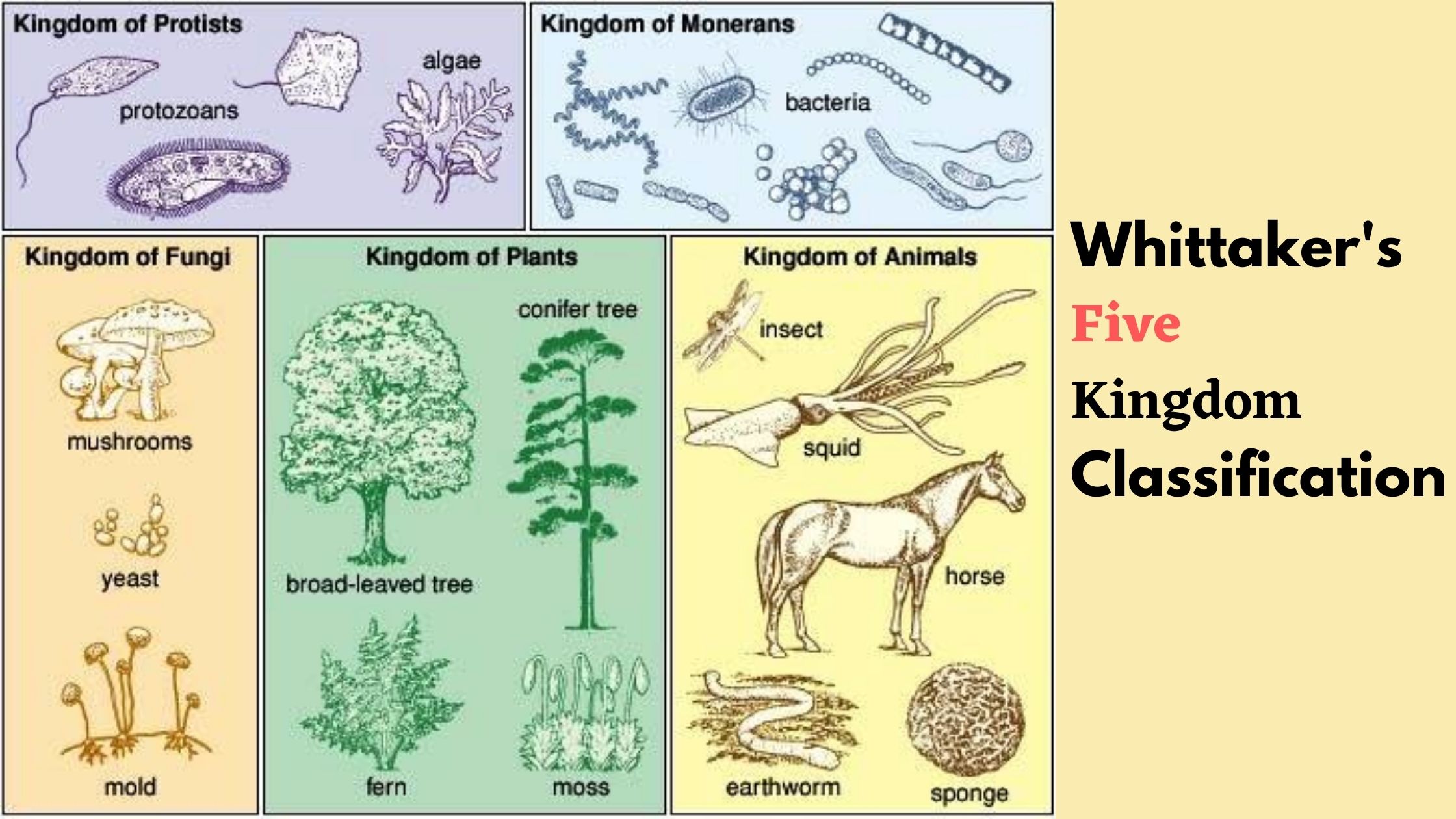
The Five Kingdom Classification
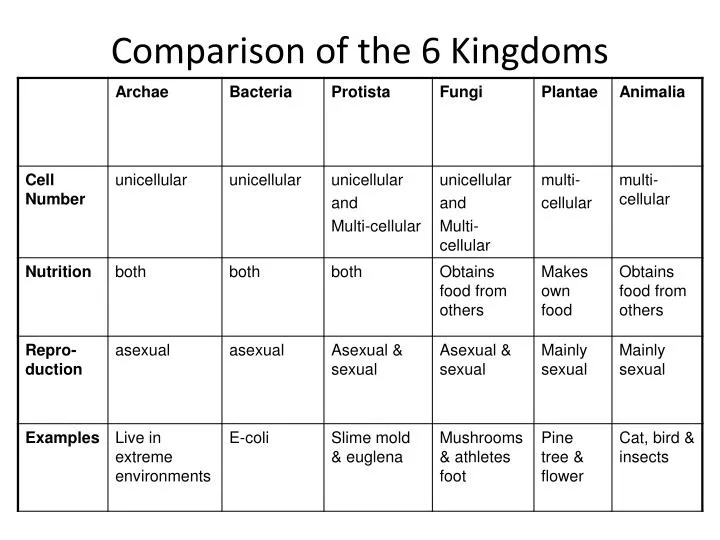
PPT Comparison of the 6 Kingdoms PowerPoint Presentation, free
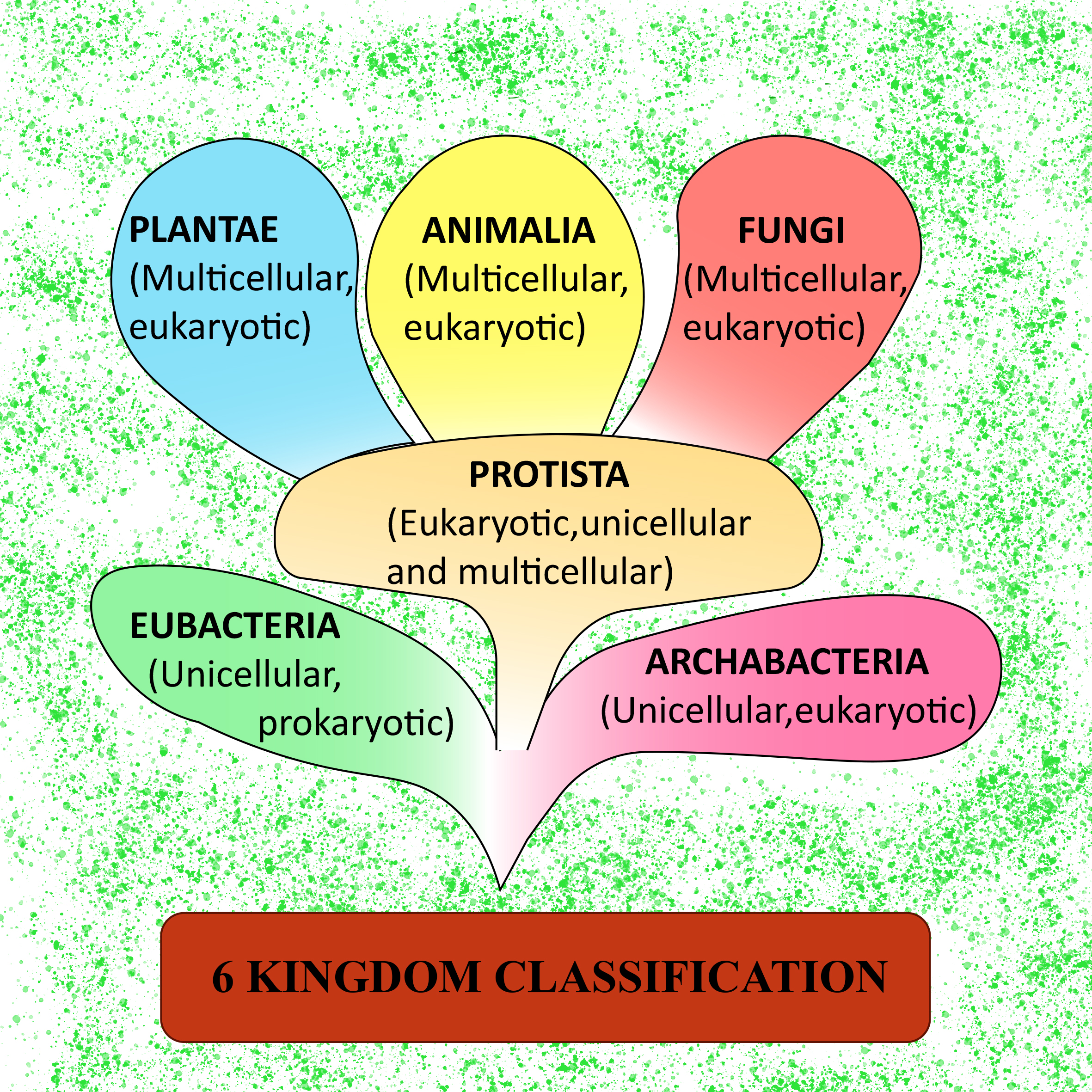
6 Kingdoms Chart
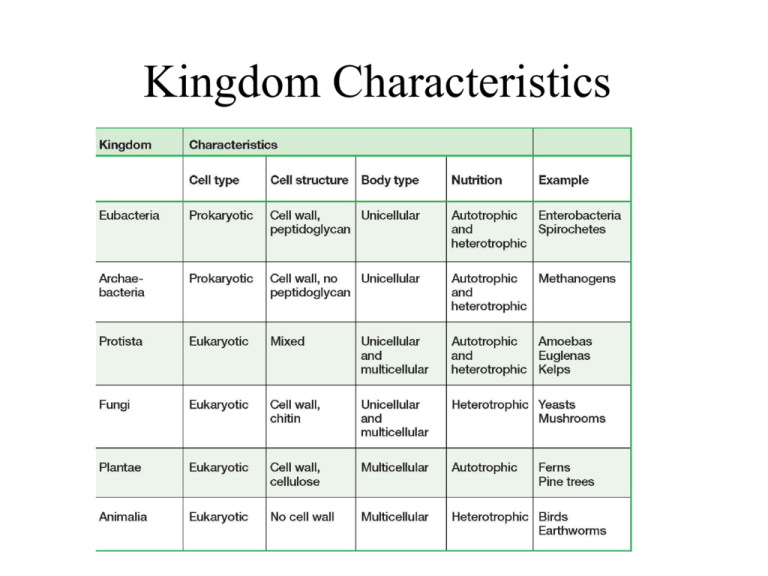
Kingdom Characteristics
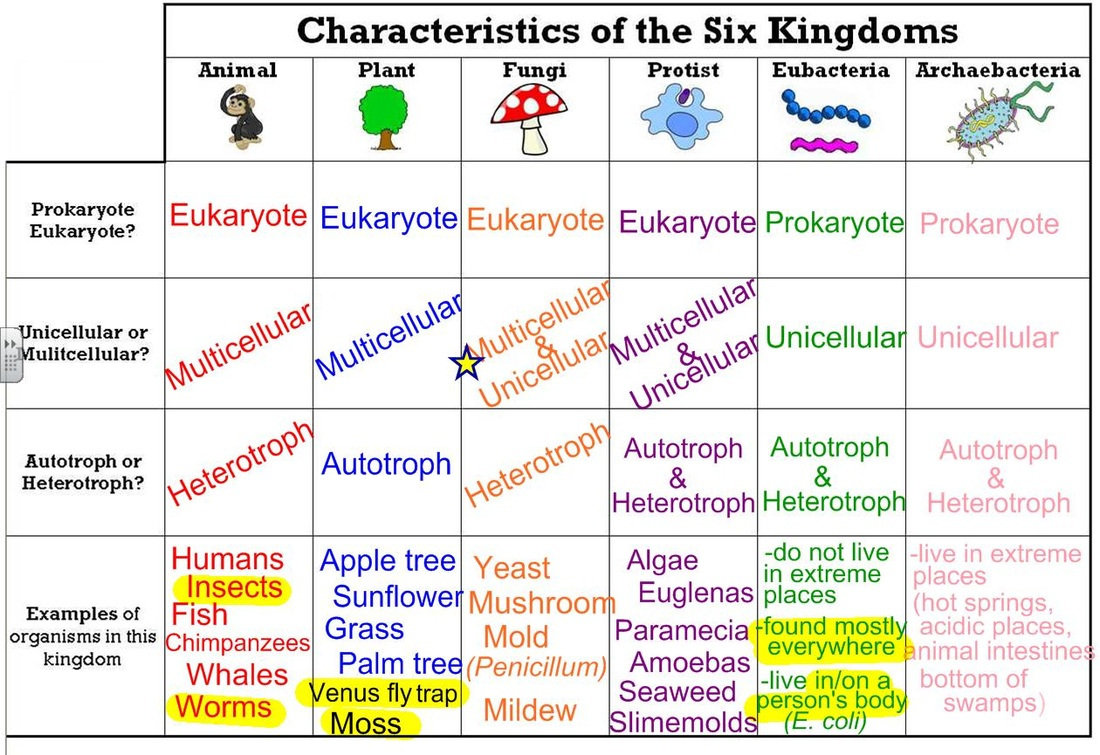
Classification Ms A Science Online

PPT Six Kingdom Notes PowerPoint Presentation ID545754
Alternation Of Generations, With The Haploid Plant Called A Gametophyte And The Diploid Plant Called A Sporophyte;
Web Describe Common Characteristics Of Organisms Grouped Into Each Of The Six Kingdoms.
Begin With Chapter 18.3 Of Your Biology Book For More Information.) Kingdom.
They Make Their Own Food And Hence Are Called Autotrophs.
Related Post: