Magnification Chart For Microscope
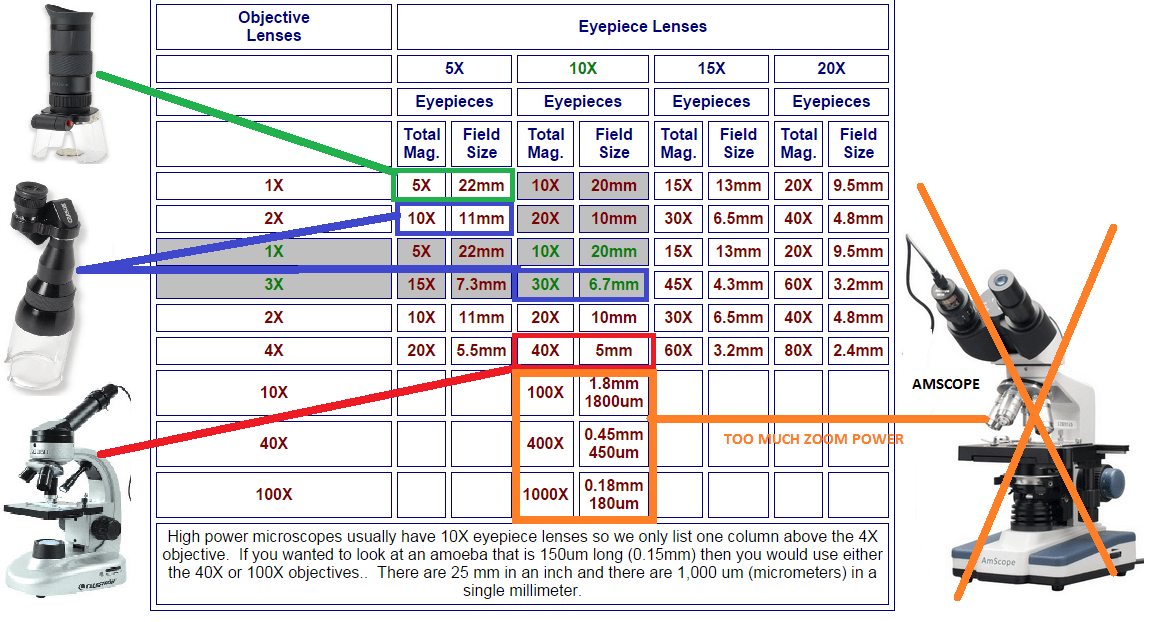
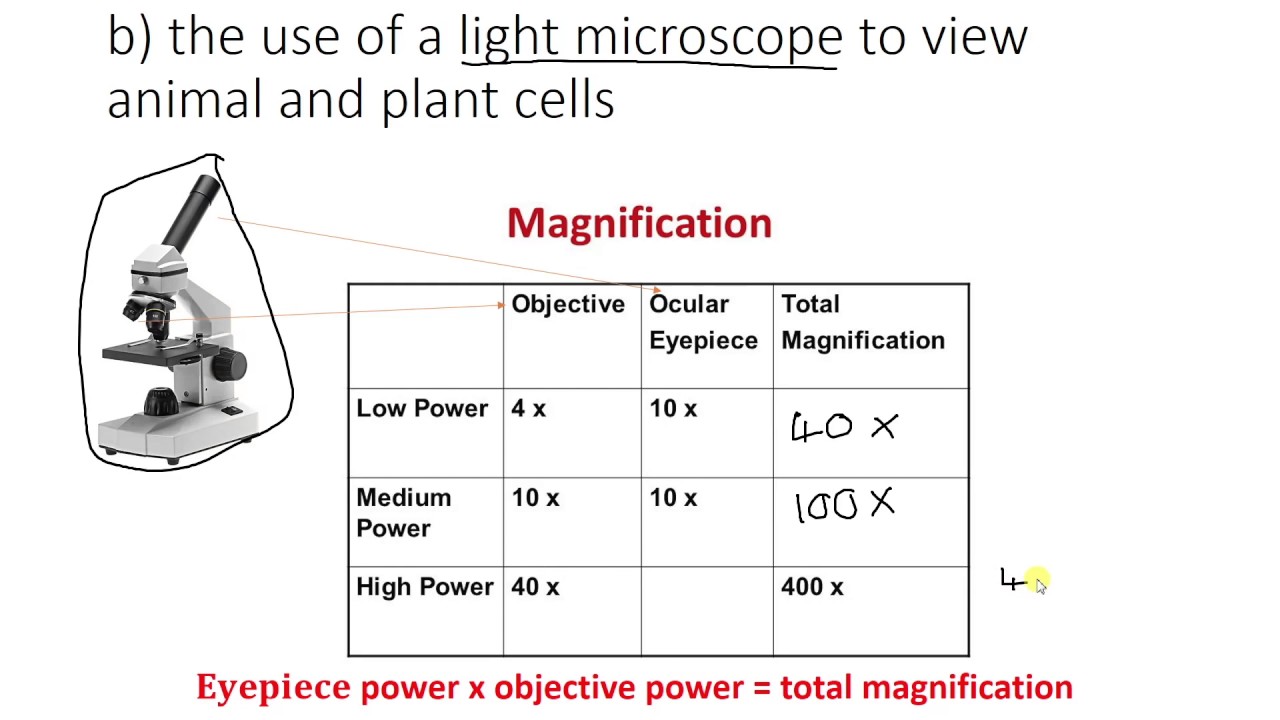
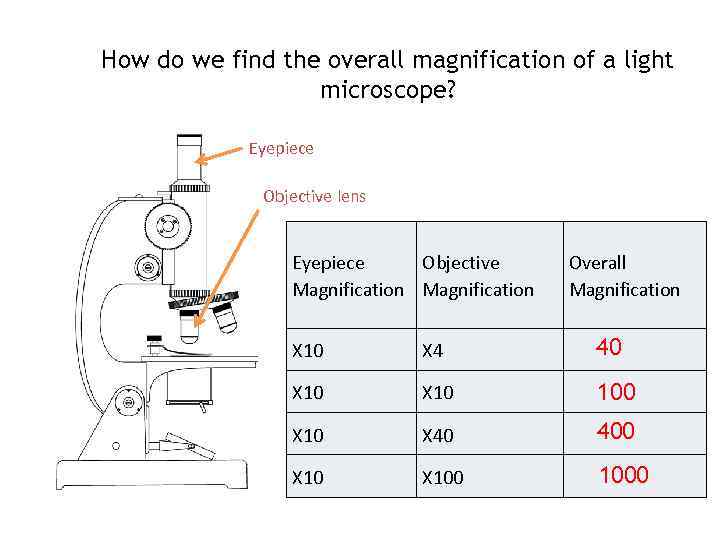
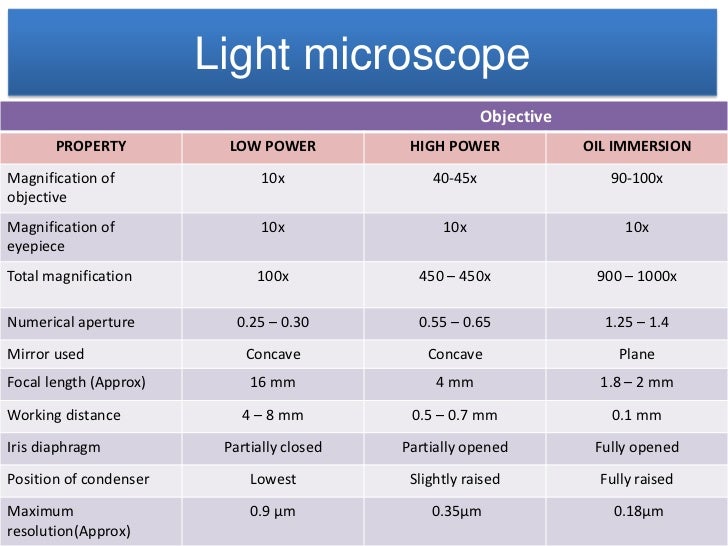
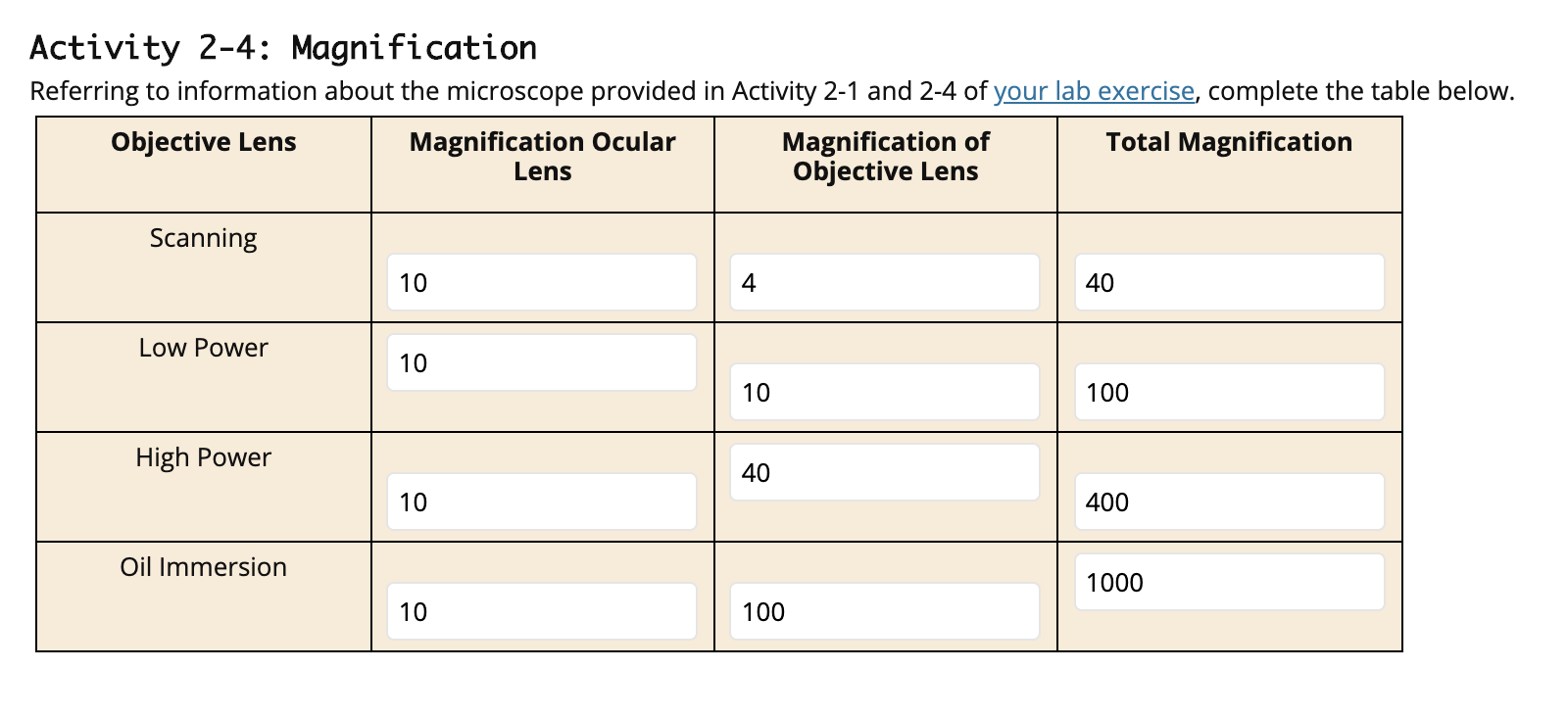
Magnification Chart For Microscope - This introduction to microscopy will include an explanation of features and adjustments of a compound brightfield light microscope, which magnifies images using a two lens system. Web describe refraction and distinguish between convex and concave lenses. Web magnification is the ability to make small objects seem larger, such as making a microscopic organism visible. However, you can find eyepieces that magnify 15x, 20x and even 30x or higher. The difference in distance between d _ s a m p l e and f o is the distance the. Web most microscope objective specifications are listed on the body of the objective itself: At 400x magnification you will be able to. Web for a single channel microscope, the practical magnification of the microscope can be measured using, for example, a graticule sample. Determine the magnification of the objective lens: Also, indicate the estimated cell size in micrometers under your drawing. Successfully use the metric system for length including unit conversion calculations. Web a standard microscope eyepiece magnifies an object 10x. Web for a single channel microscope, the practical magnification of the microscope can be measured using, for example, a graticule sample. Web the chart below will tell you (approximately) what to expect when looking through a microscope with varying combinations. Web to calculate the magnification of a microscope, follow these steps: Web to help users better understand the magnification of microscopy and how to determine the useful range of magnification values for digital microscopes, this article provides helpful guidelines. This presents a plethora of options in terms of combining the ocular and objective lenses to. However, you can find eyepieces. Web to help users better understand the magnification of microscopy and how to determine the useful range of magnification values for digital microscopes, this article provides helpful guidelines. (microscopes usually come with a set of objective lenses that can be interchanged to vary the magnification.) Web for a single channel microscope, the practical magnification of the microscope can be measured. Web these include the linear magnification, numerical aperture value, optical corrections, microscope body tube length, the type of medium the objective is designed for, and other critical factors in deciding if the objective will perform as needed. The difference in distance between d _ s a m p l e and f o is the distance the. This information is. The light microscope bends a beam of light at the specimen using a series of lenses to provide a clear image of the specimen to the observer. Refraction occurs when light travels through an area of space that has a. Web a combination of magnification and resolution is necessary to clearly view specimens under the microscope. Web these include the. Web the eyepiece lens usually magnifies 10x, and a typical objective lens magnifies 40x. Web remember with a compound light microscope you are magnifying with two lenses, so to calculate the total magnification you multiple the objective magnification by the ocular magnification. Identify the structures of a light microscope. Web explore the range of useful magnification for common nikon objective. Identify the structures of a light microscope. Web for the digital microscope, the magnification range for the objective lens is 0.32× to 2×, and the tube factor (q) including the photographic projection lens has a maximum to minimum magnification range of 8:1 (ratio of. Explore the worlds within worlds of detail in the microscopic scale. Web describe refraction and distinguish. Web with the help of proper illumination, a microscope can magnify a specimen and optically resolve fine detail. This presents a plethora of options in terms of combining the ocular and objective lenses to. Web they include information about the magnification of the image (for example, 600x) as well as a scale bar, which acts as a ruler and indicates. This presents a plethora of options in terms of combining the ocular and objective lenses to. Web remember with a compound light microscope you are magnifying with two lenses, so to calculate the total magnification you multiple the objective magnification by the ocular magnification. Determine/calculate total magnification for each objective lens. Total magnification is also dependent upon the tube length. Web to calculate the magnification of a microscope, follow these steps: It is often represented as a number followed by. Web the chart below will tell you (approximately) what to expect when looking through a microscope with varying combinations of eyepieces and objective lenses. As an example (in green below), a dual power stereo microscope with 10x eyepiece lenses and. However, you can find eyepieces that magnify 15x, 20x and even 30x or higher. The underlying principle of a microscope is that lenses refract light which allows for magnification. It is often represented as a number followed by. Explore the worlds within worlds of detail in the microscopic scale. Determine the magnification of the objective lens: At 40x magnification you will be able to see 5mm. Web for a single channel microscope, the practical magnification of the microscope can be measured using, for example, a graticule sample. Web for the digital microscope, the magnification range for the objective lens is 0.32× to 2×, and the tube factor (q) including the photographic projection lens has a maximum to minimum magnification range of 8:1 (ratio of. Web these include the linear magnification, numerical aperture value, optical corrections, microscope body tube length, the type of medium the objective is designed for, and other critical factors in deciding if the objective will perform as needed. Determine/calculate total magnification for each objective lens. Refraction occurs when light travels through an area of space that has a. Web the eyepiece lens usually magnifies 10x, and a typical objective lens magnifies 40x. Web a light microscope can see things down to about 0.002 millimeters and an electron microscope can see things down to about 0.0000001 millimeters. Web tell the importance of using microscopes in microbiology. Web magnification is the ability to make small objects seem larger, such as making a microscopic organism visible. Web to help users better understand the magnification of microscopy and how to determine the useful range of magnification values for digital microscopes, this article provides helpful guidelines.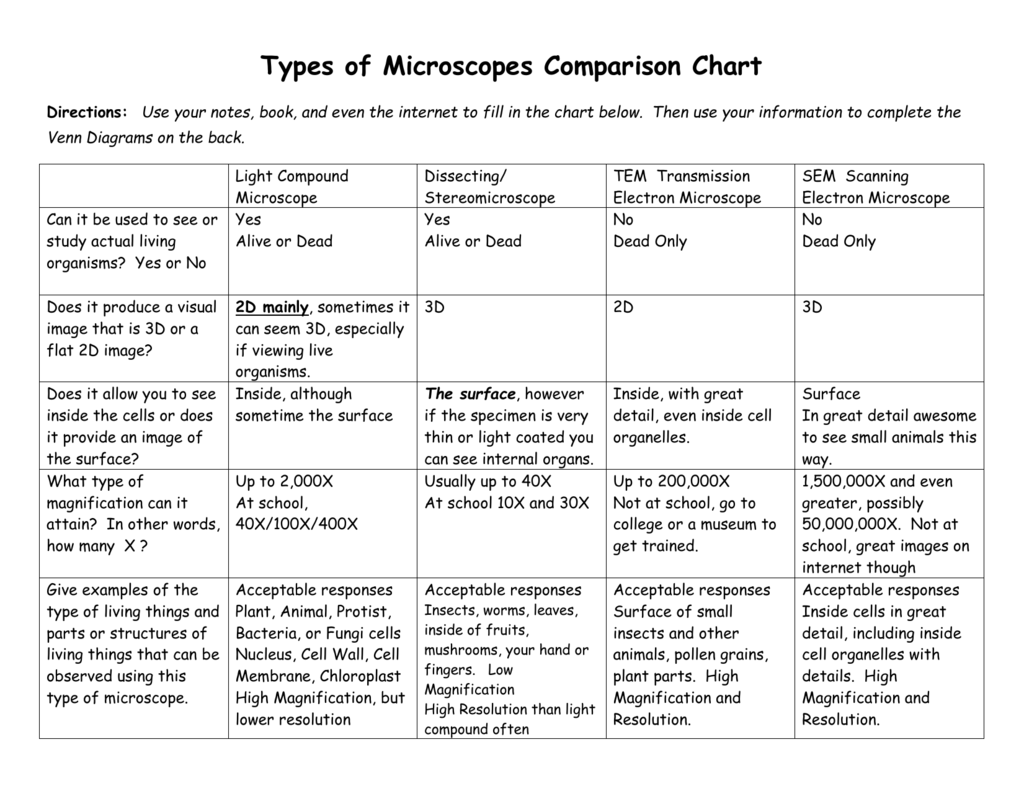
Microscope Magnification Calculation Worksheet Micropedia
Size by Size Microscopy & Optical Mineralogy Basics 911M

How microscopes magnify — Science Learning Hub
Compound Light Microscope Magnification Calculation Shelly Lighting
Cell Size Microscope Measurement How big is

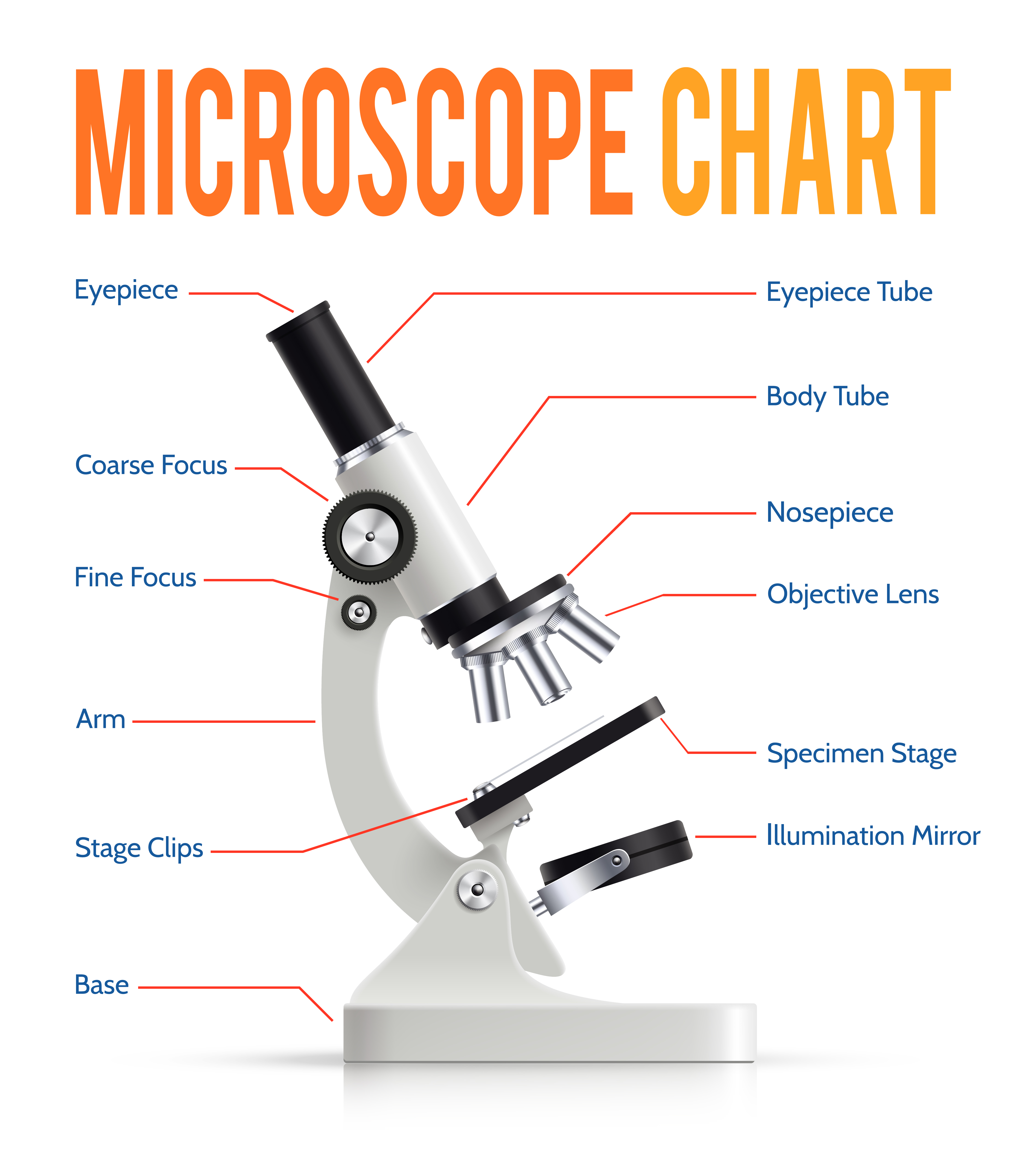
Parts of a Compound Microscope Labeled (with diagrams) Medical
Microscope

Microscope Magnification
Realistic Microscope Parts Infographic Presentation Chart 478769 Vector
Microscope Magnification Levels Chart
Web Explore The Range Of Useful Magnification For Common Nikon Objective And Eyepiece Combinations With This Interactive Tutorial.
Also, Indicate The Estimated Cell Size In Micrometers Under Your Drawing.
Identify The Structures Of A Light Microscope.
Web For Instance, Using A 5X Objective With A 10X Eyepiece Yields A Total Visual Magnification Of 50X And Likewise, At The Top End Of The Scale, Using A 100X Objective With A 30X Eyepiece Gives A Visual Magnification Of 3000X.
Related Post: