Lipids Nucleic Acids Proteins Carbohydrates Chart
Lipids Nucleic Acids Proteins Carbohydrates Chart - The four major classes of biological macromolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like elements in carbohydrates, carbohydrates monomer, functions of carbohydrates. Alongside proteins, lipids, and complex carbohydrates (polysaccharides), nucleic acids are one of the four major types of macromolecules that are essential for all known forms of life. Web carbohydrates can be represented by the stoichiometric formula (ch 2 o) n, where n is the number of carbons in the molecule. In the experiment below, we will study how pepsin, an enzyme found in the stomach, is capable of breaking protein down into smaller fragments called peptides. What are the four main types of. Nucleic acids get 3 of 4 questions to level up! Web there are four major classes of biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids); Web the breakdown and synthesis of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids connect with the metabolic pathways of glycolysis and the citric acid cycle but enter the pathways at different points. Web function of nucleic acids. Web the main substances found in every cell are a combination of lipids, carbohydrates, nucleic acids and proteins. The digestion of proteins takes place in the stomach with the help of protease and pepsin enzymes, which breaks down the proteins. Web carbohydrates can be represented by the stoichiometric formula (ch 2 o) n, where n is the number of carbons. Web function of nucleic acids. Web carbohydrates get 3 of 4 questions to level up! Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids (nucleic acids will be covered separately later). Web learn to identify the four basic biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. The four major biomolecules also called as macromolecules are proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. The four major classes of biological macromolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and. Each of these substances plays a different role in the body, and all of them must either come from the diet or be manufactured using other chemicals. Lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. While they have different structures and functions, they are all composed of long complex chains of. This formula also explains the origin of the. Biomolecules or biological molecules are molecules produced by the cells of the living organism as part of metabolism. Biological macromolecules are important cellular components and perform a wide array of functions necessary for the survival and growth of living organisms. Nucleic acids get 3 of 4 questions to level up! While they. Lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. Introduction to amino acids (opens a modal) peptide bond formation (opens a modal) introduction to proteins and. Web digestion and absorption of proteins. Web learn to identify the four basic biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Greater than 2:1 h:o (carboxyl group) fatty acid and glycerol: Thus, these macromolecules can be used as sources of. Greater than 2:1 h:o (carboxyl group) fatty acid and glycerol: Lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. Web carbohydrates can be represented by the stoichiometric formula (ch 2 o) n, where n is the number of carbons in the molecule. Web the breakdown and synthesis of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids connect. Biological macromolecules are important cellular components and perform a wide array of functions necessary for the survival and growth of living organisms. Each of these substances plays a different role in the body, and all of them must either come from the diet or be manufactured using other chemicals. Alongside proteins, lipids, and complex carbohydrates (polysaccharides), nucleic acids are one. Greater than 2:1 h:o (carboxyl group) fatty acid and glycerol: Web there are four major classes of biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids); What are the four main types of. Proteins play a vital role in the growth and replenishment of body cells and tissues. Web the main substances found in every cell are a combination of lipids,. Web the four types of macromolecules are proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. Web digestion and absorption of proteins. The digestion of proteins takes place in the stomach with the help of protease and pepsin enzymes, which breaks down the proteins. Introduction to amino acids (opens a modal) peptide bond formation (opens a modal) introduction to proteins and. Thus, these. Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. This formula also explains the origin of the. Nucleic acids get 3 of 4 questions to level up! Combined, these molecules make up the majority of a cell’s dry mass. To understand the general structure and properties of lipids and phospholipids and their. Lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. While they have different structures and functions, they are all composed of long complex chains of molecules (polymers) made up of simpler,. Web the breakdown and synthesis of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids connect with the metabolic pathways of glycolysis and the citric acid cycle but enter the pathways at different points. This session will introduce the general structure and function of the biological macromolecules: Biomolecules are the most essential organic molecules, which are involved in the maintenance and metabolic processes of living organisms. Web carbohydrates get 3 of 4 questions to level up! The digestion of proteins takes place in the stomach with the help of protease and pepsin enzymes, which breaks down the proteins. Web the main substances found in every cell are a combination of lipids, carbohydrates, nucleic acids and proteins. Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Biomolecules or biological molecules are molecules produced by the cells of the living organism as part of metabolism. Each of these substances plays a different role in the body, and all of them must either come from the diet or be manufactured using other chemicals. Web function of nucleic acids. Web carbohydrates can be represented by the stoichiometric formula (ch 2 o) n, where n is the number of carbons in the molecule. Web there are four classes of macromolecules that constitute all living matter: In other words, the ratio of carbon to hydrogen to oxygen is 1:2:1 in carbohydrate molecules. Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids (nucleic acids will be covered separately later).
Polymer Of Carbohydrates Lipids And Proteins

Compare The Chemical Structure And Functions Of Carbohydrates Lipids

Biology Chinook Academy (Kemper) February 2017

Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins And Nucleic Acids Chart
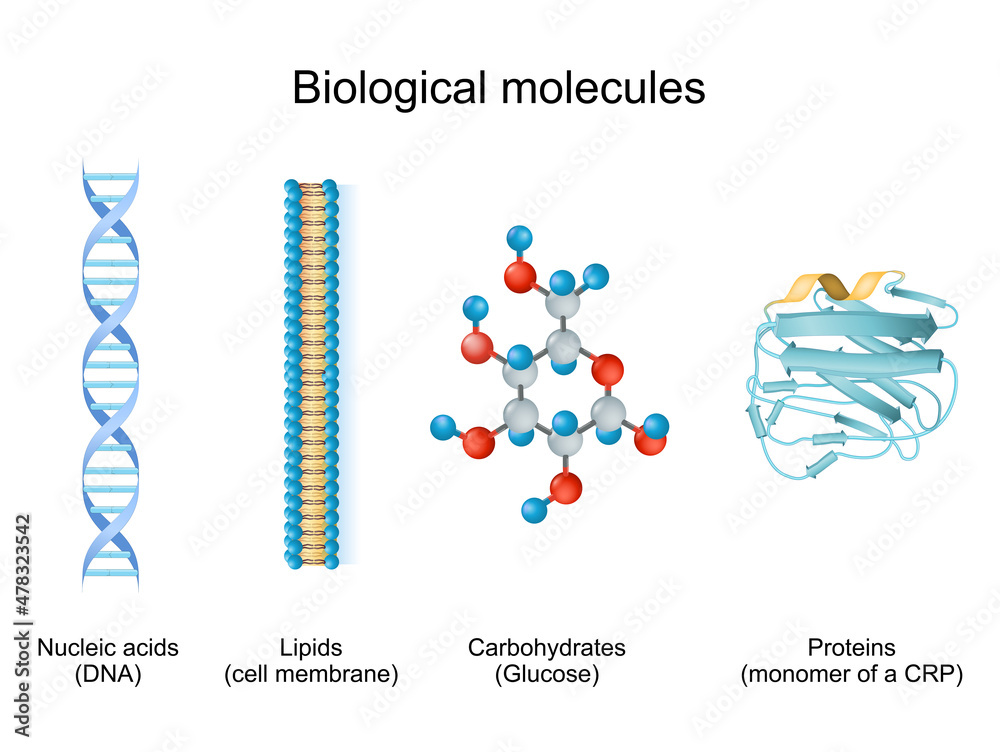
Types of biological molecule Carbohydrates, Lipids, Nucleic acids and

mixing protein and carbohydrates chart shows how food is modified

Carbohydrates Proteins Lipids And Nucleic Acids Chart Chart Walls
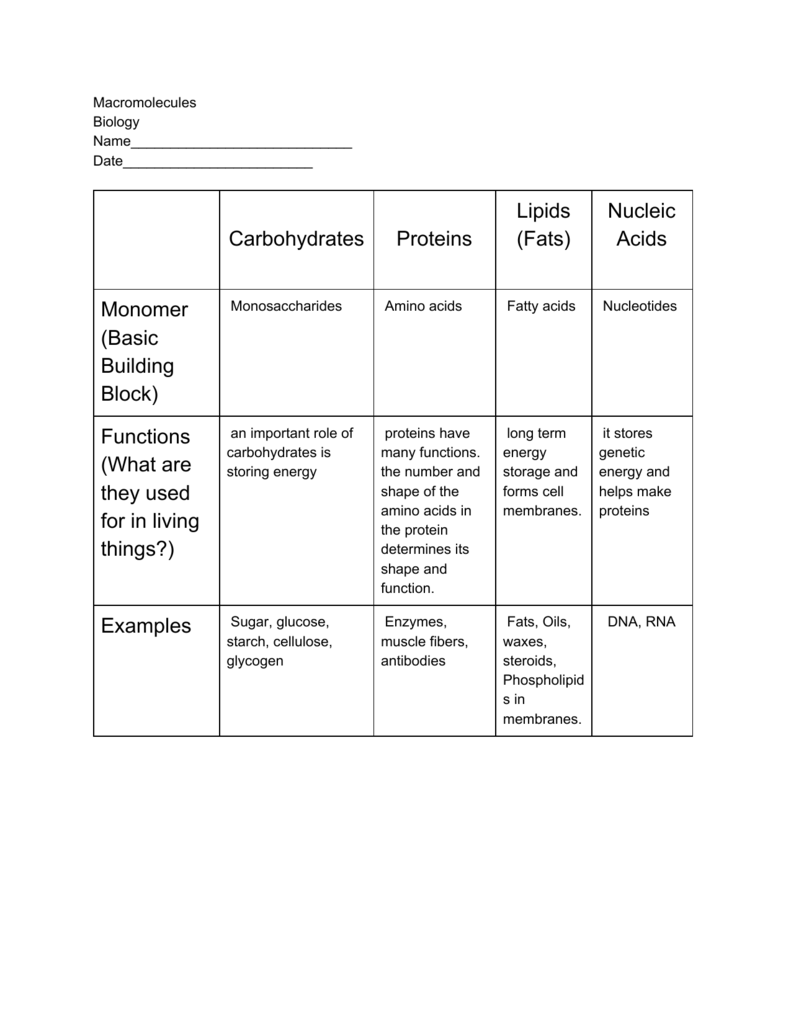
Carbohydrate Lipid Protein Nucleic Acid Chart
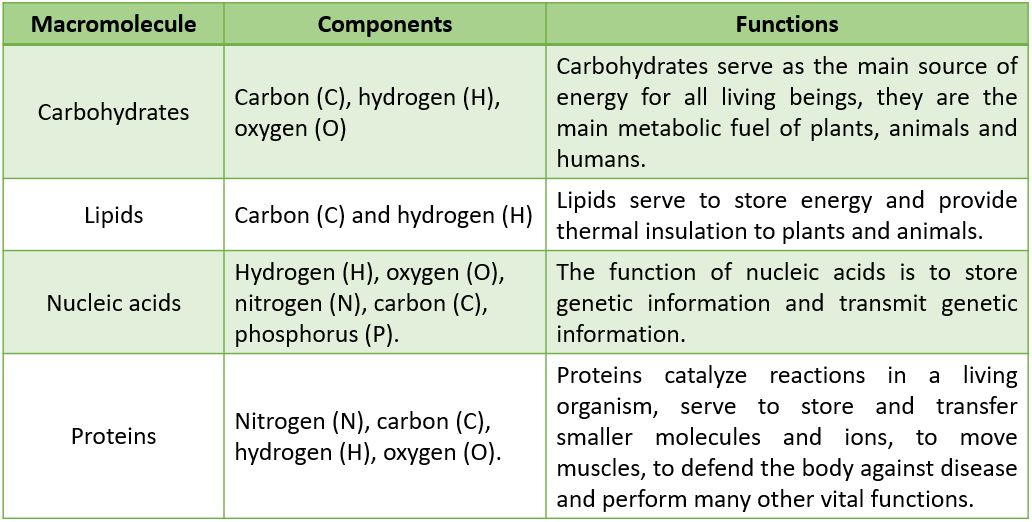
Compare The Structure And Function Of Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins

Four Biomolecules Structure and Function Comparison Chart
Nucleic Acids Get 3 Of 4 Questions To Level Up!
Web Biological Systems Are Made Up Of Four Major Classes Of Macromolecules:
Web Digestion And Absorption Of Proteins.
To Understand The General Structure And Properties Of Lipids And Phospholipids And Their.
Related Post: