Metalloids Drawing
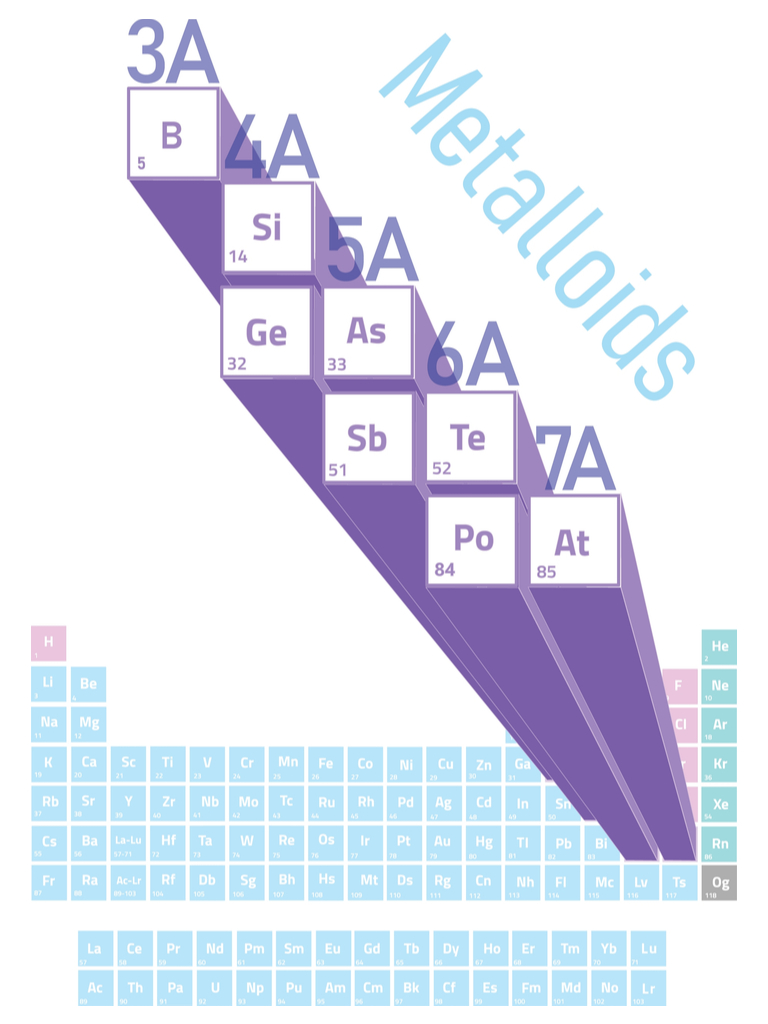
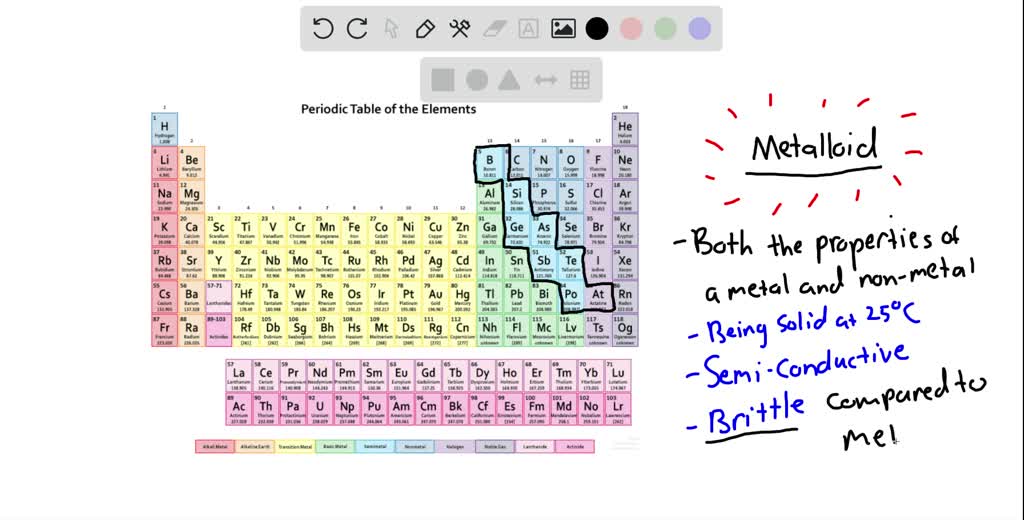
Metalloids Drawing - Visualize trends, 3d orbitals, isotopes, and mix compounds. The metalloids are boron, silicon, germanium, arsenic, antimony, and tellurium. Metalloids are all solid at room temperature. Conduct heat and electricity, but not as well as metals; Metalloids can also be called semimetals. Web a metalloid is an element that has properties that are intermediate between those of metals and nonmetals. Web interactive periodic table showing names, electrons, and oxidation states. The elements between the metals and nonmetals on the periodic table are metalloids: Examples of metalloids include boron, silicon, and arsenic. All images photos vectors illustrations 3d objects. Web what is this important element? Piece of arsenic on periodic table of elements. Web a metalloid is an element that has properties that are intermediate between those of metals and nonmetals. Web metalloids are useful in the semiconductor industry. Web period and identify whether the element is a nonmetal, metal, or metalloid: The elements between the metals and nonmetals on the periodic table are metalloids: Conduct heat and electricity, but not as well as metals; Saturday 18 may 2024 • 11:30am. Metalloids can also be called semimetals. Metalloids or semimetals possess some properties of metals and some of nonmetals. Periodic properties of the elements. The metalloids are boron, silicon, germanium, arsenic, antimony, and tellurium. The eight elements classified as metalloids are boron, silicon, germanium, arsenic, antimony, tellurium, astatine, and polonium. Its name is silicon, and it belongs to a class of elements called metalloids. Lightly color your square blue if it is a metal, green if it is a. Metalloids or semimetals possess some properties of metals and some of nonmetals. Web a metalloid is an element that has properties that are intermediate between those of metals and nonmetals. Web interactive periodic table showing names, electrons, and oxidation states. Properties of metalloids or semimetals. Classification of elements in periodic table. Properties of metalloids or semimetals. Web properties of metalloids or semimetals. Web period and identify whether the element is a nonmetal, metal, or metalloid: The metalloids are located between the metals and nonmetals on the periodic table. Metalloids can also be called semimetals. Examples of metalloids include boron, silicon, and arsenic. Metalloids are the elements on a periodic table that have properties that are intermediate between those of metals and nonmetals. Web metalloids are useful in the semiconductor industry. The eight elements classified as metalloids are boron, silicon, germanium, arsenic, antimony, tellurium, astatine, and polonium. See metalloids stock video clips. Periodic properties of the elements. Web properties of metalloids or semimetals. Saturday 18 may 2024 • 11:30am. Web a metalloid is an element that has properties that are intermediate between those of metals and nonmetals. Metalloids typically have several forms or allotropes with very different properties. Metalloids can also be called semimetals. (jurii) silicon (enricoros) germanium (jurii) arsenic (aram dulyan) Usually dense (exceptions include lithium, potassium, and sodium) may have a very high melting point. Metalloids are all solid at room temperature. Properties of metalloids or semimetals. Metalloids are the smallest class of elements. Web a metalloid is an element that has properties that are intermediate between those of metals and nonmetals. They can form alloys with other metals. Web a series of six elements called the metalloids separate the metals from the nonmetals in the periodic table. Some metalloids, such as silicon and germanium, can act. Saturday 18 may 2024 • 11:30am. Web what is this important element? Web ductile (can be drawn into wire) corrode or oxidize in air and seawater. Piece of arsenic on periodic table of elements. Could be dull or shiny; Metalloids can also be called semimetals. Properties of metals and non metals. Web the metals, nonmetals, and metalloids concept builder is shown in the iframe below. Web a metalloid is an element that has properties that are intermediate between those of metals and nonmetals. Representative metals, metalloids, and nonmetals. Structure and general properties of the metalloids. Visualize trends, 3d orbitals, isotopes, and mix compounds. Web interactive periodic table showing names, electrons, and oxidation states. Could be dull or shiny; Metalloids or semimetals possess some properties of metals and some of nonmetals. Metalloids can also be called semimetals. Metalloids are all solid at room temperature. Some metalloids, such as silicon and germanium, can act as electrical conductors under the right conditions, thus they are called semiconductors. Describe the general preparation, properties, and uses of the metalloids. The metalloids are located between the metals and nonmetals on the periodic table. Piece of arsenic on periodic table of elements.
Metalloids — Overview & Properties Expii

What are metalloids? Definition, Properties and Example

Periodic Table Line Drawing Periodic Table Timeline
Metalloids and Alloys — lesson. Science State Board, Class 9.

Metals And Metalloids On Periodic Table

Metalloids Chemistry Learner

Periodic Table With Metals Metalloids And Nonmetals Labeled Periodic

Metalloids Science Notes and Projects
SOLVEDWhat is a metalloid? Where are the metalloids found on the

Metalloids by Megan Maul
The Metalloids Are Boron, Silicon, Germanium, Arsenic, Antimony, And Tellurium.
Saturday 18 May 2024 • 11:30Am.
Usually Dense (Exceptions Include Lithium, Potassium, And Sodium) May Have A Very High Melting Point.
Examples Of Metalloids Include Boron, Silicon, And Arsenic.
Related Post: