Lymph System Chart
Lymph System Chart - ), the spleen, and the. As a vital part of your immune system, your lymphatic system protects you from infection and destroys old or abnormal cells your body doesn’t need. Web the lymphatic system is composed of lymphatic vessels and lymphoid organs such as the thymus, tonsils, lymph nodes, and spleen. The lymphatic system is the system of vessels, cells, and organs that carries excess fluids to the bloodstream and filters pathogens from the blood. The lymphatic system is the system of vessels, cells, and organs that carries excess fluids to the bloodstream and filters pathogens from the blood. The following is an overview of these lymph node regions and their subdivisions. The lymphatic vessels and capillaries; Web describe the structure of the primary and secondary lymphatic organs. Lymph fluid flows into and out of the lymph nodes via the lymphatic vessels, a network of valved vessels that are similar in structure to cardiovascular veins. Lymph nodes are located throughout the body. Web your lymphatic system is a network of organs, vessels and tissues that work together to move a colorless, watery fluid ( lymph) back into your circulatory system (your bloodstream). These assist in acquired and innate immunity, in filtering and draining the interstitial. The active part of the system is lymph fluid. Web explore the lymphatic system with innerbody's interactive. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphoid organs, lymphatic tissue and lymph. Web the lymphatic system includes tissues, vessels, and organs that move fluid throughout the body and fight infection. The lymphatic system is the system of vessels, cells, and organs that carries excess fluids to the bloodstream and filters pathogens from the blood. Web. As well as the circulatory system and comprises the. The active part of the system is lymph fluid. The lymphatic system is the system of vessels, cells, and organs that carries excess fluids to the bloodstream and filters pathogens from the blood. ), the spleen, and the. The lymphatic system helps to absorb dietary fat from the intestine, protects the. Web your lymphatic system is a network of organs, vessels and tissues that work together to move a colorless, watery fluid ( lymph) back into your circulatory system (your bloodstream). Web as stated above, lymph nodes are strategically located throughout the body at points susceptible to foreign microorganisms. ), the spleen, and the. As well as the circulatory system and. ), the spleen, and the. The following is an overview of these lymph node regions and their subdivisions. Web the lymphatic system consists of a network of lymphatic plexuses and vessels, lymph nodes, and other lymphoid organs such as the spleen and tonsils. Lymph nodes connect your lymphatic system, which moves fluid through your lymph nodes. Web the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system helps to absorb dietary fat from the intestine, protects the body from foreign invaders, and maintains extracellular fluid volume by returning excess tissue fluid to the blood. Web the lymphatic system is a series of vessels and nodes that collect and filter excess tissue fluid (lymph), before returning it to the venous circulation. Web describe the structure. Web the lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. When excess plasma (the liquid portion of blood) collects in your body’s tissues, the lymphatic system collects it and moves it back into your bloodstream. The following is an overview of these lymph node. Web the lymphatic system is a series of vessels and nodes that collect and filter excess tissue fluid (lymph), before returning it to the venous circulation. Web it includes organs such as the thymus, bone marrow, spleen, tonsils, appendix, and peyer patches in the small intestine that produce and process specialized white blood cells that fight infection and cancer. Web. Like the venous system, the lymphatic system transports fluids throughout the body. There are hundreds of lymph nodes in your body that gather at where two or more lymphatic channels come together, in your neck, armpits and groin. This diagram shows the network of lymph nodes and connecting lymphatic vessels in the human body. Web the lymphatic system partly functions. The lymphatic system is the system of vessels, cells, and organs that carries excess fluids to the bloodstream and filters pathogens from the blood. The lymphatic system is an important and often underappreciated component of the circulatory, immune, and metabolic systems. The lymphatic system helps to absorb dietary fat from the intestine, protects the body from foreign invaders, and maintains. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphoid organs, lymphatic tissue and lymph. Lymph nodes connect your lymphatic system, which moves fluid through your lymph nodes. There are hundreds of lymph nodes in your body that gather at where two or more lymphatic channels come together, in your neck, armpits and groin. As well as the circulatory system and comprises the. Web as stated above, lymph nodes are strategically located throughout the body at points susceptible to foreign microorganisms. Lymphatic cells include macrophages, dendritic cells, lymphocytes, as well as lymphatic organs such as. As a vital part of your immune system, your lymphatic system protects you from infection and destroys old or abnormal cells your body doesn’t need. It is a long held concept that the brain is the only region of the body devoid of a lymphatic system. Like the venous system, the lymphatic system transports fluids throughout the body. The lymphatic system helps to absorb dietary fat from the intestine, protects the body from foreign invaders, and maintains extracellular fluid volume by returning excess tissue fluid to the blood. Web your lymphatic system is a network of organs, vessels and tissues that work together to move a colorless, watery fluid ( lymph) back into your circulatory system (your bloodstream). The lymphatic system is an important and often underappreciated component of the circulatory, immune, and metabolic systems. Along the way, the lymph travels through the lymph nodes, which are commonly found near the groin, armpits, neck, chest, and abdomen. Web the lymphatic system is a network of vessels and organs that regulates the amount of fluid in the human body and defends it against infections. The lymphatic system is part of the. Lymphatic vessels, ducts and tracts;
Human Body Lymphatic System Carolina Biological Supply

Lymphatic System Drainage Chart
![What Is the Lymphatic System? [Infographic] DanaFarber Cancer Institute](http://blog.dana-farber.org/insight/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/7367-Lymphatic-System-Infographic.png)
What Is the Lymphatic System? [Infographic] DanaFarber Cancer Institute
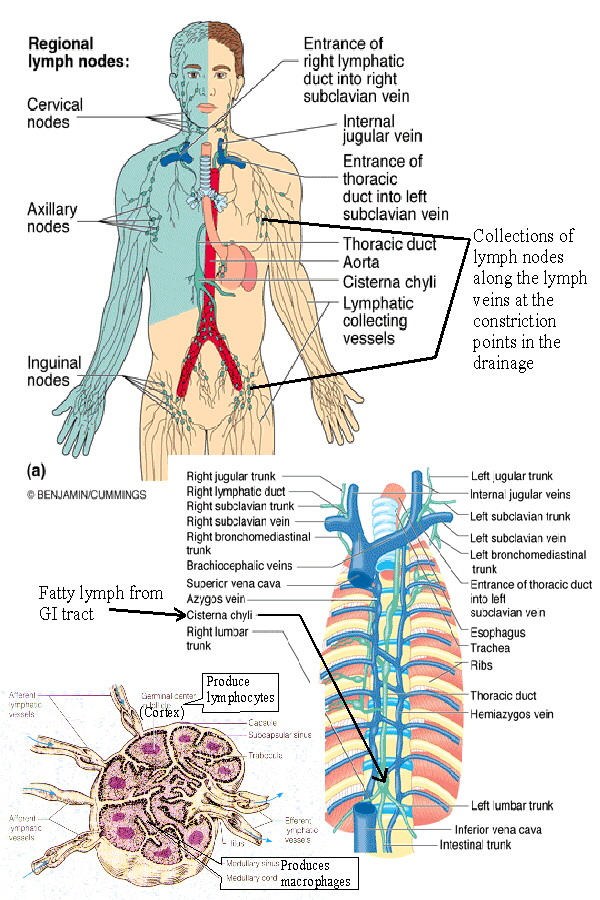
Understanding the Lymphatic System
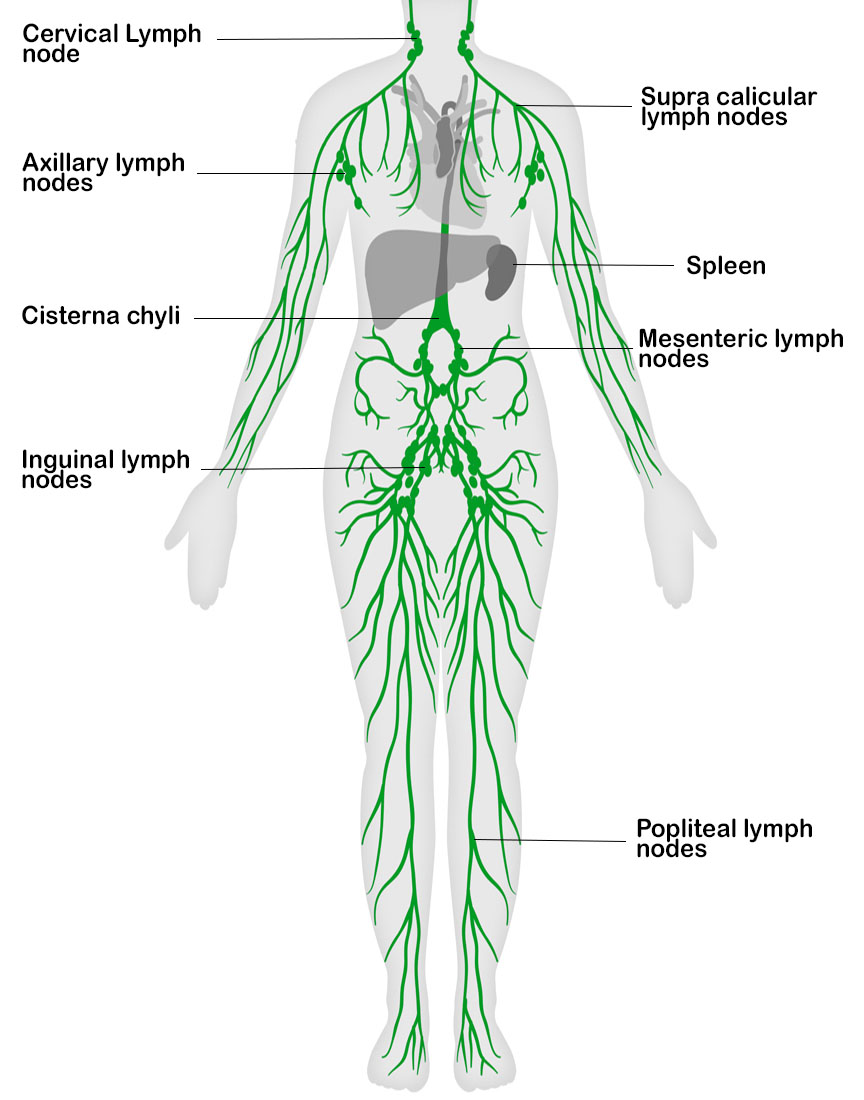
LYMPHATIC SYSTEM Lab Medica Healthcare
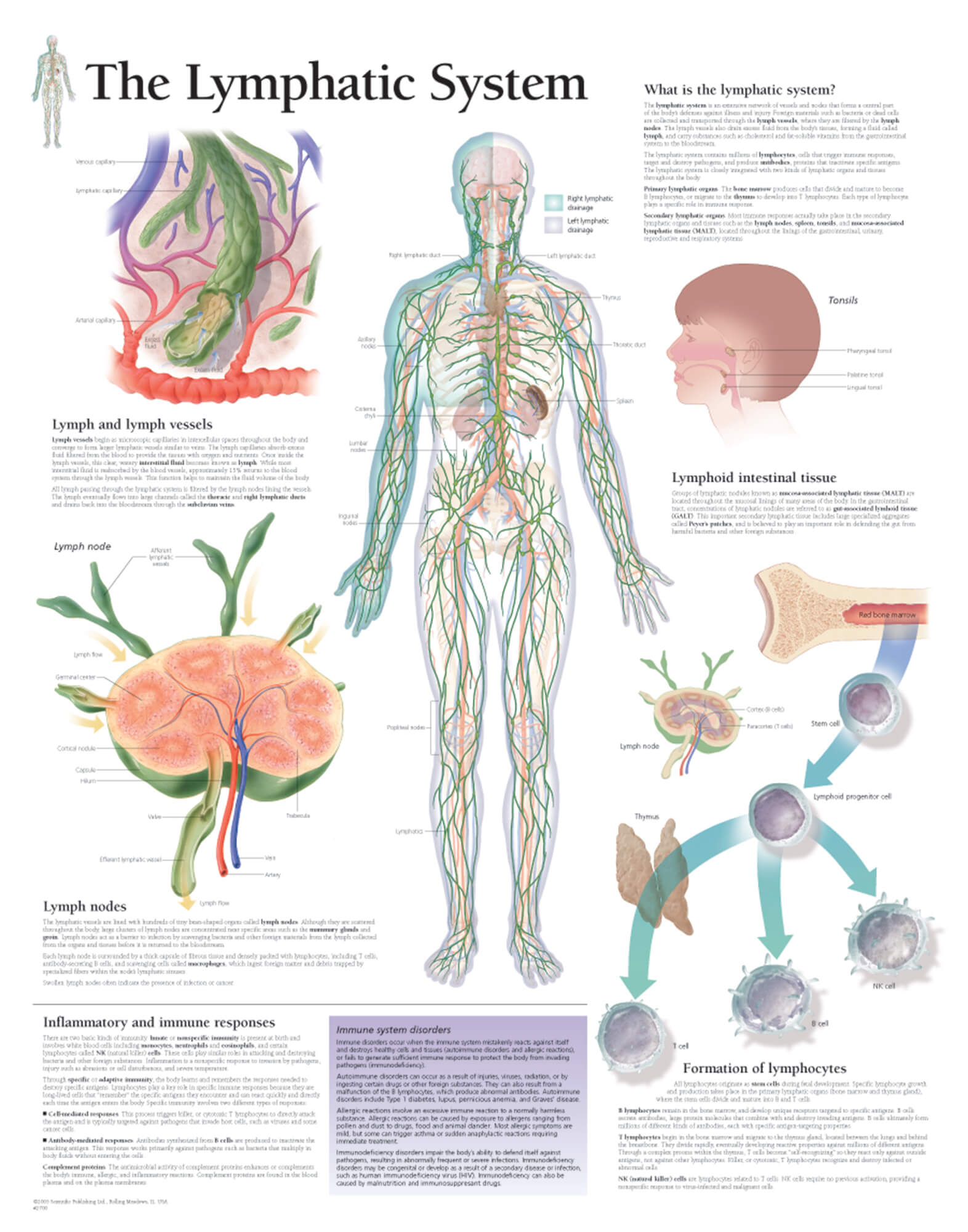
The Lymphatic System Scientific Publishing
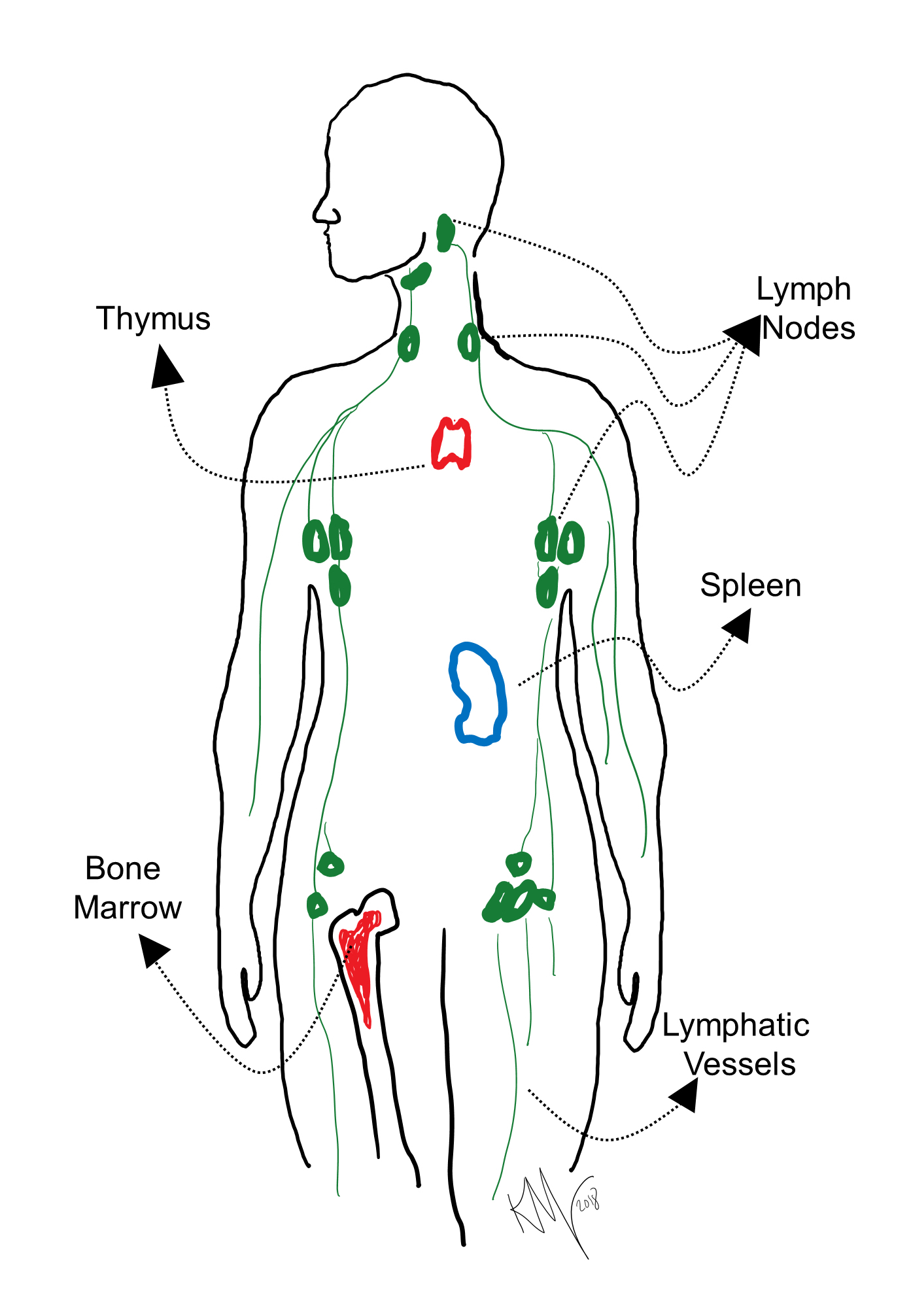
Organs of the immune system ImmunoBites

Anatomy and Physiology The Lymphatic System Sarah Wayt
/lymphatic_system_2-58110f0c5f9b58564c6e31cb.jpg)
Lymphatic System Components Spleen, Thymus, Nodes
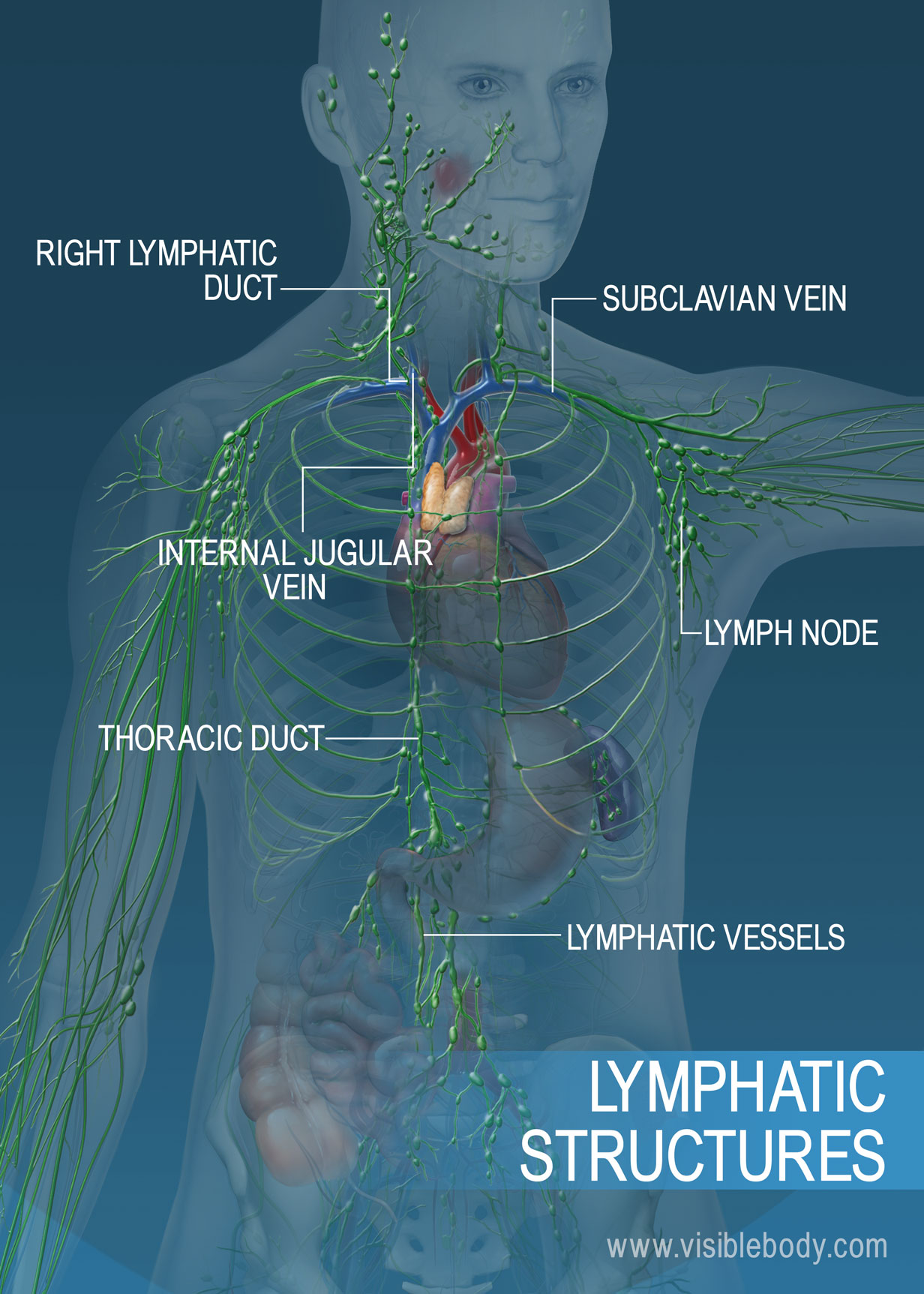
Lymphatic System
It Forms A Vital Part Of The Body’s Immune Defence.
The Lymphatic System Is The System Of Vessels, Cells, And Organs That Carries Excess Fluids To The Bloodstream And Filters Pathogens From The Blood.
Web It Includes Organs Such As The Thymus, Bone Marrow, Spleen, Tonsils, Appendix, And Peyer Patches In The Small Intestine That Produce And Process Specialized White Blood Cells That Fight Infection And Cancer.
Web The Lymphatic System Is A Series Of Vessels And Nodes That Collect And Filter Excess Tissue Fluid (Lymph), Before Returning It To The Venous Circulation.
Related Post: