Macromolecules Chart Biology
Macromolecules Chart Biology - All living things are made up of four main classes of macromolecules: Web proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids are the four major classes of biological macromolecules—large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules. Web just as you can be thought of as an assortment of atoms or a walking, talking bag of water, you can also be viewed as a collection of four major types of large biological molecules: The polymer is more than the sum of. Browse videos, articles, and exercises by topic. Now that we’ve discussed the four major classes of biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids), let’s talk about macromolecules as a whole. Carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins. Web carbohydrates are a major class of biological macromolecules that are an essential part of our diet and provide energy to the body. Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Each is an important cell component and performs a wide array of functions. The structure and function of macromolecules. Web the image below depicts how the bacterial protein barnase undergoes modifications that involve changing its conformation, or shape. Openstax college [cc by 3.0], via wikimedia commons. A molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially. This document has been uploaded by a student, just like you, who decided to remain. Comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from. In many cases, especially for synthetic polymers, a molecule can be regarded. Web biological macromolecules are large molecules, necessary for life, that are built from smaller organic molecules. Click the card to flip 👆. Web distinguish between the four classes of macromolecules carbohydrates are a group of macromolecules that. Carbohydrates (such as sugars), lipids (such as fats), proteins, and nucleic acids (such as dna and rna). Web biological macromolecules are large molecules, necessary for life, that are built from smaller organic molecules. Which of the following best describes the role that water plays in the reaction depicted above? Within all cells, small organic molecules are joined together to form. Web in biology, macromolecules refer to large organic molecules that form by polymerization, a process that joins smaller units called monomers via covalent bonds. Web biological macromolecules are large molecules, necessary for life, that are built from smaller organic molecules. Combined, these molecules make up the majority of a cell’s dry mass (recall that water makes up the majority of. Web define the term “macromolecule” distinguish between the 4 classes of macromolecules. Within all cells, small organic molecules are joined together to form larger molecules. Web distinguish between the four classes of macromolecules carbohydrates are a group of macromolecules that are a vital energy source for the cell, provide structural support to many organisms, and can be found on the. Web distinguish between the four classes of macromolecules carbohydrates are a group of macromolecules that are a vital energy source for the cell, provide structural support to many organisms, and can be found on the surface of the cell as receptors or. Now that we’ve discussed the four major classes of biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids), let’s. They are usually the product of smaller molecules, like proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates. Macromolecules are made up of single units known as monomers that are joined by covalent bonds to form larger polymers. Openstax college [cc by 3.0], via wikimedia commons. All living things are made up of four main classes of macromolecules: Click the card to flip 👆. Web proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids are the four major classes of biological macromolecules—large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules. Each is an important cell component and performs a wide array of functions. 4.0 (2 reviews) what are the 4 macromolecules? There are four major classes of biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic. Macromolecules are made up of single units known as monomers that are joined by covalent bonds to form larger polymers. Within all cells, small organic molecules are joined together to form larger molecules. Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. The structure and function of macromolecules. Combined, these molecules make up the majority of a cell’s dry mass (recall that water. Within all cells, small organic molecules are joined together to form larger molecules. Web on studocu you find all the lecture notes, summaries and study guides you need to pass your exams with better grades. Molecules of low relative molecular mass. Combined, these molecules make up the. Each is an important cell component and performs a wide array of functions. These biological macromolecules are essential for life and include proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids. In the reverse of this reaction, water is used to promote hydrolysis. The four major classes of biological macromolecules are carbohydrates,. This unit is part of the biology library. There are four major classes of biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids); 4.0 (2 reviews) what are the 4 macromolecules? This composition gives carbohydrates their name: Molecules of low relative molecular mass. Which of the following best describes the role that water plays in the reaction depicted above? Web on studocu you find all the lecture notes, summaries and study guides you need to pass your exams with better grades. Web biological macromolecules are large molecules, necessary for life, that are built from smaller organic molecules. Web 1.5 structure and function of biological macromolecules overview. Combined, these molecules make up the. Course principles of biology ii (biol 2108) university perimeter college at georgia state university. Within all cells, small organic molecules are joined together to form larger molecules. Carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins.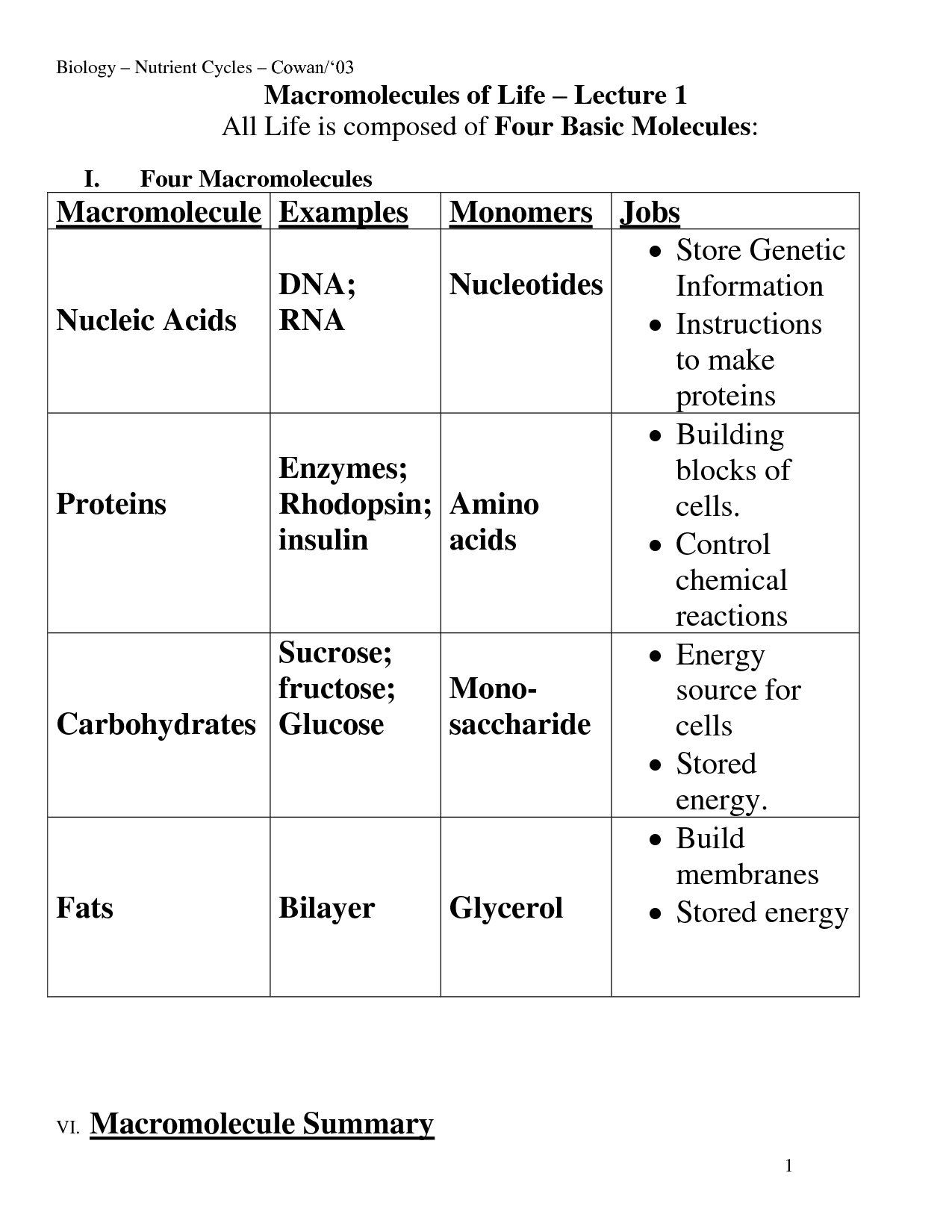
12 Biology Macromolecules Worksheets /
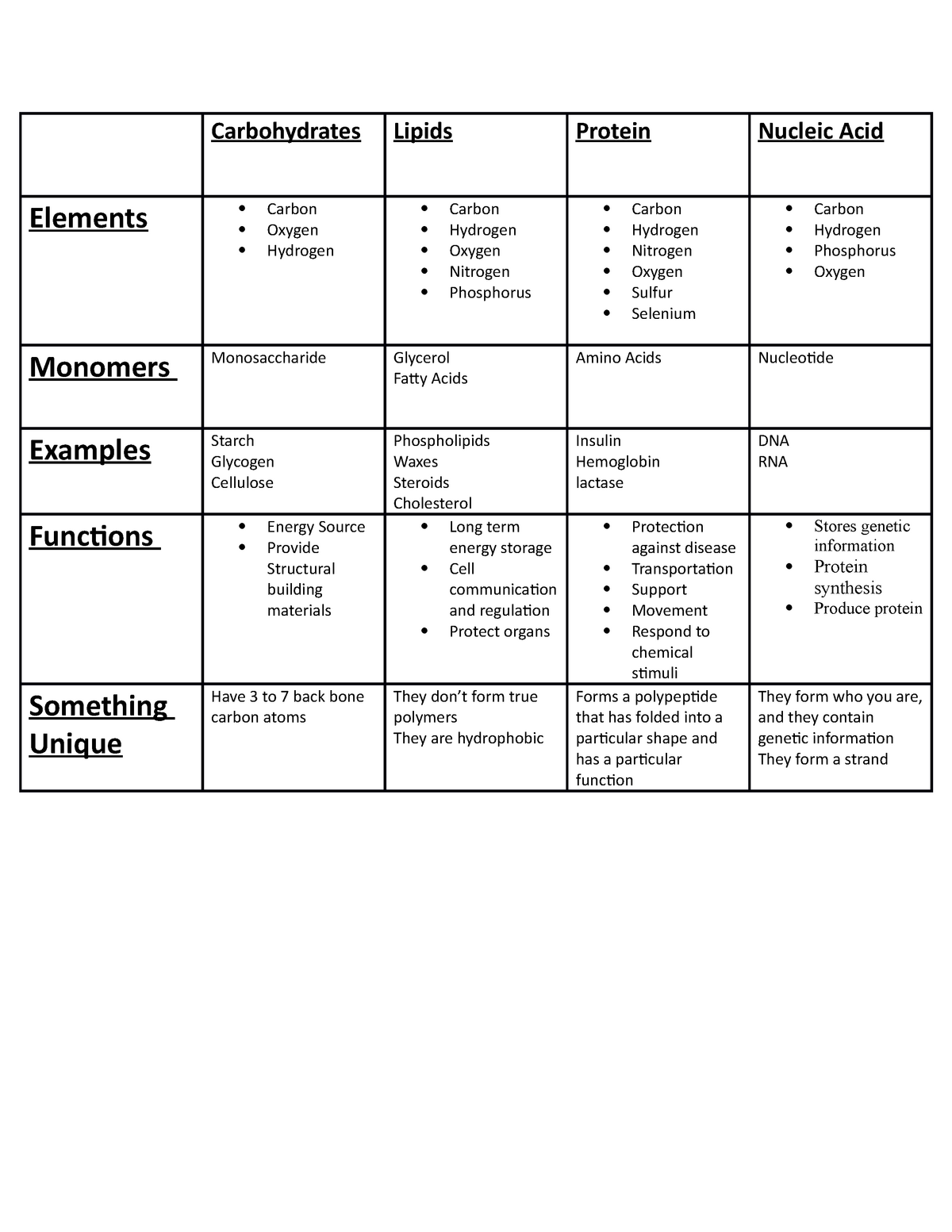
Macromolecules chart Lecture notes A Carbohydrates Elements Carbon

2.3 Biologically Important Macromolecules Biology LibreTexts

Pre IB/GT Biology 1 Macromolecules Chart Diagram Quizlet
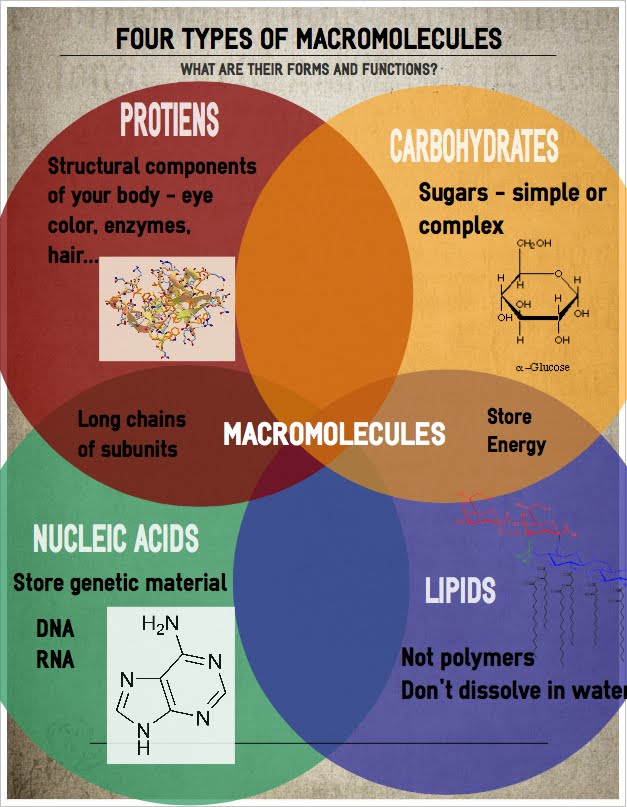
Structure and Function of Biological Macromolecules Study Guide
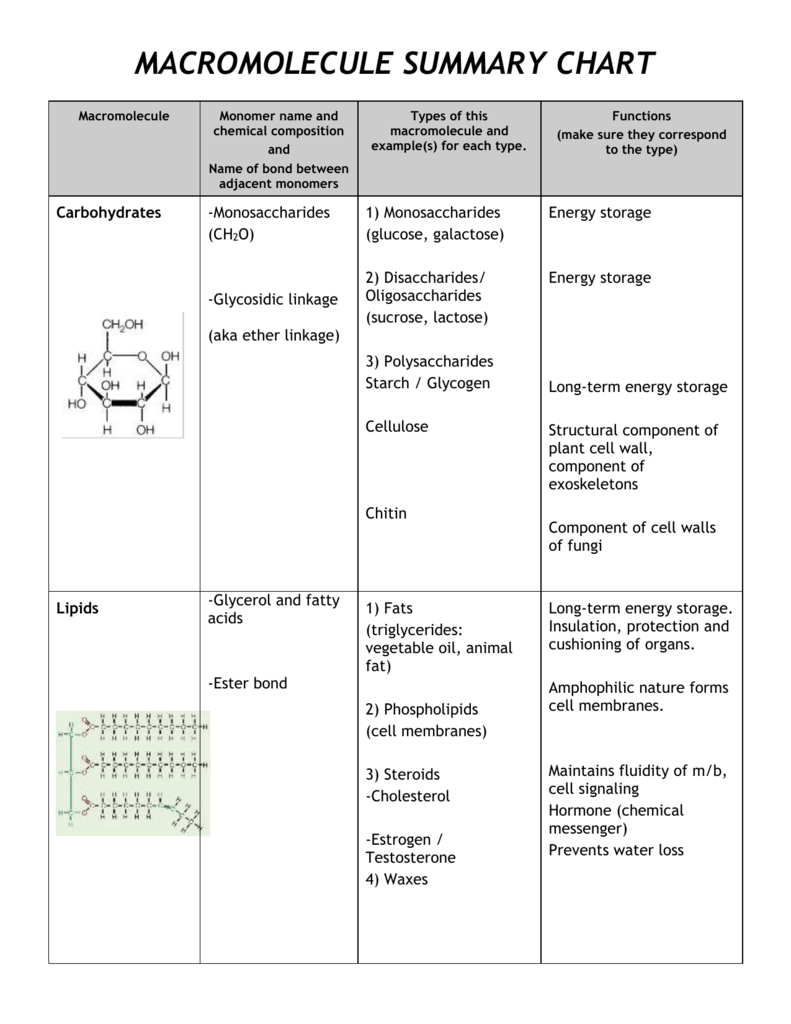
Four Macromolecules Chart
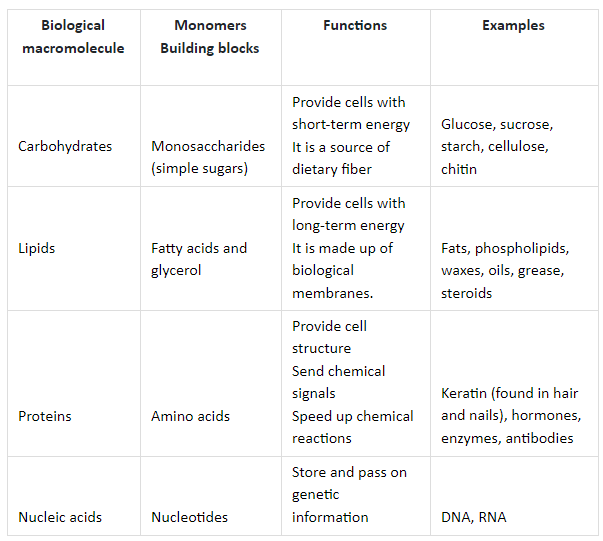
Structure and Function of Biological Macromolecules Study Guide
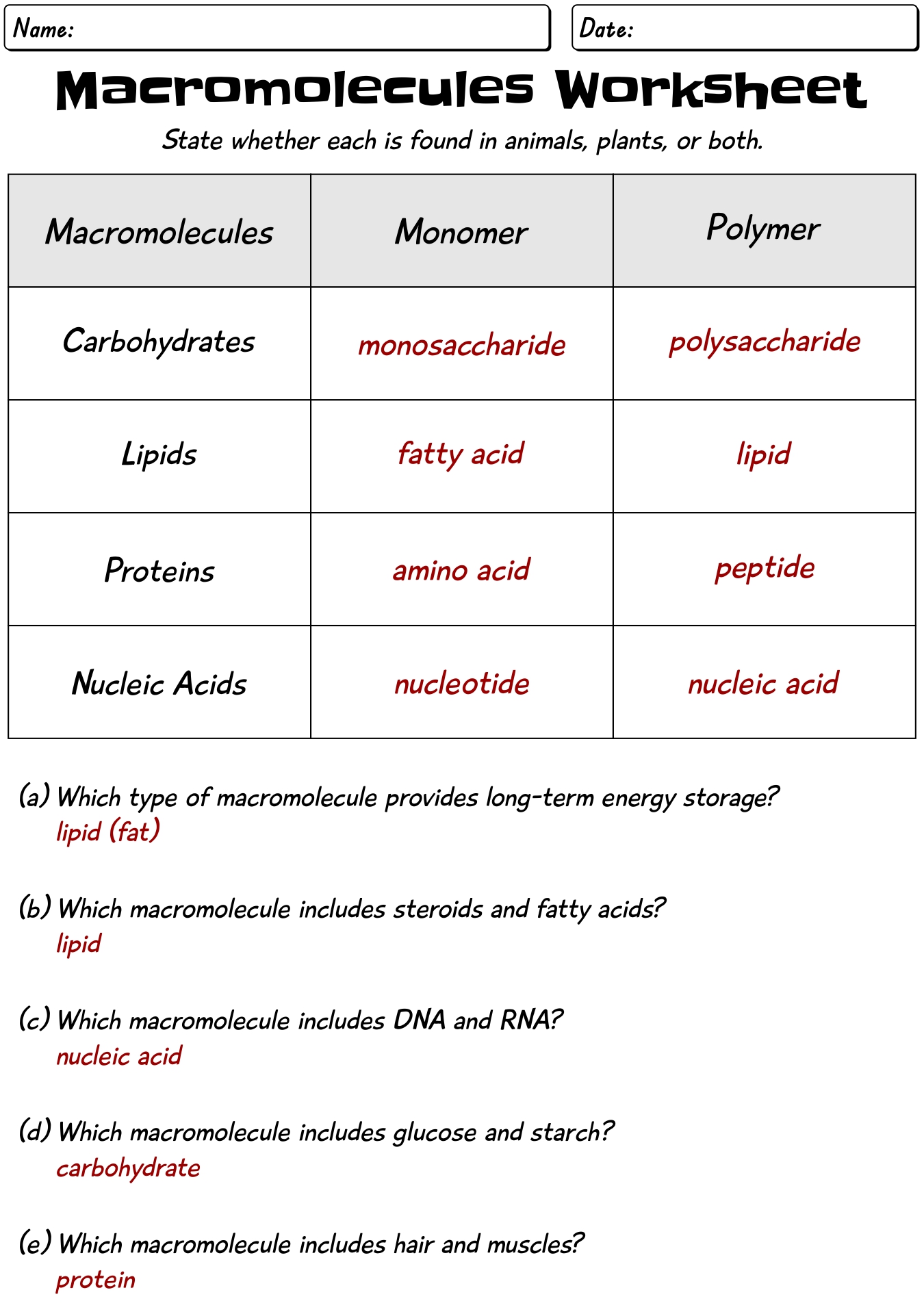
14 Biology Macromolecules Worksheets And Answers /

Biological Macromolecules Concept Map
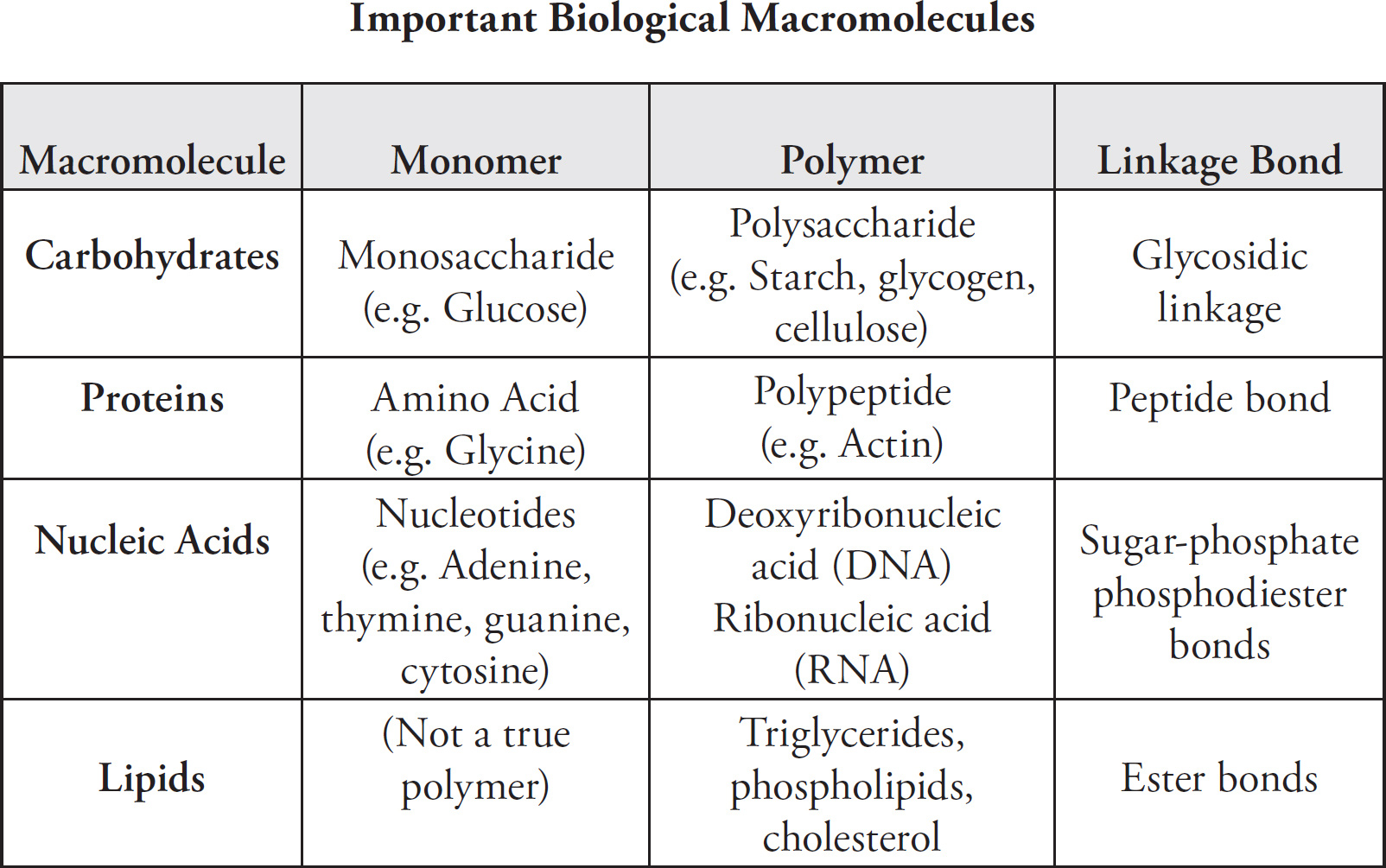
Biological macromolecules
Each Is An Important Cell Component And Performs A Wide Array Of Functions.
All Living Things Are Made Up Of Four Main Classes Of Macromolecules:
This Document Has Been Uploaded By A Student, Just Like You, Who Decided To Remain Anonymous.
Web Carbohydrates Are A Major Class Of Biological Macromolecules That Are An Essential Part Of Our Diet And Provide Energy To The Body.
Related Post: