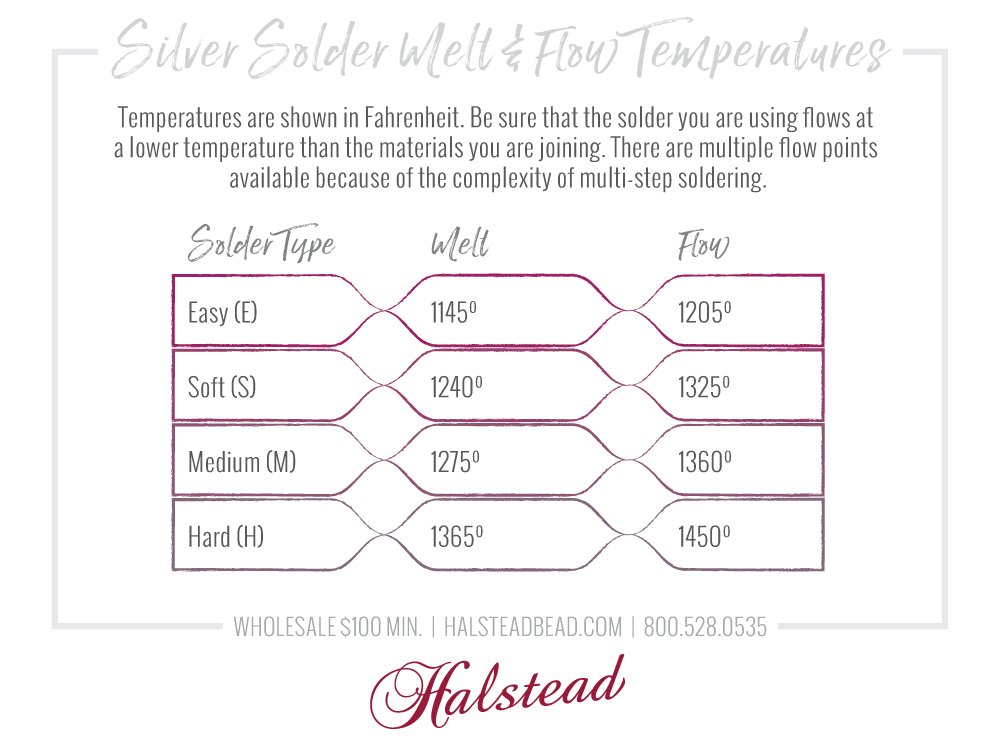
Melting Point Of Solder Chart
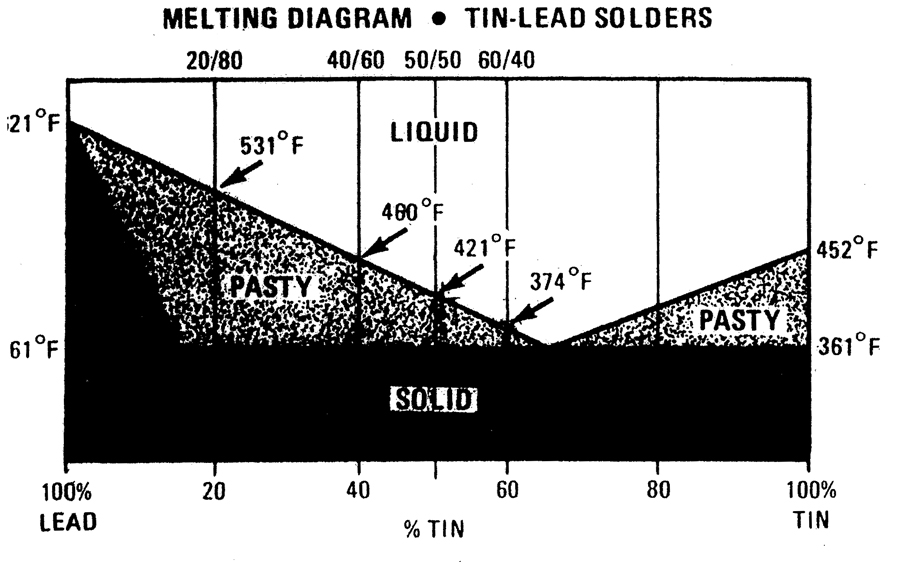
Melting Point Of Solder Chart - Wipe your tip on the soldering sponge first (makes it easier to melt) and heat the joint as fast as you can, taking care not to hold it there too long. The presence of lead in these alloys lowers the melting point, making them easier to work with. A typical solder such as 60/40, with 60 % tin, and 40 % lead, has a melting point approximately between 183 °c to 188 °c. The temperature at which solder melts can vary depending on the factors discussed above. Web the melting temperature for alloy solder, which is the most common type of solder, is around 360 to 370 degrees fahrenheit (or 180 to 190 degrees celsius, if you’re accustomed to using the metric system). The alloys listed may be available in forms other than those indicated. Solder with a composition of 60% tin and 40% lead has a varying melting range but will begin turning into liquid at 361.4°f (183°c), then completely turn into liquid at 375.8°f (191°c). If it's not working well, increase the temperature slightly and try again. Different ratios of tin and lead result in varying melting points. The typical melting point of the general solder is in the range of 90 to 450 °c (190 to 840 °f |. The selection of alloy is determined by application, melting temperature and physical properties. Web it typically consists of a mixture of tin and lead and has a low melting point, making it easy to work with. Range of melting point (°c) 95.5% sn/3.5% ag/1% zn. The temperature at which solder melts can vary depending on the factors discussed above. Web. The temperature at which solder melts can vary depending on the factors discussed above. This tin can be 60% while the lead is 40%. Web explore a curated collection of tables and charts that provide melting point data for different materials, including metals, polymers, ceramics, fluids, and more. Web the melting temperature for alloy solder, which is the most common. Range of melting point (°c) 95.5% sn/3.5% ag/1% zn. Web solder alloy melting temperature metal weight percent melting temperature. The selection of alloy is determined by application, melting temperature and physical properties. To avoid conspicuous solder lines, use the highest temperature solder feasible. The alloys listed may be available in forms other than those indicated. Wipe your tip on the soldering sponge first (makes it easier to melt) and heat the joint as fast as you can, taking care not to hold it there too long. Web i generally start at around 650°f (340°c) for desoldering and work my way up. The typical melting point of the general solder is in the range of 90. Web here is a table that shows the different alloy compositions of solder and their melting point ranges that are common in pcb manufacturing. The eutectic composition, consisting of 63% tin (sn) and 37% lead (pb), has a melting point of approximately 183°c (361°f). Other solder alloys are also available. Solder with a composition of 60% tin and 40% lead. Different ratios of tin and lead result in varying melting points. The tin/lead alloys most commonly used are sn63/pb37 and sn60/pb40 with melting points of 361°f (183°c) and 370°f (188°c) respectively. Web the alloy temperature chart lists the alloys that are available from kester. The temperature at which solder melts can vary depending on the factors discussed above. Also, you. Other solder alloys are also available. Also, you can determine the quality of a solder through its high conductivity and low flux content. Different ratios of tin and lead result in varying melting points. What is high or low temperature solder? The selection of alloy is determined by application, melting temperature and physical properties. What is high or low temperature solder? Web explore a curated collection of tables and charts that provide melting point data for different materials, including metals, polymers, ceramics, fluids, and more. A typical solder such as 60/40, with 60 % tin, and 40 % lead, has a melting point approximately between 183 °c to 188 °c. To avoid conspicuous solder. The presence of lead in these alloys lowers the melting point, making them easier to work with. The alloys listed may be available in forms other than those indicated. This temperature chart shows the different solders that are available and their melting temperatures. Web solder alloy melting temperature metal weight percent melting temperature. Web solders comprise dozens of alloy compositions,. Solder comprises an alloy of lead and tin. Web solders comprise dozens of alloy compositions, with melting points as low as 90° to as high as 400°c. The melting point of 60/40 solder is. Range of melting point (°c) 95.5% sn/3.5% ag/1% zn. Web the right melting point of solder is about 250 degree celsius. The tin/lead alloys most commonly used are sn63/pb37 and sn60/pb40 with melting points of 361°f (183°c) and 370°f (188°c) respectively. Web the right melting point of solder is about 250 degree celsius. A typical solder such as 60/40, with 60 % tin, and 40 % lead, has a melting point approximately between 183 °c to 188 °c. Other solder alloys are also available. The melting point of solder is the temperature at which the solder changes its state from solid to liquid. To avoid conspicuous solder lines, use the highest temperature solder feasible. The alloys listed may be available in forms other than those indicated. Web i generally start at around 650°f (340°c) for desoldering and work my way up. Other solder alloys are also available. Web it typically consists of a mixture of tin and lead and has a low melting point, making it easy to work with. Also, you can determine the quality of a solder through its high conductivity and low flux content. The higher the zinc content, the lower the melting temperature. The presence of lead in these alloys lowers the melting point, making them easier to work with. Web the melting temperature for alloy solder, which is the most common type of solder, is around 360 to 370 degrees fahrenheit (or 180 to 190 degrees celsius, if you’re accustomed to using the metric system). The temperature at which solder melts can vary depending on the factors discussed above. Web melting temperatures of solder are determined by the zinc content:Solders, Torches & Fuels Used in a Jewelry Studio Halstead
Soldering Iron and Controllers Lawrence Ribbecke Studios
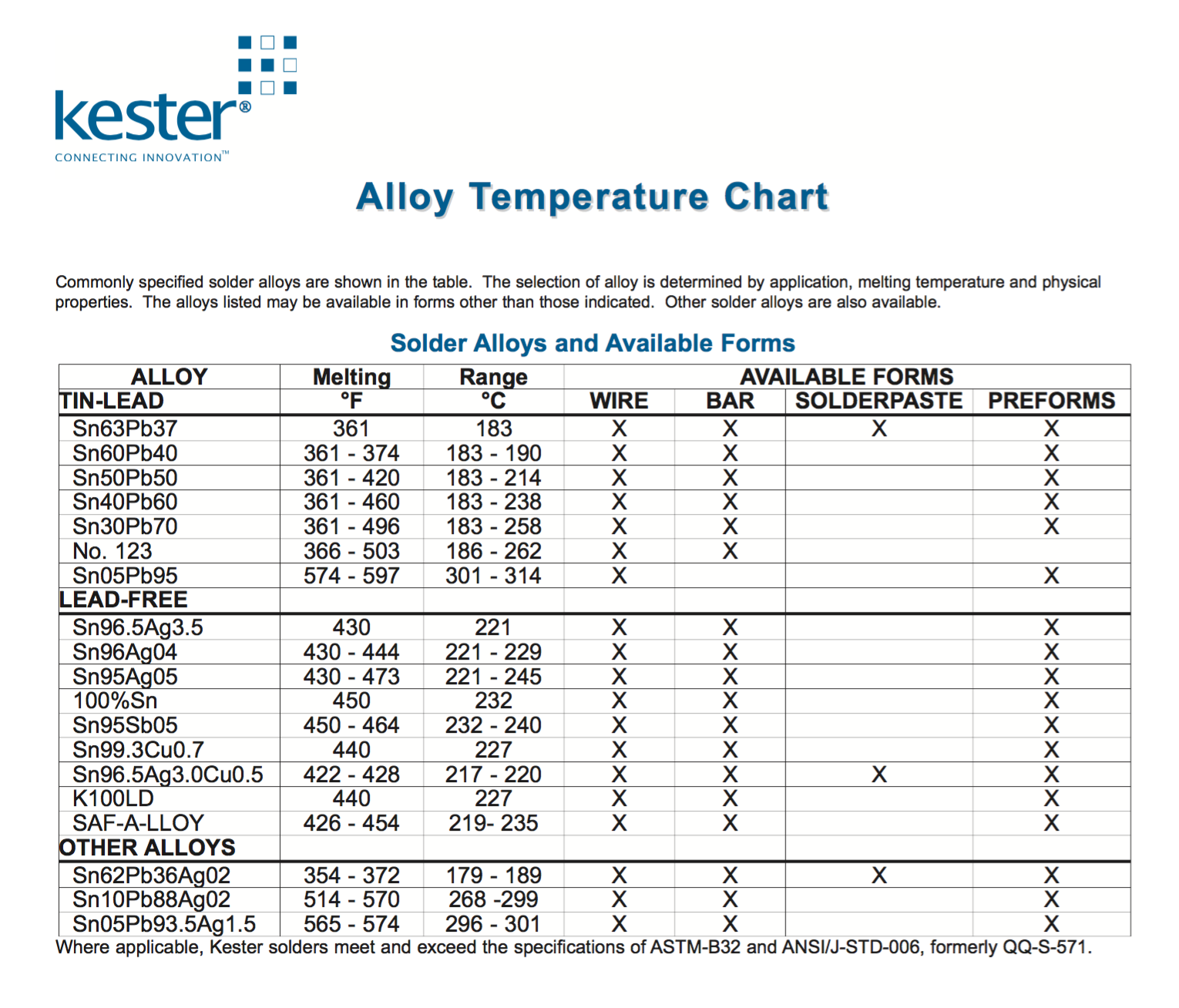
kester solder melting points

Solder and Soldering Guide Farnell element14

Silver Solder Melting Temperature Chart

Eutectic vs Leadfree solder Iron Tip temperature Japanpeuf

Solder Melting Point Chart

Patent EP0977900A4 Leadfree solder Google Patents

Electrical and Thermal conductivity of Metals r/Wallstreetsilver
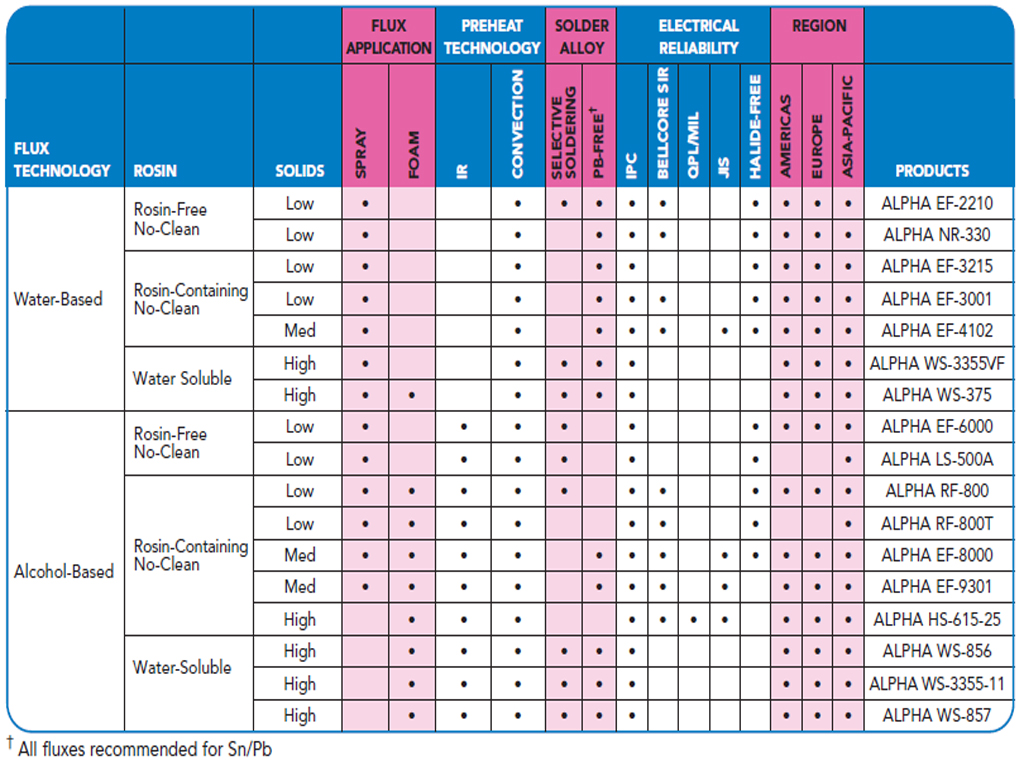
Basic Soldering Guide How to Solder Electronic Components to PCB
Different Ratios Of Tin And Lead Result In Varying Melting Points.
What Is High Or Low Temperature Solder?
Commonly Specified Solder Alloys Are Shown In The Table.
Web Explore A Curated Collection Of Tables And Charts That Provide Melting Point Data For Different Materials, Including Metals, Polymers, Ceramics, Fluids, And More.
Related Post: