Load Factor Chart
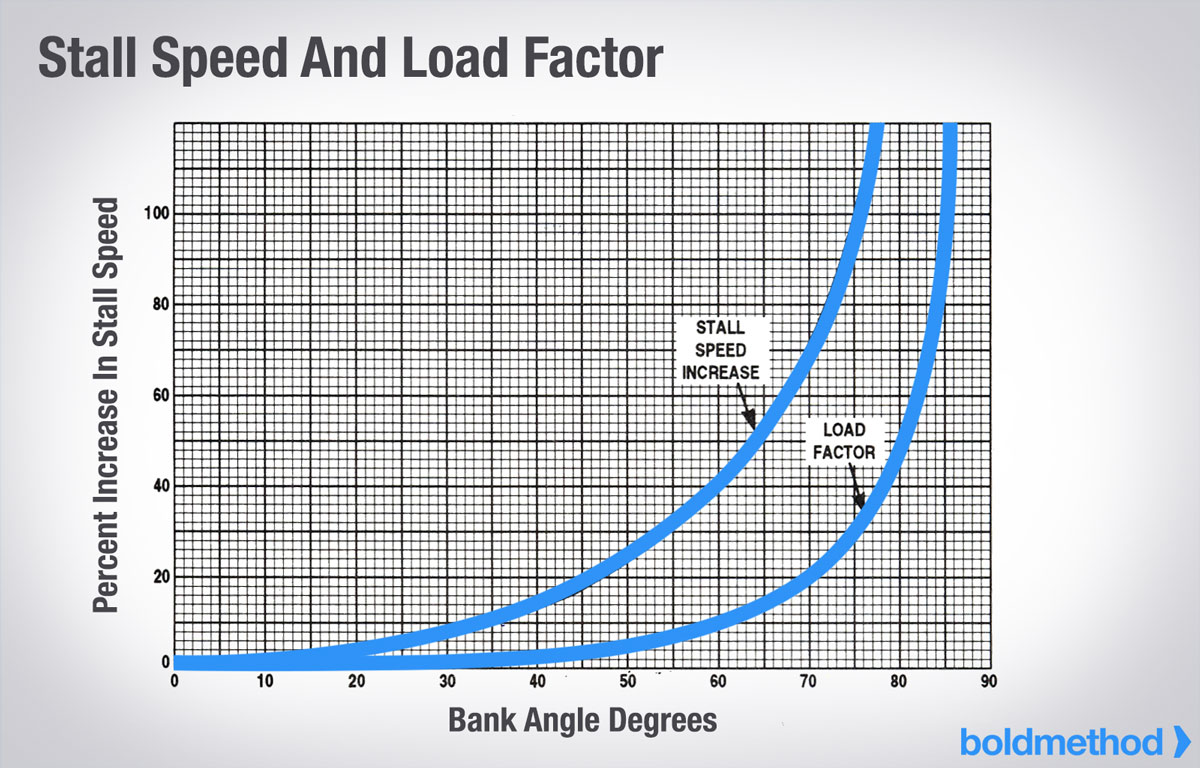
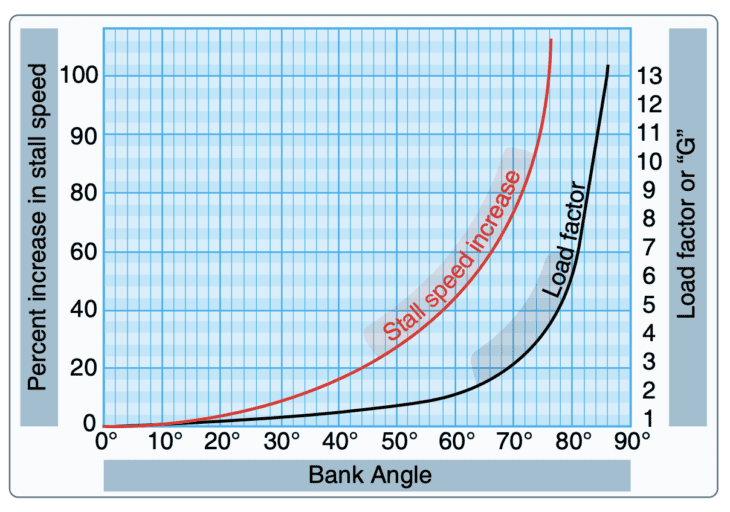
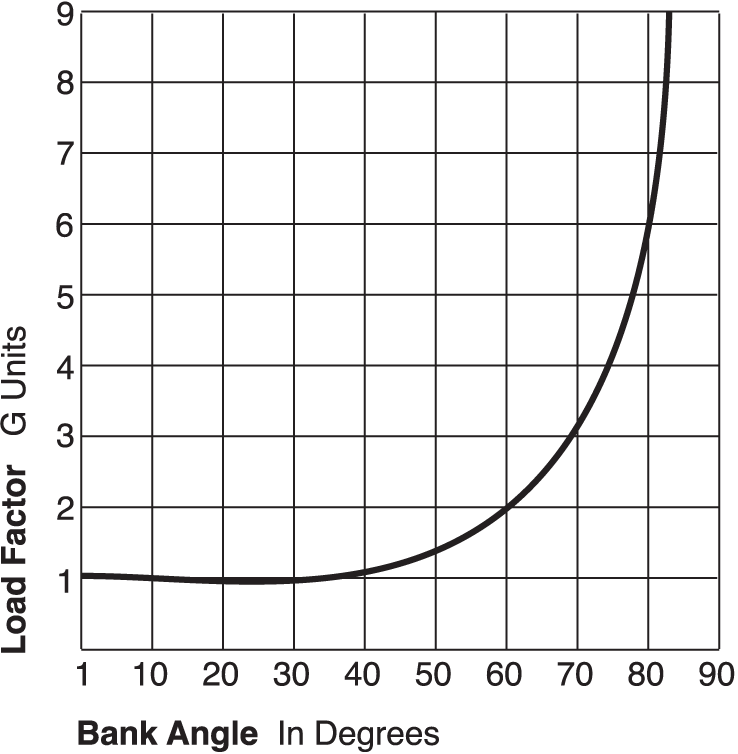
Load Factor Chart - Web a load factor of one, or 1 g, represents conditions in straight and level flight, where the lift is equal to the weight. Web here's a pretty simple example: Web determine the load factor by observing the load factor chart below. This video is lesson 11 in our private pilot ground course, which will prepare you for your faa written exam. While seat miles are calculated by multiplying the number of seats on board with the number. Assume that the leg angle will be 60°. Web a load factor is the ratio of the total airload acting on the airplane to the gross weight of the airplane. If your normal stall speed is 40 knots, and you put a load factor of 4 gs on your airplane, your plane will stall at 80 knots. A high load factor indicates that load is using the electric system more efficiently, whereas consumers or generators that. Lift is the upward force on the wing (or rotor if a quadcopter drone) and is required to counteract the weight. (2) the load factor is typically expressed as a decimal or a percentage. It is a measure of the utilization rate, or efficiency of electrical energy usage; If your normal stall speed is 40 knots, and you put a load factor of 4 gs on your airplane, your plane will stall at 80 knots. Web the passenger load factor is. 1,000 pounds times 1.154=1154 pounds. Web a load factor of one, or 1 g, represents conditions in straight and level flight, where the lift is equal to the weight. Web here's a pretty simple example: In other words, the load factor is the ratio of energy consumed in a given period of the times of hours to the peak load. Web a load factor is the ratio of the total airload acting on the airplane to the gross weight of the airplane. Here's the math on that: In other words, the load factor is the ratio of energy consumed in a given period of the times of hours to the peak load which has occurred during that particular period. Web. It shows how much load factor can be safely achieved at different airspeeds. Web this relationship is simple but important. For example, a load factor of 3 means that the total load on an airplane’s structure is three times its gross weight. Limit load and ultimate load. Web graph and download economic data for load factor for u.s. This video is lesson 11 in our private pilot ground course, which will prepare you for your faa written exam. Web a load factor is the ratio of the total airload acting on the airplane to the gross weight of the airplane. Web load factor is calculated using a few simple numbers from the electric bill. While seat miles are. It is a measure of the utilization rate, or efficiency of electrical energy usage; When boiling down the entire story on load factors into a few words, the load factor is a measure of air loads acting on an airplane. Web determine the load factor by observing the load factor chart below. Web the definition given in my university script. 87k views 7 years ago knowledge test videos. With that said, it is of utmost importance to build more ground on the study of load factors. Air carrier domestic and international, scheduled passenger flights (loadfactor) from jan 2000 to jan 2024 about flight, passenger, air travel, travel, domestic, and usa. For example, a load factor of 3 means that the. Web a load factor is the ratio of the total airload acting on the airplane to the gross weight of the airplane. By multiplying numerator and denominator of above equation by t we obtain: Air carrier domestic and international, scheduled passenger flights (loadfactor) from jan 2000 to jan 2024 about flight, passenger, air travel, travel, domestic, and usa. The square. Air carrier domestic and international, scheduled passenger flights (loadfactor) from jan 2000 to jan 2024 about flight, passenger, air travel, travel, domestic, and usa. By multiplying numerator and denominator of above equation by t we obtain: Web how much can the wing carry? In other words, the load factor is the ratio of energy consumed in a given period of. Lift is the upward force on the wing (or rotor if a quadcopter drone) and is required to counteract the weight. Web the passenger load factor is the quotient of the number of seat miles and passenger miles traveled. Web what is the load factor? 87k views 7 years ago knowledge test videos. Load factor = (average load * t)/. Web how much can the wing carry? Lift is the upward force on the wing (or rotor if a quadcopter drone) and is required to counteract the weight. And 2 x 40 knots = 80 knots. (2) the load factor is typically expressed as a decimal or a percentage. The ultimate load is the load factor applied to the aircraft beyond the limit load and at which point the. While seat miles are calculated by multiplying the number of seats on board with the number. For example, a load factor of 3 means that the total load on an airplane’s structure is three times its gross weight. Limit load and ultimate load. 1,000 pounds times 1.154=1154 pounds. Web in electrical engineering the load factor is defined as the average load divided by the peak load in a specified time period. Let’s take a closer look at some load factor examples, using more energycap charts. Web mathematical formula equation: Load factor = (average load * t)/ (max demand * t). Web in electrical engineering, the load factor is defined as a ratio of the average load divided by the maximum (or peak) load in a given time of period. This video is lesson 11 in our private pilot ground course, which will prepare you for your faa written exam. Load factor is defined as the ratio of the average load over a given period to the maximum demand (peak load) occurring in that period.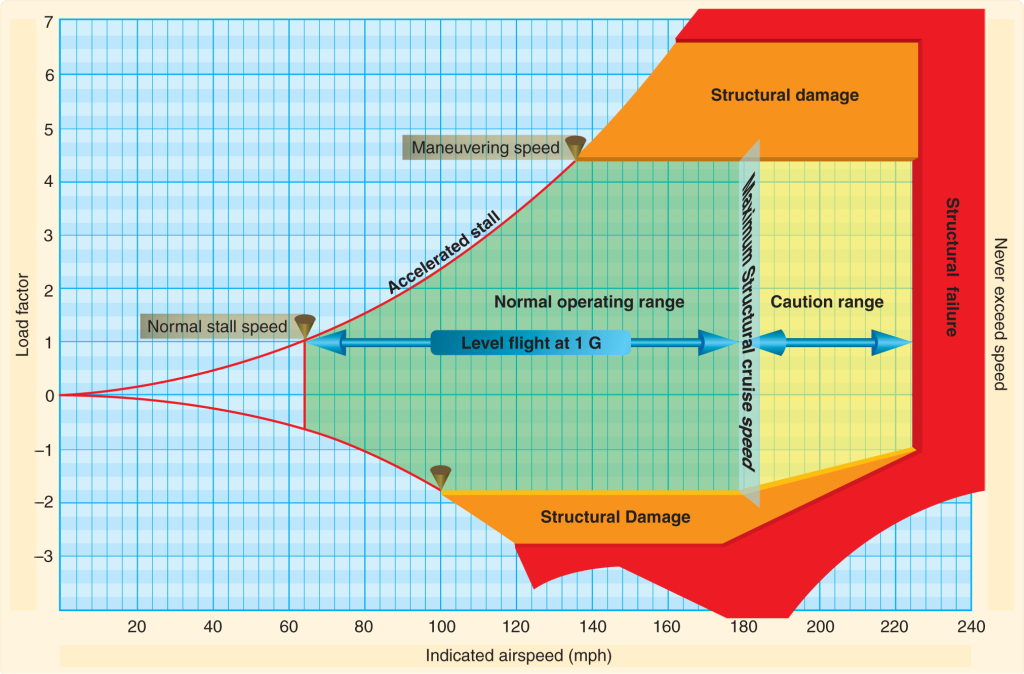
Load Factor in Aviation
Air speed in flight Page 2

3 Load factor distribution Download Table
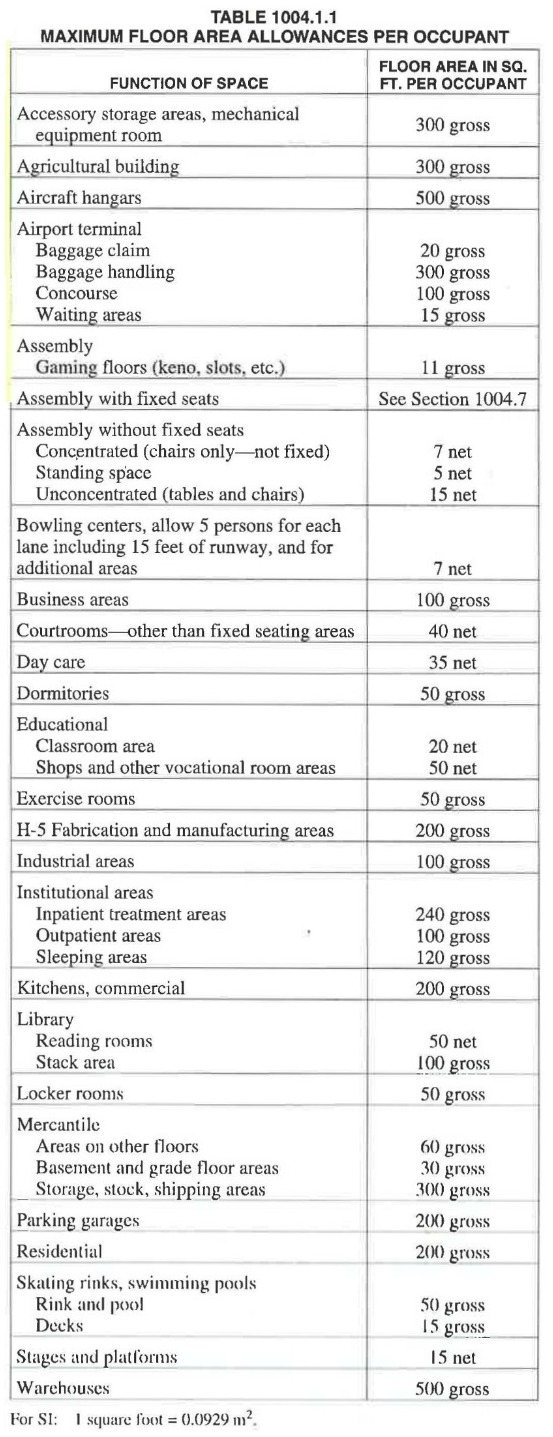
Determine Occupant Load — Croft Architects & Engineers
![FAA Part 107 Test Questions (65 Questions Explained) [2019]](https://jrupprechtlaw.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/loadfactor.jpg)
FAA Part 107 Test Questions (65 Questions Explained) [2019]
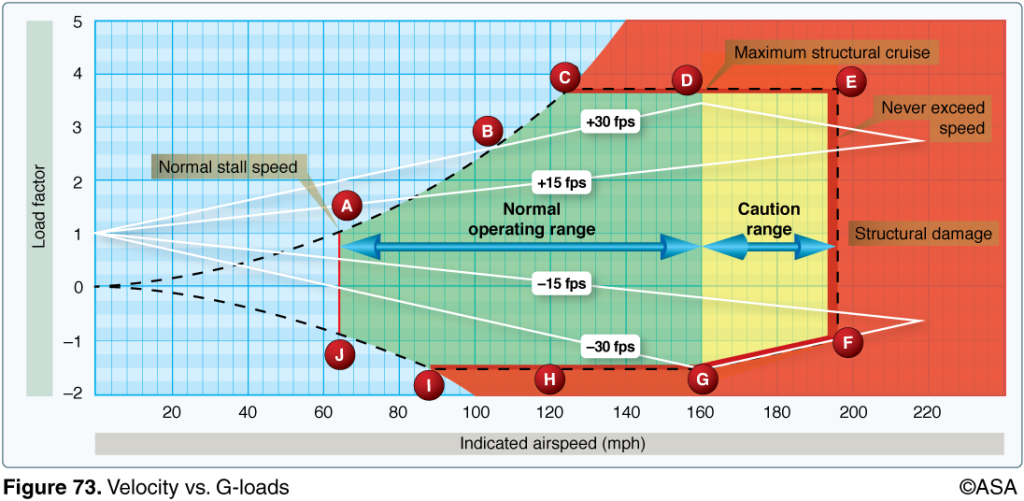
CFI Brief Velocity vs. Gloads Diagram Learn to Fly Blog ASA
What is a High Speed Stall? Aero Corner
Aircraft Performance Introduction to Weight and Balance Learn to Fly

Vg diagram explained Load Factor and Accelerated Stalls YouTube

Occupancy Load Factor Chart
In This Video We'll Explain How To Use A Vg Diagram And What It Means In Terms Of Stall Speed And Accelerated Stalls When Flying.
Multiply The Load Factor Times The Minimum Weight To Be Supported By The Leg, I.e.
Web A Load Factor Report From Your Energy Management Information System (Emis)—Like The One Below From Energycap—It’s Easy To Spot Load Factor Problems.
Web A Load Factor Of One, Or 1 G, Represents Conditions In Straight And Level Flight, Where The Lift Is Equal To The Weight.
Related Post: