Latin Participle Chart
Latin Participle Chart - A perfect participle refers to action prior to that of the main verb. A present participle refers to action contemporaneous with that of the main verb (whether the main verb is past, present or future). The participle's time reference is relative to the controlling verb. 1.2.1 meanings of the gerund. The enemies, frightened by our soldiers, fled. The participle expresses the action of the verb in the form of an adjective, but has a partial distinction of tense and may govern a case. An english noun may best represent a latin participle: Participles in latin agree with the gender, number, and case of. Web there are four important rules to remember in chapter 23: Web latin conjugations — ben crowder. Participles do not have a person, number, or mood, and there are no imperfect, pluperfect, or future perfect participles. *the translation of a subjunctive verb depends on the type of clause in which it is used. Web latin from scratch #19.38: And conditional, if causal, concessive, temporal, and conditional. Atticus familiārēs antōniī ex urbe profugientēs adiūvit. Participles in latin agree with the gender, number, and case of. *the translation of a subjunctive verb depends on the type of clause in which it is used. Hostes ab nostris territi fugerunt. Noun and adjective forms of the verb. English, aided by auxiliary participles, is able have participle phrases in many tenses. You've been working with one now for a couple of chapters. Web the participle may be translated in accordance with accepted english syntax and style, in particular : Web the participles are used as follows. The participle's time reference is relative to the controlling verb. The present active, perfect passive, future active, and future passive (the gerundive), along with discussing. Not all verbs have all forms. You've been working with one now for a couple of chapters. The perfect passive and the future passive. Present active, perfect passive, future active and future passive. Participles do not have a person, number, or mood, and there are no imperfect, pluperfect, or future perfect participles. A perfect participle refers to action prior to that of the main verb. This means that it agrees with the noun it modifies in number, case. Web this video reviews the four participles of a standard verb: Web there are four important rules to remember in chapter 23: That is, an adjective derived from a stem of a verb. Web the participles are used as follows. This participle can be translated just as a english past participle: Participles do not have a person, number, or mood, and there are no imperfect, pluperfect, or future perfect participles. (1) latin has four participles: Participles are verbs which function grammatically like adjectives. And conditional, if causal, concessive, temporal, and conditional. That is, an adjective derived from a stem of a verb. There is more than one way to translate a participle: A perfect participle refers to action prior to that of the main verb. Web participles in latin have a tense (present, perfect, or future) and a voice (active or passive). Web the participles are used as follows. Therefore, for each subjunctive clause type, you should learn the definition, how to recognize it, and how to translate it. The participle's time reference is relative to the controlling verb. This participle can be translated just as a english past participle: Mārcus brūtum in silvā ambulantem vīdit. English, aided by auxiliary participles, is able have participle phrases in many tenses. Participles are verbs which function grammatically like adjectives. It may feel more natural to add one or two words, like ‘while’, ‘who’ or ‘as’: Conjugation tables of all latin verbs, with passive, participes and translations. That is, an adjective derived from a stem of a verb. Web participles in latin have a tense (present, perfect, or future) and a voice (active or passive). The present active, perfect passive, future active, and future passive (the gerundive), along with discussing how deponent verbs form. The enemies, frightened by our soldiers, fled. Web study the chart below and observe the patterns. That is, an adjective derived from a stem. They are used far more extensively than participles in english. Web study the chart below and observe the patterns. Web there are four important rules to remember in chapter 23: Atticus familiārēs antōniī ex urbe profugientēs adiūvit. Web participles in latin have a tense (present, perfect, or future) and a voice (active or passive). Web latin conjugations — ben crowder. Web basic concepts of latin participles. Marcus saw brutus who was walking in the wood. English, aided by auxiliary participles, is able have participle phrases in many tenses. (1) latin has four participles: Web latin has four participles: Noun and adjective forms of the verb. Web the three types of participles in latin are present active participles, perfect passive participles, future active participles, and future participles (can be either active or passive). A participle is formed from a verb but looks and behaves like an adjective. The present active, the future active; Web participles in latin have a tense (present, perfect, or future) and a voice (active or passive).
New Latin Grammar
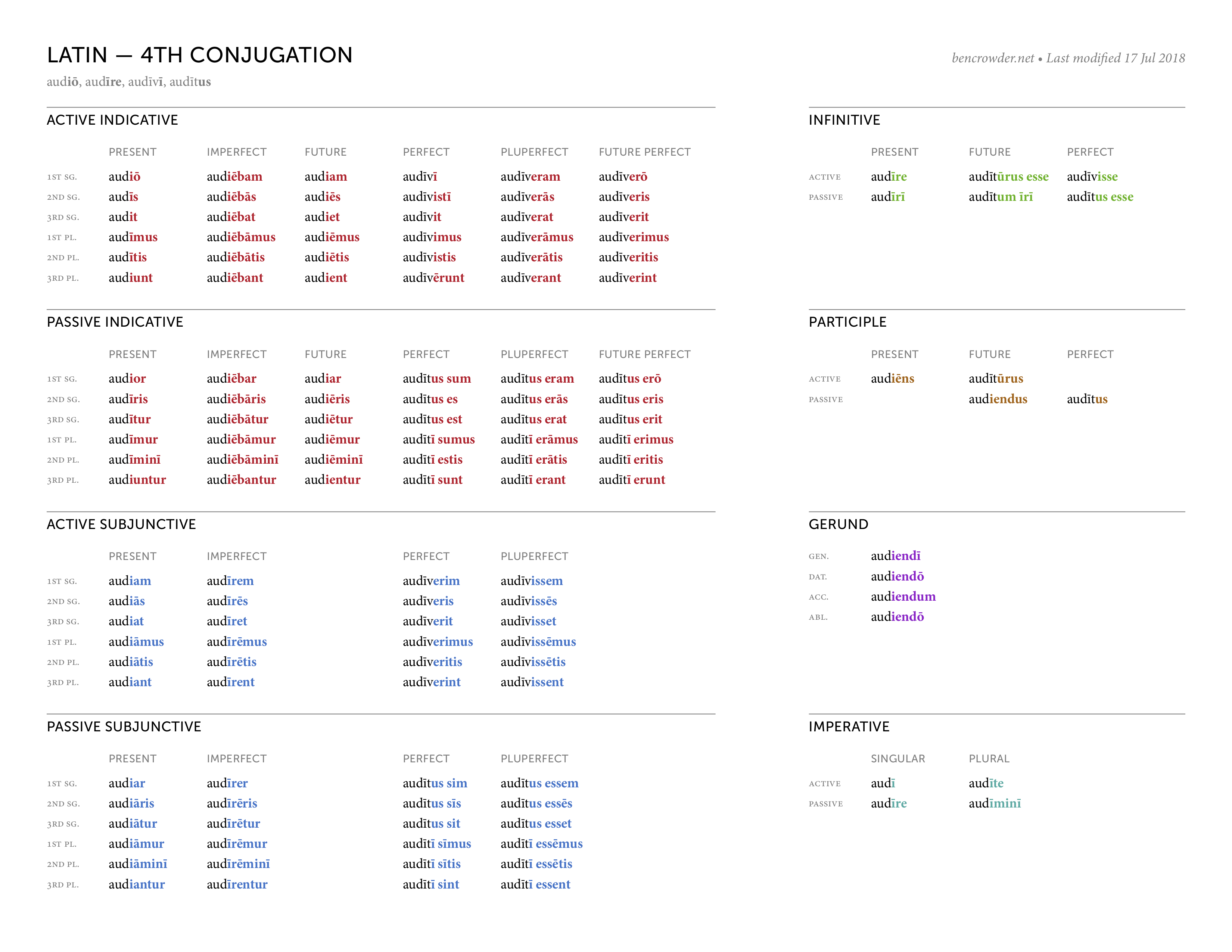
Latin Conjugations — Ben Crowder

Latin Verb Conjugations Chart Five J's Homeschool

Verbos En Latin Conjugados Satu

lectis Latin D
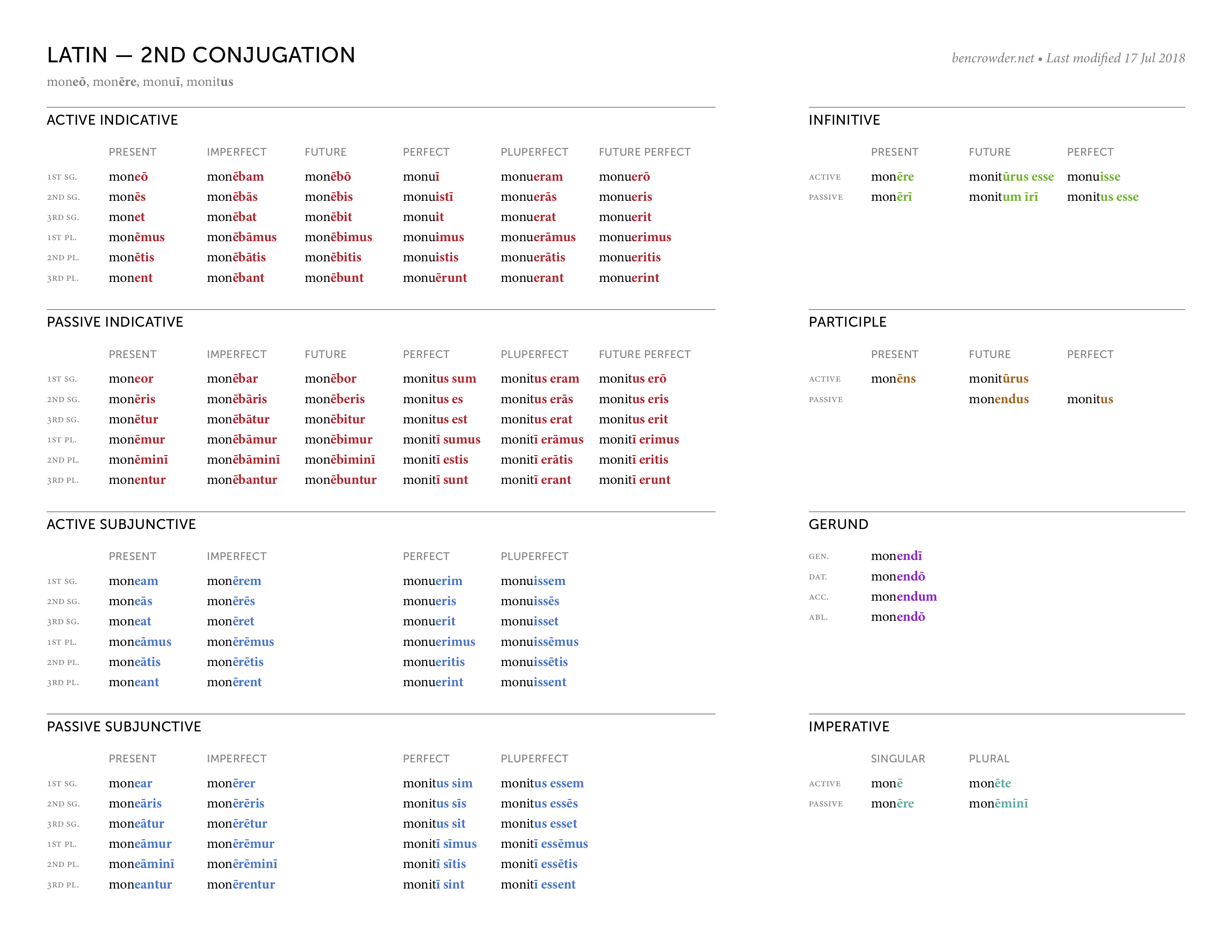
Latin Conjugations — Ben Crowder
Colorcoded chart 4 Infinitives/Participles/Gerund etc. Latin D

Latin Verb Conjugations Chart In 2020 Conjugation Cha vrogue.co
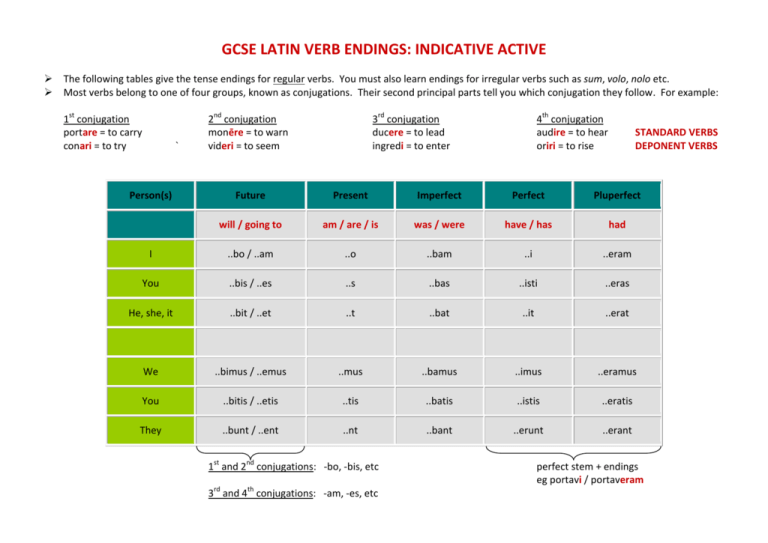
gcse latin verb endings
Colorcoded chart 4 Infinitives/Participles/Gerund etc. Latin D
This Means That It Agrees With The Noun It Modifies In Number, Case.
Not All Verbs Have All Forms.
Therefore, For Each Subjunctive Clause Type, You Should Learn The Definition, How To Recognize It, And How To Translate It.
A Perfect Participle Refers To Action Prior To That Of The Main Verb.
Related Post: