Monomer And Polymer Chart
Monomer And Polymer Chart - A large molecule made of repeating subunits (monomers). Web monomers and polymers biological macromolecules play a critical role in cell structure and function. Web monomer = amino acids. For the purpose of our study, we have chosen linear chains as topological representations. Many biomolecules (carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids) are built of one or more building blocks called monomers. For example, a carbohydrate is a polymer that is made of repeating monosaccharides. For example, an amino acid acts as the building blocks for proteins. Polymers range from synthetic polymers to natural biopolymers such as dna and proteins. Web a monosaccharide is the monomer that makes up a polysaccharide. Web in general, polymer properties are determined to a large extent by how the monomer units are interconnected. We’ll get to know important details about each of the biomolecule families later in this set of tutorials. Polymers range from synthetic polymers to natural biopolymers such as dna and proteins. How are monomers, polymers and macromolecules related? A molecule that is a building block for larger molecules (polymers). Web to comprehend the full scope of proteins, it is crucial. Web monomers and polymers biological macromolecules play a critical role in cell structure and function. If you think of a monomer as being like a bead, then you can think of a polymer as being like a necklace, a series of beads strung together. Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and phosphorus *stores and transmits genetic information. We’ll get to know important. Web the monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules known as polymers. For the purpose of our study, we have chosen linear chains as topological representations. Web polymers are very large molecules made from smaller ones. Web monomer = amino acids. This single bond is a remnant of the double bond which joined those. Web the monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules known as polymers. Meat, poultry, eggs, beans, soy, nuts, peanut butter, enzymes *one of the most important biomolecules *nitrogen makes it different. Web different types of monomers can combine in many configurations, giving rise to a diverse group of macromolecules. In doing so, monomers release water. A polymer is a chain of an unspecified number of monomers. Web to comprehend the full scope of proteins, it is crucial to understand various properties, including the basic biological molecule, peptides, polypeptide chains, amino acids, protein structures, and the processes of protein denaturation. Ethylene molecules are joined together in long chains. The process of forming polymers from monomers occurs. Web there are two general types of polymerization reactions: How those smaller units are arranged within the polymer is an issue we haven't addressed very closely yet. What are monomers and polymers? Web a molecule from which a polymer is made is called a monomer. For example, an amino acid acts as the building blocks for proteins. Web a monomer is a type of molecule that has the ability to chemically bond with other molecules in a long chain; Web in general, polymer properties are determined to a large extent by how the monomer units are interconnected. The process of forming polymers from monomers occurs in various ways, often through dehydration synthesis. Polymers range from synthetic polymers. Eine plastikflasche besteht aus ganz vielen miteinander verknüpften monomeren. This type of reaction is known as dehydration synthesis, which means “to put together while losing water.” figure 1. Web monomers and polymers biological macromolecules play a critical role in cell structure and function. (00:12) wenn du länger unterwegs bist, nimmst du dir vielleicht wasser in einer plastikflasche mit. Web polymers. Most (but not all) biological macromolecules are polymers, which are any molecules constructed by linking together many smaller molecules, called monomers. Web a polymer is a substance consisting of molecules characterised by the sequence of one or more types of monomer unit. Web the monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules known as polymers. How. Web the monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules known as polymers. (00:12) wenn du länger unterwegs bist, nimmst du dir vielleicht wasser in einer plastikflasche mit. How are monomers, polymers and macromolecules related? Addition polymerization and condensation polymerization. Your best friend tells you that they are deathly allergic to certain amino acids in food. Your best friend tells you that they are deathly allergic to certain amino acids in food. Web monomers and polymers biological macromolecules play a critical role in cell structure and function. Eine plastikflasche besteht aus ganz vielen miteinander verknüpften monomeren. Zur stelle im video springen. Web polyaniline has been utilized in various applications, yet its widespread adoption has often been impeded by challenges. Polymers range from synthetic polymers to natural biopolymers such as dna and proteins. Most large biological molecules are polymers, long chains made up of repeating molecular subunits, or building blocks, called monomers. The process of forming polymers from monomers occurs in various ways, often through dehydration synthesis. How are monomers, polymers and macromolecules related? Several important biological polymers include proteins, starch, cellulose, and dna. For example, a carbohydrate is a polymer that is made of repeating monosaccharides. Most (but not all) biological macromolecules are polymers, which are any molecules constructed by linking together many smaller molecules, called monomers. Ethylene molecules are joined together in long chains. Essentially, monomers are the building blocks of polymers, which are more complex type of molecules. In addition polymerization, the monomers add to one another in such a way that the polymer contains all the atoms of the starting monomers. Web to comprehend the full scope of proteins, it is crucial to understand various properties, including the basic biological molecule, peptides, polypeptide chains, amino acids, protein structures, and the processes of protein denaturation.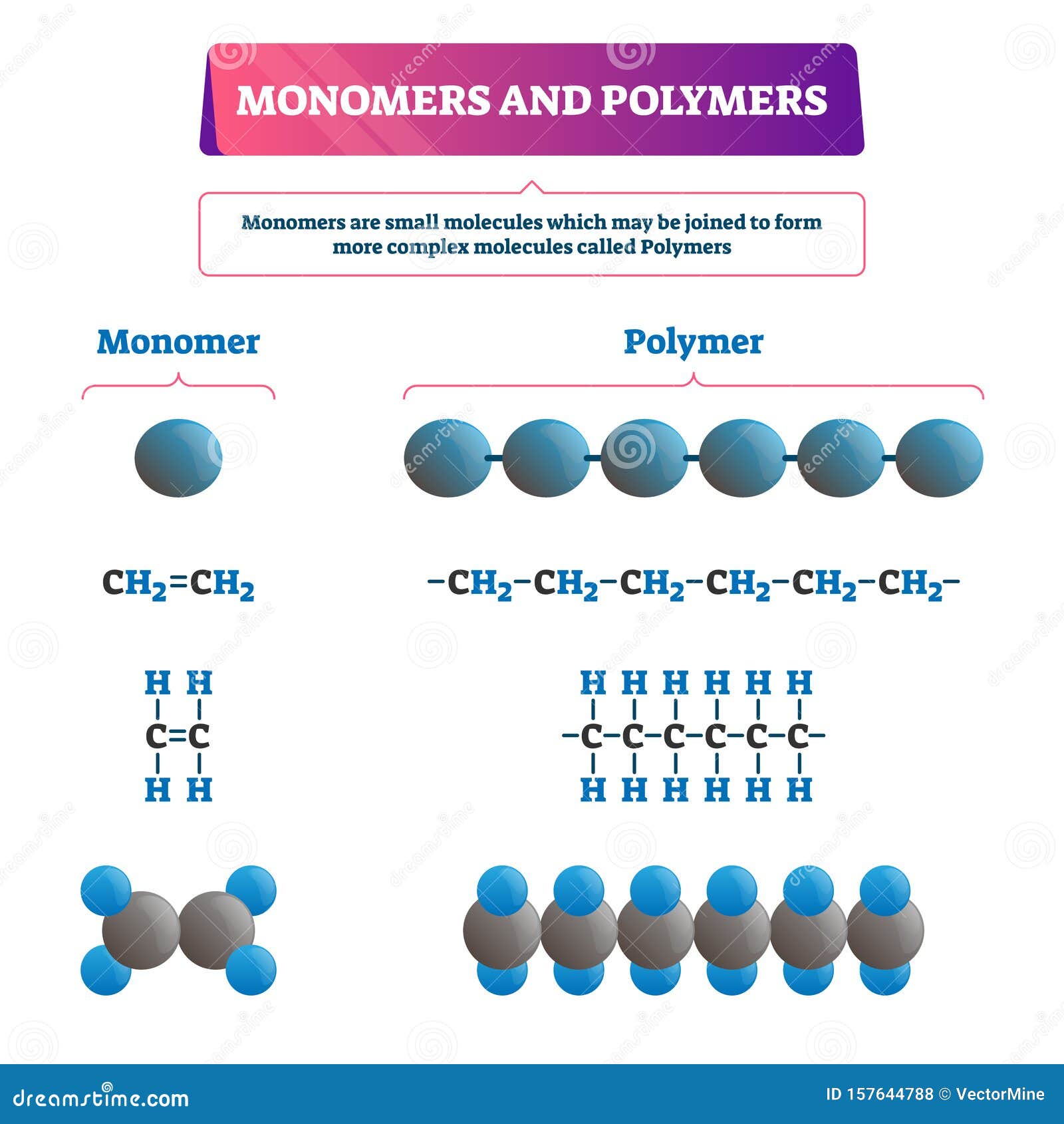
Polymers And Monomers Examples

What are the MONOMERS of each POLYMER? ppt download
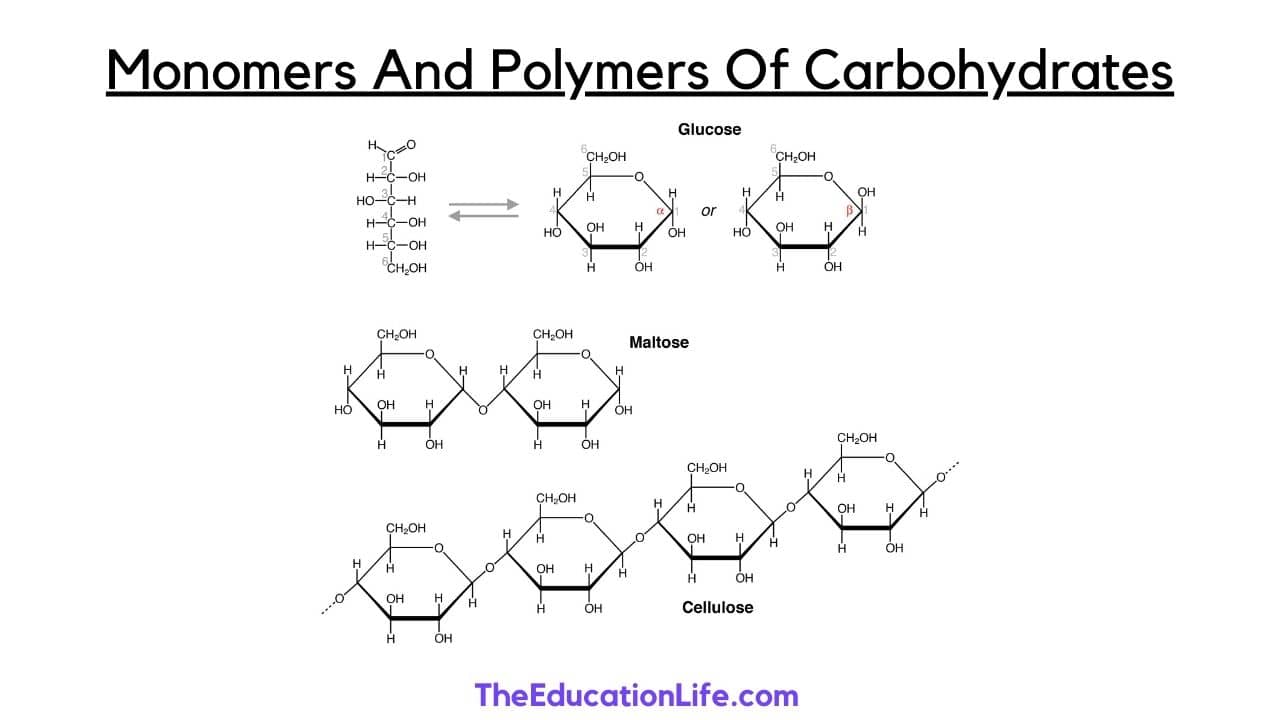
Monomers And Polymers Of Carbohydrates Explained The Education
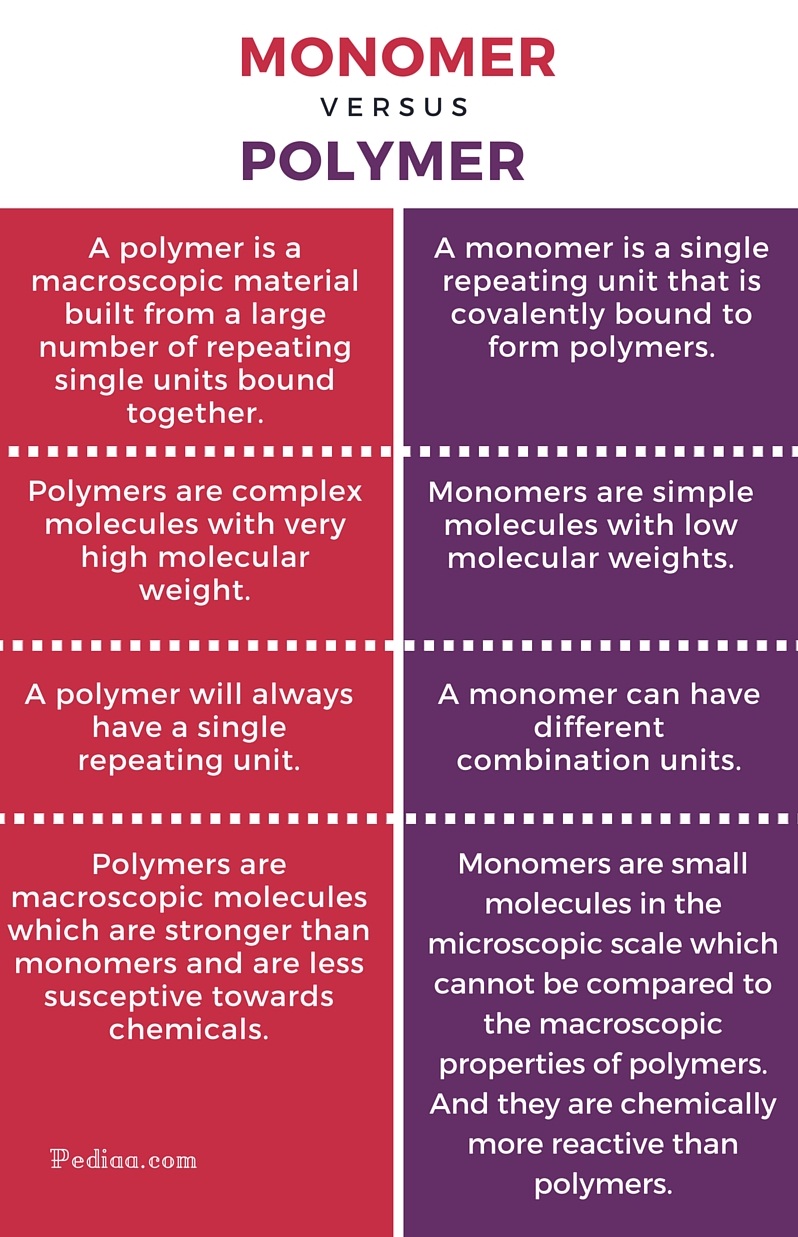
Difference Between Monomer and Polymer
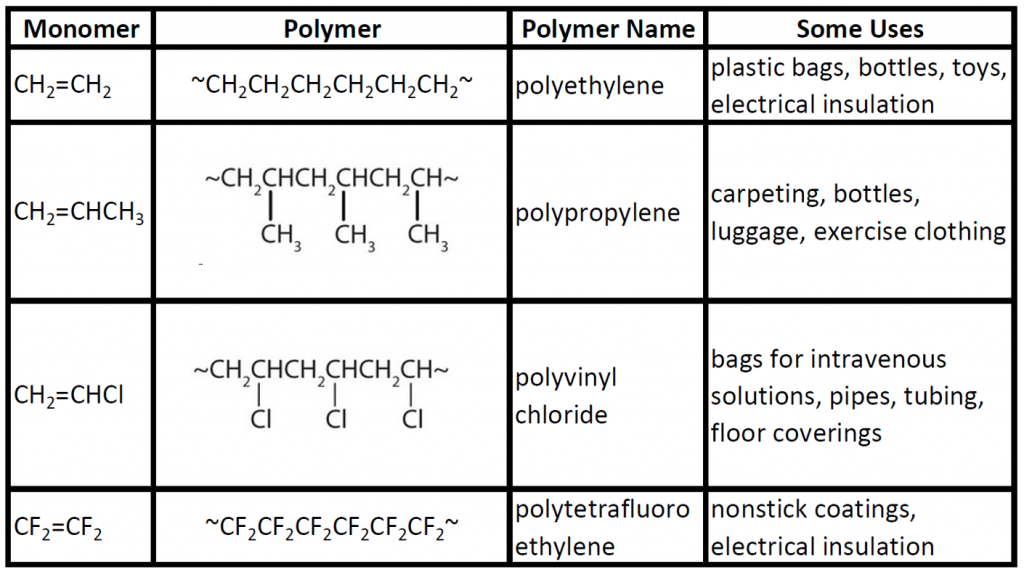
CH105 Chapter 8 Alkenes, Alkynes and Aromatic Compounds Chemistry

16.7 Polymers Chemistry LibreTexts

Quantum Science for standard 10 to 12, Innovative technique and
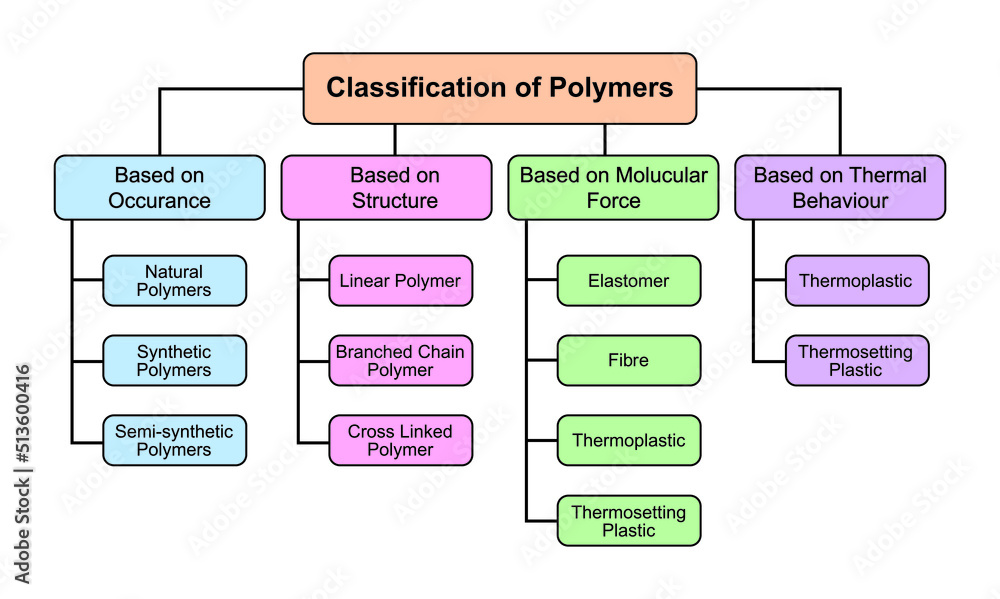
Classification of Polymers. Polymers And its Types. Vector Illustration

Bibiography Organic Chemistry & Basic Ecology
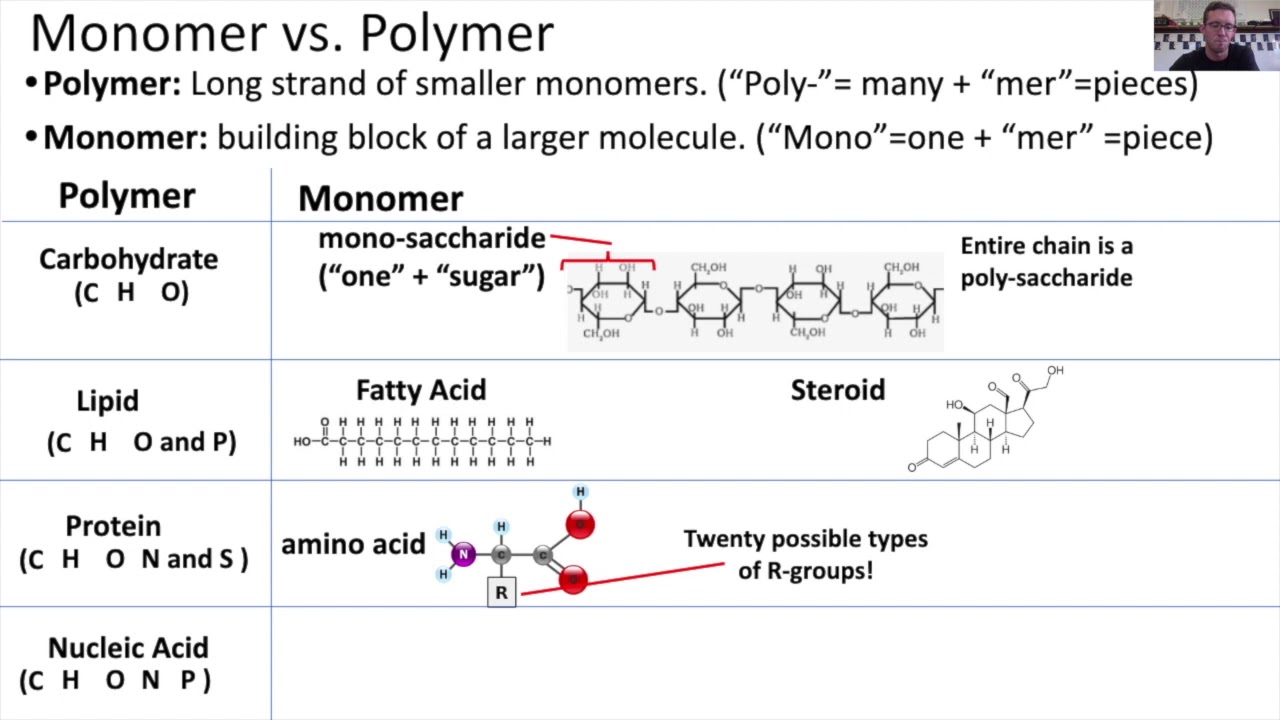
Monomers vs. Polymers YouTube
Monomers Are Smaller Molecules, And When Bonded Together, Make Up Polymers.
A Molecule That Is A Building Block For Larger Molecules (Polymers).
Web Polymers Are Very Large Molecules Made From Smaller Ones.
Web Different Types Of Monomers Can Combine In Many Configurations, Giving Rise To A Diverse Group Of Macromolecules.
Related Post: