Metal Nobility Chart
Metal Nobility Chart - For example, noble metals that are higher up the galvanic scale retain their electrons better compared to base metals at the lower end of the scale when placed within the same environment. All dissimilar materials have the potential to react with each other when they are brought together in the presence of a catalyst. Type 316 stainless steel (passive) type 304 stainless steel (passive) monel 400. It is important to remember that the tests that originally produced the tabulated values may not have identically replicated the exact scenario in which they are intended to be used on site. The dissolution and removal of alloying elements from the cathode will cause pitting corrosion, hence the inclusion of the 'element electronegativity ' list in nobility. Web metals are rated in their ability to resist electrochemical corrosion on the scale of nobility and on the galvanic series chart, which shows their electrical potential in seawater. Gold, platinum, and the other platinum group metals (ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, osmium, iridium) are most often so classified. Galvanic series chart — determine metal nobility and bimetallic corrosion. Alloys with higher nobility are at the top, and metals that are less noble (or more base) are at the bottom. Web the following galvanic table lists metals in the order of their relative activity in seawater environment. Use this chart to avoid galvanic corrosion in seawater when different metals come in to contact. Type 316 stainless steel (passive) type 304 stainless steel (passive) monel 400. Web galvanic series diagram. Web here, nobility refers to a metal's resistance to corrosion. Noble metals benefit from exceptional corrosion resistance and their (more or less) inert nature. The rate of corrosion is determined by the electrolyte and the difference in nobility. Web the different properties of noble metals are briefly discussed below: Web the following galvanic table lists metals in the order of their relative activity in seawater environment. Some texts list gold, silver and copper as the noble metals, excluding all others. Web in other words,. The galvanic series can be used to determine which combinations need special protection and which of the metals will corrode. Web the following galvanic table lists metals in the order of their relative activity in seawater environment. Usually noble metals are said to include ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, silver, osmium, iridium, platinum and gold. Web here, nobility refers to a metal's. Web the following galvanic table lists metals in the order of their relative activity in seawater environment. Web galvanic series, or nobility chart for dissimilar metals. Web this chart will help you to determine which metals are more noble than other metals. It is important to remember that the tests that originally produced the tabulated values may not have identically. Web when dissimilar metals are connected — either by simple contact or by wiring — and they are immersed in water, a current will flow which can cause galvanic corrosion. Web galvanic series of metals and alloys. It is important to remember that the tests that originally produced the tabulated values may not have identically replicated the exact scenario in. Web below, we give a brief overview of galvanic corrosion and provide a galvanic corrosion chart to help fabricators and machinists avoid using the wrong metal combinations. The list begins with the more active (anodic) metal and proceeds down the to the least active (cathodic) metal of the galvanic series. Web galvanic series of metals and alloys. Contact a corrosion. When two metals are submerged in an electrolyte, while also electrically connected by some external conductor, the less noble (base) will experience galvanic corrosion. Galvanic series chart — determine metal nobility and bimetallic corrosion. Web galvanic series diagram. The galvanic series can be used to determine which combinations need special protection and which of the metals will corrode. The below. All dissimilar materials have the potential to react with each other when they are brought together in the presence of a catalyst. Web here, nobility refers to a metal's resistance to corrosion. The dissolution and removal of alloying elements from the cathode will cause pitting corrosion, hence the inclusion of the 'element electronegativity ' list in nobility. We also provide. We also provide other helpful methods for avoiding galvanic corrosion. Zn and ag/agcl and in soil vs. All dissimilar materials have the potential to react with each other when they are brought together in the presence of a catalyst. Whilst electronegativity is not directly related to, or proportional to nobility it does give an indication as to their potential corrodibility.. The dissolution and removal of alloying elements from the cathode will cause pitting corrosion, hence the inclusion of the 'element electronegativity ' list in nobility. Web here, nobility refers to a metal's resistance to corrosion. The below diagram lists metals and alloys potential in the order of reactivity in sea water vs. Web when dissimilar metals are connected — either. Type 316 stainless steel (passive) type 304 stainless steel (passive) monel 400. Web the following galvanic table lists metals in the order of their relative activity in seawater environment. When two metals are submerged in an electrolyte, while electrically connected, the less noble (base) will experience galvanic corrosion. Web metals listed on the top of the chart (anodic) will corrode faster than the metals on the bottom of. The dissolution and removal of alloying elements from the cathode will cause pitting corrosion, hence the inclusion of the 'element electronegativity ' list in nobility. (noble metals are those that are resistant to corrosion and oxidation.) when two metals are immersed in an electrolyte, while also being connected externally by a conductor, the less noble metal experiences galvanic corrosion. Usually noble metals are said to include ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, silver, osmium, iridium, platinum and gold. It is important to remember that the tests that originally produced the tabulated values may not have identically replicated the exact scenario in which they are intended to be used on site. Top listed metals/alloys are the least active (most noble) and proceeds down to the most active (anodic) metal/alloy. Web galvanic series diagram. For example, noble metals that are higher up the galvanic scale retain their electrons better compared to base metals at the lower end of the scale when placed within the same environment. We also provide other helpful methods for avoiding galvanic corrosion. Web in other words, when two different metals are in contact with each other in the presence of moisture, there will be a flow of current from one metal (the “anode”) to the other metal (the “cathode”), and one will be eaten away, or disintegrated, while. Web when dissimilar metals are connected — either by simple contact or by wiring — and they are immersed in water, a current will flow which can cause galvanic corrosion. With the galvanic series, metals are grouped according to electrical potential measured to a known reference. Use this chart to avoid galvanic corrosion in seawater when different metals come in to contact.
The Nobility of Common Metals
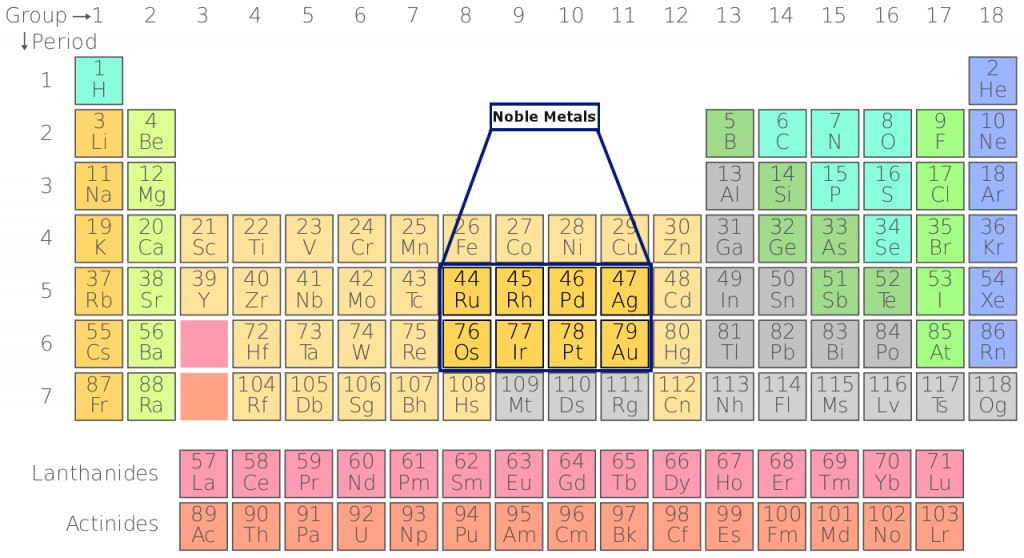
Noble Metal Definition, List, Properties, And Examples
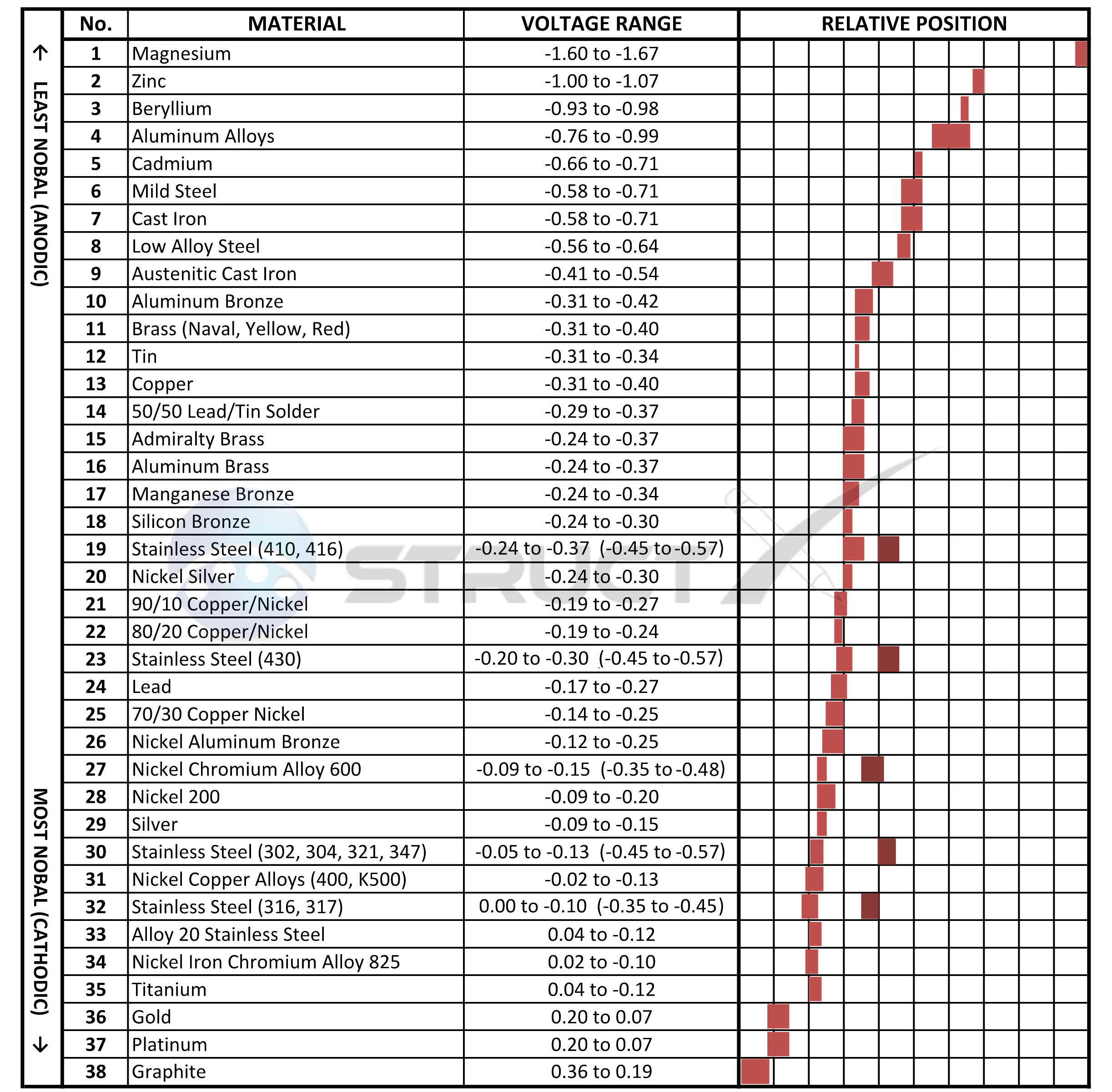
Galvanic Series (electrochemical series)

Alkaline earth metals, Transition metal, Alkali metal
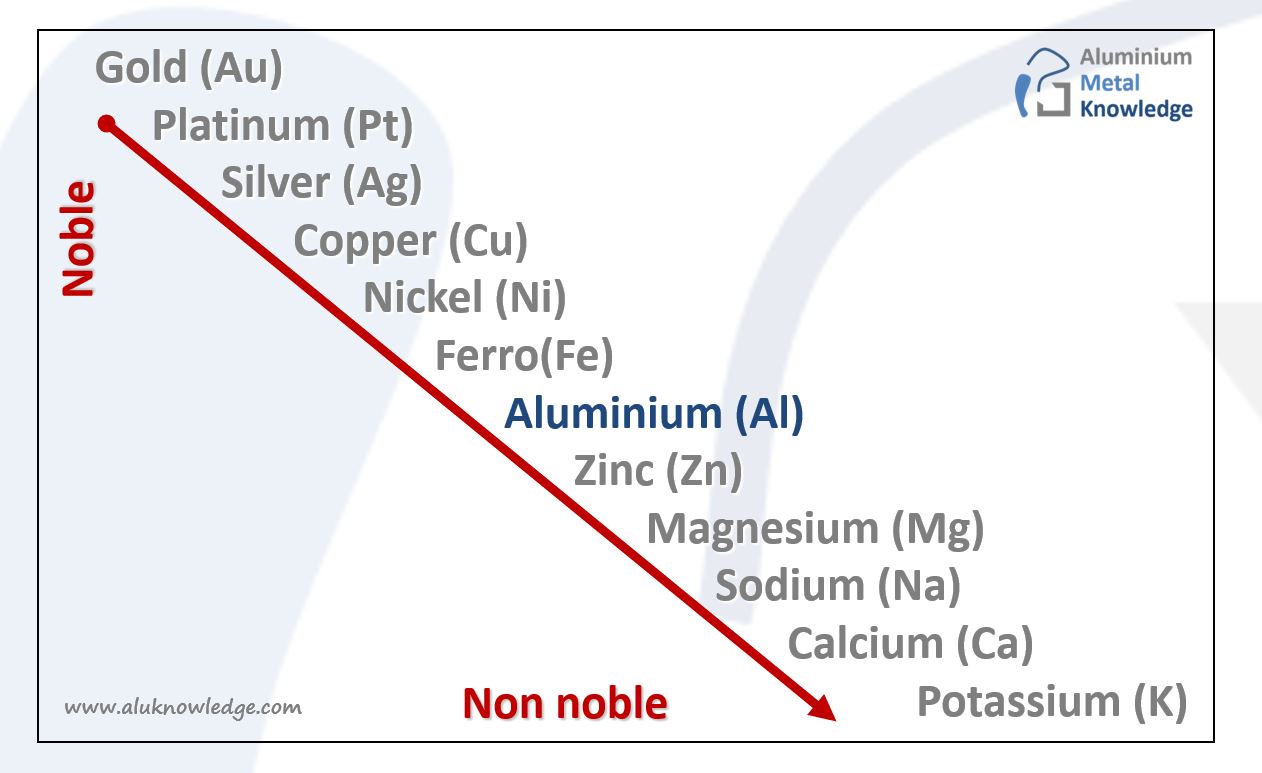
alloy Archieven Aluminium Metal Knowledge

What Are Noble Metals? Definition and List

Printable periodic table of elements noble gases fulcclas

everyday chemistry Accelerated Oxidation Of Iron When Coating Breaks
Chemical Compatibility Table For Metals

Galvanic Series, or Nobility Chart for Dissimilar Metals Fair Wind
Web Here, Nobility Refers To A Metal's Resistance To Corrosion.
Web Galvanic Series Relationships Are Useful As A Guide For Selecting Metals To Be Joined, Will Help The Selection Of Metals Having Minimal Tendency To Interact Galvanically, Or Will Indicate The Need Or Degree Of Protection To Be Applied To Lessen The Expected Potential Interactions.
The Galvanic Series Can Be Used To Determine Which Combinations Need Special Protection And Which Of The Metals Will Corrode.
The Below Diagram Lists Metals And Alloys Potential In The Order Of Reactivity In Sea Water Vs.
Related Post: